Abstract
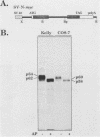
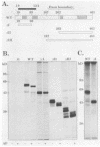
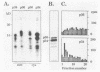
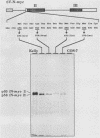
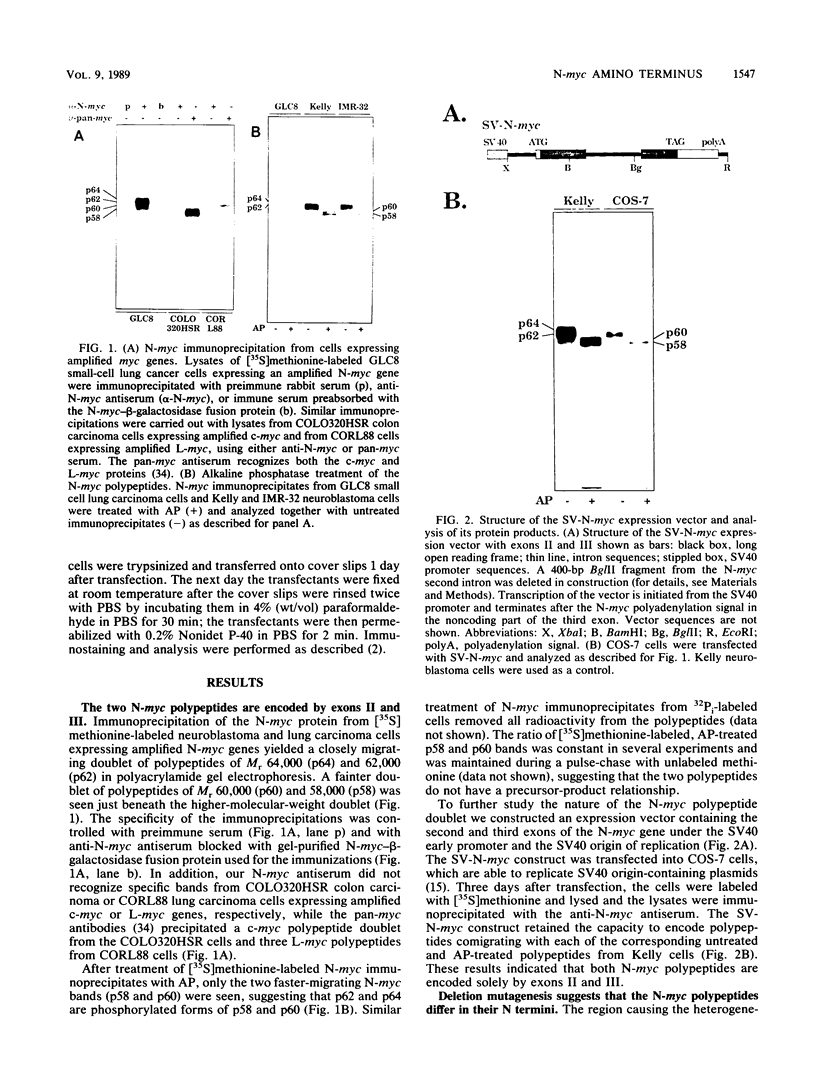
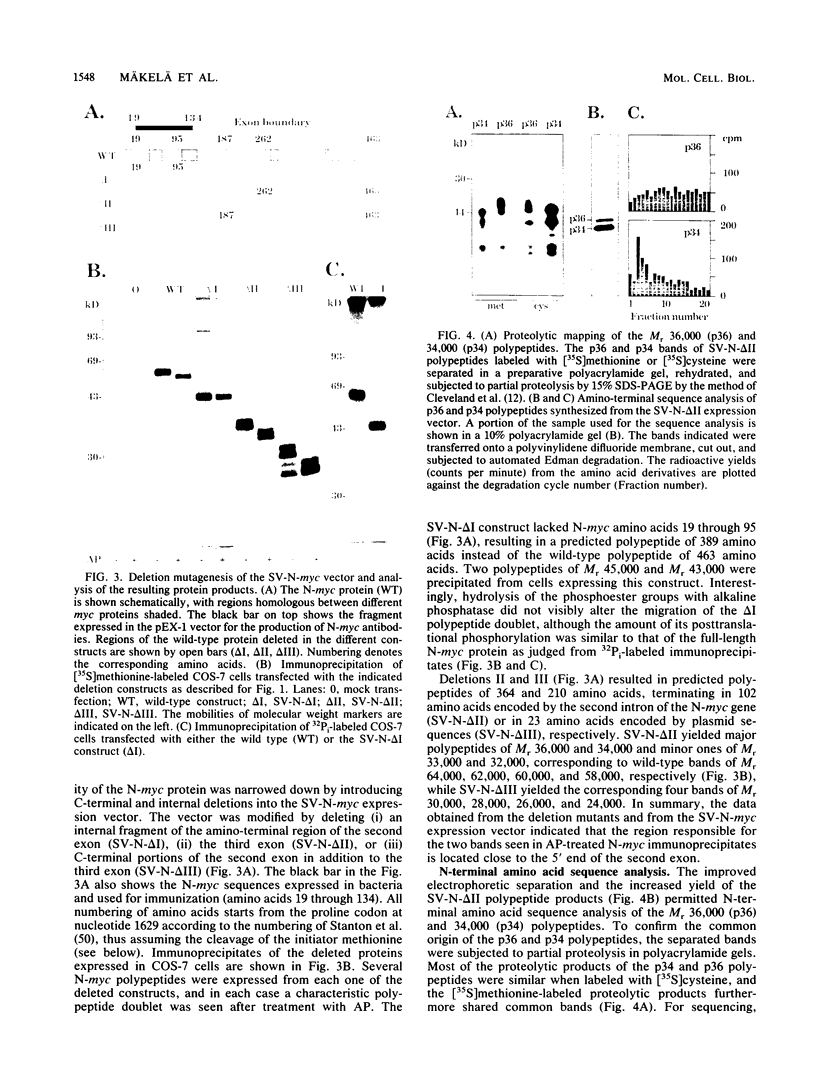
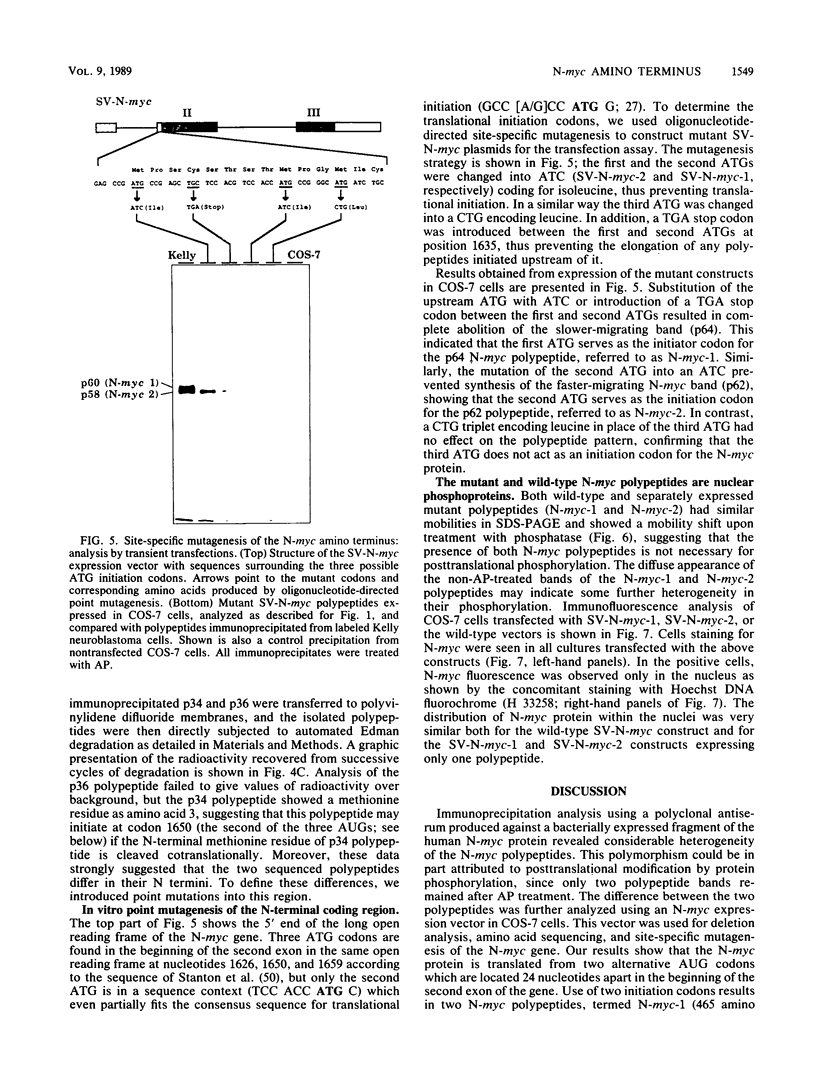
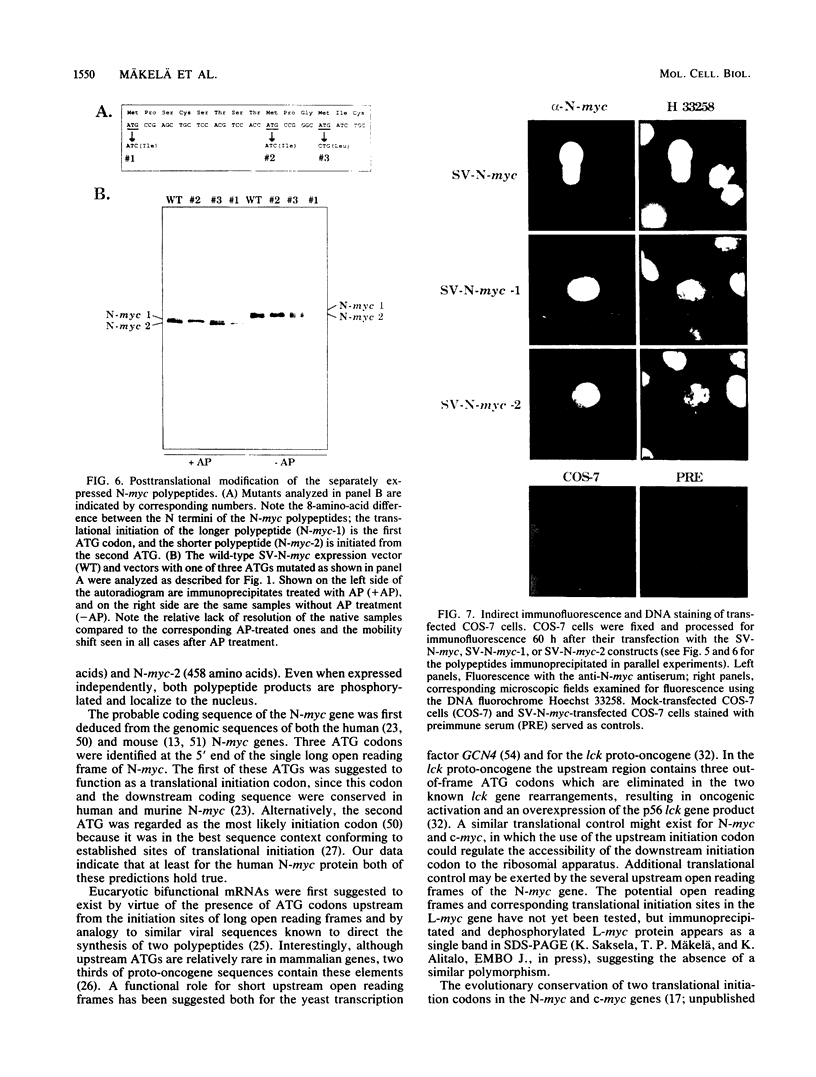
The N-myc and c-myc genes encode closely related nuclear phosphoproteins. We found that the N-myc protein from human tumor cell lines appears as four closely migrating polypeptide bands (p58 to p64) in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. This and the recent finding that the c-myc protein is synthesized from two translational initiation sites located in the first and second exons of the gene (S. R. Hann, M. W. King, D. L. Bentley, C. W. Anderson, and R. N. Eisenman, Cell 52:185-195, 1988) prompted us to study the molecular basis of the N-myc protein heterogeneity. Dephosphorylation by alkaline phosphatase reduced the four polypeptide bands to a doublet with an electrophoretic mobility corresponding to the two faster-migrating N-myc polypeptides (p58 and p60). When expressed transiently in COS cells, an N-myc deletion construct lacking the first exon produced polypeptides similar to the wild-type N-myc protein, indicating that the first exon of the N-myc gene is noncoding. Furthermore, mutants deleted of up to two thirds of C-terminal coding domains still retained the capacity to produce a doublet of polypeptides, suggesting distinct amino termini for the two N-myc polypeptides. The amino-terminal primary structure of the N-myc protein was studied by site-specific point mutagenesis of the 5' end of the long open reading frame and by N-terminal radiosequencing of the two polypeptides. Our results show that the N-myc polypeptides are initiated from two alternative in-phase AUG codons located 24 base pairs apart at the 5' end of the second exon. Both of these polypeptides are phosphorylated and localized to the nucleus even when expressed separately. Interestingly, DNA rearrangements activating the c-myc gene are often found in the 1.7-kilobase-pair region between the two c-myc translational initiation sites and correlate with the loss of the longer c-myc polypeptide. Thus the close spacing of the two N-myc initiation codons could explain the relative resistance of the N-myc gene to similar modes of oncogenic activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Koskinen P., Mäkelä T. P., Saksela K., Sistonen L., Winqvist R. myc oncogenes: activation and amplification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 20;907(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Pfeifer S. O., Colby W. W., Levinson A. D. Identification of nuclear proteins encoded by viral and cellular myc oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):274–277. doi: 10.1038/306274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader J. P., Ray D. A. MC29 virus-coded protein occurs as monomers and dimers in transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):509–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.509-514.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baillie-Johnson H., Twentyman P. R., Fox N. E., Walls G. A., Workman P., Watson J. V., Johnson N., Reeve J. G., Bleehen N. M. Establishment and characterisation of cell lines from patients with lung cancer (predominantly small cell carcinoma). Br J Cancer. 1985 Oct;52(4):495–504. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber J. R., Verma I. M. Modification of fos proteins: phosphorylation of c-fos, but not v-fos, is stimulated by 12-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate and serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2201–2211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):305–311. doi: 10.1126/science.3541204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur G. M., Seeger R. C., Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Amplification of N-myc in untreated human neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.6719137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broers J. L., Carney D. N., de Ley L., Vooijs G. P., Ramaekers F. C. Differential expression of intermediate filament proteins distinguishes classic from variant small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4409–4413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri F., Goldfarb M. N-myc proto-oncogene expression can induce DNA replication in Balb/c 3T3 fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1988 Mar;2(3):289–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Classon M., Henriksson M., Sümegi J., Klein G., Hammarskjöld M. L., Hammaskjöld M. L. Elevated c-myc expression facilitates the replication of SV40 DNA in human lymphoma cells. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):272–274. doi: 10.1038/330272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePinho R. A., Legouy E., Feldman L. B., Kohl N. E., Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Structure and expression of the murine N-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1827–1831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson J. A., Clayton J., McIntyre P., Kemshead J. T. N-myc oncogene amplification in rhabdomyosarcoma at release. Lancet. 1986 Jun 28;1(8496):1496–1496. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91527-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Abrams H. D., Rohrschneider L. R., Eisenman R. N. Proteins encoded by v-myc and c-myc oncogenes: identification and localization in acute leukemia virus transformants and bursal lymphoma cell lines. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., King M. W., Bentley D. L., Anderson C. W., Eisenman R. N. A non-AUG translational initiation in c-myc exon 1 generates an N-terminally distinct protein whose synthesis is disrupted in Burkitt's lymphomas. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Itani T., Kiji Y., Ariga H. Possible function of the c-myc product: promotion of cellular DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2365–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegaki N., Bukovsky J., Kennett R. H. Identification and characterization of the NMYC gene product in human neuroblastoma cells by monoclonal antibodies with defined specificities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5929–5933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Schwab M., Bishop J. M., Martin G. R. Expression of N-myc in teratocarcinoma stem cells and mouse embryos. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):188–191. doi: 10.1038/318188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):280–282. doi: 10.1038/312280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Klein E. Evolution of tumours and the impact of molecular oncology. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):190–195. doi: 10.1038/315190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Legouy E., DePinho R. A., Nisen P. D., Smith R. K., Gee C. E., Alt F. W. Human N-myc is closely related in organization and nucleotide sequence to c-myc. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):73–77. doi: 10.1038/319073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. At least six nucleotides preceding the AUG initiator codon enhance translation in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/c 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Murphree A. L., Benedict W. F. Expression and amplification of the N-myc gene in primary retinoblastoma. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):458–460. doi: 10.1038/309458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucher L. A., Brackmann K. H., Symington J. S., Green M. Posttranslational modification at the N terminus of the human adenovirus type 12 E1A 235R tumor antigen. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):592–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.592-599.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Overell R. W., Meier K. E., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Translational activation of the lck proto-oncogene. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):171–173. doi: 10.1038/332171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Hancock D. C., Littlewood T. D., Evan G. I. A sensitive and quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbence assay for the c-myc and N-myc oncoproteins. Oncogene Res. 1987;2(1):65–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau M. M., Brooks B. J., Jr, Carney D. N., Gazdar A. F., Battey J. F., Sausville E. A., Minna J. D. Human small-cell lung cancers show amplification and expression of the N-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1092–1096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Leder P. Nuclear localization and DNA binding properties of a protein expressed by human c-myc oncogene. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):718–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6463648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the human proto-oncogene c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Stanton L., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Human proto-oncogene N-myc encodes nuclear proteins that bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4450–4457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela K., Bergh J., Nilsson K. Amplification of the N-myc oncogene in an adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Cell Biochem. 1986;31(4):297–304. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240310407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M. Direct interaction between fos and jun nuclear oncoproteins: role of the 'leucine zipper' domain. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):692–695. doi: 10.1038/336692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumour. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Human N-myc gene contributes to neoplastic transformation of mammalian cells in culture. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):160–162. doi: 10.1038/316160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Boone T. C., Seeger R. C., Keith D. E., Chazin V., Lee H. C., Souza L. M. Identification and characterization of the protein encoded by the human N-myc oncogene. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):768–772. doi: 10.1126/science.3008339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavicek J. M., Jones N. C., Richter J. D. Rapid turnover of adenovirus E1A is determined through a co-translational mechanism that requires an aminoterminal domain. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3171–3180. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small M. B., Hay N., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Neoplastic transformation by the human gene N-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1638–1645. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Watt R. A., Sullivan N. F. The v- and c-myc oncogene proteins colocalize in situ with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton L. W., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the human N-myc gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1772–1776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taya Y., Mizusawa S., Nishimura S. Nucleotide sequence of the coding region of the mouse N-myc gene. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1215–1219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04349.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele C. J., Reynolds C. P., Israel M. A. Decreased expression of N-myc precedes retinoic acid-induced morphological differentiation of human neuroblastoma. 1985 Jan 31-Feb 6Nature. 313(6001):404–406. doi: 10.1038/313404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Wong-Staal F., Gelmann E. P., Dalla-Favera R., Papas T. S., Lautenberger J. A., Eva A., Reddy E. P., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Expression of cellular homologues of retroviral onc genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2490–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. P., Mueller P. P., Hinnebusch A. G. The positive regulatory function of the 5'-proximal open reading frames in GCN4 mRNA can be mimicked by heterologous, short coding sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3827–3836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingrove T. G., Watt R., Keng P., Macara I. G. Stabilization of myc proto-oncogene proteins during Friend murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8918–8924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Nisen P. D., Tesfaye A., Kohl N. E., Goldfarb M. P., Alt F. W. N-myc can cooperate with ras to transform normal cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. J., Machlin P. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulated instability of beta-tubulin mRNAs by recognition of the nascent amino terminus of beta-tubulin. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):580–585. doi: 10.1038/334580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman K. A., Yancopoulos G. D., Collum R. G., Smith R. K., Kohl N. E., Denis K. A., Nau M. M., Witte O. N., Toran-Allerand D., Gee C. E. Differential expression of myc family genes during murine development. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):780–783. doi: 10.1038/319780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]