Abstract
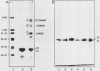
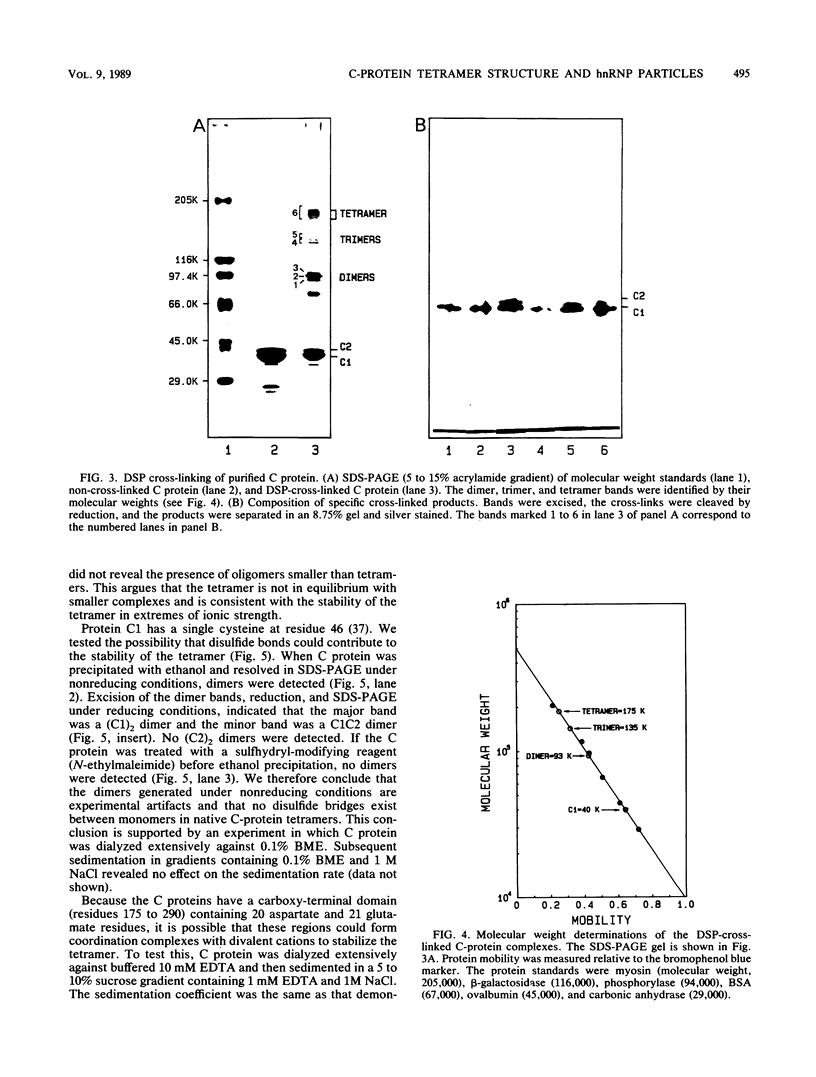
The C proteins (C1 and C2) of HeLa 40S heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles copurify under native conditions as a stable complex with a fixed molar protein ratio (S.F. Barnett, W.M. LeStourgeon, and D.L. Friedman, J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 16:87-97, 1988). Gel filtration chromatography and velocity sedimentation analyses of these complexes revealed a large Stokes radius (6.2 nm) and a sedimentation coefficient of 5.8S. On the basis of these values and a partial specific volume of 0.70 cm3/g based on the amino acid composition, the molecular weight of the complex was calculated to be 135,500. This corresponds well to 129,056, the sequence-determined molecular weight of a (C1)3C2 tetramer. Reversible chemical cross-linking with dithiobis(succinimidyl propionate) and analysis of cross-linked and cleaved complexes in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis confirmed that the C proteins exist as tetramers, most or all of which are composed of (C1)3C2. The tetramer is stable in a wide range of NaCl concentrations (0.09 to 2.0 M) and is not dissociated by 0.5% sodium deoxycholate. This stability is not the result of disulfide bonds or interactions with divalent cations. The hydrodynamic properties of highly purified C-protein tetramers are the same for C-protein complexes released from intact particles with RNase or high salt. These findings support previous studies indicating that the core particle protein stoichiometry of 40S heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins is N(3A1-3A2-1B1-1B2-3C1-1C2), where N = 3 to 4, and demonstrate that the C-protein tetramer is a fundamental structural element in these RNA-packaging complexes. The presence of at least three tetramers per 40S monoparticle, together with the highly anisotropic nature of the tetramer, suggesting that one-third of the 700-nucleotide pre-mRNA moiety packaged in monoparticles is associated through a sequence-independent mechanism with the C protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERS G. K. MOLECULAR EXCLUSION AND RESTRICTED DIFFUSION PROCESSES IN MOLECULAR-SIEVE CHROMATOGRAPHY. Biochemistry. 1964 May;3:723–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00893a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett S. F., LeStourgeon W. M., Friedman D. L. Rapid purification of native C protein from nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1988 May;16(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(88)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Bouton A. H., Miller O. L., Jr Correlation of hnRNP structure and nascent transcript cleavage. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification and characterization of the packaging proteins of core 40S hnRNP particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. Ultrastructural analysis of the ribonucleoprotein structure of nascent hnRNA. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):49–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00777473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. W., Williams K. R. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins required for DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:103–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Isolation of the heterogeneous nuclear RNA-ribonucleoprotein complex (hnRNP): a unique supramolecular assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7471–7475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Monoclonal antibody characterization of the C proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes in vertebrate cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1997–1204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Rodbard D. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):440–451. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. Y., Wooley J. Set of novel, conserved proteins fold pre-messenger RNA into ribonucleosomes. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):195–210. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway G., Wooley J., Bibring T., LeStourgeon W. M. Ribonucleoproteins package 700 nucleotides of pre-mRNA into a repeating array of regular particles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2884–2895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D. Physical change in cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleoproteins in cells treated with inhibitors of mRNA transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):415–423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Choi Y. D., Adam S. A. Characterization of heterogeneous nuclear RNA-protein complexes in vivo with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenner C., Traut R. R., Mason D. T., Wikman-Coffelt J. Quantification of Coomassie Blue stained proteins in polyacrylamide gels based on analyses of eluted dye. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami P., Goldenberg C. J. Intron sequences and the length of the downstream second exon affect the binding of hnRNP C proteins in an in vitro splicing reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):4995–5011. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.4995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holcomb E. R., Friedman D. L. Phosphorylation of the C-proteins of HeLa cell hnRNP particles. Involvement of a casein kinase II-type enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):31–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowler J. T. An assessment of the evidence for the role of ribonucleoprotein particles in the maturation of eukaryote mRNA. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;84:103–153. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeStourgeon W. M., Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., Poupore S. M., Daniels L. P. The packaging proteins of core hnRNP particles and the maintenance of proliferative cell states. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):885–898. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomant A. J., Fairbanks G. Chemical probes of extended biological structures: synthesis and properties of the cleavable protein cross-linking reagent [35S]dithiobis(succinimidyl propionate). J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 14;104(1):243–261. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lothstein L., Arenstorf H. P., Chung S. Y., Walker B. W., Wooley J. C., LeStourgeon W. M. General organization of protein in HeLa 40S nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1570–1581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheim Y. N., Miller O. L., Jr, Beyer A. L. RNP particles at splice junction sequences on Drosophila chorion transcripts. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Choi Y. D., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G. Immunopurification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles reveals an assortment of RNA-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):215–227. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman J. M., Martin T. E. Reconstitution of nucleoprotein complexes with mammalian heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) core proteins. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):99–111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekeris C. E., Niessing J. Evidence for the existence of a structural RNA component in the nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles containing heterogeneous RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):642–650. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsanev R. G., Djondjurov L. P. Ultrastructure of free ribonucleoprotein complexes in spread mammalian nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):662–666. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk H. E., Angeli G., Schäfer K. P. In vitro reconstitution of 35S ribonucleoprotein complexes. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 13;22(19):4592–4600. doi: 10.1021/bi00288a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk H. E., Werr H., Friedrich D., Kiltz H. H., Schäfer K. P. The core proteins of 35S hnRNP complexes. Characterization of nine different species. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 2;146(1):71–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley J., Chung S. Y., Wall J., Lestourgeon W. Architecture of pre-messenger, nuclear ribonucleoprotein monoparticles. Biophys J. 1986 Jan;49(1):17–19. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83575-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]