Abstract
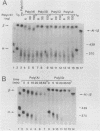
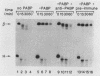
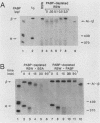
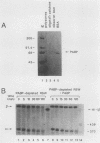
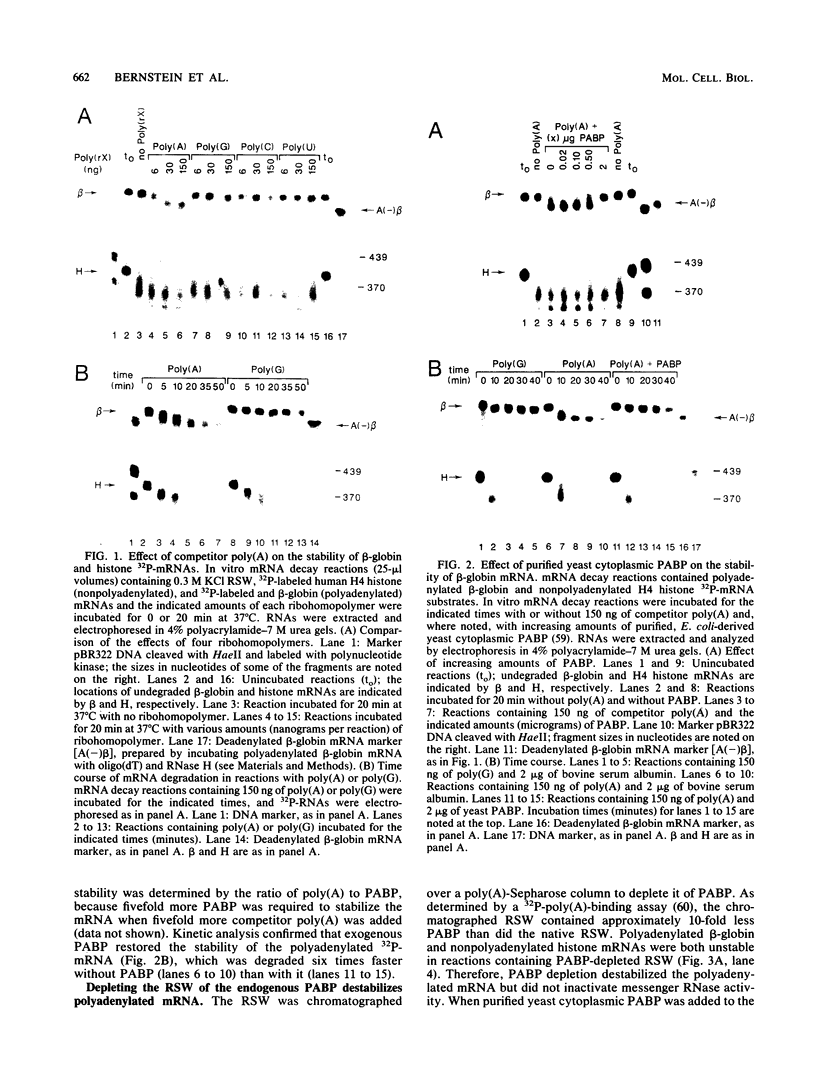
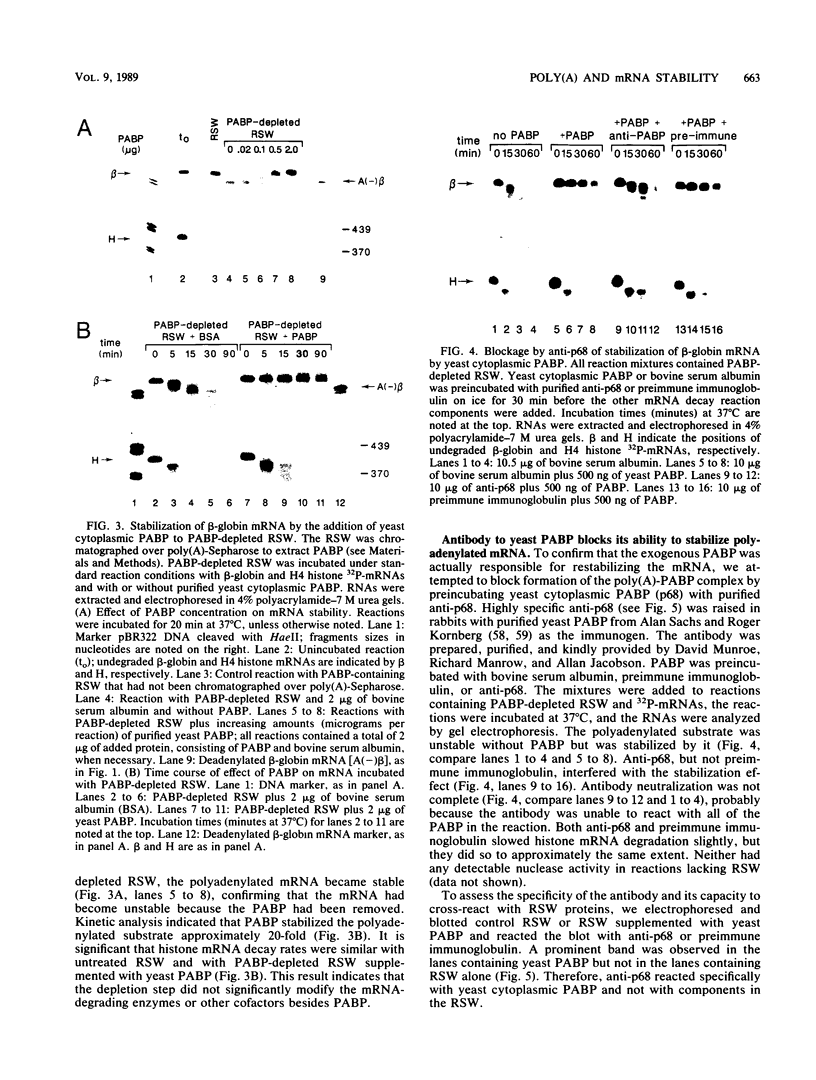
Using an in vitro mRNA decay system, we investigated how poly(A) and its associated poly(A)-binding protein (PABP) affect mRNA stability. Cell extracts used in the decay reactions were depleted of functional PABP either by adding excess poly(A) competitor or by passing the extracts over a poly(A)-Sepharose column. Polyadenylated mRNAs for beta-globin, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase, and simian virus 40 virion proteins were degraded 3 to 10 times faster in reactions lacking PABP than in those containing excess PABP. The addition of purified Saccharomyces cerevisiae or human cytoplasmic PABP to PABP-depleted reactions stabilized the polyadenylated mRNAs. In contrast, the decay rates of nonpolyadenylated mRNAs were unaffected by PABP, indicating that both the poly(A) and its binding protein were required for maintaining mRNA stability. A nonspecific single-stranded binding protein from Escherichia coli did not restore stability to polyadenylated mRNA, and the stabilizing effect of PABP was inhibited by anti-PABP antibody. The poly(A) tract was the first mRNA segment to be degraded in PABP-depleted reactions, confirming that the poly(A)-PABP complex was protecting the 3' region from nucleolytic attack. These results indicate that an important function of poly(A), in conjunction with its binding protein, is to protect polyadenylated mRNAs from indiscriminate destruction by cellular nucleases. A model is proposed to explain how the stability of an mRNA could be affected by the stability of its poly(A)-PABP complex.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Interaction of mRNA with proteins in vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):614–622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.614-622.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adesnik M., Darnell J. E. Biogenesis and characterization of histone messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni Y., Shani M., Reuveni Y. RNAs of simian virus 40 in productively infected monkey cells: kinetics of formation and decay in enucleate cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2587–2591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Edmonds M., Nakazato H., Phillips B. A., Vaughn M. H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the virion RNA of poliovirus and Eastern Equine Encephalitis virus. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):526–528. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer B. W., Kornberg R. D. Repeating structure of cytoplasmic poly(A)-ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1890–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer B. W., Kornberg R. D. The protein responsible for the repeating structure of cytoplasmic poly(A)-ribonucleoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):717–721. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann I. E., Brawerman G. Control of breakdown of the polyadenylate sequence in mammalian polyribosomes: role of poly(adenylic acid)-protein interactions. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 25;16(2):259–264. doi: 10.1021/bi00621a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. A protein of molecular weight 78,000 bound to the polyadenylate region of eukaryotic messenger RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):924–928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Poly(A) shortening and degradation of the 3' A+U-rich sequences of human c-myc mRNA in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1697–1708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Behavior of individual maternal pA+ RNAs during embryogenesis of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1982 Nov;94(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I. O., Maquat L. E. Premature translation termination mediates triosephosphate isomerase mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):802–813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande A. K., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. Translation and stability of rat liver messenger RNA for alpha 2 mu-globulin in Xenopus oocyte. The role of terminal poly(A). J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8937–8942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doel M. T., Carey N. H. The translational capacity of deadenylated ovalbumin messenger RNA. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. R., Armstrong J., Colman A. The effect of capping and polyadenylation on the stability, movement and translation of synthetic messenger RNAs in Xenopus oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7375–7394. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Summers D. F. Adenylate-rich sequences in vesicular stomatitis virus messenger ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.683-688.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Rech J., Vie A., Piechaczyk M., Bonnieu A., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Regulation of c-fos gene expression in hamster fibroblasts: initiation and elongation of transcription and mRNA degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5657–5667. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili G., Kawata E. E., Smith L. D., Larkins B. A. Role of the 3'-poly(A) sequence in translational regulation of mRNAs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5764–5770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoghegan T. E., McCoy L. Biogenesis and cell cycle relationship of poly(A)- actin mRNA in mouse ascites cells. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jan;162(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., de Sa C. M., Oddos J., Pictet R. Human mRNA polyadenylate binding protein: evolutionary conservation of a nucleic acid binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4771–4787. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. L., Dove W. F. Correlation between tubulin mRNA stability and poly(A) length over the cell cycle of Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 20;200(2):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R., Perry R. P. Relative occurrence of polyadenylic acid sequences in messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA of L cells as determined by poly (U)-hydroxylapatite chromatography. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 14;72(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Misher L. Stability of RNA in developing Xenopus embryos and identification of a destabilizing sequence in TFIIIA messenger RNA. Development. 1988 Apr;102(4):837–852. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.4.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huez G., Marbaix G., Gallwitz D., Weinberg E., Devos R., Hubert E., Cleuter Y. Functional stabilisation of HeLa cell histone messenger RNAs injected into Xenopus oocytes by 3'-OH polyadenylation. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):572–573. doi: 10.1038/271572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huez G., Marbaix G., Hubert E., Cleuter Y., Leclercq M., Chantrenne H., Devos R., Soreq H., Nudel U., Littauer U. Z. Readenylation of polyadenylate-free globin messenger RNA restores its stability in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 15;59(2):589–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A., Favreau M. Possible involvement of poly(A) in protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6353–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenh C. H., Geyer P. K., Johnson L. F. Control of thymidylate synthase mRNA content and gene transcription in an overproducing mouse cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2527–2532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann Y., Milcarek C., Berissi H., Penman S. HeLa cell poly(A)- mRNA codes for a subset of poly(A)+ mRNA-directed proteins with an actin as a major product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krowczynska A., Brawerman G. Structural features in the 3'-terminal region of polyribosome-bound rabbit globin messenger RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krowczynska A., Yenofsky R., Brawerman G. Regulation of messenger RNA stability in mouse erythroleukemia cells. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. W., Brawerman G. A particle associated with the polyadenylate segment in mammalian messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3247–3250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manrow R. E., Jacobson A. Identification and characterization of developmentally regulated mRNP proteins of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1986 Jul;116(1):213–227. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manrow R. E., Jacobson A. Increased rates of decay and reduced levels of accumulation of the major poly(A)-associated proteins of Dictyostelium during heat shock and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Pandey N. B. Multiple regulatory steps control histone mRNA concentrations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. F., Wake S. A. An analysis of the rate of metallothionein mRNA poly(A)-shortening using RNA blot hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):7929–7943. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.7929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Dubroff L. M., Graham M. Properties of sea urchin embryo messenger RNA containing and lacking poly(A). Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Belasco J. G., Cohen S. N., von Gabain A. Growth-rate dependent regulation of mRNA stability in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1984 Nov 1;312(5989):75–77. doi: 10.1038/312075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Degradation of cellular mRNA during infection by herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2370–2374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Soreq H., Littauer U. Z. Globin mRNA species containing poly(A) segments of different lengths. Their functional stability in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):115–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paek I., Axel R. Glucocorticoids enhance stability of human growth hormone mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1496–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Storti R. V., Capone A. K., Jacobson A. Messenger RNA stability in Dictyostelium discoideum: does poly(A) have a regulatory role? J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 5;141(2):99–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Wilkins C., Jacobson A. Translational control during early Dictyostelium development: possible involvement of poly(A) sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Brewer G., Kobs G., Ross J. Substrate specificity of the exonuclease activity that degrades H4 histone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9382–9388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Ross J. Autogenous regulation of histone mRNA decay by histone proteins in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4345–4356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. Processing of RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:605–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restifo L. L., Guild G. M. Poly(A) shortening of coregulated transcripts in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1986 Jun;115(2):507–510. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G., Brewer G., Peltz S. W. Properties of the exonuclease activity that degrades H4 histone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9374–9381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G. H4 histone messenger RNA decay in cell-free extracts initiates at or near the 3' terminus and proceeds 3' to 5'. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):579–593. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. Messenger RNA turnover in eukaryotic cells. Mol Biol Med. 1988 Feb;5(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Peltz S. W., Kobs G., Brewer G. Histone mRNA degradation in vivo: the first detectable step occurs at or near the 3' terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4362–4371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Pizarro A. Human beta and delta globin messenger RNAs turn over at different rates. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 5;167(3):607–617. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Bond M. W., Kornberg R. D. A single gene from yeast for both nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylate-binding proteins: domain structure and expression. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W., Kornberg R. D. A single domain of yeast poly(A)-binding protein is necessary and sufficient for RNA binding and cell viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3268–3276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Kornberg R. D. Nuclear polyadenylate-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1993–1996. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Blume J. E., Nielsen D. A. Regulation of messenger RNA stability in eukaryotic cells. Bioessays. 1987 May;6(5):221–226. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R. A., Herrick D., Manrow R. E., Blinder D., Jacobson A. Determinants of mRNA stability in Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae: differences in poly(A) tail length, ribosome loading, and mRNA size cannot account for the heterogeneity of mRNA decay rates. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1957–1969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Sagar A. D., Sehgal P. B. Translational activity and functional stability of human fibroblast beta 1 and beta 2 interferon mRNAs lacking 3'-terminal RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1741–1745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. Classification and purification of proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by RNA-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartwout S. G., Preisler H., Guan W. D., Kinniburgh A. J. Relatively stable population of c-myc RNA that lacks long poly(A). Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2052–2058. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorakis N. G., Morimoto R. I. Posttranscriptional regulation of hsp70 expression in human cells: effects of heat shock, inhibition of protein synthesis, and adenovirus infection on translation and mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4357–4368. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw E., Proudfoot N. Alpha-thalassaemia caused by a poly(A) site mutation reveals that transcriptional termination is linked to 3' end processing in the human alpha 2 globin gene. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2915–2922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04587.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Sawicki S. G., White P. A., Darnell J. E., Jr A correlation between the rate of poly(A) shortening and half-life of messenger RNA in adenovirus transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G., Stein J., Stein G. Targeting of a chimeric human histone fusion mRNA to membrane-bound polysomes in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2683–2687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeevi M., Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Newly formed mRNA lacking polyadenylic acid enters the cytoplasm and the polyribosomes but has a shorter half-life in the absence of polyadenylic acid. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 May;2(5):517–525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.5.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeevi M., Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Nuclear RNA is spliced in the absence of poly(A) addition. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]