Abstract
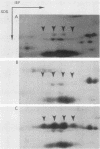
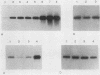
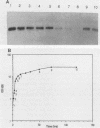
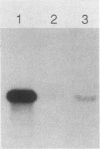
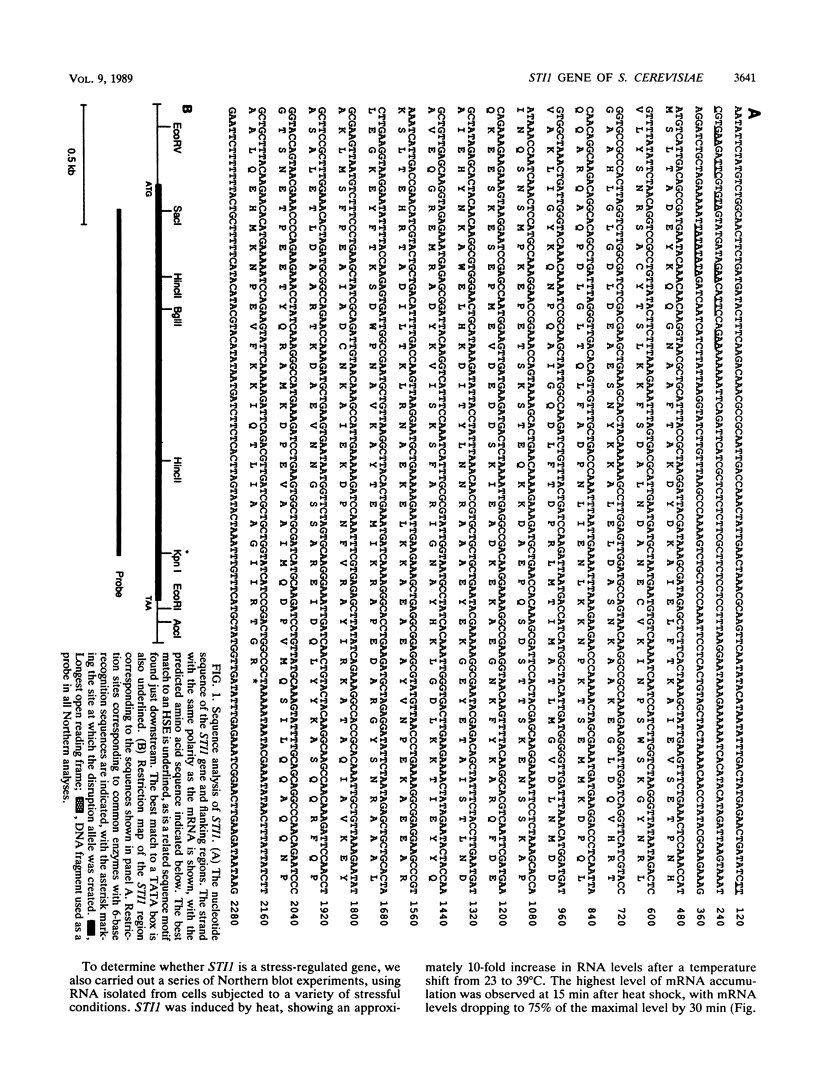
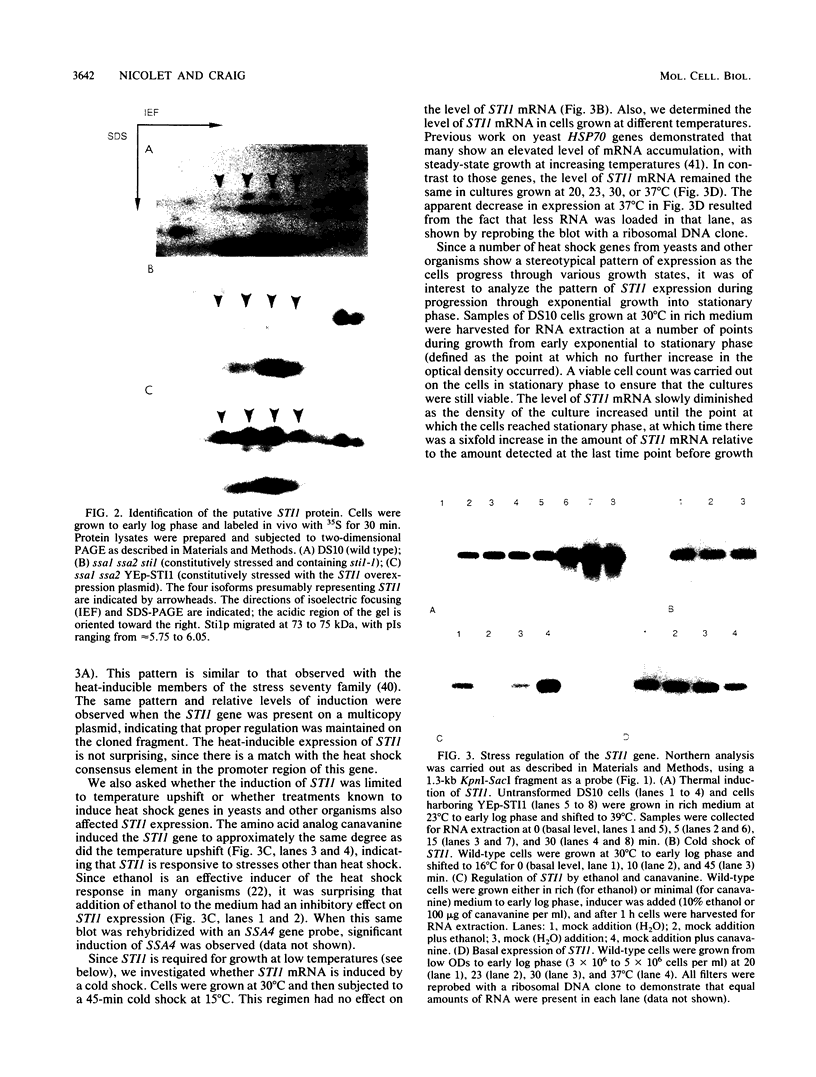
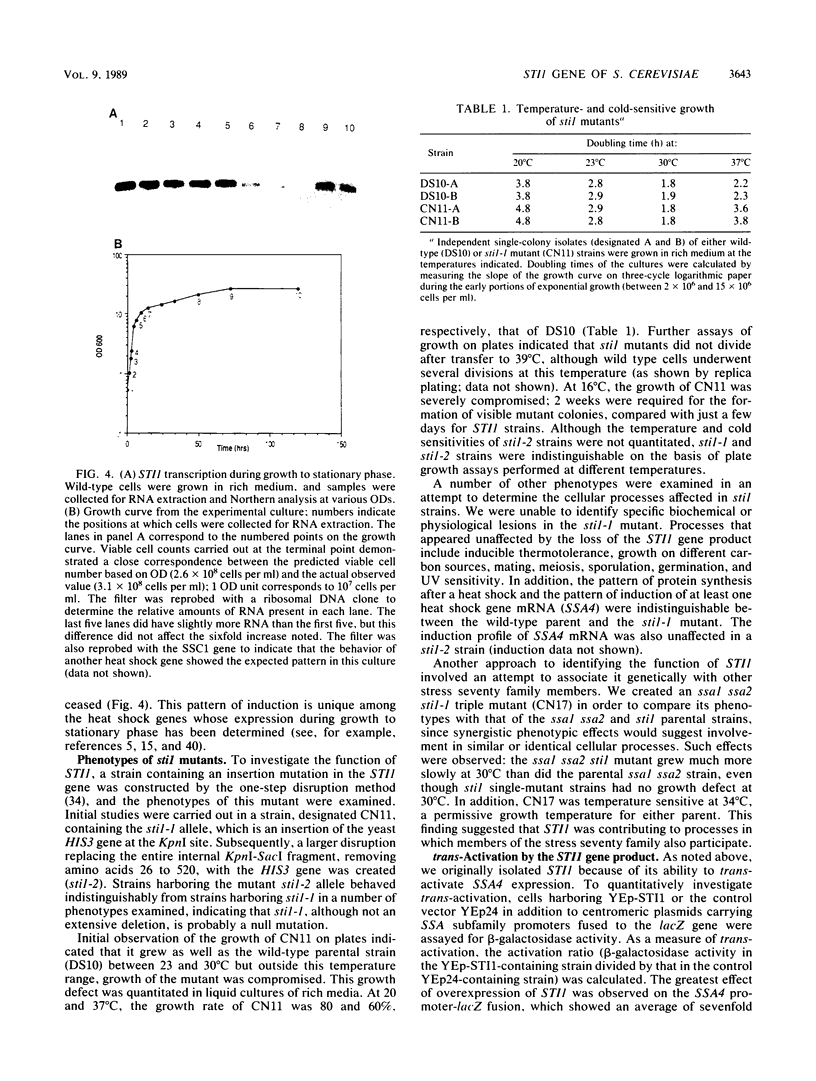
We have isolated a gene from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae that encodes a 2.0-kilobase heat-inducible mRNA. This gene, which we have designated STI1, for stress inducible, was also induced by the amino acid analog canavanine and showed a slight increase in expression as cells moved into stationary phase. The STI1 gene encodes a 66-kilodalton protein, as determined from the sequence of the longest open reading frame. The putative STI1 protein, as identified by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, migrated in the region of 73 to 75 kilodaltons as a series of four isoforms with different isoelectric points. STI1 is not homologous to the other conserved HSP70 family members in yeasts, despite similarities in size and regulation. Cells carrying a disruption mutation of the STI1 gene grew normally at 30 degrees C but showed impaired growth at higher and lower temperatures. Overexpression of the STI1 gene resulted in substantial trans-activation of SSA4 promoter-reporter gene fusions, indicating that STI1 may play a role in mediating the heat shock response of some HSP70 genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Ancient heat shock gene is dispensable. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):2977–2983. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.2977-2983.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazzell C., Ingolia T. D. Stimuli that induce a yeast heat shock gene fused to beta-galactosidase. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2573–2579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F. Sequence and structural features associated with translational initiator regions in yeast--a review. Gene. 1987;59(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Jacobsen K. Mutations in cognate genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae hsp70 result in reduced growth rates at low temperatures. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3517–3524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Jacobsen K. Mutations of the heat inducible 70 kilodalton genes of yeast confer temperature sensitive growth. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):841–849. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Kramer J., Kosic-Smithers J. SSC1, a member of the 70-kDa heat shock protein multigene family of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is essential for growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4156–4160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Ozkaynak E., Varshavsky A. The yeast polyubiquitin gene is essential for resistance to high temperatures, starvation, and other stresses. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90711-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. Regulation of protein synthesis during heat shock. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):311–314. doi: 10.1038/293311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Genetic analysis of the role of cAMP in yeast. Yeast. 1985 Sep;1(1):15–24. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClanahan T., McEntee K. DNA damage and heat shock dually regulate genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):90–96. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima A., Miyajima I., Arai K., Arai N. Expression of plasmid R388-encoded type II dihydrofolate reductase as a dominant selective marker in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):407–414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet C. M., Chenevert J. M., Friedberg E. C. The RAD2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence and transcript mapping. Gene. 1985;36(3):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petko L., Lindquist S. Hsp26 is not required for growth at high temperatures, nor for thermotolerance, spore development, or germination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90563-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. W., Curran B., Davies M. W., Hirst K., Lockheart A., Ogden J. E., Stanway C. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. A heat shock element in the phosphoglycerate kinase gene promoter of yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1333–1348. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Tuohy T. M., Mosurski K. R. Codon usage in yeast: cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5125–5143. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. R., Craig E. A. Transcriptional regulation of an hsp70 heat shock gene in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1906–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton A., Broach J. R. Signals for transcription initiation and termination in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae plasmid 2 micron circle. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2770–2780. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Washburne M., Becker J., Kosic-Smithers J., Craig E. A. Yeast Hsp70 RNA levels vary in response to the physiological status of the cell. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2680–2688. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2680-2688.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Washburne M., Stone D. E., Craig E. A. Complex interactions among members of an essential subfamily of hsp70 genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2568–2577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]