Abstract
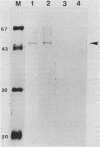
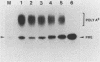
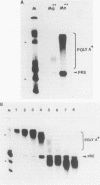
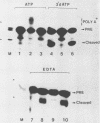
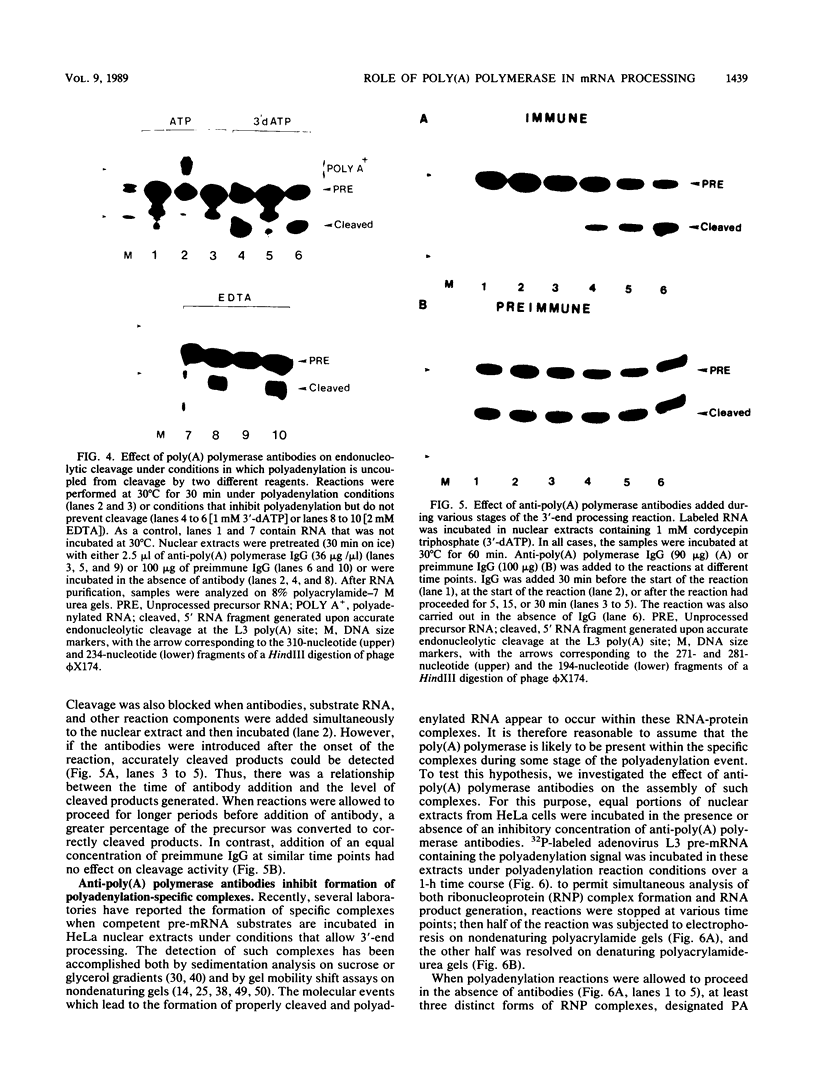
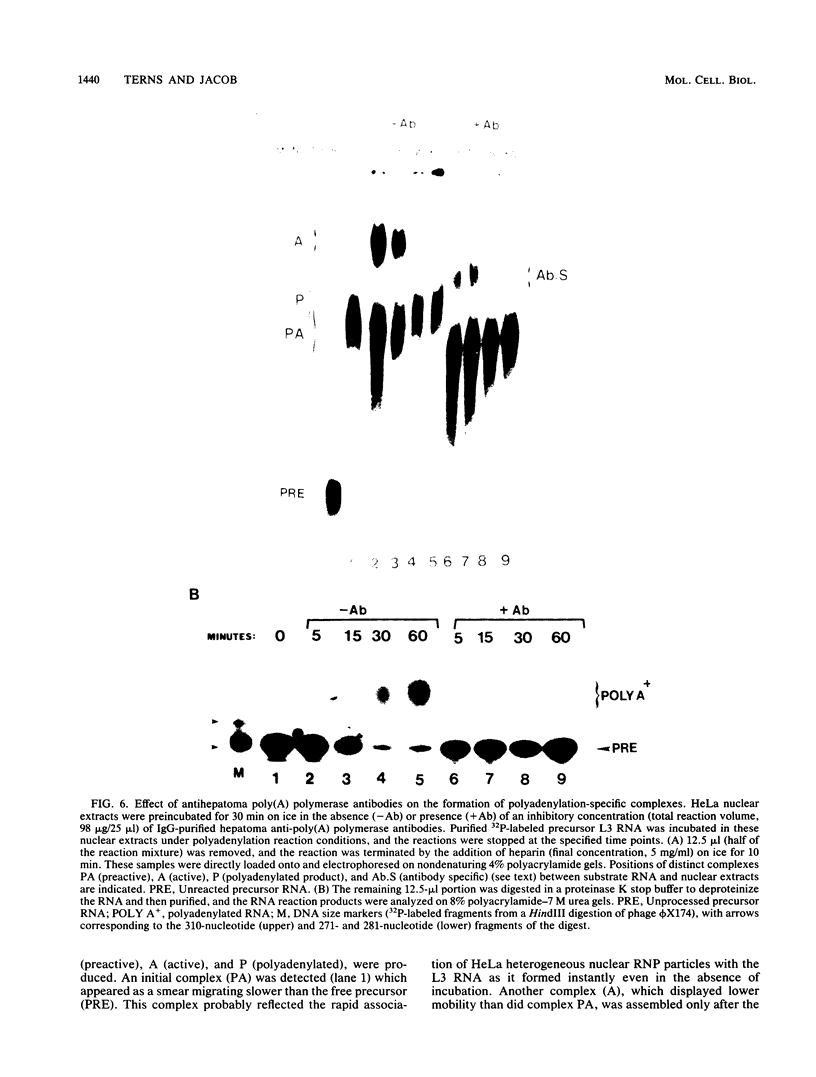
To determine the role of poly(A) polymerase in 3'-end processing of mRNA, the effect of purified poly(A) polymerase antibodies on endonucleolytic cleavage and polyadenylation was studied in HeLa nuclear extracts, using adenovirus L3 pre-mRNA as the substrate. Both Mg2+- and Mn2+-dependent reactions catalyzing addition of 200 to 250 and 400 to 800 adenylic acid residues, respectively, were inhibited by the antibodies, which suggested that the two reactions were catalyzed by the same enzyme. Anti-poly(A) polymerase antibodies also inhibited the cleavage reaction when the reaction was coupled or chemically uncoupled with polyadenylation. These antibodies also prevented formation of specific complexes between the RNA substrate and components of nuclear extracts during cleavage or polyadenylation, with the concurrent appearance of another, antibody-specific complex. These studies demonstrate that (i) previously characterized poly(A) polymerase is the enzyme responsible for addition of the poly(A) tract at the correct cleavage site and probably for the elongation of poly(A) chains and (ii) the coupling of these two 3'-end processing reactions appears to result from the potential requirement of poly(A) polymerase for the cleavage reaction. The results suggest that the specific endonuclease is associated with poly(A) polymerase in a functional complex.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Keller W. 3' cleavage and polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in vitro requires a poly(A) polymerase, a cleavage factor, and a snRNP. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):875–889. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L., Wickens M. A sequence downstream of A-A-U-A-A-A is required for formation of simian virus 40 late mRNA 3' termini in frog oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3949–3953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. A sequence downstream of AAUAAA is required for rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3'-end formation. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):473–474. doi: 10.1038/312473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Multiple factors are required for specific RNA cleavage at a poly(A) addition site. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):578–587. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein associates with the AAUAAA polyadenylation signal in vitro. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Lamb J., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Proudfoot N. J. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a polyadenylation signal mutation. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):398–400. doi: 10.1038/306398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T., Christofori G., Lucijanic V., Keller W. Cleavage and polyadenylation of messenger RNA precursors in vitro occurs within large and specific 3' processing complexes. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4159–4168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02762.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Rose K. M. Phosphorylation and immunology of poly(A) polymerase. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1984;22:485–497. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(84)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of complexes involved in the splicing of precursors to mRNAs. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):845–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Accurate and specific polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in a soluble whole-cell lysate. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 6;950(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Yu H., Ryner L. RNA sequence containing hexanucleotide AAUAAA directs efficient mRNA polyadenylation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):373–379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Gilmartin G. M., Reeves W. H., Nevins J. R. Multiple factors are required for poly(A) addition to a mRNA 3' end. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):588–597. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Moore C. L., Simpson S., Clements J. B. Components required for in vitro cleavage and polyadenylation of eukaryotic mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5323–5344. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Site-specific polyadenylation in a cell-free reaction. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Skolnik-David H., Sharp P. A. Analysis of RNA cleavage at the adenovirus-2 L3 polyadenylation site. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1929–1938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Skolnik-David H., Sharp P. A. Sedimentation analysis of polyadenylation-specific complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju V. S., Jacob S. T. Association of poly(A) polymerase with U1 RNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11067–11070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Bell L. E., Jacob S. T. Specific inhibition of chromatin-associated poly(A) synthesis in vitro by cordycepin 5'-triphosphate. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):178–180. doi: 10.1038/267178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Jacob S. T. Nuclear poly(A) polymerase from rat liver and a hepatoma. Comparison of properties, molecular weights and amino acid compositions. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K. M., Roe F. J., Jacob S. T. Two functional states of poly(adenylic acid) polymerase in isolated nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 20;478(2):180–191. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadofsky M., Connelly S., Manley J. L., Alwine J. C. Identification of a sequence element on the 3' side of AAUAAA which is necessary for simian virus 40 late mRNA 3'-end processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2713–2719. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Stephenson P., Wickens M. P. Products of in vitro cleavage and polyadenylation of simian virus 40 late pre-mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1518–1529. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik-David H., Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of polyadenylation-specific complexes. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):672–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperry A. O., Berget S. M. In vitro cleavage of the simian virus 40 early polyadenylation site adjacent to a required downstream TG sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4734–4741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E., Adams D. E. Assembly of a polyadenylation-specific 25S ribonucleoprotein complex in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2052–2062. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D. A., Jacob S. T. Structurally and immunologically distinct poly(A) polymerases in rat liver. Occurrence of a tumor-type enzyme in normal liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7239–7244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D. A., Wrenshall L. E., Park Y., Jacob S. T. Induction of a distinct nuclear poly(A) polymerase and the production of anti-tumor poly(A) polymerase antibodies in hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Oct;5(10):1363–1366. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.10.1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Separation and characterization of a poly(A) polymerase and a cleavage/specificity factor required for pre-mRNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90411-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T. A 64 kd nuclear protein binds to RNA segments that include the AAUAAA polyadenylation motif. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik R. P., Lyons R. H., Post L., Rottman F. M. Requirement for the 3' flanking region of the bovine growth hormone gene for accurate polyadenylylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3944–3948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Stephenson P., Sheets M., Wickens M. The AAUAAA sequence is required both for cleavage and for polyadenylation of simian virus 40 pre-mRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2317–2323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Wickens M. Formation of mRNA 3' termini: stability and dissociation of a complex involving the AAUAAA sequence. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):177–186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Wickens M. Specific pre-cleavage and post-cleavage complexes involved in the formation of SV40 late mRNA 3' termini in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4185–4192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02765.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Cole C. N. Identification of a complex associated with processing and polyadenylation in vitro of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase precursor RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3277–3286. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]