Abstract
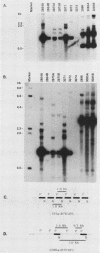
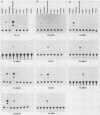
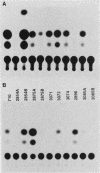
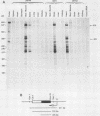
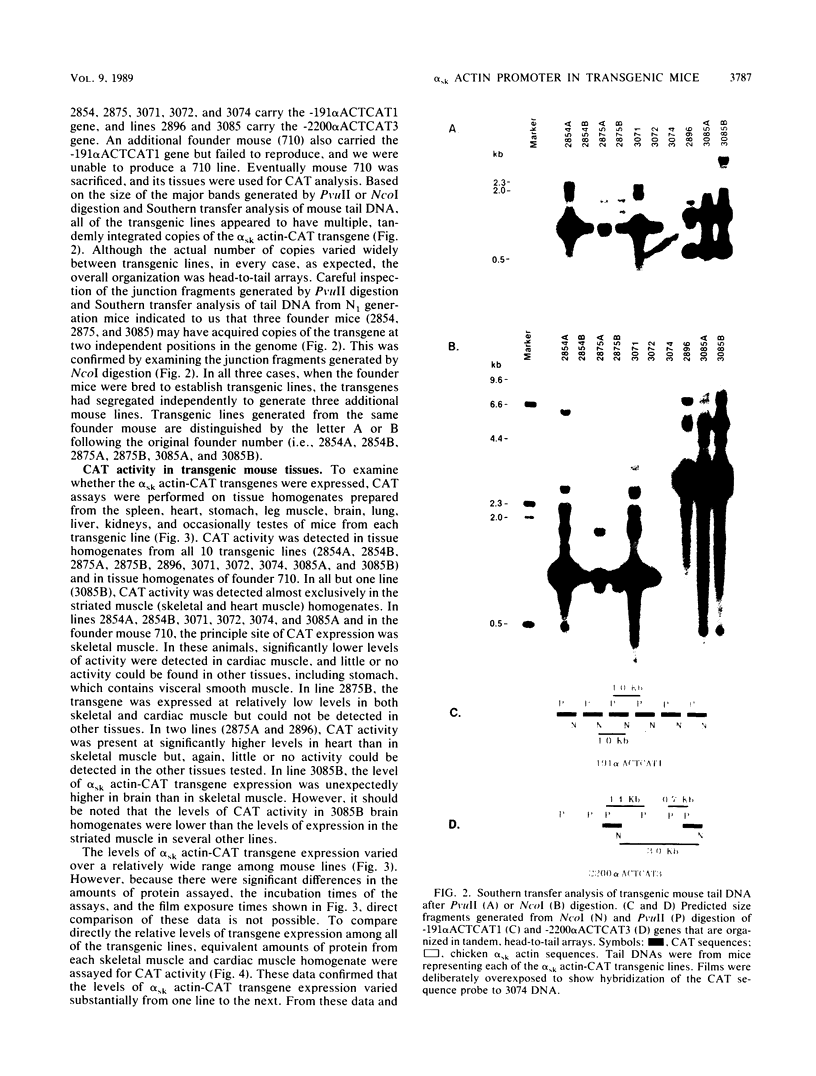
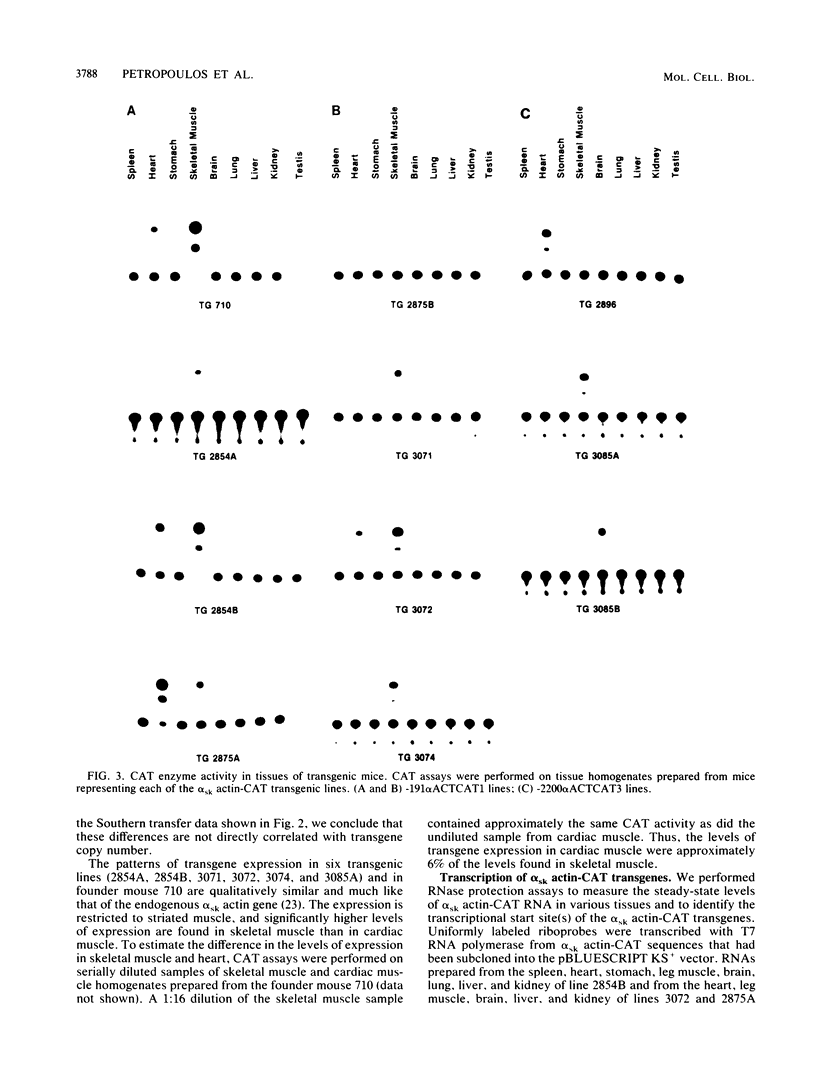
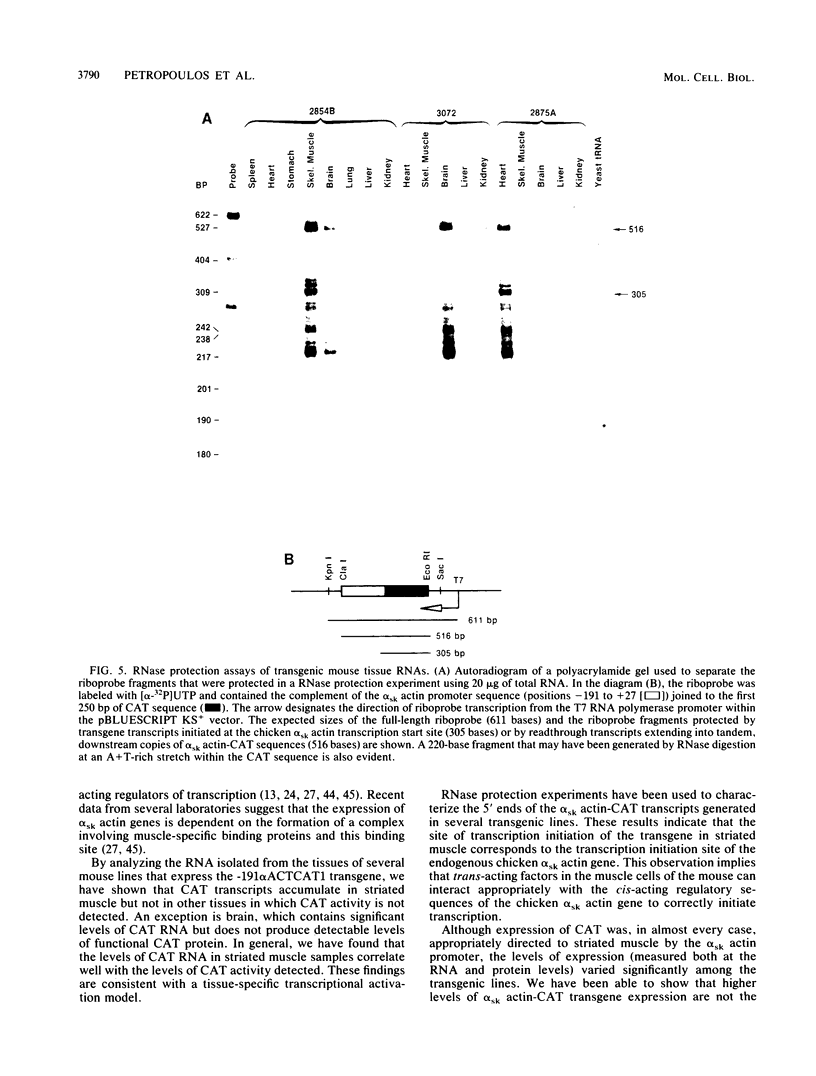
We have generated transgenic mouse lines that carry the promoter region of the chicken skeletal muscle alpha (alpha sk) actin gene linked to the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene. In adult mice, the pattern of transgene expression resembled that of the endogenous alpha sk actin gene. In most of the transgenic lines, high levels of CAT activity were detected in striated muscle (skeletal and cardiac) but not in the other tissues tested. In striated muscle, transcription of the transgene was initiated at the normal transcriptional start site of the chicken alpha sk actin gene. The region from nucleotides -191 to +27 of the chicken alpha sk actin gene was sufficient to direct the expression of CAT in striated muscle of transgenic mice. These observations suggest that the mechanism of tissue-specific actin gene expression is well conserved in higher vertebrate species.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos L. A. Structure of muscle filaments studied by electron microscopy. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:291–313. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.001451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bains W., Ponte P., Blau H., Kedes L. Cardiac actin is the major actin gene product in skeletal muscle cell differentiation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1449–1453. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Grichnik J. M., Gossett L. M., Schwartz R. J. Delimitation and characterization of cis-acting DNA sequences required for the regulated expression and transcriptional control of the chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2462–2475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. L., Bergsma D. J., Schwartz R. J. Structure and complete nucleotide sequence of the chicken alpha-smooth muscle (aortic) actin gene. An actin gene which produces multiple messenger RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8965–8976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M. Transgenic mice and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:25–48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Schmid E., Winter S., Chaponnier C., de Ckhastonay C., Vandekerckhove J., Weber K., Franke W. W. Vascular smooth muscle cells differ from other smooth muscle cells: predominance of vimentin filaments and a specific alpha-type actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):298–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Gibson W. Identification and characterization of multiple forms of actin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):793–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grichnik J. M., Bergsma D. J., Schwartz R. J. Tissue restricted and stage specific transcription is maintained within 411 nucleotides flanking the 5' end of the chicken alpha-skeletal actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1683–1701. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Hardeman E., Wade R., Ponte P., Bains W., Blau H. M., Kedes L. Differential patterns of transcript accumulation during human myogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4100–4114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Blau H., Kedes L. alpha-skeletal and alpha-cardiac actin genes are coexpressed in adult human skeletal muscle and heart. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):1985–1995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Miwa T., Boxer L. M., Kedes L. Interaction of nuclear proteins with muscle-specific regulatory sequences of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4110–4119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward L. J., Schwartz R. J. Sequential expression of chicken actin genes during myogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1485–1493. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey R., Skoultchi A., Gunning P., Kedes L. Regulation of a human cardiac actin gene introduced into rat L6 myoblasts suggests a defect in their myogenic program. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3287–3290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Sharp S. B., Davidson N. The complete sequence of the mouse skeletal alpha-actin gene reveals several conserved and inverted repeat sequences outside of the protein-coding region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):15–25. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Transgenic animals. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1468–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.3287623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer Y., Czosnek H., Zeelon P. E., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Expression of the genes coding for the skeletal muscle and cardiac actions in the heart. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1087–1100. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloul D., Aloni B., Calvo J., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Developmentally regulated expression of chimeric genes containing muscle actin DNA sequences in transfected myogenic cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):983–990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Alonso S., Caravatti M., Buckingham M. E. A fetal skeletal muscle actin mRNA in the mouse and its identity with cardiac actin mRNA. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Blau H., Kedes L. Two-level regulation of cardiac actin gene transcription: muscle-specific modulating factors can accumulate before gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Boxer L. M., Kedes L. CArG boxes in the human cardiac alpha-actin gene are core binding sites for positive trans-acting regulatory factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6702–6706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Kedes L. Duplicated CArG box domains have positive and mutually dependent regulatory roles in expression of the human alpha-cardiac actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2803–2813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. Upstream sequences required for tissue-specific activation of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus laevis embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3185–3193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. A common factor regulates skeletal and cardiac alpha-actin gene transcription in muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4120–4133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Multiple 5'-flanking regions of the human alpha-skeletal actin gene synergistically modulate muscle-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4089–4099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordahl C. P. The skeletal and cardiac alpha-actin genes are coexpressed in early embryonic striated muscle. Dev Biol. 1986 Oct;117(2):488–492. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90315-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordahl C. P., Tilghman S. M., Ovitt C., Fornwald J., Largen M. T. Structure and developmental expression of the chick alpha-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4989–5005. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Rosenberg M. P., Keller S. A., Meisler M. H. Tissue-specific and insulin-dependent expression of a pancreatic amylase gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):326–334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Eldridge J. D. alpha-Cardiac actin is the major sarcomeric isoform expressed in embryonic avian skeletal muscle. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1436–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6729461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Eldridge J. D., Paterson B. M. Expression and regulation of chicken actin genes introduced into mouse myogenic and nonmyogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M. Tissue-specific and developmentally regulated expression of a chimeric actin-globin gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2624–2631. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokunaga K., Takeda K., Kamiyama K., Kageyama H., Takenaga K., Sakiyama S. Isolation of cDNA clones for mouse cytoskeletal gamma-actin and differential expression of cytoskeletal actin mRNAs in mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3929–3933. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Bugaisky G., Buckingham M. Simultaneous expression of skeletal muscle and heart actin proteins in various striated muscle tissues and cells. A quantitative determination of the two actin isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1838–1843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Actin typing on total cellular extracts: a highly sensitive protein-chemical procedure able to distinguish different actins. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):595–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. At least six different actins are expressed in a higher mammal: an analysis based on the amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal tryptic peptide. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):783–802. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Chordate muscle actins differ distinctly from invertebrate muscle actins. The evolution of the different vertebrate muscle actins. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 5;179(3):391–413. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Mammalian cytoplasmic actins are the products of at least two genes and differ in primary structure in at least 25 identified positions from skeletal muscle actins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Schimmel P. DNA-binding site for two skeletal actin promoter factors is important for expression in muscle cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1800–1802. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K., Schimmel P. Two nuclear factors compete for the skeletal muscle actin promoter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9429–9432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut R., Shani M., Givol D., Neuman S., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Nucleotide sequence of the rat skeletal muscle actin gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):857–859. doi: 10.1038/298857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]