Abstract
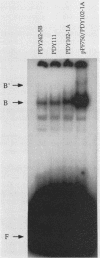
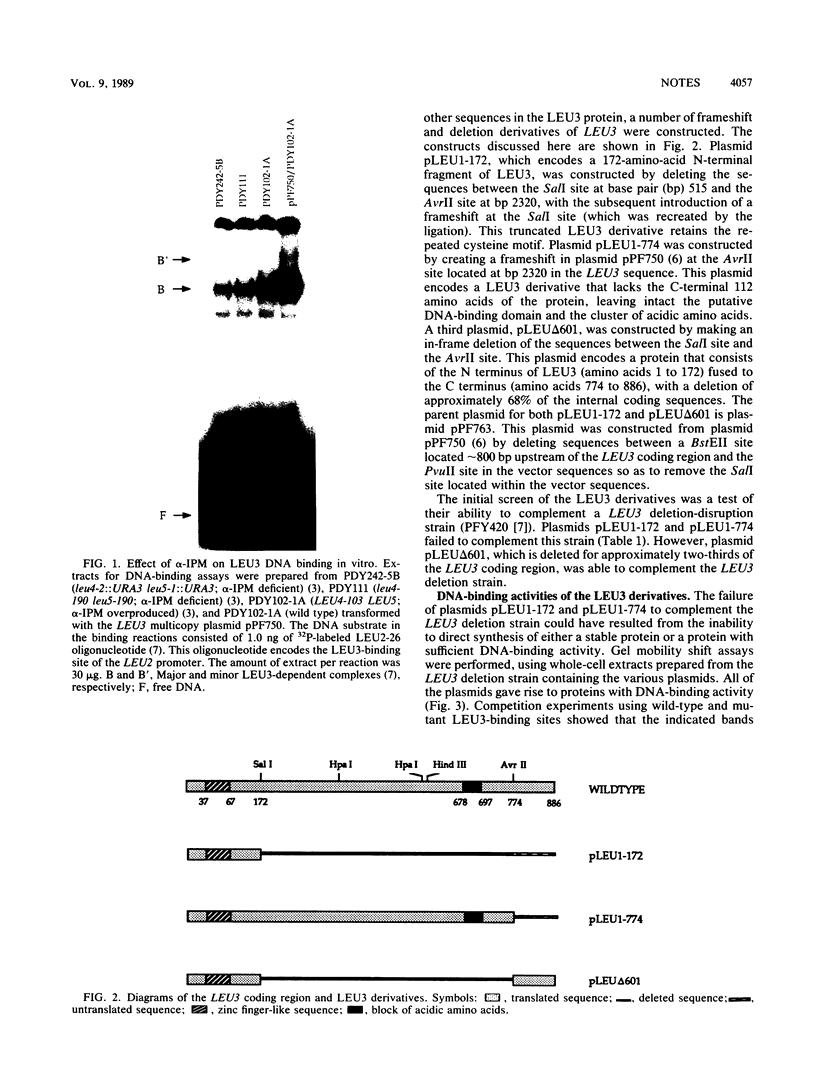
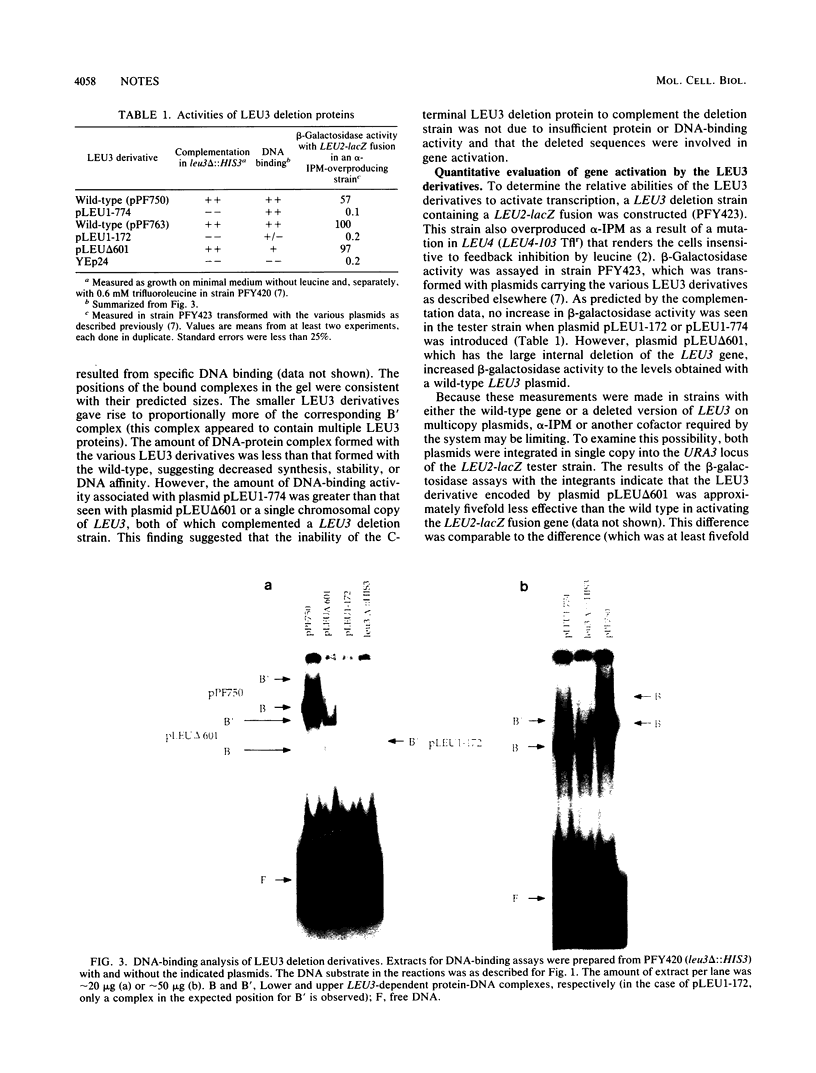
LEU3 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an 886-amino-acid polypeptide that activates transcription of at least five genes by binding to an upstream decanucleotide sequence. This activation is dependent on the inducer alpha-isopropylmalate, the synthesis of which is repressed by leucine. We created a 285-amino-acid LEU3 derivative by removing a large block of internal sequences, including a dense cluster of acidic residues. This deletion protein bound to the decanucleotide sequence in vitro and activated gene expression in vivo. In contrast to wild-type LEU3, the truncated LEU3 protein was an effective transcriptional activator when alpha-isopropylmalate synthesis was repressed by leucine.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreadis A., Hsu Y. P., Hermodson M., Kohlhaw G., Schimmel P. Yeast LEU2. Repression of mRNA levels by leucine and primary structure of the gene product. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8059–8062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drain P., Schimmel P. Yeast LEU5 is a PET-like gene that is not essential for leucine biosynthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Sep;204(3):397–403. doi: 10.1007/BF00331015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friden P., Schimmel P. LEU3 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae activates multiple genes for branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis by binding to a common decanucleotide core sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2690–2697. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friden P., Schimmel P. LEU3 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a factor for control of RNA levels of a group of leucine-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2708–2717. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Oestradiol induction of a glucocorticoid-responsive gene by a chimaeric receptor. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):75–78. doi: 10.1038/325075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu Y. P., Schimmel P. Yeast LEU1. Repression of mRNA levels by leucine and relationship of 5'-noncoding region to that of LEU2. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3714–3719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Dover J. Mutations that inactivate a yeast transcriptional regulatory protein cluster in an evolutionarily conserved DNA binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2401–2405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Salmeron J. M., Jr, Dincher S. S. Interaction of positive and negative regulatory proteins in the galactose regulon of yeast. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90671-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. The carboxy-terminal 30 amino acids of GAL4 are recognized by GAL80. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90670-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Kim K. S., Kogan S., Guarente L. Functional dissection and sequence of yeast HAP1 activator. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90903-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satyanarayana T., Umbarger H. E., Lindegren G. Biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids in yeast: regulation of leucine biosynthesis in prototrophic and leucine auxotrophic strains. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2018–2024. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2018-2024.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulm E. H., Böhme R., Kohlhaw G. Alpha-isopropylmalate synthase from yeast: purification, kinetic studies, and effect of ligands on stability. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1118–1126. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1118-1126.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]