Abstract
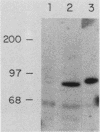
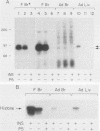
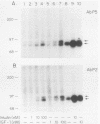
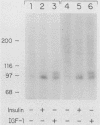
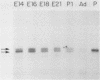
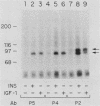
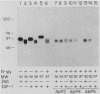
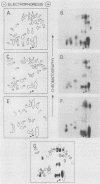
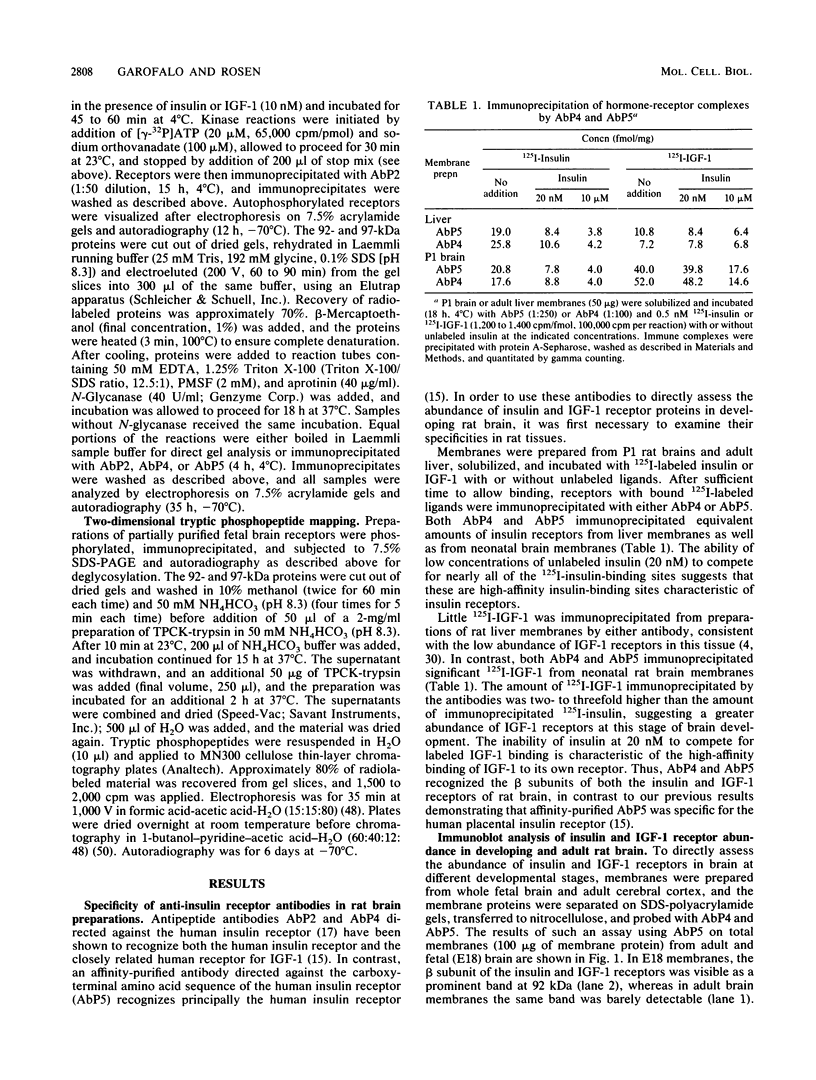
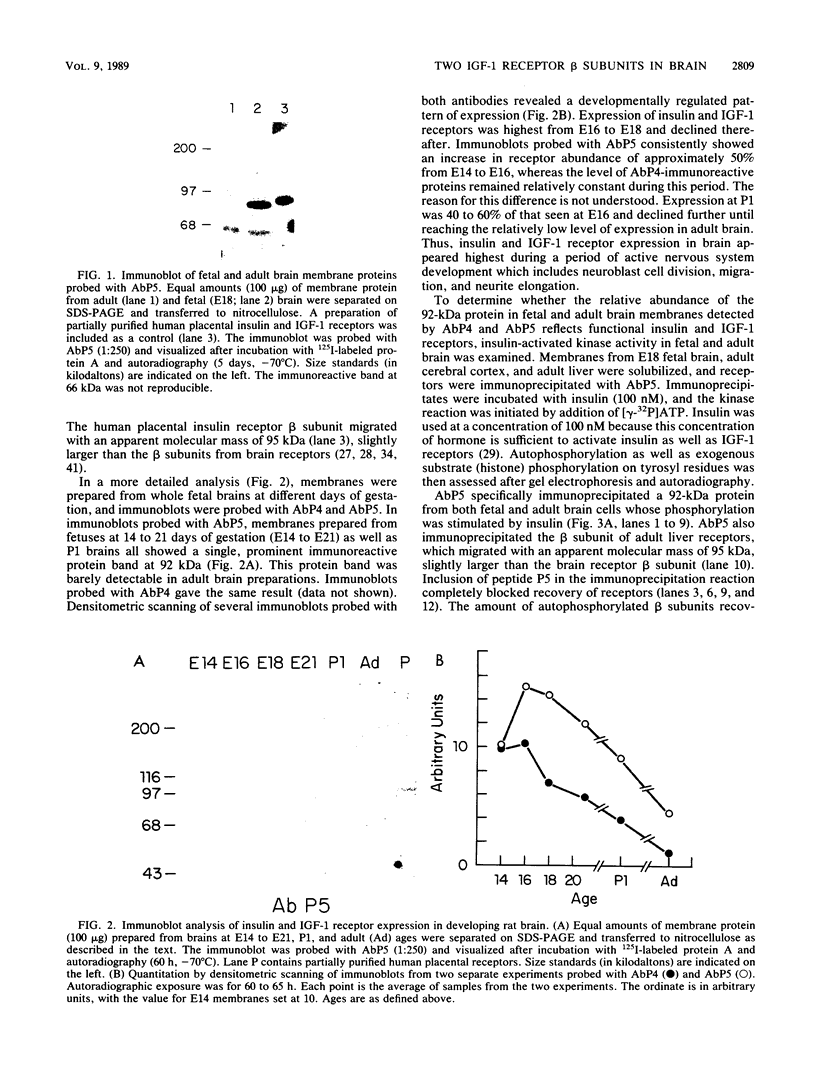
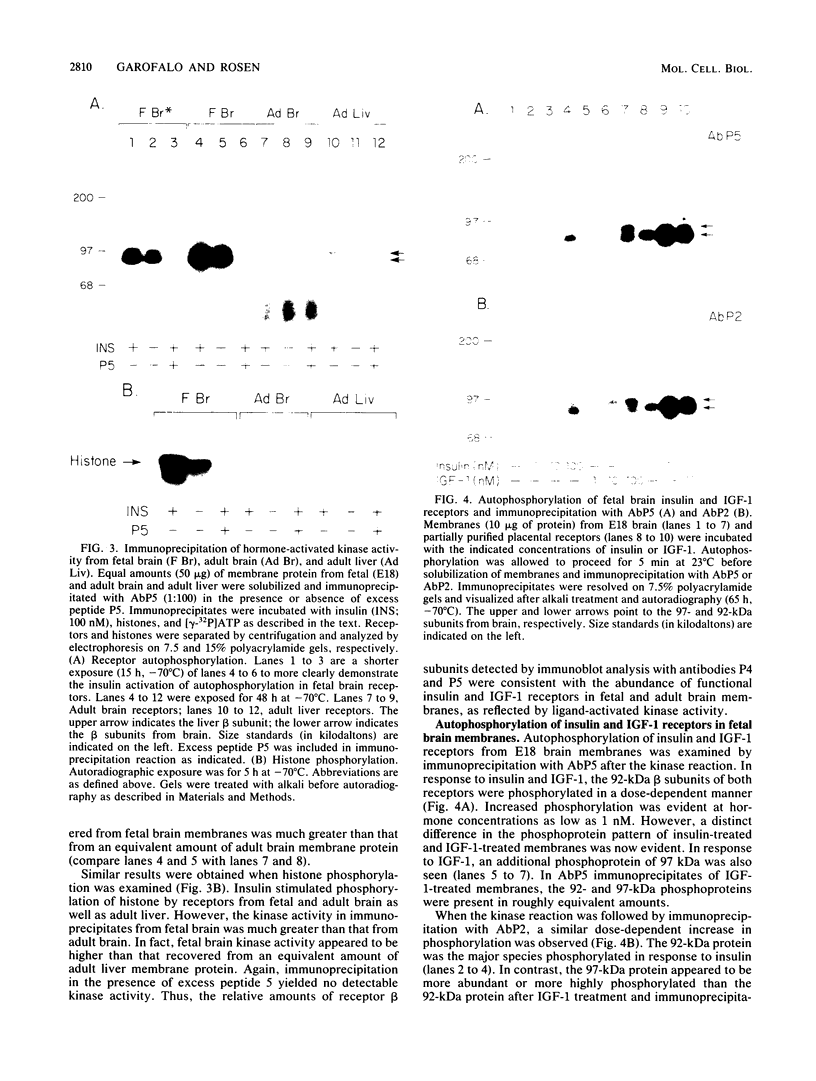
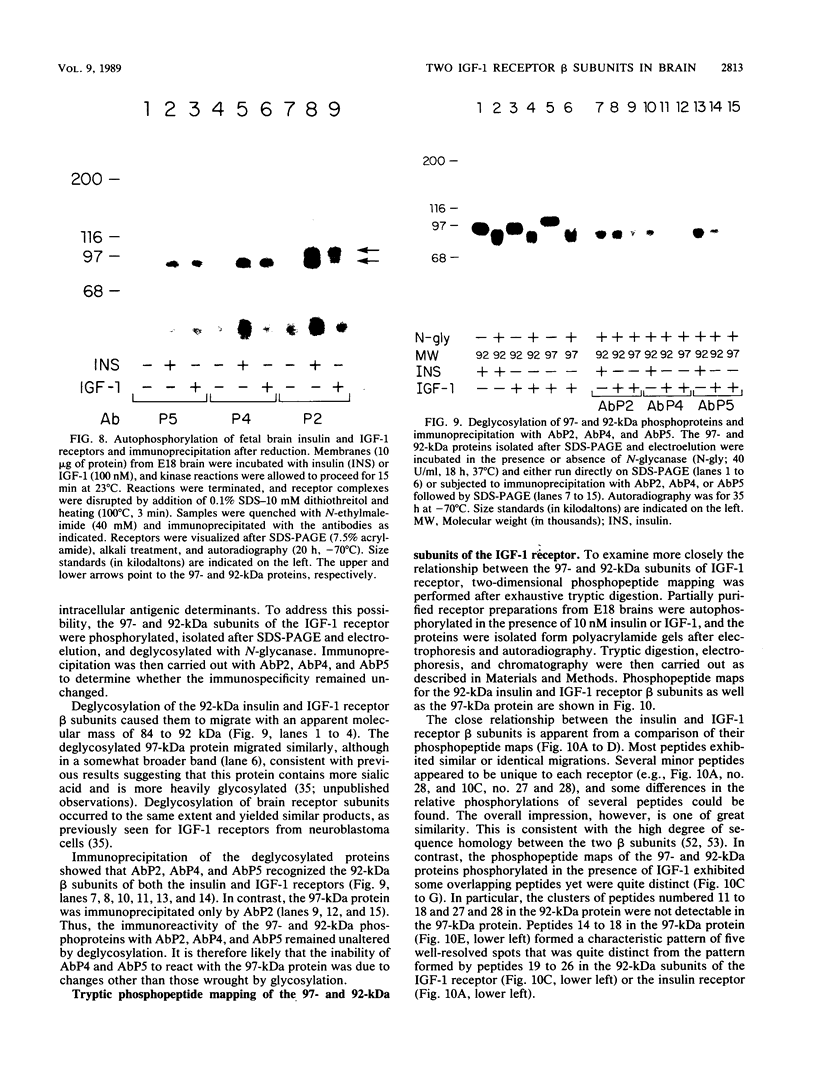
Insulin and insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptors are present in brain, yet their function remains obscure. Expression of these tyrosine kinase-bearing growth factor receptors during rat brain development was examined by using three antipeptide antibodies directed against epitopes in the beta subunits (AbP2, AbP4, and AbP5). All three antibodies recognized both insulin and IGF-1 receptors. Membranes were prepared from fetal brains (14 to 21 days of gestation), neonatal brain (postnatal day 1), and adult brain. Immunoblot analyses using AbP4 and AbP5 revealed a 92-kilodalton (kDa) protein that corresponded to the beta subunit of the insulin and IGF-1 receptors. Densitometric scanning of immunoblots indicated that receptor proteins were 4- to 10-fold more abundant in fetal brain membranes than in membranes from adult brain. Expression was highest during 16 to 18 days of gestation and declined thereafter to the relatively low level found in adult brain. Immunoblot analyses with AbP2 as well as ligand-activated receptor autophosphorylation revealed an additional protein of 97 kDa. This protein was phosphorylated in response to IGF-1 and was not directly recognized by AbP4 or AbP5. The covalent association of the 97-kDa protein with the 92-kDa beta subunit was indicated by the ability of AbP4 and AbP5 to immunoprecipitate both proteins under nonreducing conditions but only the 92-kDa protein after reduction. In contrast, AbP2 immunoprecipitated both proteins regardless of their association. This immunospecificity remained unchanged after deglycosylation of the isolated proteins. Two-dimensional tryptic phosphopeptide analysis showed that the 92- and 97-kDa subunits of the IGF-1 receptor are related but distinct proteins. Taken together, the data suggest that the 92- and 97-kDa subunits differ in primary amino acid sequence. Thus, two distinct beta subunits may be present in a single IGF-1 receptor in brain. These subunits have in common an epitope recognized by an antibody to the tyrosine kinase domain (AbP2) but differ in regions thought to be important in receptor kinase regulation and signal transduction.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Almonacid R., Rosen O. M. Structure and ligand specificity of the Drosophila melanogaster insulin receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2718–2727. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Haselbacher G. K., Humbel R. E., Fehlmann M., Van Obberghen E. Two types of receptor for insulin-like growth factors in mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3407–3412. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo R. S., Rosen O. M. Tissue localization of Drosophila melanogaster insulin receptor transcripts during development. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1638–1647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havrankova J., Roth J., Brownstein M. Insulin receptors are widely distributed in the central nervous system of the rat. Nature. 1978 Apr 27;272(5656):827–829. doi: 10.1038/272827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Harrison L. C., Roth J. Binding of insulin receptors to lectins: evidence for common carbohydrate determinants on several membrane receptors. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 9;20(12):3385–3393. doi: 10.1021/bi00515a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks S. A., de Pablo F., Roth J. Early development and tissue-specific patterns of insulin binding in chick embryo. Endocrinology. 1984 Oct;115(4):1315–1323. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-4-1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Rosen O. M. Antibodies to deduced sequences of the insulin receptor distinguish conserved and nonconserved regions in the IGF-I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2489–2491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Petruzzelli L., Thomas N., Bramson H. N., Kaiser E. T., Rosen O. M. An antipeptide antibody that specifically inhibits insulin receptor autophosphorylation and protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7899–7903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Rosen O. M. Autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor in vitro. Designation of phosphorylation sites and correlation with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11980–11985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Phosphorylation of receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Effects of hormones and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):934–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Earp H. S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Somatomedin-C stimulates the phosphorylation of the beta-subunit of its own receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9581–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Harrison L. C. The human placenta contains two distinct binding and immunoreactive species of insulin-like growth factor-I receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2288–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Koyasu S., Nishida E., Tobe K., Izumi T., Takaku F., Sakai H., Yahara I., Kasuga M. Tyrosine phosphorylation of common and specific sets of cellular proteins rapidly induced by insulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and epidermal growth factor in an intact cell. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7342–7350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappy M. S., Raizada M. K. Adult-level insulin binding is present in term fetal rat CNS membranes. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):390–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappy M., Sellinger S., Raizada M. Insulin binding in four regions of the developing rat brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):198–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe W. L., Jr, Boyd F. T., Clarke D. W., Raizada M. K., Hart C., LeRoith D. Development of brain insulin receptors: structural and functional studies of insulin receptors from whole brain and primary cell cultures. Endocrinology. 1986 Jul;119(1):25–35. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe W. L., Jr, LeRoith D. Tyrosine kinase activity of brain insulin and IGF-1 receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):532–538. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80453-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe W., Jr, LeRoith D. Insulin receptors from guinea pig liver and brain: structural and functional studies. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1669–1677. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Blinderman L. A., Czech M. P. The high affinity insulin receptor mediates growth stimulation in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13958–13963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Lee J., Dull T. J., Ulrich A., Olefsky J. M. A mutant insulin receptor with defective tyrosine kinase displays no biologic activity and does not undergo endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14663–14671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Jarnagin K., Roth R. A. Purification and characterization of the receptor for insulin-like growth factor I. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5560–5564. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Roth R. A. Acute insulin action requires insulin receptor kinase activity: introduction of an inhibitory monoclonal antibody into mammalian cells blocks the rapid effects of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocrant I., Valentino K. L., Eng L. F., Hintz R. L., Wilson D. M., Rosenfeld R. G. Structural and immunohistochemical characterization of insulin-like growth factor I and II receptors in the murine central nervous system. Endocrinology. 1988 Aug;123(2):1023–1034. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-2-1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota A., Wilson G. L., Leroith D. Insulin-like growth factor I receptors on mouse neuroblastoma cells. Two beta subunits are derived from differences in glycosylation. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jun 15;174(3):521–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacold S. T., Blackard W. G. Central nervous system insulin receptors in normal and diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 1979 Dec;105(6):1452–1457. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-6-1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzelli L., Herrera R., Arenas-Garcia R., Fernandez R., Birnbaum M. J., Rosen O. M. Isolation of a Drosophila genomic sequence homologous to the kinase domain of the human insulin receptor and detection of the phosphorylated Drosophila receptor with an anti-peptide antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4710–4714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerance M., Gavaret J. M., Jacquemin C., Matricon C., Toru-Delbauffe D., Pierre M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors during postnatal development of rat brain. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 1;470(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90203-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Ishii D. N. Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II and nerve growth factor on neurite outgrowth in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 8;302(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Rechler M. M., Ishii D. N. Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II, and nerve growth factor on neurite formation and survival in cultured sympathetic and sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1211–1219. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01211.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees-Jones R. W., Hendricks S. A., Quarum M., Roth J. The insulin receptor of rat brain is coupled to tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3470–3474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Morgan D. O., Beaudoin J., Sara V. Purification and characterization of the human brain insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3753–3757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Johnson E. L., Chou C. K., Rosen O. M. The protein-tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor is necessary for insulin-mediated receptor down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11833–11840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Hall K., Misaki M., Fryklund L., Christensen N., Wetterberg L. Ontogenesis of somatomedin and insulin receptors in the human fetus. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1084–1094. doi: 10.1172/JCI110858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer J., Adamo M., Wilson G. L., Heffez D., Zick Y., LeRoith D. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I stimulate a common endogenous phosphoprotein substrate (pp185) in intact neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15476–15482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer J., Raizada M. K., Masters B. A., Ota A., LeRoith D. Insulin-like growth factor I receptors in neuronal and glial cells. Characterization and biological effects in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7693–7699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtmauer L., Rosen O. M. Phosphorylation of synthetic insulin receptor peptides by the insulin receptor kinase and evidence that the preferred sequence containing Tyr-1150 is phosphorylated in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):10000–10005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele-Perkins G., Turner J., Edman J. C., Hari J., Pierce S. B., Stover C., Rutter W. J., Roth R. A. Expression and characterization of a functional human insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11486–11492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama S., White M. F., Lauris V., Kahn C. R. Phorbol esters modulate insulin receptor phosphorylation and insulin action in cultured hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7797–7801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toran-Allerand C. D., Ellis L., Pfenninger K. H. Estrogen and insulin synergism in neurite growth enhancement in vitro: mediation of steroid effects by interactions with growth factors? Brain Res. 1988 Jun 1;469(1-2):87–100. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis I., Ellis L., Suh K., Pfenninger K. H. Immunolocalization of a neuronal growth-dependent membrane glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1990–1998. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Peters M. A., Czech M. P. Similar control mechanisms regulate the insulin and type I insulin-like growth factor receptor kinases. Affinity-purified insulin-like growth factor I receptor kinase is activated by tyrosine phosphorylation of its beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11341–11349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]