Abstract
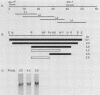
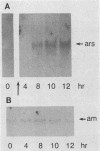
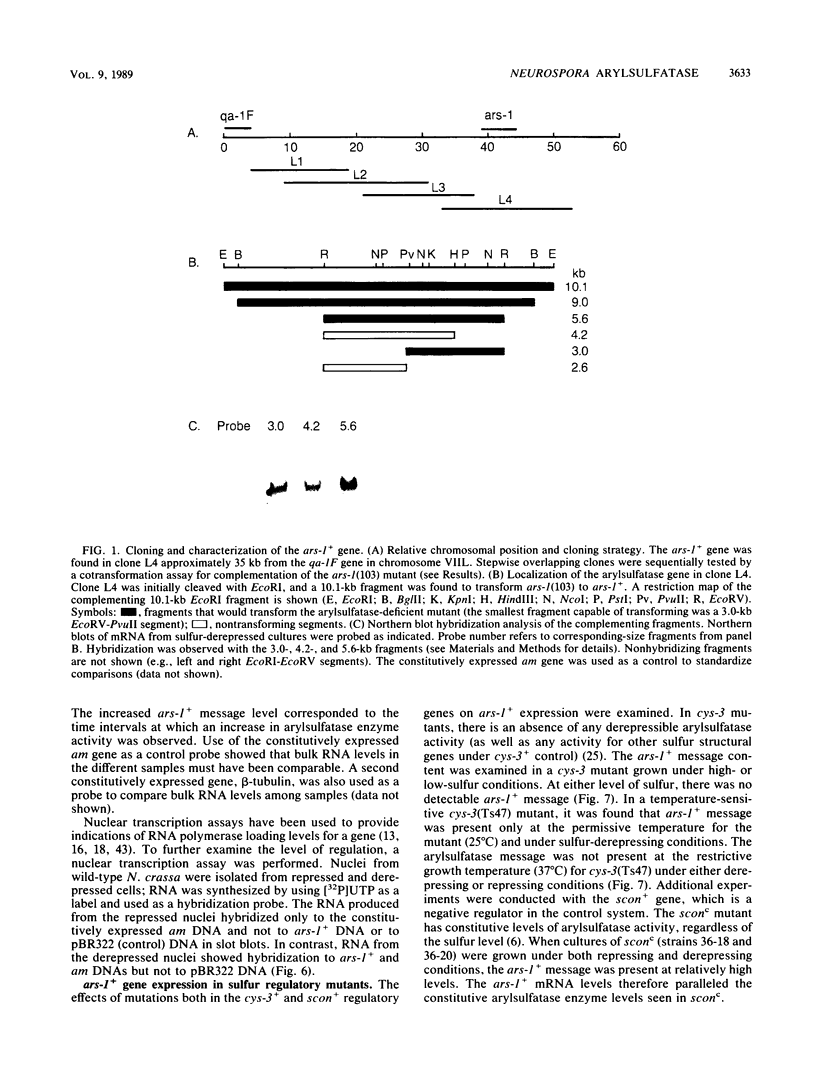
The ars-1+ gene of Neurospora crassa encodes the enzyme arylsulfatase. ars-1+ is in a group of highly regulated sulfur-related structural genes that are expressed under conditions of sulfur limitation and are under coordinate control of the cys-3+ and scon+ regulatory genes. The ars-1+ gene was cloned by chromosome walking from the qa gene cluster, using a lambda library. Cotransformation of an N. crassa ars-1 mutant with the isolated lambda clones and the benomyl resistance gene, followed by assay for arylsulfatase activity, was used to screen for the ars-1+ gene. Further confirmation that the cloned segment mapped to the ars-1+ locus was obtained by restriction-fragment-length polymorphism analysis. Northern (RNA) blot analysis showed that the ars-1+ gene was transcribed to give an mRNA of 2.3 kilobases. In wild-type cells, the ars-1+ transcript was abundant under sulfur-derepressing conditions but absent under repressing conditions. Time course analysis showed that the appearance of ars-1+ message in sulfur-derepressed cultures paralleled the appearance of arylsulfatase enzyme activity. In addition, transcription of ars-1+ was detected only under derepressing conditions in a nuclear transcription assay. In a cys-3 regulatory mutant that was unable to synthesize arylsulfatase (or other sulfur-controlled enzymes), there was no ars-1+ transcript under repressing or derepressing conditions. In a temperature-sensitive cys-3 mutant, the ars-1+ transcript was present only at the permissive growth temperature and under sulfur derepression. A negative regulatory mutant, sconc, displayed both constitutive expression of arylsulfatase enzyme activity and content of ars-1+ message.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apte B. N., Bhavsar P. N., Siddiqi O. The regulation of aryl sulphatase in Aspergillus nidulans. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 5;86(3):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90186-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armaleo D., Gross S. R. Structural studies on Neurospora RNA polymerases and associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16174–16180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton E. G., Metzenberg R. L. Novel mutation causing derepression of several enzymes of sulfur metabolism in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):140–151. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.140-151.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich P. S., Metzenberg R. L. Metabolic suppressors of a regulatory mutant in Neurospora. Biochem Genet. 1973 Jan;8(1):73–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00485558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Paietta J. V., Mannix D. G., Marzluf G. A. cys-3, the positive-acting sulfur regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa, encodes a protein with a putative leucine zipper DNA-binding element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1120–1127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson M. A., Marzluf G. A. Regulation of a sulfur-controlled protease in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):785–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.785-789.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hautala J. A., Conner B. H., Jacobson J. W., Patel G. L., Giles N. H. Isolation and characterization of nuclei from Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):704–713. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.704-713.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. S., Metzenberg R. L. Control of arylsulfatase in a serine auxotroph of Neurospora. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1397–1398. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1397-1398.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerome J. F., Jaehning J. A. mRNA transcription in nuclei isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1633–1639. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketter J. S., Marzluf G. A. Molecular cloning and analysis of the regulation of cys-14+, a structural gene of the sulfur regulatory circuit of Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1504–1508. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaird J. H., Keighren M. A., Kinsey J. A., Eaton M., Fincham J. R. Cloning of the am (glutamate dehydrogenase) gene of Neurospora crassa through the use of a synthetic DNA probe. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthe D. S., Quatrano R. S. Transcription in Isolated Wheat Nuclei: I. ISOLATION OF NUCLEI AND ELIMINATION OF ENDOGENOUS RIBONUCLEASE ACTIVITY. Plant Physiol. 1980 Feb;65(2):305–308. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluf G. A. Genetic and metabolic control of sulfate metabolism in Neurospora crassa: a specific permease for choline-O-sulfate. Biochem Genet. 1972 Dec;7(3):219–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00484820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluf G. A., Metzenberg R. L. Positive control by the cys-3 locus in regulation of sulfur metabolism in Neurospora. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):423–437. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluf G. A. Regulation of nitrogen metabolism and gene expression in fungi. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):437–461. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.437-461.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L., Ahlgren S. K. Mutants of Neurospora deficient in aryl sulfatase. Genetics. 1970 Mar-Apr;64(3):409–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L., Ahlgren S. K. Structural and regulatory control of aryl sulfatase in Neurospora: the use of interspecific differences in structural genes. Genetics. 1971 Jul;68(3):369–381. doi: 10.1093/genetics/68.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L., Chen G. S., Ahlgren S. K. Reversion of aryl sulfataseless mutants of Neurospora. Genetics. 1971 Jul;68(3):359–368. doi: 10.1093/genetics/68.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L. Implications of some genetic control mechanisms in Neurospora. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):361–383. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.361-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L., Parson J. W. Altered repression of some enzymes of sulfur utilization in a temperature-conditional lethal mutant of Neurospora. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):629–635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach M. J., Porro E. B., Yanofsky C. Cloning and characterization of the gene for beta-tubulin from a benomyl-resistant mutant of Neurospora crassa and its use as a dominant selectable marker. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2452–2461. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paietta J. V., Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M., Marzluf G. A. Molecular cloning and characterization of the cys-3 regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2506–2511. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paietta J. V., Marzluf G. A. Gene disruption by transformation in Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1554–1559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall M. L. Amino acid transport in Neurospora crassa. IV. Properties and regulation of a methionine transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):201–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90372-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins D. D., Radford A., Newmeyer D., Björkman M. Chromosomal loci of Neurospora crassa. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Dec;46(4):426–570. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.4.426-570.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinert W. R., Patel V. B., Giles N. H. Genetic regulation of the qa gene cluster of Neurospora crassa: induction of qa messenger ribonucleic acid and dependency on qa-1 function. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):829–835. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Yamada K., Akasaka K., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Saito A., Sato M., Shimada H. cDNA cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression of the gene for arylsulfatase in the sea urchin (Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus) embryo. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):9–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Metzenberg R. L. Location of Aryl Sulfatase in Conidia and Young Mycelia of Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1254–1265. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1254-1265.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Munkres K. D., Metzenberg R. L. A particulate fraction from Neurospora crassa exhibiting aryl sulfatase activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Feb;142(2):623–632. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverthorne J., Tobin E. M. Demonstration of transcriptional regulation of specific genes by phytochrome action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1112–1116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Gieselmann V., Kreysing J., Schmidt B., Pohlmann R., Waheed A., Meyer H. E., O'Brien J. S., von Figura K. Cloning and expression of human arylsulfatase A. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1252–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Maniatis T. Simian virus 40 enhancer increases number of RNA polymerase II molecules on linked DNA. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):73–75. doi: 10.1038/315072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer S. J., Yanofsky C. Efficient cloning of genes of Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4869–4873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hostos E. L., Togasaki R. K., Grossman A. Purification and biosynthesis of a derepressible periplasmic arylsulfatase from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):29–37. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]