Abstract
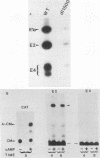
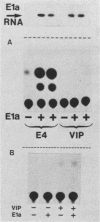
The sequence motif CGTCA is critical for binding of a group of cellular transcription factors (ATF, CREB, E4F, and EivF) and for activation of certain E1a-inducible and cyclic AMP (cAMP)-inducible promoters. We have tested different promoter elements containing the CGTCA motif (referred to here as ATF-binding sites) for the ability to function as E1a or cAMP response elements. The adenovirus E4 promoter and the cellular vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) promoter responded differently to E1a and cAMP, demonstrating that the activating potential of ATF-binding sites within these promoters is not equivalent. While particular ATF-binding sites were sufficient for the activity of both the E4 (E1a inducibility) and VIP (cAMP inducibility) enhancers, these two enhancers had contrasting effects on E1a- and cAMP-inducible transcription. Thus, the relationship between E1a- and cAMP-inducible transcription is not simply explained by the action of these two inducers through the same promoter elements.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrisani O. M., Hayes T. E., Roos B., Dixon J. E. Identification of the promoter sequences involved in the cell specific expression of the rat somatostatin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5715–5728. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrisani O. M., Pot D. A., Zhu Z., Dixon J. E. Three sequence-specific DNA-protein complexes are formed with the same promoter element essential for expression of the rat somatostatin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1947–1956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Meselson M. Periodic interactions of heat shock transcriptional elements. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):856–858. doi: 10.1038/332856a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Buckbinder L., Leza M. A., Rak N., Hearing P., Merino A., Reinberg D. EivF, a factor required for transcription of the adenovirus EIV promoter, binds to an element involved in EIa-dependent activation and cAMP induction. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell R. B., Boime I. Differential expression of the human gonadotropin alpha gene in ectopic and eutopic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3157–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delegeane A. M., Ferland L. H., Mellon P. L. Tissue-specific enhancer of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene: dependence on cyclic AMP-inducible elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3994–4002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Hoeffler J. P., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP and phorbol ester-stimulated transcription mediated by similar DNA elements that bind distinct proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7922–7926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch P. J., Jameson J. L., Habener J. F. Cyclic AMP responsiveness of human gonadotropin-alpha gene transcription is directed by a repeated 18-base pair enhancer. Alpha-promoter receptivity to the enhancer confers cell-preferential expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12169–12174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel D. A., Hardy S., Shenk T. cAMP acts in synergy with E1A protein to activate transcription of the adenovirus early genes E4 and E1A. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1517–1528. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. S., Verhave M., Kasper S., Tsukada T., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. The CGTCA sequence motif is essential for biological activity of the vasoactive intestinal peptide gene cAMP-regulated enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6662–6666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi P., Perricaudet M. The E4 promoter of adenovirus type 2 contains an E1A dependent cis-acting element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9035–9049. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Allegretto E. A., Karin M., Green M. R. A family of immunologically related transcription factors that includes multiple forms of ATF and AP-1. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1216–1226. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy S., Shenk T. Adenoviral control regions activated by E1A and the cAMP response element bind to the same factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4171–4175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington C. A., Lewis E. J., Krzemien D., Chikaraishi D. M. Identification and cell type specificity of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2363–2384. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst H. C., Jones N. C. Identification of factors that interact with the E1A-inducible adenovirus E3 promoter. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1132–1146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman S. E., Comb M., Lin Y. S., Pearlberg J., Green M. R., Goodman H. M. A common trans-acting factor is involved in transcriptional regulation of neurotransmitter genes by cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4225–4233. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klock G., Strähle U., Schütz G. Oestrogen and glucocorticoid responsive elements are closely related but distinct. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):734–736. doi: 10.1038/329734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Green M. R. A cellular transcription factor E4F1 interacts with an E1a-inducible enhancer and mediates constitutive enhancer function in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Harrington C. A., Chikaraishi D. M. Transcriptional regulation of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene by glucocorticoid and cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3550–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leza M. A., Hearing P. Cellular transcription factor binds to adenovirus early region promoters and to a cyclic AMP response element. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3003–3013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3003-3013.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Interaction of a common cellular transcription factor, ATF, with regulatory elements in both E1a- and cyclic AMP-inducible promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Rooney R., Nevins J. R. Identification of an E1A-inducible cellular factor that interacts with regulatory sequences within the adenovirus E4 promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4073–4081. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P. Cyclic AMP induction of early adenovirus promoters involves sequences required for E1A trans-activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7192–7196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver B. J., Bokar J. A., Virgin J. B., Vallen E. A., Milsted A., Nilson J. H. Cyclic AMP regulation of the human glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene is mediated by an 18-base-pair element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2198–2202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Subramanian S., Thimmappaya B. Identification of a factor in HeLa cells specific for an upstream transcriptional control sequence of an EIA-inducible adenovirus promoter and its relative abundance in infected and uninfected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5914–5918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Fink J. S., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a region in the human vasoactive intestinal polypeptide gene responsible for regulation by cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8743–8747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X. M., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Chambon P. A general transcription factor forms a stable complex with RNA polymerase B (II). Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):361–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90490-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Ahe D., Janich S., Scheidereit C., Renkawitz R., Schütz G., Beato M. Glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors bind to the same sites in two hormonally regulated promoters. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):706–709. doi: 10.1038/313706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]