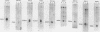Abstract
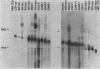
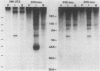
Activation of transforming potential of the cellular raf gene has uniformly been associated with the deletion of amino-terminal coding sequences. In order to determine whether 5' truncation alone could activate cellular raf, we constructed 21 human c-raf-1 cDNAs with variable BAL 31-generated deletions distal to a Moloney murine sarcoma virus long terminal repeat and a consensus translation initiation sequence. The deletions ranged from 136 to 1,399 nucleotides of coding sequence and shortened the 648-amino-acid raf protein by 44 to 465 amino acids. The full-length c-raf-1 cDNA was nontransforming upon transfection of NIH 3T3 cells, as were four mutants with deletions of 142 or fewer amino acids. Seven of nine mutants with deletions of 154 to 273 amino acids induced transformation with efficiencies ranging from 0.25 to 70 foci per micrograms of DNA. Mutants with deletions of 303 to 324 amino acids displayed high transforming activities (comparable with that of v-raf), with a peak activity of 2,400 foci per microgram of DNA when 305 amino acids were deleted. Deletions of greater than 383 amino acids, extending into the raf kinase domain, lacked transforming activity. Northern (RNA) blotting and immunoprecipitation assays indicated that transfected NIH cells expressed raf RNAs and proteins of the expected sizes. Thus, 5' truncation alone can activate raf transforming potential, with a sharp peak of activation around amino acid 300. Analysis of three raf genes previously detected by transfection of tumor DNAs indicated that these genes were activated by recombination in raf intron 7 and encoded fusion proteins containing amino-terminal non-raf sequences. The extend of deletion of raf sequences in these recombinant genes corresponded to BAL 31 mutants which did not display high transforming activity, suggesting that the fused non-raf coding sequences may also contribute to biological activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck T. W., Huleihel M., Gunnell M., Bonner T. I., Rapp U. R. The complete coding sequence of the human A-raf-1 oncogene and transforming activity of a human A-raf carrying retrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):595–609. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., McClements W. L., Oskarsson M. K., Fischinger P. J., Vande Woude G. F. Biological activity of cloned Moloney sarcoma virus DNA: Terminally redundant sequences may enhance transformation efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Kerby S. B., Sutrave P., Gunnell M. A., Mark G., Rapp U. R. Structure and biological activity of human homologs of the raf/mil oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1400–1407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Oppermann H., Seeburg P., Kerby S. B., Gunnell M. A., Young A. C., Rapp U. R. The complete coding sequence of the human raf oncogene and the corresponding structure of the c-raf-1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1009–1015. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. H., Pirollo K. F., Zou Z. Q., Cheung H. Y., Lawler E. L., Garner R., White E., Bernstein W. B., Fraumeni J. W., Jr, Blattner W. A. Oncogenes in radioresistant, noncancerous skin fibroblasts from a cancer-prone family. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):1036–1039. doi: 10.1126/science.3616624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland J. L., Jansen H. W., Bister K., Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd, Ihle J. N., Rapp U. R. Interaction between Raf and Myc oncogenes in transformation in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 1986;30(3):195–218. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240300303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Cooper G. M. Transfection by exogenous and endogenous murine retrovirus DNAs. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., McClements W. L., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequences of integrated Moloney sarcoma provirus long terminal repeats and their host and viral junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui M., Yamamoto T., Kawai S., Maruo K., Toyoshima K. Detection of a raf-related and two other transforming DNA sequences in human tumors maintained in nude mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5954–5958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui M., Yamamoto T., Kawai S., Mitsunobu F., Toyoshima K. Molecular cloning and characterization of an activated human c-raf-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1776–1781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa S., Fukui M., Ueyama Y., Tamaoki N., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. B-raf, a new member of the raf family, is activated by DNA rearrangement. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2651–2654. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Takaku F., Hayashi K., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Activation of rat c-raf during transfection of hepatocellular carcinoma DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3209–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Takaku F., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Rat c-raf oncogene activation by a rearrangement that produces a fused protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1226–1232. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Takaku F., Ochiai M., Hayashi K., Hirohashi S., Terada M., Takayama S., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Activated c-raf gene in a rat hepatocellular carcinoma induced by 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 15;132(1):186–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasid U., Pfeifer A., Weichselbaum R. R., Dritschilo A., Mark G. E. The raf oncogene is associated with a radiation-resistant human laryngeal cancer. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):1039–1041. doi: 10.1126/science.3616625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Buchanan J. M. Phosphorylation of tyrosine in the carboxyl-terminal tryptic peptide of pp60c-src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):892–896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark G. E., Rapp U. R. Primary structure of v-raf: relatedness to the src family of oncogenes. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):285–289. doi: 10.1126/science.6324342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark G. E., Seeley T. W., Shows T. B., Mountz J. D. Pks, a raf-related sequence in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6312–6316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moelling K., Heimann B., Beimling P., Rapp U. R., Sander T. Serine- and threonine-specific protein kinase activities of purified gag-mil and gag-raf proteins. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):558–561. doi: 10.1038/312558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mölders H., Defesche J., Müller D., Bonner T. I., Rapp U. R., Müller R. Integration of transfected LTR sequences into the c-raf proto-oncogene: activation by promoter insertion. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):693–698. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03685.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Müller D. Co-transfection of normal NIH/3T3 DNA and retroval LTR sequences: a novel strategy for the detection of potential c-onc genes. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1121–1127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01939.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsu Y., Nomoto S., Oh-uchida M., Shimizu K., Sekiguchi M. Structure of the activated c-raf-1 gene from human stomach cancer. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 2):1001–1008. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. New mammalian transforming retrovirus: demonstration of a polyprotein gene product. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):914–924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.914-924.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Nakatsu Y., Sekiguchi M., Hokamura K., Tanaka K., Terada M., Sugimura T. Molecular cloning of an activated human oncogene, homologous to v-raf, from primary stomach cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5641–5645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton V. P., Jr, Cooper G. M. Activation of human raf transforming genes by deletion of normal amino-terminal coding sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1171–1179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutrave P., Bonner T. I., Rapp U. R., Jansen H. W., Patschinsky T., Bister K. Nucleotide sequence of avian retroviral oncogene v-mil: homologue of murine retroviral oncogene v-raf. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):85–88. doi: 10.1038/309085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahira T., Ochiai M., Hayashi K., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Activation of human c-raf-1 by replacing the N-terminal region with different sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4809–4820. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Scheidtmann K. H., Carbone A., Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Antibodies specific for the carboxy- and amino-terminal regions of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5197–5200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]