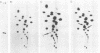Abstract
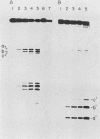
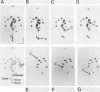
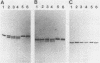
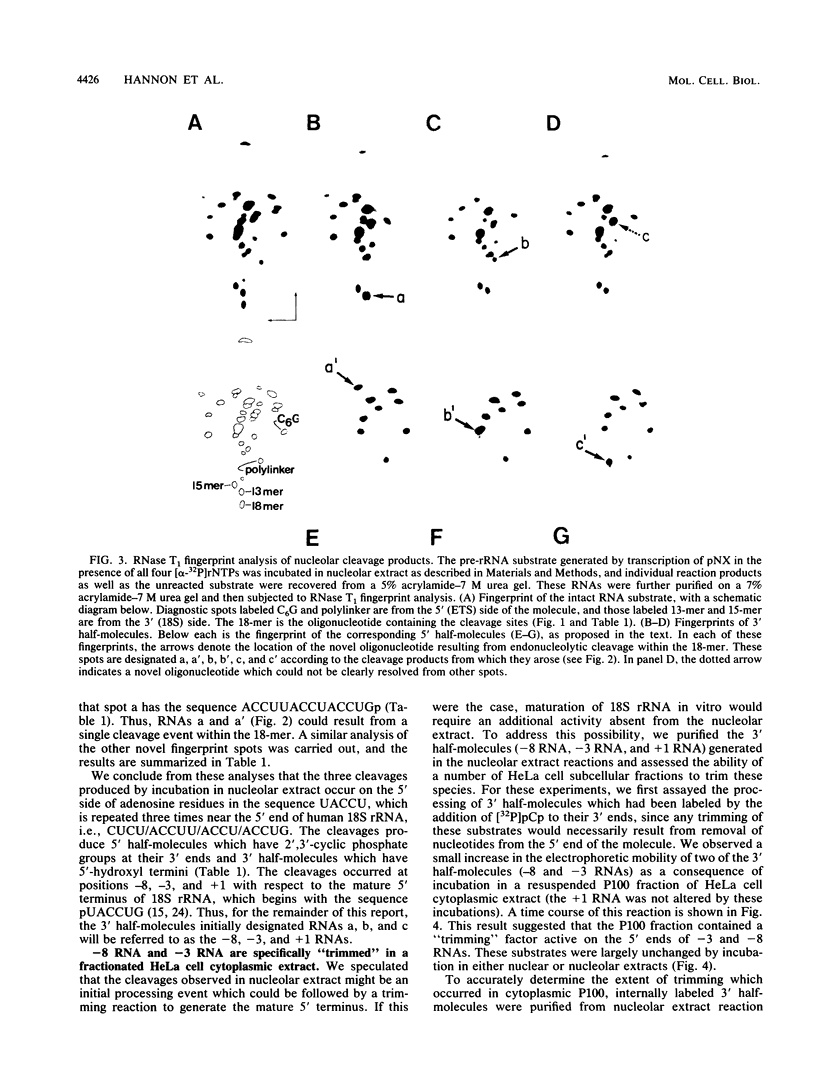
We report here that the mature 5' terminus of human 18S rRNA is generated in vitro by a two-step processing reaction. In the first step, SP6 transcripts were specifically cleaved in HeLa cell nucleolar extract at three positions near the external transcribed spacer (ETS)-18S boundary. Of these cleavage sites, two were major and the other was minor. RNase T1 fingerprint and secondary nuclease analyses placed the two major cleavage sites 3 and 8 bases upstream from the mature 5' end of 18S rRNA and the minor cleavage site 1 base into the 18S sequence. All three cleavages yielded 5'-hydroxyl, 2'-3'-cyclic phosphate termini and were 5' of adenosine residues in the sequence UACCU, which was repeated three times near the ETS-18S boundary. In the second step, the initial cleavage product containing 3 bases of ETS was converted to an RNA with a 5' terminus identical to that of mature 18S RNA by an activity found in HeLa cell cytoplasmic extracts.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenas J., Hurwitz J. Purification of a RNA debranching activity from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4274–4279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman L. H., Goldman W. E., Goldberg G. I., Hebert M. B., Schlessinger D. Location of the initial cleavage sites in mouse pre-rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1501–1510. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman L. H., Rabin B., Schlessinger D. Multiple ribosomal RNA cleavage pathways in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4951–4966. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G., Sanger F. Chromatography of 32P-labelled oligonucleotides on thin layers of DEAE-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):395–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N., Kass S., Sollner-Webb B. Nucleotide sequence determining the first cleavage site in the processing of mouse precursor rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Bruce A. G., Uhlenbeck O. C. Specific labeling of 3' termini of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. M., Rushford C. L., Dorney D. J., Wilson G. N., Schmickel R. D. Structure and variation of human ribosomal DNA: molecular analysis of cloned fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez I. L., Schmickel R. D. The human 18S ribosomal RNA gene: evolution and stability. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Apr;38(4):419–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S., Craig N., Sollner-Webb B. Primary processing of mammalian rRNA involves two adjacent cleavages and is not species specific. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2891–2898. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. C., Sirdeskmukh R., Schlessinger D. Nucleolytic processing of ribonucleic acid transcripts in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):428–451. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.428-451.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum F. S., Maden B. E. Human 18 S ribosomal RNA sequence inferred from DNA sequence. Variations in 18 S sequences and secondary modification patterns between vertebrates. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):725–733. doi: 10.1042/bj2320725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Sollner-Webb B. Transcription of mouse rRNA genes by RNA polymerase I: in vitro and in vivo initiation and processing sites. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Mitsuma T., Ogata K. Coupled transcription and processing of mouse ribosomal RNA in a cell-free system. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3879–3886. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A. W., Frankfort H. M., Davis N. G., Ferrari S., Lamb R. A., Robertson H. D. Direct characterization of influenza viral NS1 mRNA and related sequences from infected HeLa cells and a cell-free transcription system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 13;868(2-3):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Baglioni C. Synthesis of (2'-5')oligoadenylate and activation of an endoribonuclease in interferon-treated HeLa cells infected with reovirus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1039-1045.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Wood D. L., Baglioni C. Presence of 2',5'-oligo(A) and of enzymes that synthesize, bind, and degrade 2',5'-oligo(A) in HeLa cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1602–1605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. Processing of RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:605–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rairkar A., Rubino H. M., Lockard R. E. Chemical probing of adenine residues within the secondary structure of rabbit 18S ribosomal RNA. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):582–592. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma K., Kominami R., Muramatsu M., Sugiura M. Conservation of the 5'-terminal nucleotide sequences of ribosomal 18-S RNA in eukaryotes. Differential evolution of large and small ribosomal RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):339–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance V. B., Thompson E. A., Bowman L. H. Transfection of mouse ribosomal DNA into rat cells: faithful transcription and processing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7499–7513. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]