Abstract
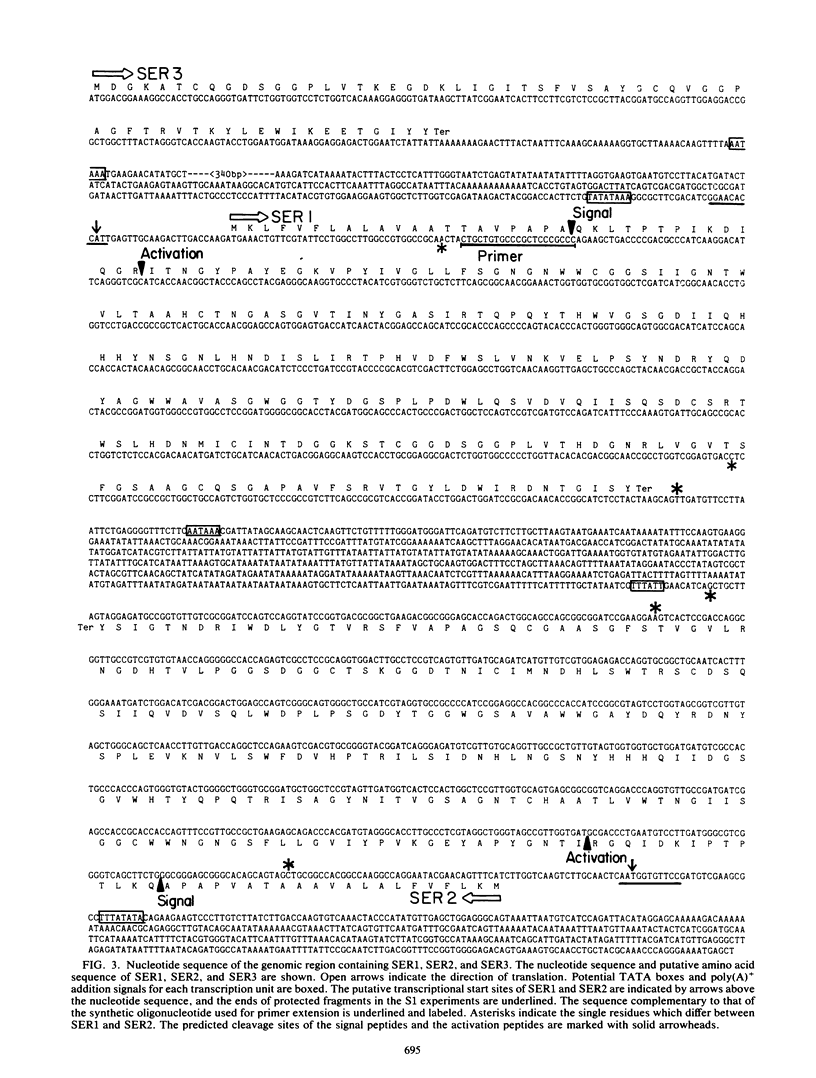
We have isolated several genes expressed at abnormal levels in the memory mutant, dunce (dnc), of Drosophila melanogaster. These mutants have an elevated cyclic AMP (cAMP) content due to a mutation in the structural gene for cAMP phosphodiesterase, so the isolated genes are potentially ones regulated by cAMP. Here, we describe the characterization of a genomic clone and corresponding cDNA clones which contain sequences that are underexpressed in dnc mutants. Sequence analysis of portions of the genomic clone and representative cDNAs revealed the presence of two uninterrupted and complete open reading frames (SER1 and SER2) and part of a third (SER3). The predicted amino acid sequences of all of these were found to be homologous to the serine protease family of enzymes. The genomic clone was localized to the polytene chromosome region 99C-D, although genome-blotting experiments indicated the existence of several other genes related to the cloned serine protease-like genes. Hybridization experiments with probes representing each of the three sequenced genes showed that only the SER1-related genes were differentially expressed in dnc mutants. The putative serine protease genes were abundantly expressed in the larval gut, suggesting a major function in digestion. Feeding normal flies cAMP, isobutylmethylxanthine, or forskolin resulted in a decreased RNA level of the SER1-related genes. Thus, RNA levels of this serine protease gene family are negatively regulated by cAMP.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aceves-Piña E. O., Booker R., Duerr J. S., Livingstone M. S., Quinn W. G., Smith R. F., Sziber P. P., Tempel B. L., Tully T. P. Learning and memory in Drosophila, studied with mutants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhya S., Garges S. How cyclic AMP and its receptor protein act in Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):287–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benkel B. F., Hickey D. A. Glucose Repression of Amylase Gene Expression in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1986 Sep;114(1):137–144. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birktoft J. J., Blow D. M. Structure of crystalline -chymotrypsin. V. The atomic structure of tosyl- -chymotrypsin at 2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):187–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Neuberg M., Burckhardt J., Almendral J., Wallich R., Müller R. Involvement of common and cell type-specific pathways in c-fos gene control: stable induction of cAMP in macrophages. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher P., Trifonov E. N. Compilation and analysis of eukaryotic POL II promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):10009–10026. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.10009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carne T., Scheele G. Amino acid sequences of transport peptides associated with canine exocrine pancreatic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4133–4140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. N., Denome S., Davis R. L. Molecular analysis of cDNA clones and the corresponding genomic coding sequences of the Drosophila dunce+ gene, the structural gene for cAMP phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9313–9317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Meselson M. Separate regulatory elements for the heat-inducible and ovarian expression of the Drosophila hsp26 gene. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):737–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. A., Riddell D. C., Higgins M. J., Holden J. J., White B. N. A gene family in Drosophila melanogaster coding for trypsin-like enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6605–6619. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Davidson N. The memory gene dunce+ encodes a remarkable set of RNAs with internal heterogeneity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1464–1470. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Kiger J. A., Jr Dunce mutants of Drosophila melanogaster: mutants defective in the cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase enzyme system. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):101–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLotto R., Spierer P. A gene required for the specification of dorsal-ventral pattern in Drosophila appears to encode a serine protease. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):688–692. doi: 10.1038/323688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudai Y., Jan Y. N., Byers D., Quinn W. G., Benzer S. dunce, a mutant of Drosophila deficient in learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1684–1688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg I., Rybak S., Kimhi Y., Littauer U. Z. Biphasic regulation by dibutyryl cyclic AMP of tubulin and actin mRNA levels in neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant G. A., Henderson K. O., Eisen A. Z., Bradshaw R. A. Amino acid sequence of a collagenolytic protease from the hepatopancreas of the fiddler crab, Uca pugilator. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 30;19(20):4653–4659. doi: 10.1021/bi00561a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Greene L. A., Ziff E. B. Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14101–14110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. M., Castellucci V. F., Bayley H., Schwartz J. H. A molecular mechanism for long-term sensitization in Aplysia. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):62–65. doi: 10.1038/329062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Price D. J., Goodman H. M., Avruch J. Recombinant fragment of protein kinase inhibitor blocks cyclic AMP-dependent gene transcription. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):530–533. doi: 10.1126/science.2821622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S., Schmid W., Schütz G. Transcriptional activation of the rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase gene by cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6637–6641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isackson P. J., Bradshaw R. A. The alpha-subunit of mouse 7 S nerve growth factor is an inactive serine protease. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5380–5383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson J. L., Deutsch P. J., Gallagher G. D., Jaffe R. C., Habener J. F. trans-acting factors interact with a cyclic AMP response element to modulate expression of the human gonadotropin alpha gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3032–3040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jany K. D., Bekelar K., Pfleiderer G., Ishay J. Amino acid sequence of an insect chymotrypsin from the larvae of the hornet, Vespa orientalis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91251-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungmann R. A., Kelley D. C., Miles M. F., Milkowski D. M. Cyclic AMP regulation of lactate dehydrogenase. Isoproterenol and N6,O2-dibutyryl cyclic amp increase the rate of transcription and change the stability of lactate dehydrogenase a subunit messenger RNA in rat C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5312–5318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsuwan K., Yu Q., Vincent A., Frisardi M. C., Rosbash M., Lengyel J. A., Merriam J. A Drosophila Minute gene encodes a ribosomal protein. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):555–558. doi: 10.1038/317555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraut J. Serine proteases: structure and mechanism of catalysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:331–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosky A., Barnett D. R., Lee T. H., Touchstone B., Hay R. E., Arnott M. S., Bowman B. H., Fitch W. M. Covalent structure of human haptoglobin: a serine protease homolog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3388–3392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer-Safer P. R., Levine M., Ward D. C. Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Harrington C. A., Chikaraishi D. M. Transcriptional regulation of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene by glucocorticoid and cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3550–3554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Swift G. H., Quinto C., Swain W., Pictet R. L., Nikovits W., Rutter W. J. Primary structure of two distinct rat pancreatic preproelastases determined by sequence analysis of the complete cloned messenger ribonucleic acid sequences. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 16;21(6):1453–1463. doi: 10.1021/bi00535a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A. Transcriptional regulation of the prolactin gene by ergocryptine and cyclic AMP. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):94–97. doi: 10.1038/294094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamine Y., Reich E. Gene expression and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4606–4610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ran W., Dean M., Levine R. A., Henkle C., Campisi J. Induction of c-fos and c-myc mRNA by epidermal growth factor or calcium ionophore is cAMP dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8216–8220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salz H. K., Davis R. L., Kiger J. A. Genetic Analysis of Chromomere 3d4 in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER: The DUNCE and SPERM-AMOTILE Genes. Genetics. 1982 Apr;100(4):587–596. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.4.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L., Shotton D. M., Campbell J. W., Wendell P. L., Muirhead H., Watson H. C. The atomic structure of crystalline porcine pancreatic elastase at 2.5 A resolution: comparisons with the structure of alpha-chymotrypsin. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 15;118(2):137–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Wynshaw-Boris A., Short H. P., Hanson R. W. Characterization of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) promoter-regulatory region. II. Identification of cAMP and glucocorticoid regulatory domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9721–9726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratowa C., Rutter W. J. Selective regulation of trypsin gene expression by calcium and by glucose starvation in a rat exocrine pancreas cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4292–4296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontano D., Chin W. W., Moses A. C., Ingbar S. H. Thyrotropin and dibutyryl cyclic AMP increase levels of c-myc and c-fos mRNAs in cultured rat thyroid cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):3919–3922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Fink J. S., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a region in the human vasoactive intestinal polypeptide gene responsible for regulation by cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8743–8747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Munnich A., Decaux J. F., Kahn A. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of L-type pyruvate kinase gene expression in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7621–7625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Sequence and structure of the serendipity locus of Drosophila melanogaster. A densely transcribed region including a blastoderm-specific gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):149–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M., Murdoch G. H., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Cyclic AMP regulation of eukaryotic gene transcription by two discrete molecular mechanisms. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):267–269. doi: 10.1126/science.2990047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Walsh D. A. Mg X ATP2-dependent interaction of the inhibitor protein of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase with the catalytic subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3682–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Katunuma N., Kobayashi K., Titani K., Neurath H., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. Covalent structure of a group-specific protease from rat small intestine. Appendix: crystallographic data for a group specific protease from rat intestine. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):811–819. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. S., Johnson L. F. Regulation of dihydrofolate reductase gene transcription in methotrexate-resistant mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Feb;110(2):183–189. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









