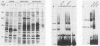Abstract
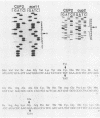
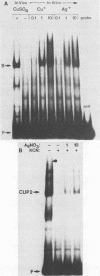
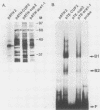
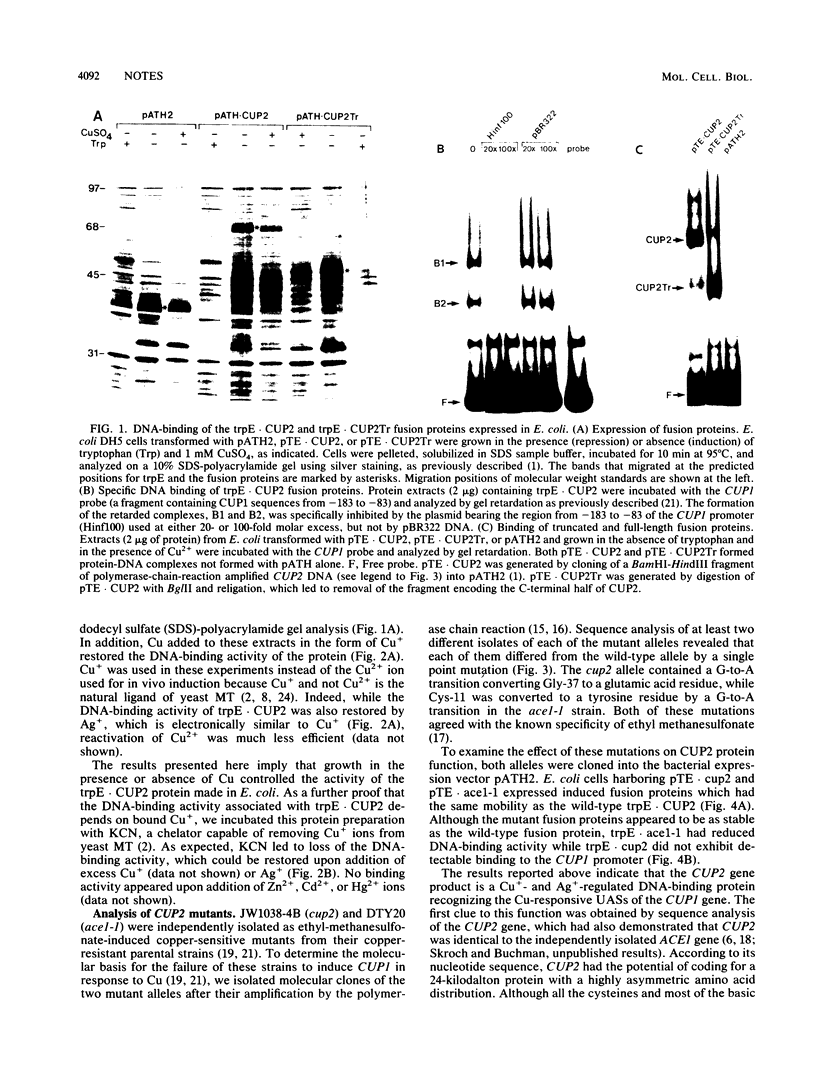
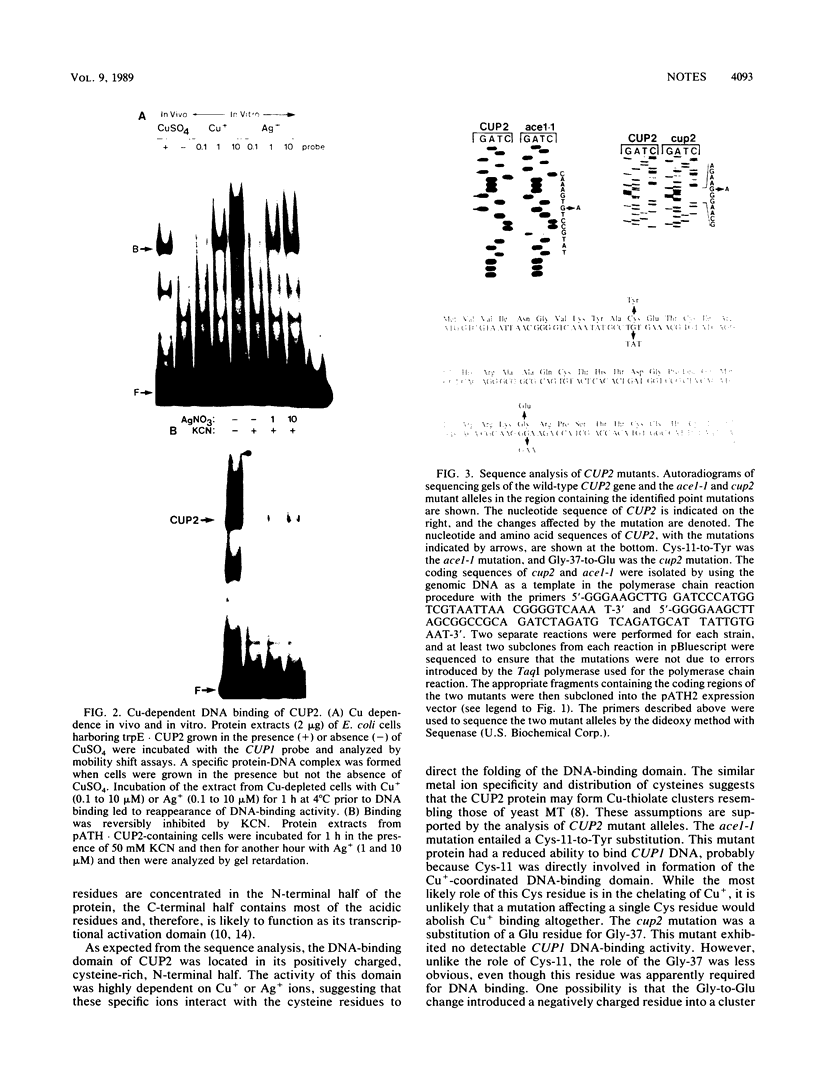
CUP2 is a regulatory gene controlling expression of CUP1, which encodes the Cu-binding yeast metallothionein. CUP2, which is identical to the ACE1 gene, encodes a Cu-regulated DNA-binding protein. The CUP2 protein contains a cysteine-rich DNA-binding domain dependent on Cu+ and Ag+ ions which bind the cysteine residues and direct the refolding of the metal-free apoprotein. CUP2 mutant alleles from Cu-sensitive yeast strains have point mutations affecting the DNA-binding activity. These results establish CUP2 as the primary sensor of intracellular Cu+ in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, functioning as a Cu+-regulated transcriptional activator.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd J., Berger R. M., McMillin D. R., Wright C. F., Hamer D., Winge D. R. Characterization of the copper-thiolate cluster in yeast metallothionein and two truncated mutants. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6688–6694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel S., Welch J. W. Tandem gene amplification mediates copper resistance in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5342–5346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hu S., Hackett R., Hamer D. Copper activates metallothionein gene transcription by altering the conformation of a specific DNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George G. N., Byrd J., Winge D. R. X-ray absorption studies of yeast copper metallothionein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8199–8203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H. Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:913–951. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Engelke D. R., Thiele D. J. Copper-induced binding of cellular factors to yeast metallothionein upstream activation sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):65–69. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Metallothioneins: proteins in search of function. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Najarian R., Haslinger A., Valenzuela P., Welch J., Fogel S. Primary structure and transcription of an amplified genetic locus: the CUP1 locus of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):337–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczypka M. S., Thiele D. J. A cysteine-rich nuclear protein activates yeast metallothionein gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):421–429. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J. ACE1 regulates expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae metallothionein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J., Hamer D. H. Tandemly duplicated upstream control sequences mediate copper-induced transcription of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae copper-metallothionein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1158–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J. W., Fogel S., Cathala G., Karin M. Industrial yeasts display tandem gene iteration at the CUP1 region. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1353–1361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J. W., Maloney D. H., Fogel S. Synaptic relations in meiotic gene conversion at the iterated CUP1r locus of S. cerevisiae. Experientia Suppl. 1987;52:431–437. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6784-9_42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J., Fogel S., Buchman C., Karin M. The CUP2 gene product regulates the expression of the CUP1 gene, coding for yeast metallothionein. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):255–260. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winge D. R., Nielson K. B., Gray W. R., Hamer D. H. Yeast metallothionein. Sequence and metal-binding properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14464–14470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]