Abstract
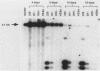
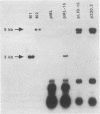
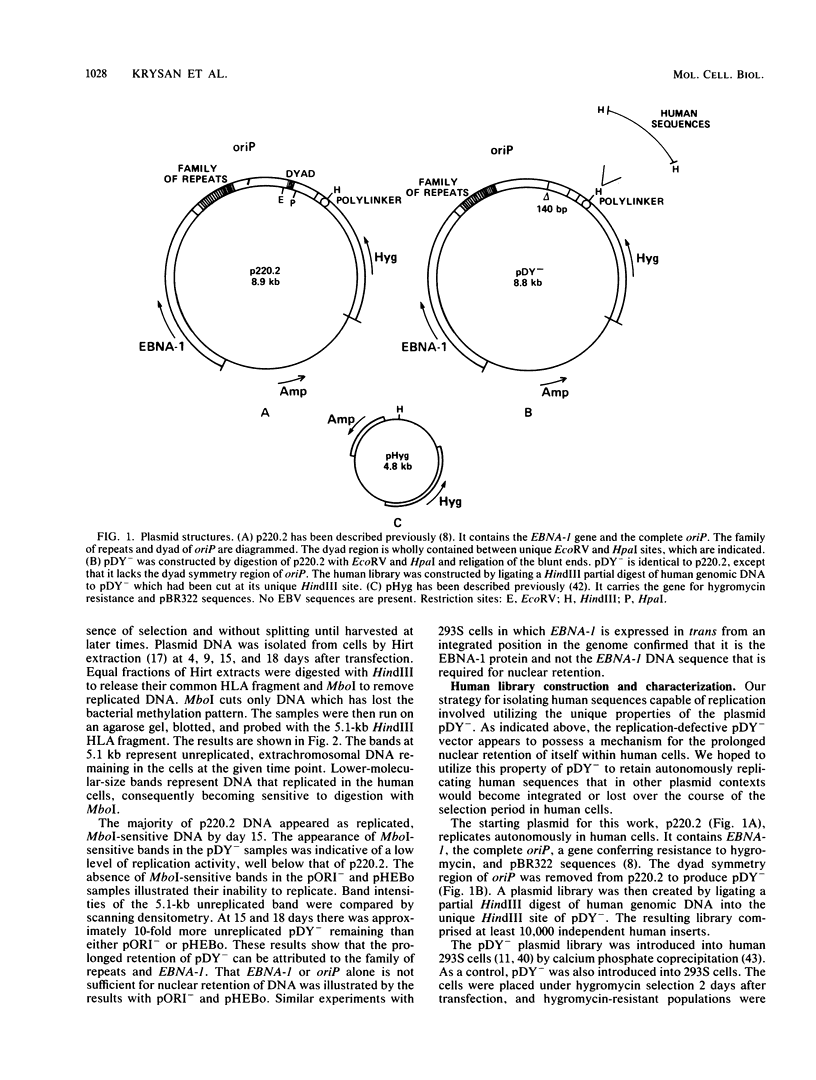
We have isolated a heterogeneous collection of human genomic sequences which replicate autonomously when introduced into human cells. The novel strategy for the isolation of these sequences involved cloning random human DNA fragments into a defective Epstein-Barr virus vector. This vector alone was unable to replicate in human cells, but appeared to provide for the nuclear retention of linked DNA. The human sequences persist in a long-term replication assay (greater than 2 months) in the presence of the viral nuclear retention sequences. Using a short-term (4-day) assay, we showed that the human sequences are able to replicate in the absence of all viral sequences. The plasmids bearing human sequences were shown to replicate based on the persistence of MboI-sensitive plasmid DNA in the long-term assay and the appearance of DpnI-resistant DNA in the short-term assay. The human sequences were shown to be responsible for the replication activity and may represent authentic human origins of replication.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. Replication of latent Epstein-Barr virus genomes in Raji cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1743–1746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1743-1746.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchetti S., Graham F. L. Transfer of the gene for thymidine kinase to thymidine kinase-deficient human cells by purified herpes simplex viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1590–1594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biamonti G., Della Valle G., Talarico D., Cobianchi F., Riva S., Falaschi A. Fate of exogenous recombinant plasmids introduced into mouse and human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5545–5561. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Selegue J. E., Heintz N. H. Isolation of the origin of replication associated with the amplified Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7790–7794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Gaudray P., De Rose M. L., Emery J. F., Meinkoth J. L., Nakkim E., Subler M., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Characterization of an episome produced in hamster cells that amplify a transfected CAD gene at high frequency: functional evidence for a mammalian replication origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1740–1750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBridge R. B., Tang P., Hsia H. C., Leong P. M., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):379–387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frappier L., Zannis-Hadjopoulos M. Autonomous replication of plasmids bearing monkey DNA origin-enriched sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6668–6672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E. A., Summers W. P., Dowling S., Shedd D., Gradoville L., Miller G. Two Epstein-Barr viral nuclear neoantigens distinguished by gene transfer, serology, and chromosome binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7650–7653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A., Young B. D., Griffin B. E. Random association of Epstein-Barr virus genomes with host cell metaphase chromosomes in Burkitt's lymphoma-derived cell lines. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):328–332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.328-332.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton K. S., Dhar V., Brown E. H., Iqbal M. A., Stuart S., Didamo V. T., Schildkraut C. L. Replication program of active and inactive multigene families in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2149–2158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Hamlin J. L. An amplified chromosomal sequence that includes the gene for dihydrofolate reductase initiates replication within specific restriction fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4083–4087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel S. S., Krysan P. J., Calos M. P., DuBridge R. B. Use of simian virus 40 replication to amplify Epstein-Barr virus shuttle vectors in human cells. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3738–3746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3738-3746.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst A., Müller F., Zastrow G., Zentgraf H., Schwender S., Dinkl E., Grummt F. Murine genomic DNA sequences replicating autonomously in mouse L cells. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao C. L., Carbon J. High-frequency transformation of yeast by plasmids containing the cloned yeast ARG4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3829–3833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Riggs A. D. On the mechanism of DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Blaisdell B. E. A model for the development of the tandem repeat units in the EBV ori-P region and a discussion of their possible function. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(3):215–229. doi: 10.1007/BF02100015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Orr H. T. Cloning and complete sequence of an HLA-A2 gene: analysis of two HLA-A alleles at the nucleotide level. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2727–2733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Clancy S., Calos M. P. Simian virus 40 replication in adenovirus-transformed human cells antagonizes gene expression. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):169–171. doi: 10.1038/317169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Peden K. W., Dixon R. A., Kelly T. Functional organization of the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1117–1128. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupton S., Levine A. J. Mapping genetic elements of Epstein-Barr virus that facilitate extrachromosomal persistence of Epstein-Barr virus-derived plasmids in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2533–2542. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Hwang E. S. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen forms a complex that binds with high concentration dependence to a single DNA-binding site. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):465–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.465-471.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tjian R. Construction and analysis of simian virus 40 origins defective in tumor antigen binding and DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6491–6495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawotka K. A., Huberman J. A. Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic method for mapping DNA replicons. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1408–1413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Sugden B. trans activation of an Epstein-Barr viral transcriptional enhancer by the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3838–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Yates J., Sugden B. A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1822–1832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Schmid C. W. Partial nucleotide sequence of the 300-nucleotide interspersed repeated human DNA sequences. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):372–374. doi: 10.1038/284372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Sapolsky R. J., Davis R. W. Transcription interferes with elements important for chromosome maintenance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2184–2194. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W., Gluzman Y. Replication and supercoiling of simian virus 40 DNA in cell extracts from human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2051–2060. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Isolation and characterisation of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):39–43. doi: 10.1038/282039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Thomas M., Kelly J., Selker E., Davis R. W. Eukaryotic DNA segments capable of autonomous replication in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4559–4563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Marsh K., Yates J. A vector that replicates as a plasmid and can be efficiently selected in B-lymphoblasts transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):410–413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H. The yeast ARS element, six years on: a progress report. Yeast. 1985 Sep;1(1):1–14. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda S., Hirota Y. Cloning and mapping of the replication origin of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5458–5462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis-Hadjopoulos M., Persico M., Martin R. G. The remarkable instability of replication loops provides a general method for the isolation of origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]