Abstract
Accumulating data suggest that the CD4 T-cell surface antigen transduces an independent intracellular signal during antigen-mediated T-cell activation. CD4 is physically associated with the internal membrane tyrosine protein kinase p56lck and can mediate, after antibody-mediated cross-linking, the rapid enzymatic activation of Lck, implying that CD4 signalling may involve changes in tyrosine protein phosphorylation. In this report, we describe that cross-linking of CD4 results in a series of rapid changes in intracellular tyrosine protein phosphorylation. The most prominent CD4-induced tyrosine phosphorylation change involved p56lck, which became extensively phosphorylated on the carboxy-terminal tyrosine residue 505 and, to a lesser extent, lymphocytes can transduce an intracellular signal resulting in tyrosine protein phosphorylation and strongly suggest that this property of CD4 is mediated through p56lck.
Full text
PDF


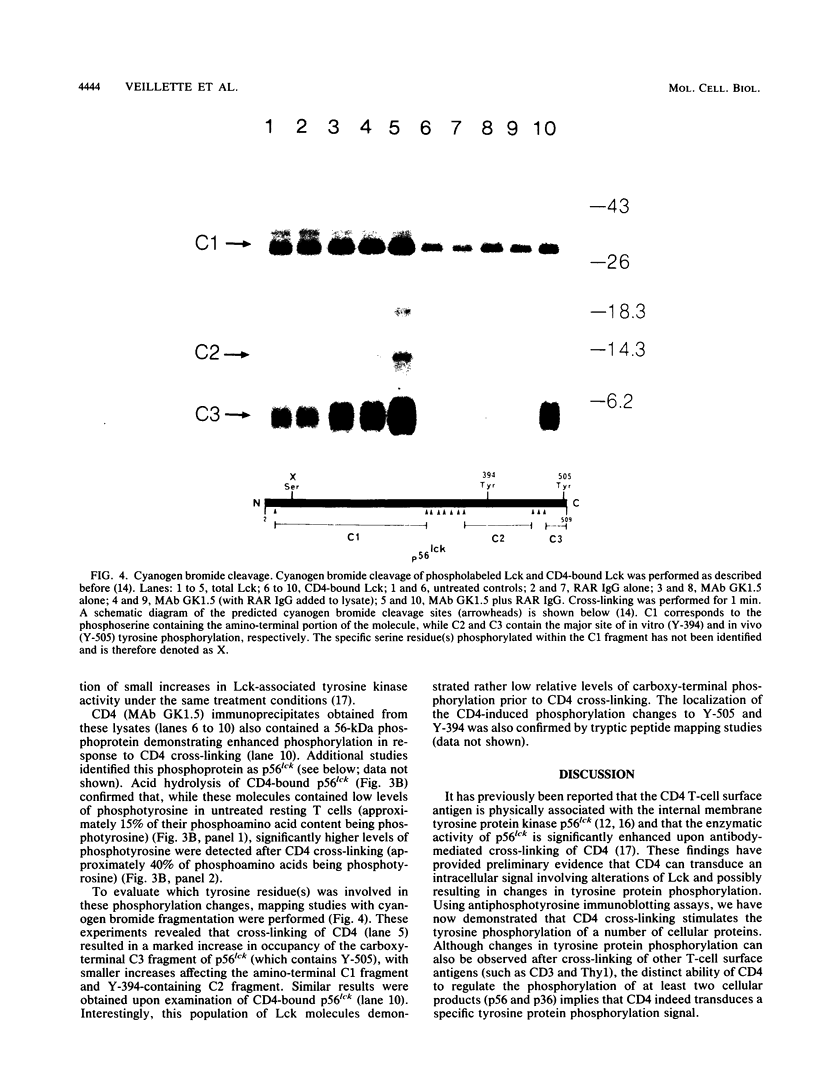


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein K. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of a site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase, p56lck, reveals its oncogenic potential in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4247–4251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Blue M. L., Schlossman S. F. Comodulation of CD3 and CD4. Evidence for a specific association between CD4 and approximately 5% of the CD3:T cell receptor complexes on helper T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1732–1737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Sleckman B. P., Ratnofsky S. E., Burakoff S. J. The biologic roles of CD2, CD4, and CD8 in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:579–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookman M. A., Swerdlow R., Matis L. A. Adoptive chemoimmunotherapy of murine leukemia with helper T lymphocyte clones. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):3166–3170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Zokas L., Kamps M. P. Monoclonal antibodies to phosphotyrosine. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 9;109(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunter K. C., Malek T. R., Shevach E. M. T cell-activating properties of an anti-Thy-1 monoclonal antibody. Possible analogy to OKT3/Leu-4. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):716–730. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchildon G. A., Casnellie J. E., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Covalently bound myristate in a lymphoma tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7679–7682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Cooper J. A., King C. S., Ziegler S. F., Tinker D. A., Overell R. W., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Neoplastic transformation induced by an activated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (pp56lck). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):540–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Peet R., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. A lymphocyte-specific protein-tyrosine kinase gene is rearranged and overexpressed in the murine T cell lymphoma LSTRA. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Samelson L. E., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD4 receptor involves the activation of the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):257–259. doi: 10.1038/338257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Foss F. M., Sausville E. A., Bolen J. B., Rosen N. Expression of the lck tyrosine kinase gene in human colon carcinoma and other non-lymphoid human tumor cell lines. Oncogene Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;1(4):357–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Bolen J. B. Post-translational alterations of the tyrosine kinase p56lck in response to activators of protein kinase C. Oncogene Res. 1988 May;2(4):385–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Horak E. M., Bookman M. A., Bolen J. B. Alterations of the lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (p56lck) during T-cell activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4353–4361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Buss J. E., Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Characterization of the protein apparently responsible for the elevated tyrosine protein kinase activity in LSTRA cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2705–2713. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Sefton B. M. Expression of a new tyrosine protein kinase is stimulated by retrovirus promoter insertion. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):682–685. doi: 10.1038/319682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Kappler J., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W. Evidence implicating L3T4 in class II MHC antigen reactivity; monoclonal antibody GK1.5 (anti-L3T4a) blocks class II MHC antigen-specific proliferation, release of lymphokines, and binding by cloned murine helper T lymphocyte lines. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2178–2183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]