Abstract
Ocean acidification due to rising atmospheric CO2 is expected to affect the physiology of important calcifying marine organisms, but the nature and magnitude of change is yet to be established. In coccolithophores, different species and strains display varying calcification responses to ocean acidification, but the underlying biochemical properties remain unknown. We employed an approach combining tandem mass-spectrometry with isobaric tagging (iTRAQ) and multiple database searching to identify proteins that were differentially expressed in cells of the marine coccolithophore species Emiliania huxleyi (strain NZEH) between two CO2 conditions: 395 (∼current day) and ∼1340 p.p.m.v. CO2. Cells exposed to the higher CO2 condition contained more cellular particulate inorganic carbon (CaCO3) and particulate organic nitrogen and carbon than those maintained in present-day conditions. These results are linked with the observation that cells grew slower under elevated CO2, indicating cell cycle disruption. Under high CO2 conditions, coccospheres were larger and cells possessed bigger coccoliths that did not show any signs of malformation compared to those from cells grown under present-day CO2 levels. No differences in calcification rate, particulate organic carbon production or cellular organic carbon: nitrogen ratios were observed. Results were not related to nutrient limitation or acclimation status of cells. At least 46 homologous protein groups from a variety of functional processes were quantified in these experiments, of which four (histones H2A, H3, H4 and a chloroplastic 30S ribosomal protein S7) showed down-regulation in all replicates exposed to high CO2, perhaps reflecting the decrease in growth rate. We present evidence of cellular stress responses but proteins associated with many key metabolic processes remained unaltered. Our results therefore suggest that this E. huxleyi strain possesses some acclimation mechanisms to tolerate future CO2 scenarios, although the observed decline in growth rate may be an overriding factor affecting the success of this ecotype in future oceans.
Introduction
Anthropogenic increases in CO2 are expected to cause a reduction in ocean pH within the next century [1] with unknown consequences for marine organisms. Dissolution of CO2 in seawater causes the formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3), which dissociates to form bicarbonate (HCO3 −) and H+ ions, causing a reduction in pH [2]. Liberated H+ ions react with carbonate ions (CO3 2−), further increasing [HCO3 −] whilst simultaneously causing a decrease in [CO3 2−]. This reaction results in a drop in the saturation state of the mineral form of calcite (Ω-cal). When Ω-cal is <1.0, CaCO3 (hereafter referred to as calcite) becomes thermodynamically unstable and dissolution can exceed precipitation, resulting in CaCO3 loss. Ocean acidification is therefore expected to affect calcifying marine organisms that produce external CaCO3 structures such as shells, plates and exoskeletons [3], [4].
Coccolithophores, a group of unicellular eukaryotic phytoplankton with an external coating of biogenically precipitated CaCO3 plates (coccoliths), have been extensively studied in the context of ocean acidification [5]. This is because coccoliths are produced in intracellular compartments where Ω-cal >1.0 and CaCO3 saturation is tightly controlled. Coccoliths are subsequently extruded to the cell surface where they are subjected to the inorganic carbon chemistry conditions of surrounding seawater as modified by cell acid-base chemistry in the cell's diffusion boundary layer. Coccolithophores play a significant role in the biological carbon pump through the combined effects of photosynthesis and calcification, via the sedimentation of coccoliths, which are considered a major component of marine CaCO3 sediments [6], [7]. So far, only a limited number of studies have investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying the responses of coccolithophores to future CO2 scenarios, including a few mRNA-led studies [8], [9] and a recent microarray approach [10]. However, a poor correlation between protein and mRNA levels has often been found in mammalian, yeast and bacterial cells [11]–[15] and the coupling of protein and transcript abundance can be as low as 40% depending on the system [16]. Recent results suggesting an uncoupling between transcript and protein levels in coccolithophores under ocean acidification [8] also indicate that a proteomic approach is an appropriate method to define the functional responses of these species to changing CO2.
To investigate the proteomic response of coccolithophores to ocean acidification, cultures of Emiliania huxleyi (Lohmann) Hay et Mohler strain NZEH were grown under 395 and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2, representing current day and projected CO2 levels for circa 2300 if all fossil fuel resources were released to the atmosphere [17]. We previously developed methods to enable quantitative proteomics on this species including a suite of bioinformatics tools to enable protein identification from a range of reference databases [18]. Therefore in addition to commonly measured physiological parameters such as cellular organic carbon and CaCO3, iTRAQ MS-based methods were applied to determine quantitative cellular proteomic differences between pCO2 conditions. iTRAQ tagging has recently been applied to other phytoplankton species, for example studies on light adaptation in marine cyanobacteria [19] and diatom toxicology [20] both utilize this approach as a means to investigate relative cellular proteome responses to environmental perturbations. For the current study, we used E. huxleyi NZEH, a heavy calcified strain, previously shown to exhibit an increase in calcification [21], [22] and a lower growth rate under high CO2 [21]. In view of a number of conflicting results previously reported for coccolithophore calcification under high CO2 [21]–[25], the aims of the present study were: (i) to extend the upper pCO2 level applied to E. huxleyi and examine its physiological responses, and (ii) survey the responses of its proteome to elevated CO2 levels. Extending the upper pCO2 level previously applied to NZEH [21] provided an opportunity to determine if our previous findings about calcification rates applied at worse case scenarios projected for CO2.
Materials and Methods
Culturing conditions
Oceanic seawater from the English Channel, offshore Plymouth (U.K.) was filtered through 0.22 µm Polycap capsules (Whatman, Maidstone, U.K.) and stored in the dark at 6°C. Emiliania huxleyi strain NZEH (also known as “PLY M219” and “CAWPO 6 A”) was obtained from the Plymouth Culture Collection of the Marine Biological Association of the U.K. This is a morphotype R strain that was isolated from the South Pacific in 1992. In all instances, cells were cultured in seawater supplemented with a modified f medium containing 100 µmol kg−1 nitrate, 6.24 µmol kg−1 phosphate and f/2 concentrations of trace metals and vitamins [26]–[28]. Cells were grown at 19.0±0.5°C in a 12∶12 h light: dark cycle typically between 80–120 µmol photons m−1 s−1 under Sylvania Standard F36W/135-T8 white fluorescent lighting (Havells Sylvania, Newhaven, U.K.). Cultures were bubbled with air containing either 385 or 1500 p.p.m.v. CO2 (BOC, Guildford, U.K.), filtered through 0.3 µm using sterile Hepavent discs (Whatman), which subsequently equilibrated to 395 and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2.
Exponentially growing E. huxleyi cells were initially inoculated to a concentration of 7×103 cells mL−1 into 2.4 L media that were previously bubbled for 72 h with the appropriate pCO2 in custom-built 3 L glass flasks fitted with Dreschel heads [21]. Cultures (<105 cells mL−1) were bubbled very gently for ∼2–4 generations to allow cells to adjust to the bubbling regime. Aliquots of these cultures were inoculated into 20 L Nalgene polycarbonate culture vessels (Thermo Scientific Nalgene, Roskilde, Denmark) containing 14.7 L media to reach a starting cell density of 1.6×103 cells mL−1. To enable dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) equilibration, media within these vessels were bubbled for 7 days prior to the inoculation of cells. Cultures were continuously bubbled and, approximately 5–6 generations after inoculation (when cells were acclimated and cell density was ∼5×104 to 105 mL−1), samples were taken (start of experiment [“t1”] was day 6 and 7 for cells grown under 395 and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 respectively). Cells from this acclimation culture were used to inoculate a final 14.7 L culture to a starting concentration of 5×103 cells mL−1. Cells were harvested after ∼4 generations, when cell density was ≤1×105 cells mL−1 (time of harvest [“t2”] was day 8 for cells grown under 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 and day 9 or 10 for those grown under 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2). The treatment-dependent differences in sample days for t1 and 2 relate to differences in growth rates between the two CO2 conditions. Experiments were conducted in triplicate and one flask for each air-CO2 mixture was left without cells to act as a blank for each experiment. Daily pH readings were taken using a calibrated pH meter to monitor changes through the experiment.
Coccosphere volume, cell density and growth rate
Cell density and coccosphere (cells and their surrounding coccoliths) volume was measured daily. Aliquots of cultures were diluted 1∶10 with 3% NaCl (w/v) and analyzed using a Beckman Coulter Counter III fitted with a 70 µm aperture (Beckman Coulter, High Wycombe, UK). Mean coccosphere volume and cell density were calculated from triplicate samples and the growth rate (μ) was calculated as follows:
whereby C 1 and C 0 refer to the end and initial cell densities during the exponential phase of growth and Δt refers to the duration of this phase. Following derivations from Novick and Szilard [29], the number of generations of growth (g) for each stage of the experiment was defined according to:
whereby N 1 and N 0 refer to the end and inoculum cell densities respectively.
Particulate organic carbon and nitrogen
Samples for particulate organic carbon (POC) and nitrogen (PON) were obtained in triplicate at t1 and 2 by filtration of culture aliquots onto pre-combusted 25 mm GF/F filters (Whatman). PIC was removed by acidification of the filters for 48 hours in a desiccator saturated with sulphuric acid fumes. Filters were then dried, pelleted and analyzed as previously described [14]. Cellular POC production (PPOC, pmol POC cell −1 day −1) was calculated according as follows:
Particulate inorganic carbon
Samples for cellular particulate inorganic carbon (specifically CaCO3) were obtained as previously described [21]. Coccolith-derived CaCO3 was dissolved by placing the filters in ∼20 mL 0.1 M HNO3, and [Ca2+] was determined using a Varian Vista Pro inductively coupled plasma emission spectrophotometer (ICP-OES; Agilent, Stockport, UK). Instrument calibration followed procedures used for the determination of Mg/Ca in foraminiferal calcite [30]. [Na+] was measured as a proxy for residual seawater Ca2+. Filters rinsed with the control media were also analyzed to confirm that the seawater contribution to measured [Ca2+] was negligible. Following the conversion of measured [Ca2+] to cellular CaCO3, production (PCaCO3, pmol CaCO3 cell −1 day −1) was calculated according as follows:
Seawater nitrate, phosphate and silicate
Aliquots of 25 mL of culture were filtered through 0.22 µM for determination of nitrate, phosphate and silicate concentrations using a Seal QuAATro Autoanalyzer (Seal Analytical, Fareham, U.K.) with appropriate standards in the bracket of the expected concentrations.
Dissolved inorganic carbon and total alkalinity
Culture aliquots were sampled for DIC and total alkalinity (TA) as previously described [21] and analyzed using the Versatile INstrument for Determination of Total Alkalinity (VINDTA; Marianda, Germany), a combined DIC and TA measuring system. Certified reference materials to calibrate and establish correction factors for VINDTA measurements were obtained from Professor Andrew Dickson at the Marine Physics Laboratory of the Scripps Institute of Oceanography, University of California San Diego, U.S.A. VINDTA-derived values for TA and DIC were corrected for various parameters including titration acid density, the nutrient concentration of the sample, temperature, salinity and reference material values. Final carbonate system parameters and pH were obtained with CO2SYS software [31] using a total pH scale (mol/kg-SW), K1 and K2 constants [32] with refits [33] and the acidity constant of the ion HSO4 − in sea water taken into account [34].
Scanning electron microscopy and coccolith morphometrics
Samples for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were pipetted onto 25 mm Isopore polycarbonate filters (Millipore), washed three times with alkaline milli-Q water (pH∼9) and dried at 37°C overnight. Filters were coated with a gold-palladium alloy and microscopic analysis was undertaken at the Natural History Museum, London, UK using a Zeiss Gemini Ultra Plus scanning electron microscope (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). The ImageJ software suite [35] was used to measure coccolith distal shield length and central area width [36]. A minimum of 23 detached coccoliths was considered for each replicate at t2. In total, 115 and 82 coccoliths were analyzed from cultures bubbled with 395 and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 respectively.
Photochemical quantum efficiency
Maximum quantum efficiency of photosystem II (PSII) was analyzed at both t1 and 2 using a Satlantic FIRe (Fluorescence Induction and RElaxation) system (Satlantic, Halifax, Canada) [37]. Measurements of Fv/Fm were taken four hours into the 12 h light phase, after samples were kept in the dark for 5 min.
Protein extraction
At t2, cells were spun down at ∼500–1,000 g for 5 min and washed four times with calcium-free artificial seawater (pH 8) followed by hypersonication in 100 mM triethylammonium bicarbonate (pH 8.0) with 0.1% (w/v) SDS [18]. Proteins were subsequently precipitated using acetone (1∶10) and solubilized as previously described [18]. Protein concentrations in each sample were then assayed using the bicinchoninic method (Sigma Aldrich, Gillingham, U.K.).
8plex iTRAQ peptide labeling
Proteins were reduced, alkylated and then digested by adding 10 µL of 1 mg/mL trypsin in 80 mM CaCl2 followed by an overnight incubation at 37°C. The resulting trypsin digests were lyophilized and 90 µg of each sample were labeled with 8plex iTRAQ tags according to manufacturer's instructions (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, U.S.A.). iTRAQ tags 113, 115, 117 and 119 were added to peptides extracted from first, second, third and fourth 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 replicates respectively. Tags 114, 116, 118 and 121 were added to peptides from the first, second, third and fourth 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 replicates. Protein digests were incubated at room temperature for 2 hours and vigorously vortexed because of the presence of a heavy CaCO3-like pellet. Resuspensions were spun down at 21,250 g for 30 min and supernatants were combined, dried overnight and stored at 4°C prior to tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) analysis. Data from the fourth replicate (reporter ions 119 and 121) were analyzed but excluded from further investigation because cell density thresholds of 105 cells mL−1 were exceeded.
2D-UPLC and MS/MS
Two-dimensional separations were performed using a nanoAcquity 2D high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) system (Waters, Elstree, UK) as described in Methods S1. All data were acquired using a Q-Tof Global Ultima (Waters, U.K.) and peak lists were generated as previously described [18]. MS/MS spectra were processed using a normal background subtraction with a 25% background threshold and medium de-isotoping with a threshold of 1%. No smoothing was performed. All spectra (24,119) obtained in these experiments were converted using PRIDE Converter [38] and are available in the PRIDE database [39] (www.ebi.ac.uk/pride) under accession number 20984.
Protein identification and quantification
Peak lists from the MS/MS analysis were submitted to the Mascot search engine version 2.2.1 (Matrix Science, London, UK) against a database containing 130,000 E. huxleyi expressed sequence tags (ESTs) obtained from the NCBI EST database [40]–[43]. Searches were performed in all 6 EST reading frames and results were processed using BUDAPEST [18]. Output files from BUDAPEST analysis can be found in Data S1 and at http://bioware.soton.ac.uk/research/ehux/jones2012/
Additional analyses were performed against the E. huxleyi CCMP1516 draft genome produced by the US Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute (JGI; http://www.jgi.doe.gov) in collaboration with the user community. Searches were conducted against a non-redundant set of E. huxleyi CCMP1516 draft genome proteins using the “Emihu1_all_proteins.fasta” file downloaded on 02/16/12, which originally contained 217,034 filtered sequences from all models generated by the JGI Annotation Pipeline. This file was reduced to 115,995 non-redundant sequences for search purposes. Further searches were also conducted against a taxonomically restricted database constructed from UniProtKB sequences as described [18] with the addition of Chlorophyta. Mascot search criteria can be found in Methods S1. Pfam domain searches (e≤1.00e-04) [44] were conducted for any sequences that either lacked BLAST homology or only had homology to “hypothetical”, “predicted” or “unknown” proteins. Because of identification redundancy relating to the use of multiple search databases, we clustered identifications into Homologous Protein Groups (HPGs) using a combination of alignment and BLAST-based comparative analyses (similarity threshold of e≤1.00e-10 and >5% identity) [45].
Protein expression ratios were calculated using Mascot software, whereby peptide ratios were weighted and median normalization was performed, automatic outlier removal was selected and the peptide threshold was set to ‘at least homology’. If a protein identification only contained data for a single iTRAQ associated peptide, it was not further considered. Additionally, if an iTRAQ ratio was derived from only 2 peptides and one of these showed erroneously high or negative values, the protein was no longer considered for quantitative analysis. Geometric means, G, for the ratios of protein expression from each individual high: current day CO2 incubation were calculated and variance assessed by determination of the 95% confidence interval (CI). If the G±CI was ≥1.5, the protein was considered up-regulated and if the value was ≤0.67 then it was classed as down-regulated.
To expand our knowledge of the E. huxleyi proteome, data generated from the current study were combined with proteins identified from our previous proteomic investigation of E. huxleyi [18]. A combination of direct (accession number), indirect (protein name) and BLAST-based homology enabled the compilation of identifications from both studies. Results can be found in Data S2.
Statistical analyses
We performed unpaired t-tests on physiological data using Sigma Stat 3.5 (Systat software, Hounslow, UK).
Results
Carbonate chemistry and culturing conditions
Measurements of DIC and TA were conducted at various times of the experiment and were analyzed by the VINDTA system. The remaining carbonate chemistry parameters (CO3 2−, HCO3 −, CO2, pH, and Ω-cal) were calculated ( Table 1 ). At the time of cell harvest (t2), the media of cultures grown under 395.0 p.p.m.v. CO2 had a pH of 7.94 and an Ω-cal of 3.96 whilst cells grown under ∼1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 were in media with a pH of 7.47 and an Ω-cal of 1.52 ( Table 1 ). At t2, less than ∼5% DIC was utilized by cells under 395 and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 compared to the blank, thus indicating that a semi-constant chemistry state was maintained throughout these experiments by keeping cell densities<105 cells mL−1. Data from the fourth incubation were excluded from the analyses because cell densities exceeded this value. Carbonate chemistry values for t1 and bubbled media prior to cell addition can be found in Tables 1 , S1 and S2.
Table 1. Mean carbonate chemistry values associated with experimental cultures (t2).
| Ambient | 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 | ||
| p CO2 (p.p.m.v.) | Initiala | 433.1(395.9)b , c | 1398.4 (1376.8) |
| Endd | 395.0 (397.6) | 1340.6 (1412.7) | |
| [CO2] (µmol kg SW−1) | Initial | 14.4 (13.2) | 47 (46.3) |
| End | 13.2 (13.4) | 44.7 (47.7) | |
| [CO32−] (µmol kg SW−1) | Initial | 167.4 (172.4) | 65.6 (66.4) |
| End | 166.7 (174.2) | 63.8 (64.3) | |
| [HCO3−] (µmol kg SW−1) | Initial | 1870.9 (1863.4) | 2136.5 (2132.9) |
| End | 1785.5 (1856.3) | 2037.1 (2140.6) | |
| [DIC] (µmol kg SW−1) | Initial | 2052.8 (2049.2) | 2249 (2245.5) |
| End | 1965.4 (2043.8) | 2145.7 (2252.6) | |
| Ω-cal | Initial | 3.97 (4.16) | 1.57 (1.59) |
| End | 3.96 (4.18) | 1.52 (1.55) | |
| pH | Initial | 7.92 (8.05) | 7.48 (7.48) |
| End | 7.94 (7.95) | 7.47 (7.48) | |
| TA (µmol kg SW−1) | Initital | 2292.4 (2293.2) | 2304.2 (2302.5) |
| End | 2206.5 (2291.0) | 2200.4 (2302.8) |
Average values at the beginning of the experiment before the inoculation of cells.
Figures in parentheses represent blank seawater medium bubbled with the appropriate pCO2 mixture.
There was only one sample available for the initial pre-inoculation blank of the ambient/current day CO2 condition. For this instance alone, values in parentheses are from the second 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 treatment.
Average values at the end of the experiment (t2).
Cells were nutrient-replete throughout the entire experiment and, at the end of the experiment (t2), nitrate values ranged from 56.7–103.8 µmol kg−1 and phosphate values ranged from 2.4–4.2 µmol kg−1 (Tables S3, S4). At the end of the experiment (t2), there was no difference in nitrate utilization [t(4) = −0.0263; p = 0.980] between the low and high CO2 conditions, with respective decreases of 23.2%±4.7 and 23.3%±4.7. Also, even though there was a trend towards increased phosphate utilization under high CO2 at t2, this was not statistically significant [t(4) = −1.830; p = 0.141]. Cells incubated under 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 used 29.4%±6.3 of phosphate compared to 41.7%±9.8 for cells grown under the 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 treatment.
Cellular physiology
At the time of harvest (t2), substantial differences in cell physiology were observed for cells incubated under 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2. There was a significant increase in the cellular content of POC [t(4) = −3.233; p = 0.032], CaCO3 [t(4) = −7.015; p = 0.002] and PON [t(4) = −4.399; p = 0.012] at the end of the experiment and a significantly lower growth rate [μ; t(4) = 3.556; p = 0.024; Table 2 ]. However, no differences were encountered in CaCO3 [t(4) = −0.173; p = 0.871] and POC production rates [t(4) = −0.662; p = 0.544] or in CaCO3:POC [t(4) = 0.672; p = 0.538] and POC:PON [t(4) = 0.836; p = 0.450] cellular ratios. Similarly, there was no change in the photosynthetic energy conversion efficiency of PSII, with Fv/Fm values of 0.64±0.01 and 0.65±0.01 for cells incubated under 395 and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 respectively [t(4) = −0.164; p = 0.878; Table S5].
Table 2. Physiological parameters of Emiliania huxleyi NZEH grown under 395 and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 at t1 and 2.
| Condition | μ | pmol POC cell−1 | pmol POC cell−1 day−1 |
| 395 t1 | 1.63±0.36 | 0.87±0.03** b | 1.43±0.35 |
| 1340 t1 | 1.30±0.23 | 1.43±0.15** | 1.87±0.48 |
| 395 t2 | 1.29±0.04* | 1.37±0.13* b | 1.76±0.12 |
| 1340 t2 | 1.05±0.11* | 1.84±0.22* | 1.92±0.40 |
Significant results from t-tests comparing results from different pCO2 treatments at the same time point (i.e. 395 v 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 at t1; 395 v. 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 at t2) are designated as follows: * p≤0.05; ** p≤0.01; *** p≤0.001.
Significant results from t-tests comparing results from the same pCO2 treatment at different time points (e.g. 395 t1 v 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 t2) are defined according to: a p≤0.05; b p≤0.01.
We observed differences in physiology between cells at different stages of the experiment (t1 and t2). For example, there was a significantly higher cellular POC [t(4) = −6.385; p = 0.003] and PON content [t(4) = −5.790; p = 0.004] at t2 compared to t1 for cells grown under 395 p.p.m.v. CO2. Similarly, there was also a significantly higher cellular CaCO3 content at t2 for cells incubated under both 395 [t(4) = −4.735; p = 0.009] and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 [t(4) = −3.927; p = 0.017; Table 2 ].
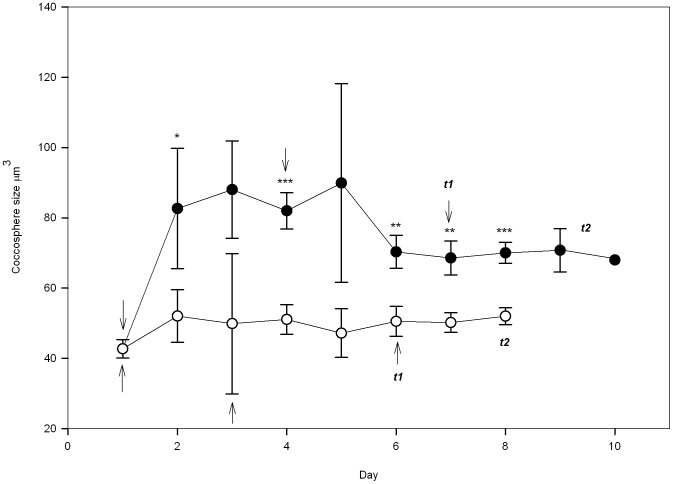
At the end of the experiment, increases in cellular CaCO3, POC and PON in cells grown under 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 coincided with an increase in coccosphere volume ( Figure 1 ). Cells grown in nutrient-replete media equilibrated to this high CO2 condition showed an increase in coccosphere volume 24 h after inoculation, with a mean volume of 82.7 µm3±17.1 compared to 52.0 µm3±7.5 under 395 p.p.m.v. CO2. The difference in coccosphere volume between conditions was not always significant ( Figure 1 ). However, as generational time increased and cells acclimated, the variability in coccosphere volume decreased ( Figure 1 ). Consequently, coccosphere volumes at the time of harvest were significantly different, with a mean value of 69.44 µm3±8.37 for cells grown under the high CO2 treatment compared to 52.00 µm3±2.26 for cells grown under 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 [t(4) = −3.465; p = 0.026].
Figure 1. Comparison of Emiliania huxleyi NZEH coccosphere sizes at 395 and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2.
* p≤0.05; ** p≤0.01; *** p≤0.001. A point with no star indicates differences were non-significant. Arrows indicate inoculations into media with different pCO2 conditions, as outlined in Materials and Methods. Open circles represent cells grown under under 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 that were harvested after 12–13 generations (t2 = day 8). Solid circles indicate cells grown under 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2. In order to ensure suitable biomass for proteomics, these were harvested after 9–12 generations (t2 = day 9 or 10) because of their lower growth rates.
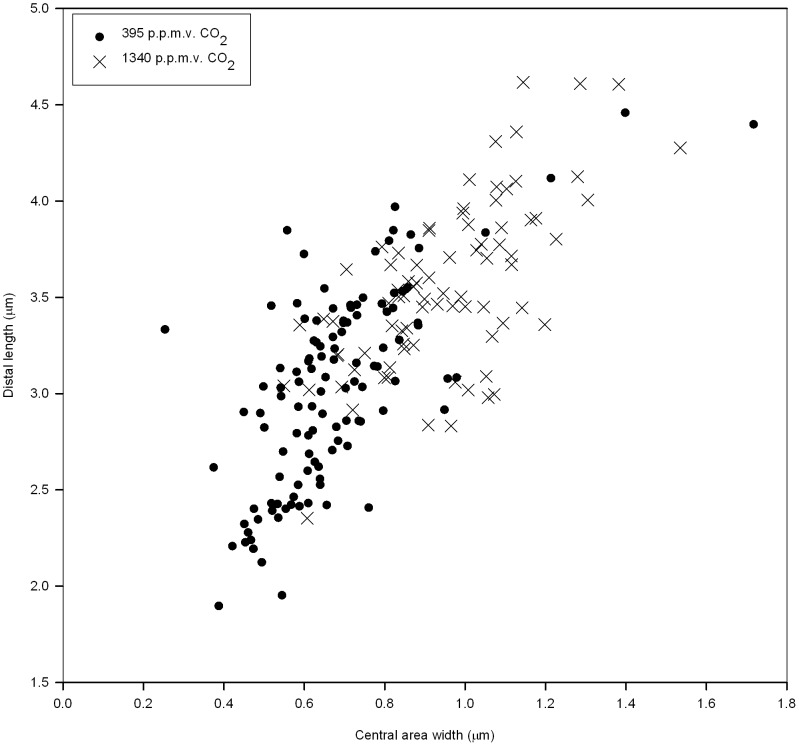
An increase in coccosphere volume at the time of harvest (t2) was accompanied by a significant increase in the size of individual coccoliths ( Figure 2 ). Specifically, the mean distal length of coccoliths for cells grown under the high CO2 condition was 3.56 µm±0.44, whereas values for 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 were 3.03 µm±0.52 [t(195) = −7.526; p<0.001]. Coccoliths from cells incubated under 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 did not show any sign of dissolution or malformation ( Figures 3a and 3b ). However, they were less calcified, possessing a central area width of 0.95 µm±0.19 compared to those from current conditions that had an average width of 0.67 µm±0.19 [t(195) = −10.080; p<0.001]. Despite these clear trends, we still found variation within the dataset that is typical for coccoliths derived from cultures.
Figure 2. Morphometric analysis of detached coccoliths obtained at the end of the experiment (t2) from monoclonal cultures of Emiliania huxleyi NZEH bubbled with 395 and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2.
Figure 3. Example of coccoliths derived at the end of the experiment (t2).
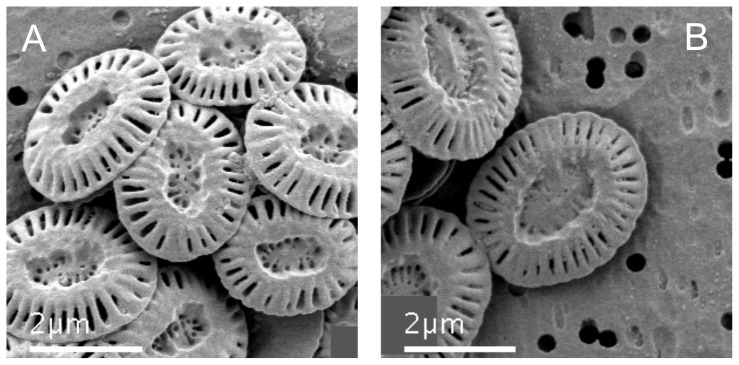
Panel A: typical coccoliths from 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 treatment; B: coccoliths from the lower pH (∼7.6) and 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 treatment which are typically larger and are slighly less calcified but possess no signs of dissolution or malformation.
Proteomic identifications
MS/MS spectra of peptides derived from E. huxleyi protein extracts were searched against protein sequences from the E. huxleyi CCMP1516 draft genome. This yielded 40 matches from 37 homologous protein groups (HPGs) and the identification of 21 HPGs with iTRAQ quantification. Data were also searched against a taxonomically-restricted subset of UniProtKB. This resulted in the identification of 21 HPGs based on the assignment of at least two peptides, of which 10 could be quantified ( Tables 3 and 4 ). Data were also searched against a database containing ∼130,000 E. huxleyi ESTs using Mascot, which resulted in 180 matches possessing ≥2 peptides. Following BUDAPEST analysis, 97 clusters were formed that comprised of 128 consensus sequences assembled from 150 ESTs. The manual removal of identifications with data for only one iTRAQ-tagged peptide resulted in 37 HPGs with quantification information ( Tables 3 and 4 ). When all identifications from the genome project, the taxonomically restricted UniProtKB database and EST searches were considered and combined, we were able to identify 115 HPGs. Of these, 46 could be quantified; in depth information regarding all quantified and non-quantified identifications can be found in Data S2.
Table 3. Proteins (Homolgous Protein Groups) down-regulated in Emilania huxleyi NZEH under high CO2.
| Identification | Accessiona/EST cluster | 114∶113b | 116∶115 | 118∶117 | Rangec |
| 30S ribosomal protein S7 | Q4G343 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.61 | 0.27–0.66 |
| Histone H2A | D0MWJ7 | 0.49 | 0.41 | 0.39 | 0.37–0.49 |
| 87a | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.45–0.64 | |
| EHUXJGI72235 | 0.49 | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.38–0.50 | |
| Histone H3 | EHUXJGI255477 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.20–0.40 |
| Histone H4 | C1MUM2 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 0.56 | 0.24–0.59 |
| 92a | 0.37 | 0.25 | 0.56 | 0.24–0.59 | |
| EHUXJGI201707 | 0.37 | 0.22 | 0.39 | 0.21–0.46 |
Identifications are associated with either UniProtKB accession, Emiliania huxleyi genome protein ID or BUDAPEST consensus sequence. Further information can be found in Data S2; BUDAPEST sequence files can be found in Data S1.
Ratio of protein identified between the two CO2 treatments for each replicate incubation, whereby 114∶113 is the first replicate, 116∶115 is the second and 118∶117 the third. Reporter ions 114, 116 and 118 were applied to peptides extracted from the high CO2 treatments and 113, 115, 117 to the current day treatment.
“Range” (G−CI)–(G+CI) as defined in Materials and Methods.
Table 4. Proteins (Homologous Protein Groups) exhibiting non-significant expressional change in Emilania huxleyi NZEH under high CO2.
| Identification | Accessiona/EST cluster | 114∶113b | 116∶115 | 118∶117 | Rangec |
| 40S ribosomal protein S12 | 81a | 2.09 | 2.01 | 0.27 | 0.28–3.90 |
| EHUXJGI240824 | 2.01 | 1.87 | 0.28 | 0.29–3.60 | |
| 50S ribosomal protein L12 (chloroplastic) | 86a | 1.95 | 1.88 | 0.24 | 0.25–3.70 |
| EHUXJGI86748 | 1.86 | 1.83 | 0.23 | 0.24–3.60 | |
| Acyl carrier protein | 97a | 1.81 | 2.47 | 1.01 | 0.99–2.76d |
| Adenosylhomocysteinase | 26a | 0.27 | 1.05 | 1.27 | 0.27–1.86 |
| Adenylate kinase (putative) | 33a | 1.45 | 1.82 | 0.68 | 0.67–2.18 |
| Ankyrin repeat protein (putative) | 51a | 1.69 | 1.86 | 0.47 | 0.47–2.72 |
| Apocytochrome f (precursor) | Q4G3D7 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.61 | 0.61–0.94 |
| 35a | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.61 | 0.61–0.94 | |
| ATP ase/synthase (vacuolar) | 91a | 2.57 | 1.97 | 0.44 | 0.45–3.83 |
| EHUXJGI210241 | 2.48 | 1.88 | 0.45 | 0.45–3.62 | |
| ATP synthase subunit alpha | 07a | 0.71 | 0.96 | 1.24 | 0.69–1.30 |
| EHUXJGI199000 | 0.65 | 1.36 | 1.06 | 0.64–1.50 | |
| ATP synthase F(1) sector subunit alpha (chloroplastic) | Q4G397 | 0.32 | 0.78 | 1.12 | 0.32–1.35 |
| C7BEK1 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.11 | 0.38–1.20 | |
| ATP synthase F (0) sector subunit b′ (chloroplastic) | Q4G3A0 | 0.95 | 0.57 | 0.77 | 0.56–1.00 |
| ATP synthase F(1) sector subunit beta (chloroplastic) | Q4G3C8 | 0.62 | 1.02 | 1.09 | 0.63–1.24 |
| Chloroplast light harvesting protein isoform | 12a | 0.33 | 0.57 | 0.78 | 0.32–0.87d |
| 12b | 0.24 | 0.44 | 0.90 | 0.22–0.96 | |
| Clathrin small chain (putative) | 18a | 1.21 | 1.36 | 0.84 | 0.83–1.48 |
| Clp protease ATP binding subunit | Q4G3D0 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 0.74 | 0.42–0.78 |
| Cold shock DNA-binding protein (putative) | 96a | 2.22 | 6.00 | 0.47 | 0.43–7.87 |
| EHUXJGI111020 | 1.23 | 1.32 | 0.70 | 0.71–1.55 | |
| Demethylmenaquinone methyltransferase (putative) | 09a | 1.98 | 1.91 | 0.40 | 0.41–3.23 |
| ETC complex I protein (putative) | 44a | 1.29 | 1.25 | 0.73 | 0.73–1.51 |
| Ferredoxin–NADP reductase | 29a | 0.59 | 0.90 | 0.79 | 0.58–0.96 |
| FKBP-type peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | 50a | 1.68 | 4.68 | 0.71 | 0.61–5.15 |
| 50b | 0.75 | 1.34 | 0.67 | 0.58–1.34 | |
| EHUXJGI239227 | 1.58 | 3.20 | 0.76 | 0.70–3.53 | |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase EC 1.1.1.8 | 45a | 0.77 | 0.91 | 0.67 | 0.66–0.92d |
| EHUXJGI87542 | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.75–0.86 | |
| Histone H2B | 89a | 0.43 | 0.40 | 1.04 | 0.31–1.03 |
| EHUXJGI96192 | 0.43 | 0.52 | 0.89 | 0.38–0.90 | |
| Nascent polypetide-associated complex protein/transcription factor (putative) | 52a | 1.84 | 1.82 | 0.34 | 0.34–3.15 |
| No BLAST hit | 08a | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.32 | 0.32–0.94d |
| EHUXJGI349877 | 0.82 | 0.67 | 0.32 | 0.32–0.99 | |
| No BLAST hit | 13a | 3.28 | 1.01 | 0.43 | 0.36–3.57 |
| EHUXJGI205571 | 2.51 | 1.01 | 0.53 | 0.45–2.67 | |
| No BLAST hit | 57a | 1.80 | 1.42 | 0.39 | 0.40–2.53 |
| No BLAST hit | 76a | 1.16 | 1.27 | 0.76 | 0.76–1.42 |
| EHUXJGI237243 | 1.17 | 1.36 | 0.78 | 0.78–1.48 | |
| No BLAST hit | 83a | 1.90 | 1.70 | 0.42 | 0.42–2.87 |
| EHUX110219 | 1.32 | 1.35 | 0.87 | 0.88–1.53 | |
| No BLAST hit | EHUXJGI218259 | 3.12 | 2.52 | 0.31 | 0.31–5.73 |
| Periplasmic binding/iron transport lipoprotein (putative) | EHUXJGI269712 | 1.16 | 0.95 | 1.23 | 0.95–1.29 |
| Phosphoglycerate kinase | Q5ENR8 | 0.91 | 1.44 | 1.48 | 0.91–1.70 |
| 11a | 0.95 | 1.06 | 1.06 | 0.95–1.10d | |
| EHUXJGI270670 | 1.05 | 0.99 | 1.05 | 0.99–1.07 | |
| Phosphoribulokinase (chloroplastic) | 14a | 0.70 | 1.35 | 0.86 | 0.63–1.36d |
| Photosystem II 12 kDa extrinsic protein (chloroplastic) | 12f | 0.70 | 0.99 | 0.56 | 0.53–1.01 |
| Photosystem II oxygen evolving enhancer (chloroplastic) | 34a | 1.29 | 1.09 | 0.73 | 0.73–1.40d |
| 27a | 1.46 | 0.89 | 0.82 | 0.72–1.45d | |
| 27b | 1.38 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.71–1.37 | |
| EHUXJGI265795 | 1.12 | 1.10 | 0.72 | 0.72–1.27 | |
| Predicted protein | 65a | 1.85 | 1.55 | 0.54 | 0.54–2.46 |
| Predicted protein | 82a | 1.51 | 1.67 | 0.29 | 0.30–2.73d |
| Predicted protein | 21a | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.72 | 0.72–1.04d |
| 21b | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.72 | 0.72–1.04 | |
| 21c | 1.46 | 1.47 | 0.67 | 0.68–1.88 | |
| Predicted protein | 72a | 1.72 | 1.45 | 0.56 | 0.56–2.22 |
| Predicted protein | 84a | 2.31 | 7.08 | 0.48 | 0.43–9.20 |
| EHUXJGI96453 | 2.22 | 7.28 | 0.47 | 0.41–9.32 | |
| EHUXJGI243179 | 2.26 | 7.38 | 0.46 | 0.41–9.54 | |
| Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain | Q4G3F4 | 0.17 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.17–1.29 |
| S-adenosylmethionine synthetase | 06a | 0.92 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.57–0.91 |
| 06b | 0.96 | 0.54 | 0.49 | 0.42–0.96 | |
| 06c | 0.96 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 0.40–0.96 | |
| EHUXJGI62235 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.51 | 0.51–1.05 | |
| EHUXJGI267646 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.49 | 0.49–1.09 | |
| Ubiquitin family protein (putative) | 01f | 1.77 | 2.18 | 0.74 | 0.74–2.71 |
As defined for table 3.
If an identification was made from numerous ESTs with valid iTRAQ quantification, an geometric average has been made (see Materials and Methods). Please refer to Data S2 for individual EST quantification.
Proteomic correlates
Ratios of peptide abundance from each high: low CO2 replicate incubation were calculated (114∶113, 116∶115 and 118∶117) and values of G±CI≥1.5 or ≤0.67 used to determine up and down-regulation respectively ( Table 3 ). According to these strict criteria, no HPGs were up-regulated in response to high CO2, while only four HPGs were down-regulated (histones H2A, H3 H4 and chloroplastic 30S ribosomal protein S7). When results from the E. huxleyi genome searches, protein databases and EST searches were combined, 43 HPGs showed no difference in regulation under high CO2 when all three replicates were considered. A number of proteins, however, showed trends of up- or down-regulation in the first two replicates, with a reduced/ambivalent response in the third replicate ( Table 4 ).
Discussion
Physiological properties of Emiliania huxleyi NZEH under high CO2
This study extends our knowledge of the physiological response of Emiliania huxleyi strain NZEH (morphotype R) to increasing pCO2 through the use of traditional approaches and by quantitative proteomic analysis. Although previous studies have investigated the responses of this strain to varying CO2, our levels (1340 p.p.m.v.) were the highest applied so far, compared to 750 [14], [15] and 909 p.p.m.v. CO2 [46] used in previous studies.
In our study, cells were under nutrient repletion for the duration of the experiments (nitrate and phosphate levels at t1 and 2 being between 86.18–103.79 and 3.23–4.32 µmol kg−1 respectively). Therefore, the observed increases in coccosphere volumes and cellular CaCO3, POC and PON content are not attributable to nutrient limitation. Using multiple generations of growth (∼9–12 and ∼12–13 generations for cells incubated under 1340 and 395 p.p.m.v. CO2 respectively), we found that multiple generations are a necessary step for the population to achieve acclimation despite some studies reporting acclimation after one or a few cell generations [47]. In our study, there were periods at the start of the acclimation phase when there was no difference in coccosphere size, but these trends were changed towards the end of the experiment, after multiple generations of growth during which the majority of cells had grown and divided under the experimental conditions. Calcification also changed, since cells contained significantly less cellular CaCO3 at the beginning of the experiment compared to after ∼5–8 generations (t2). Another example, in this case, showing the opposite trend, is growth rate, which displayed comparable values between the different treatments at start of the experiment, but declined after subsequent generations of incubation under 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2.
Observed increases in cellular POC content at elevated CO2 levels compared to current conditions are in agreement with other studies on strain NZEH [21], [22], [46]. Similarly, the observed increase in cellular CaCO3 is in agreement with some results using this strain [21], [22]. Despite an increase in CaCO3 content, coccosphere volume, and coccolith size under the high CO2 condition, coccoliths were slightly less calcified but with larger central area widths on the distal shield. However, there appeared to be no sign of coccolith malformation or dissolution under either pCO2 condition.
Cellular CaCO3:POC ratios did not change under high CO2, comparable to trends found by Iglesias-Rodriguez et al. [21] but in disagreement with findings by Hoppe et al. [46]. The CaCO3:POC ratio indicates the balance of CO2 fluxes as a result of calcification and photosynthesis, which appeared not to be altered under these “worst case” high (1340 p.p.m.v.) CO2 scenario. Furthermore, the CaCO3:POC ratio was <1.5 in all conditions tested, which means that the cells are likely to be a sink of CO2 to the surrounding environment [48]. CaCO3:POC ratios associated with 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 were virtually identical to values reported in bubbling experiments under the highest pCO2 used on this strain by Iglesias-Rodriguez et al. [21] and by Hoppe et al. [46]. There was no difference in the cellular POC:PON ratio between the two CO2 conditions; this ratio was only 6.43% higher than previously reported for NZEH cells grown under 750 p.p.m.v. CO2 [21].
Cellular production rates of CaCO3 and POC did not vary significantly under 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 compared to present-day conditions, unlike previous observations by Iglesias-Rodriguez et al. [21] and Shi et al. [22] who found increases in these parameters for this strain under 750 p.p.m.v. CO2. Hoppe et al. [46] also found an increase in POC production under elevated pCO2 but a decline in cellular CaCO3 production at 909 p.p.m.v. CO2. Since CaCO3 and POC production did not differ between treatments, the higher cellular CaCO3, PON and POC values that we found are related to the lower growth rate of cells incubated under 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2. At present, the source of the variability in carbon production under varying CO2 levels between our results and other studies on NZEH remains unresolved.
Changes in carbonate chemistry were not associated with any difference in the maximum quantum efficiency of PSII (as measured by Fv/Fm), a proxy of cellular photosynthetic health. This result was previously reported for cells of this strain incubated under 750 p.p.m.v. CO2 [21]. A decline in cellular growth rate (μ) under high CO2 is also in agreement with some investigations on this strain [21]; however others [22], [46] have found no change in growth under elevated pCO2. Eukaryote cells often undergo growth delay or arrest when threatened with damage to cellular components such as DNA [49] and significant growth rate reductions in the current study suggests that E. huxleyi cells are exhibiting one of the hallmarks of cellular stress response (CSR) to prevent damage to macromolecular components under high CO2 [50], [51].
Proteomic responses of Emiliania huxleyi to ocean acidification
Four E. huxleyi HPGs from all three replicate experiments conducted under 1340 p.p.m.v. CO2 were down-regulated: histones H2A, H3 and H4 and a chloroplast located 30S ribosomal protein S7 (rps7). This is likely related to the lower rate of cell division observed under high CO2, which may be accompanied by a reduction in DNA and chromatin synthesis and a consequent decrease in the requirement for histone proteins [52]. Reduced rps7 expression is also likely related to lower growth rates, although this has not been rigorously examined in phytoplankton [53]. Our results suggest that E. huxleyi cells grown under high CO2 undergo a reduction in translation initiation in some instances [54]. The non-differential expression of histone H2B under different CO2 conditions may be explained by indications that this protein is involved in processes other than nucleosome packaging since our identification the identified H2B from the E. huxleyi genome (protein ID 96192) also contained a 50S ribosome-binding GTPase (Pfam: CL0023) and a peptidase domain (Pfam: CL0012).
By nomenclature, we found that the expression of 43 HPGs (over 93% of those quantified) was unchanged in all three incubations under elevated pCO2. However, there was a tendency for some proteins to show differential expression within the first two of the three incubations ( Table 4 ), which while not significant, is potentially indicative of sub-lethal CSR in E. huxleyi [50], [51]. For example, HPGs with homology to FKBP-type peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase and ubiquitin family proteins were substantially up-regulated within the first two high CO2 replicates ( Table 4 ). Additionally a cold shock protein HPG was also up-regulated under high CO2 in the same two replicates; these proteins have roles in multiple stress responses [55]. Meanwhile, 40S and 50S ribosomal proteins were up-regulated almost twofold ( Table 4 ) within these two high CO2 incubations, which might relate to induction of translational processes to replace damaged proteins or a role in extraribosomal functioning [56]. The potential up-regulation of an HPG containing an ankyrin repeat domain also suggests an increase in protein-protein interactions under high CO2 but it is difficult to decipher the role of this HPG because of the diverse functionality exhibited by proteins containing this domain [57]. Similarly, a trend for reduction of S-adenosylmethionine synthetase under high CO2 in the second and third incubations is difficult to discuss because of the multiple roles of this enzyme involved in methylation [58].
Trends from the first two incubations indicate that membrane related processes have the potential to be affected by high CO2. For example up-regulation of an acyl carrier protein from the first two incubations could be responsible for increased lipid production [59] that may be involved in membrane remodeling under low pH [60]. An up-regulation of vacuolar membrane bound V-ATPases in these two incubations could also relate to stress responses to cellular pH regulation under high CO2/low pH [61], [62]. However, none of these trends are significant and therefore they must be interpreted with caution.
Despite the disrupted cell cycle and some evidence for a proteomic CSR under high CO2, there are also indications of cellular tolerance to ocean acidification. We identified a broad range of HPGs whose expression remained unchanged ( Table 4 ). These included processes such as electron transport (ETC complex I protein, apocytochrome f), photosynthesis (ferredoxin—NADP reductase, PSII 12KDa extrinsic protein, PSII oxygen evolving enhancer, various chloroplastic ATP synthase subunits), carbon fixation (phosphoribulokinase, RuBisCO large chain), glycolysis (phosphoglycerate kinase) and other metabolic processes (adenosylhomocysteinase). It should be noted that the lack of change in the relative levels of these proteins does not preclude effects on their activities due to the elevated pCO2 growth conditions. For example, it is well known that some of these central metabolic enzymes are regulated by post-translational modifications such protein phosphorylation. Collectively, however, the results suggest that this particular strain of E. huxleyi does not undergo major metabolic perturbations with respect to numerous photosynthetic and other metabolic processes once acclimated to high CO2 levels in these short-term experiments. Indeed, the down-regulation of a chloroplastic clp protease in the first two incubations ( Table 4 ) suggests that E. huxleyi chloroplasts are not undergoing stress under high CO2.
The unknown biochemistry of Emiliania huxleyi
Of the 115 quantified and non-quantified HPGs identified, 79 were not found within the current draft of the E. huxleyi genome (strain CCMP1516) and only 6 were found in the genome and both the EST and taxonomically restricted UniProt databases. This is likely a result of genomic variability within the E. huxleyi species group and we expect proteomic identifications to be assisted by the availability of sequences of other strains in the near future. However, it is worth noting that approximately 38% of quantified and non-quantified HPGs identified in the current study did not match any database homologue, Pfam conserved domain or only matched protein sequences defined as “unknown”, “predicted” or “hypothetical.” We also found unusual proteins, for example searches against the E. huxleyi genome uncovered an alanine-rich sulfotransferase protein (ID 270658) exhibiting homology to several mucin-associated surface proteins (MASPs) identified in the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi (Data S2). MASPs are members of a recently discovered gene family containing ∼1400 members that comprises ∼6% of the parasite diploid genome [63], [64] and are thought to have a role in host immune system evasion. Interestingly, we found homologs to this HPG in the Thalassiosira pseudonana genome (e.g. UniProtKB accessions B8BX85 and B8BTN5). At present, we are unable to propose a role for MASP-like proteins within marine eukaryotic algae.
The large number of highly expressed proteins with unknown features that we found within E. huxleyi highlights the multiple unknown biochemical facets of these species and illustrates that our incomplete knowledge on cellular processes, such as calcification. It is therefore likely that components other than those currently described for coccolithophores including proteins typically involved in carbon acquisition, proton extrusion or Ca2+ transport remain to be identified. For example, in two of our three high CO2 replicates, an HPG containing a structural motif found in demethylmenaquinone methyltransferases (DMMMs) was up-regulated. This was particularly interesting since DMMMs catalyze the last step of the biosynthesis of menaquinione (vitamin K2; MK) through the conversion of demenaquinone to MK, a pathway predominantly found within bacteria [65]. Within E. huxleyi, it is possible that this HPG could be involved in calcification since vitamin K is an essential cofactor of a γ-carboxylase that facilitates calcium ion chelation via the post-translational conversion of glutamic acid to γ-carboxyglutamyl residues. Through this process, vitamin K2 has been shown to regulate biomineralization by modulating the proliferation of osteoblastic cells [66]. Since similar DMMM proteins are present in a handful of other eukaryote phytoplankton such as T. pseudonana and Phaeodactylum tricornutum, MK could instead be an isoprenoid quinone within the photosynthetic or respiratory electron transport chains, as in some prokaryotes [67]–[69]. A further investigation of the role of this HPG and confirmation of its up-regulation in association with cellular high CO2 responses is therefore warranted.
To help develop future directions for research and assist the E. huxleyi genomics community, we combined data from the current study with those from our previous proteomic investigations of E. huxleyi [18] resulting in the experimental validation of 189 HPGs. There was limited overlap between the datasets from these two studies (26 HPGs), which is likely to reflect incomplete proteome sampling in each experiment as a result of the different protein extraction protocols and identification approaches.
Could cellular tolerance lead to a competitive disadvantage in future oceans?
This study adds to the increasing body of literature highlighting variable responses in coccolithophore calcification relating to ocean acidification. For example, it has been recently shown that some coccolithophores may show increased [21], [22], [25] or negligible changes in calcification in response to increasing partial pressures of CO2 [9], [70]. Our results are particularly interesting in light of recent field data showing that heavily calcified E. huxleyi cells of the same morphotype (R) were associated with naturally low pH waters [71]. Another recent study found that E. huxleyi cells of another morphotype (A), different from that used in our study, possessed more CaCO3 in low pH waters [72]. Additionally, recent models propose that coccolithophores might become more heavily calcified and grow more slowly under high CO2 [73]. We argue that the strain of E. huxleyi used in this study exhibits reduced growth that may relate to cellular stress, suggested by the reduction in growth rate and the potential induction of a sub-lethal CSR proteome. This may, in part, explain these field results, since we found reduced cell division resulted in an increase in cellular CaCO3. The induction of shifts in the activities of these, and other pathways, may act as a trade-offs to enable the maintenance of cellular processes required in the short term, perhaps ensuring cellular homeostasis or remodelling during acclimation [51]. However, the decline in growth rates observed in our study could ultimately be disadvantageous for E. huxleyi under high CO2 [5] despite its ability to maintain many biological functions. This could be particularly detrimental in scenarios of phytoplankton group assemblages where other groups outnumber coccolithophores. For example some studies have shown that diatoms are able to maintain [22], [74] or even increase growth rates under increased pCO2 [75], [76], which could lead to increased interspecific competition and assemblage shifts in regions where coccolithophores currently dominate. Long-term investigations into coccolithophore CSRs are therefore required to confirm the extent to which they are responsible for cellular resilience to variations in pH and to determine the conditions under which cells are capable of adaptation to high CO2. This would elucidate whether a catastrophic metabolic collapse relating to acute stress occurs in this particular ecotype of E. huxleyi through time or if cellular mechanisms responding to high CO2 levels resulted in a steady recovery of growth rates, thus preventing outcompetition by other taxa that could otherwise cause a decrease in oceanic CaCO3 fluxes in a future high CO2 world.
Supporting Information
Output files from BUDAPEST analysis.
(ZIP)
Detailed information regarding proteins identified in the current study.
(XLS)
UPLC and MS/MS parameters; Mascot protein identification search parameters.
(DOCX)
Mean carbonate chemistry parameters of 14.7L acclimation cultures before cell addition.
(DOCX)
Mean carbonate chemistry parameters associated with 14.7L acclimation cultures at t1 .
(DOCX)
Nitrate, phosphate and silicate information for cells at t1 .
(DOCX)
Nitrate, phosphate and silicate information for cells at t2 .
(DOCX)
Fv/Fm values of PSII at t2 .
(DOCX)
Acknowledgments
We thank Mrs Sue Hartman for help during VINDTA analysis and the following for analytical assistance: Dr Tom Bibby (Fv/Fm), Mr Mark Stinchcombe (nitrate, phosphate and silicate) and Mr Robert Head (organic carbon and nitrogen). We are extremely grateful to Dr John Gittins and Ms Shanon Pead for technical support and would like to thank Dr Stephen Widdecombe and Ms Sarah Dashfield at Plymouth Marine Laboratory (U.K.) for access to seawater. We also thank Dr Maria-Nefeli Tsaloglou for access to laboratory facilities and Mr Robert Jones for his extensive help during seawater collection. We are grateful to the three anonymous reviewers of this manuscript who provided constructive and useful comments.
Funding Statement
BMJ was supported in part by a Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) PhD studentship (NER/S/A2006/14211). This work is a contribution to the “European Project on Ocean Acidification” (EPOCA), which received funding from the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) under grant agreement no. 211384. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Caldeira K, Wickett ME (2003) Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature 425: 365 doi:10.1038/425365a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zeebe RE, Wolf-Gladrow D (2001) CO2 in seawater: Equilibrium, kinetics, isotopes. New York: Elsevier. 360pp.
- 3.Raven JA, Caldeira K, Elderfield H, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Liss P, et al.. (2005) Ocean acidification due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide. London: The Royal Society. 60pp.
- 4. Orr JC, Fabry VJ, Aumont O, Bopp L, Doney SC, et al. (2005) Anthropogenic ocean acidification over the twenty-first century and its impact on calcifying organisms. Nature 437: 681–686 doi:10.1038/nature04095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Ridgwell A, Schmidt DN, Turley C, Brownlee C, Maldonado MT, et al. (2009) From laboratory manipulations to Earth system models: scaling calcification impacts of ocean acidification. Biogeosciences 6: 2611–2623 doi:10.5194/bg-6-2611-2009. [Google Scholar]
- 6. Milliman JD (1993) Production and accumulation of calcium carbonate in the ocean: budget of a nonsteady state. Global Biogeochem Cycles 7: 927–957 doi:10.1029/93GB02524. [Google Scholar]
- 7. Westbroek P, Brown CW, van Bleijswijk J, Brownlee C, Brummer GJ, et al. (1993) A model system approach to biological climate forcing. The example of Emiliania huxleyi . Glob Planet Change 8: 27–46 doi:10.1016/0921-8181(93)90061-R. [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lefebvre SC, Harris G, Webster R, Leonardos N, Geider RJ, et al. (2009) Characterization and expression analysis of the Lhcf gene family in Emiliania huxleyi (Haptophyta) reveals differential responses to light and CO2 . J Phycol 46: 123–134 doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2009.00793.x. [Google Scholar]
- 9. Richier S, Fiorini S, Kerros M-E, von Dassow P, Gattuso J-P (2011) Response of the calcifying coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi to low pH/high pCO2: from physiology to molecular level. Mar Biol 158: 551–560 doi:10.1007/s00227-010-1580-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Rokitta S, John U, Rost B (2012) Ocean acidification affects redox-balance and ion-homeostasis in the life-cycle stages of Emiliania huxleyi . PLoS ONE 7: e52212 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Anderson L, Seilhamer J (1997) A comparison of selected mRNA and protein abundances in human liver. Electrophoresis 18: 533–537 doi:10.1002/elps.1150180333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Gygi SP, Rochon,Y, Franza BR, Aebersold R (1999) Correlation between protein and mRNA abundance in yeast. Mol Cell Biol 19: 1720–1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Chen G, Gharib TG, Huang C-C, Taylor JMG, Misek DE, et al. (2002) Discordant protein and mRNA expression in lung adenocarcinomas. Mol Cell Proteomics 1: 304–313 doi:10.1074/mcp.M200008-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Tian Q, Stepaniants SB, Mao M, Weng L, Feetham MC, et al. (2004) Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Proteomics 3: 960–969 doi:10.1074/mcp.M400055-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Choi,YW, Park SA, Lee HW, Kim DS, Lee NG (2008) Analysis of growth phase-dependent proteome profiles reveals differential regulation of mRNA and protein in Helicobacter pylori . Proteomics 8: 2665–2675 doi:10.1002/pmic.200700689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Vogel C, Marcotte EM (2012) Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from protein and transcriptomic analyses. Nat Rev Genet 13: 227–232 doi:10.1038/nrg3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Bala G, Caldeira K, Mirin A, Wickett M, Delire C (2005) Multicentury changes to the global climate and carbon cycle: results from a coupled climate and carbon cycle model. J Clim 18: 4531–4544 doi:10.1175/JCLI3542.1. [Google Scholar]
- 18. Jones BM, Edwards RJ, Skipp PJ, O'Connor CD, Iglesias-Rodriguez MD (2011) Shotgun proteomic analysis of Emiliania huxleyi, a marine phytoplankton species of major biogeochemical importance. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 13: 496–504 doi:10.1007/s10126-010-9320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Pandal J, Wright PC, Biggs CA (2007) A quantitative proteomic analysis of light adaptation in a globally significant marine cyanobacterium Prochlorococcus marinus MED4. J Proteome Res 6: 996–1005 doi:10.1021/pr060460c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Carvalho RN, Lettieri T (2011) Proteomic analysis of the marine diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana upon exposure to benzo(a)pyrene. BMC Genomics 12: 159 doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Iglesias-Rodriguez MD, Halloran P, Rickaby R, Hall I, Colmenero-Hidalgo E, et al. (2008) Phytoplankton calcification in a high-CO2 world. Science 320: 336–340 doi:10.1126/science.1154122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Shi D, Xu Y, Morel FMM (2009) Effects of the pH/pCO2 method on medium chemistry and phytoplankton growth. Biogeosciences 6: 1199–1207 doi:10.5194/bg-6-1199-2009. [Google Scholar]
- 23. Riebesell U, Zondervan I, Rost B, Tortell PD, Zeebe RE, et al. (2000) Reduced calcification of marine plankton in response to increased atmospheric CO2 . Nature 407: 364–367 doi:10.1038/35030078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Zondervan I, Rost B, Riebesell U (2002) Effect of CO2 concentration on the PIC/POC ratio in the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi grown under light- limiting conditions and different daylengths. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 272: 55–70 doi:10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00037-0. [Google Scholar]
- 25. Fiorini S, Middelburg JJ, Gattuso J-P (2011) Testing the effects of elevated pCO2 on coccolithophores (Prymnesiophyceae): comparison between haploid and diploid life stages. J Phycol 47: 1281–1291 doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2011.01080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea Cleve. Can J Microbiol 8: 229–239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith, WL, Chanley, MH, editors. Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals. New York: Plenum Press. pp. 26–60.
- 28. Langer G, Geisen M, Baumann K-H, Kläs J, Riebesell U, et al. (2006) Species-specific responses of calcifying algae to changing seawater carbonate chemistry. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems 7: Q09006 doi:10.1029/2005GC001227. [Google Scholar]
- 29. Novick A, Szilard L (1950) Experiments with the chemostat on spontaneous mutations in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 36: 708–719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. de Villiers S, Greaves M, Elderfield H (2002) An intensity ratio calibration method for the accurate determination of Mg/Ca and Sr/Ca of marine carbonates by ICP-AES. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems 3: 10.1029/2001GC000169 doi:10.1029/2001GC000169. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pierrot D, Lewis E, Wallace DWR (2006) MS Excel Program Developed for CO2 System Calculations. ORNL/CDIAC-105a. Oak Ridge, Tennessee: Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
- 32. Mehrbach C, Culberson CH, Hawley JE, Pytkowicz RN (1973) Measurement of the apparent dissociation constants of carbonic acid in seawater at atmospheric pressure. Limnol Oceanogr 18: 897–907. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Dickson AG, Millero FJ (1987) A comparison of the equilibrium constants for the dissociation of carbonic acid in seawater media. Deep Sea Res Part 1 Oceanogr Res Pap 34: 1733–1743 doi:10.1016/0198-0149(87)90021-5. [Google Scholar]
- 34. Dickson AG (1990) Standard potential of the reaction: AgCl (s) +1/2 H2 (g) = Ag (s) +HCl (aq), and and the standard acidity constant of the ion HSO4- in synthetic sea water from 273.15 to 318.15 K. J Chem Thermodyn 22: 113–127 doi:10.1016/0021-9614(90)90074-Z. [Google Scholar]
- 35. Abramoff M, Magelhaes P, Ram S (2004) Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics International 11: 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- 36. Young J, Westbroek P (1991) Genotypic variation in the coccolithophorid species Emiliania huxleyi . Marine Micropaleontology 18: 5–23 doi:10.1016/0377-8398(91)90004-P. [Google Scholar]
- 37. Kolber Z, Prasil O, Falkowski PG (1998) Measurements of variable chlorophyll fluorescence using fast repetition rate techniques. I. Defining methodology and experimental protocols. Biochim Biophys Acta 1367: 88–106 doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(98)00135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Barsnes H, Vizcaíno JA, Eidhammer I, Martens L (2009) PRIDE converter: making proteomics data-sharing easy. Nat Biotechnol 27: 598–599 doi:10.1038/nbt0709-598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Vizcaíno JA, Côté R, Reisinger F, Barsnes H, Foster JM, et al. (2010) The Proteomics Identifications database: 2010 update. Nucleic Acids Res 38 suppl 1: D736–742 doi:10.1093/nar/gkp964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Wahlund TM, Hadaegh AR, Clark R, Nguyen B, Fanelli M, et al. (2004) Analysis of expressed sequence tags from calcifying cells of marine coccolithophorid (Emiliania huxleyi). Mar Biotechnol 6: 278–290 doi:10.1007/s10126-003-0035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Wahlund TM, Zhang X, Read BA (2004) Expressed sequence tag profiles from calcifying and non-calcifying cultures of Emiliania huxleyi . Micropaleontology 50: 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- 42. von Dassow P, Ogata H, Probert I, Wincker P, Da Silva C, et al. (2009) Transcriptome analysis of functional differentiation between haploid and diploid cells of Emiliania huxleyi, a globally significant photosynthetic calcifying cell. Genome Biol 10: R114 doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-10-r114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Kegel JU, Blaxter M, Allen MJ, Metfies K, Wilson WH, et al. (2010) Transcriptional host-virus interaction of Emiliania huxleyi (Haptophyceae) and EhV-86 deduced from combined analysis of expressed sequence tags and microarrays. Eur J Phycol 45: 1–12 doi:10.1080/09670260903349900. [Google Scholar]
- 44. Bateman A, Coin L, Durbin R, Finn RD, Holich V, et al. (2004) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 32: D138–141 doi:10.1093/nar/gkh121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Davey NE, Shields DC, Edwards RJ (2006) SLiMDisc: short, linear motif discovery, correcting for common evolutionary descent. Nucleic Acids Res 34: 3546–3554 doi:10.1093/nar/gkl486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Hoppe CJM, Langer G, Rost B (2011) Emiliania huxleyi shows identical responses to elevated pCO2 in TA and DIC manipulations. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 406: 54–62 doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2011.06.008. [Google Scholar]
- 47. Barcelos e Ramos J, Muller MN, Riebesell U (2010) Short-term response of the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi to an abrupt change in seawater carbon dioxide concentrations. Biogeosciences 7: 177–186 doi:10.5194/bg-7-177-2010. [Google Scholar]
- 48. Frankignoulle M, Canon C, Gattuso J-P (1994) Marine calcification as a source of carbon dioxide: positive feedback of increasing atmosphere CO2 . Limnol Oceanogr 39: 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- 49. Zhou BB, Elledge SJ (2000) The DNA damage response: putting checkpoints in perspective. Nature 408: 433–439 doi:10.1038/35044005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Kültz D (2003) Evolution of the cellular stress proteome: from monophyletic origin to ubiquitous function. J Exp Biol 206: 3119–3124 doi:10.1242/jeb.00549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Evans TG, Hofmann GE (2012) Defining the limits of physiological plasticity: how gene expression can assess and predict the consequences of ocean change. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367: 1733–1745 doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Meshi T, Taoka K-I, Iwabuchi M (2000) Regulation of histone gene expression during the cell cycle. Plant Mol Biol 43: 643–657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Flynn KJ, Raven JA, Rees TAV, Finkel Z, Quigg A, et al. (2010) Is the growth rate hypothesis applicable to microalgae? J Phycol 46: 1–12 doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2009.00756.x. [Google Scholar]
- 54. Fargo DC, Boynton JE, Gillham NW (2001) Chloroplast ribosomal protein S7 of Chlamydomonas binds to chloroplast mRNA leader sequences and may be involved in translation initiation. Plant Cell 13: 207–218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Phadare S (2004) Recent developments in bacterial cold shock response. Curr Issues Mol Biol 6: 125–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Bortoluzzi S, d'Alessi F, Romualdi C, Danieli GA (2002) Differential expression of genes coding for ribosomal proteins in different human tissues. Bioinformatics 17: 1152–1157 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/17.12.1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Mosavi LK, Cammett TJ, Desrosiers DC, Peng Z-Y (2004) The ankryin repeat as molecular architecture for protein recognition. Protein Sci 13: 1435–1448 doi:10.1110/ps.03554604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Chiang P, Gordon R, Tal J, Zeng G, Doctor B, et al. (1996) S-Adenosylmethionine and methylation. FASEB J 10: 471–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Ohlrogge JB, Kuhn DN, Stumpft PK (1979) Subcellular localization of acyl carrier protein in leaf protoplasts of Spinacia oleracea . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 1194–1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Petrackova D, Vecer J, Svobodova J, Herman P (2010) Long-term adaptation of Bacillus subtilis 168 to extreme pH affects chemical and physical properties of the cellular membrane. J Membrane Biol 233: 73–83 doi:10.1007/s00232-010-9226-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Dietz KJ, Tavakoli N, Kluge C, Mimura T, Sharma SS, et al. (2001) Significance of the V-type ATPase for the adaptation to stressful growth conditions and its regulation on the molecular and biochemical level. J Exp Botany 52: 1969–1980 doi:10.1093/jexbot/52.363.1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Sasaki T, Pronina NA, Maeshima M, Iwasaki I, Kurano N, et al. (1999) Development of vacuoles and vacuolar H+ -ATPase activity under extremely high CO2 conditions in Chlorococcum littorale cells. Plant Biol 1: 68–75 doi:10.1111/j.1438-8677.1999.tb00710.x. [Google Scholar]
- 63. El-Sayed NM, Myler PJ, Blandin G, Berriman M, Crabtree J, et al. (2005) Comparative genomics of trypanosomatid parasitic protozoa. Science 309: 404–409 doi:10.1126/science.1112181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. El-Sayed NM, Myler PJ, Bartholomeu DC, Nilsson D, Aggarwal G, et al. (2005) The genome sequence of Trypanosoma cruzi, etiologic agent of Chagas disease. Science 309: 409–415 doi:10.1126/science.1112631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Daines AM, Payne RJ, Humphries ME, Abell AD (2003) The synthesis of naturally occurring vitamin K and vitamin K analogues. Curr Org Chem 7: 1625–1634 doi:10.2174/1385272033486279. [Google Scholar]
- 66. Akedo Y, Hosoi T, Inoue S, Ikegami A, Mizuno Y, et al. (1992) Vitamin K2 modulates proliferation and function of osteoblastic cells in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 187: 814–820 doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)91269-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Lübben M (1995) Cytochromes of archael electron transfer chains. Biochim Biophys Acta 1229: 1–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Schoepp-Cothenet B, Lieutaud C, Baymann F, Vermeglio A, Friedrich T, et al. (2009) Menaquinone as pool quinone in a purple bacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 8549–8554 doi:10.1073/pnas.0813173106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Kuroso M, Begari E (2010) Vitamin K2 in electron transport system: are enzymes involved in vitamin K2 biosynthesis promising drug targets? Molecules 15: 1531–1553 doi:10.3390/molecules15031531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Langer G, Nehrke G, Probert I, Ly J, Ziveri P (2009) Strain-specific responses of Emiliania huxleyi to changing seawater carbonate chemistry. Biogeosciences 6: 2637–2646 doi:10.5194/bg-6-2637-2009. [Google Scholar]
- 71. Beaufort L, Probert I, de Garidel-Thoron T, Bendif EM, Ruiz-Pino D, et al. (2011) Sensitivity of coccolithophores to carbonate chemistry and ocean acidification. Nature 476: 80–83 doi:10.1038/nature10295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Smith HEK, Tyrrell T, Charalampopoulou A, Dumousseaud C, Legge OJ, et al. (2012) Predomindance of heavily calcified coccolithophores at low CaCO3 during winter in the Bay of Biscay. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 109: 8845–8849 doi:10.1073/pnas.1117508109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Irie T, Bessho K, Findlay HS, Calosi P (2010) Increasing costs due to ocean acidification drives phytoplankton to be more heavily calcified: optimal growth strategy of coccolithophores. PLoS ONE 5: e13436 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Crawfurd KJ, Raven JA, Wheeler GL, Baxter EJ, Joint I (2011) The response of Thalassiosira pseudonana to long-term exposure to increased CO2 and decreased pH. PLoS ONE 6: e26695 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Kim J-M, Lee K, Shin K, Kang J-H, Lee H-W, et al. (2006) The effect of seawater CO2 concentration on growth of a natural phytoplankton assemblage in a controlled mesocosm experiment. Limnol Oceanogr 51: 1629–1636 doi:10.4319/lo.2006.51.4.1629. [Google Scholar]
- 76. Tortell PD, Payne CD, Li Y, Trimborn S, Rost B, et al. (2008) CO2 sensitivity of Southern Ocean phytoplankton. Geophys Res Lett 35: L04605 doi:10.1029/2007GL032583. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Output files from BUDAPEST analysis.
(ZIP)
Detailed information regarding proteins identified in the current study.
(XLS)
UPLC and MS/MS parameters; Mascot protein identification search parameters.
(DOCX)
Mean carbonate chemistry parameters of 14.7L acclimation cultures before cell addition.
(DOCX)
Mean carbonate chemistry parameters associated with 14.7L acclimation cultures at t1 .
(DOCX)
Nitrate, phosphate and silicate information for cells at t1 .
(DOCX)
Nitrate, phosphate and silicate information for cells at t2 .
(DOCX)
Fv/Fm values of PSII at t2 .
(DOCX)