Abstract
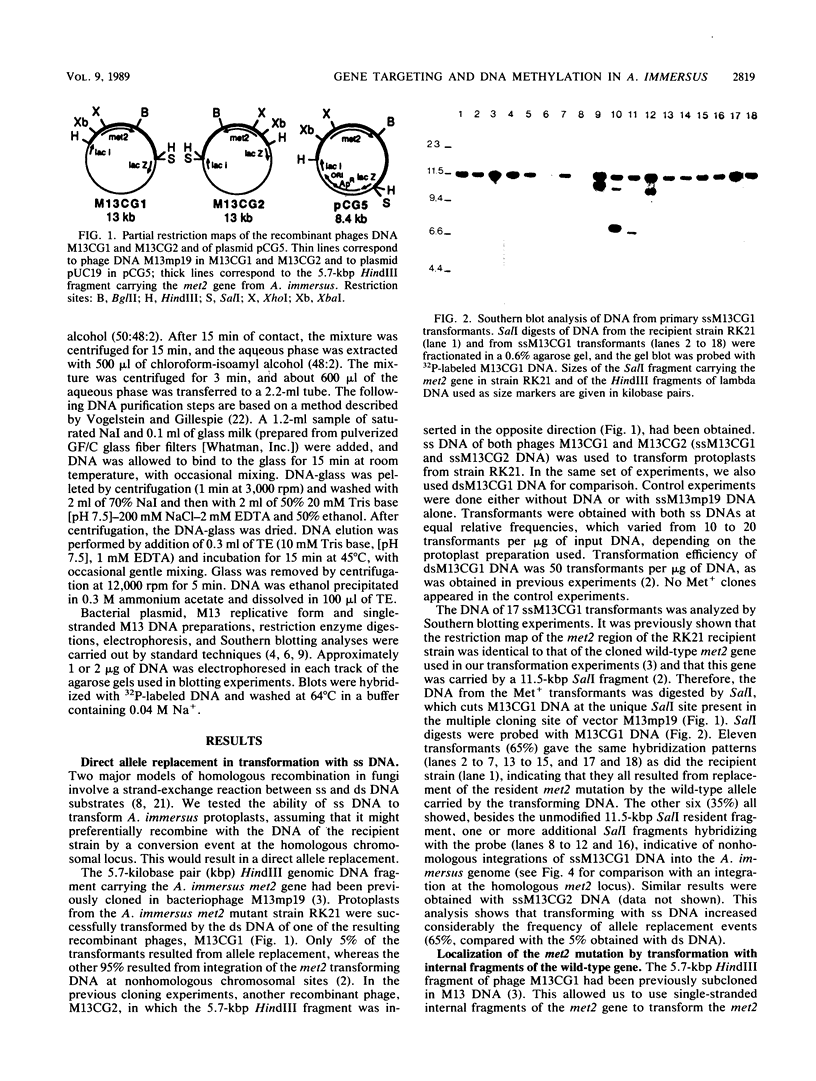
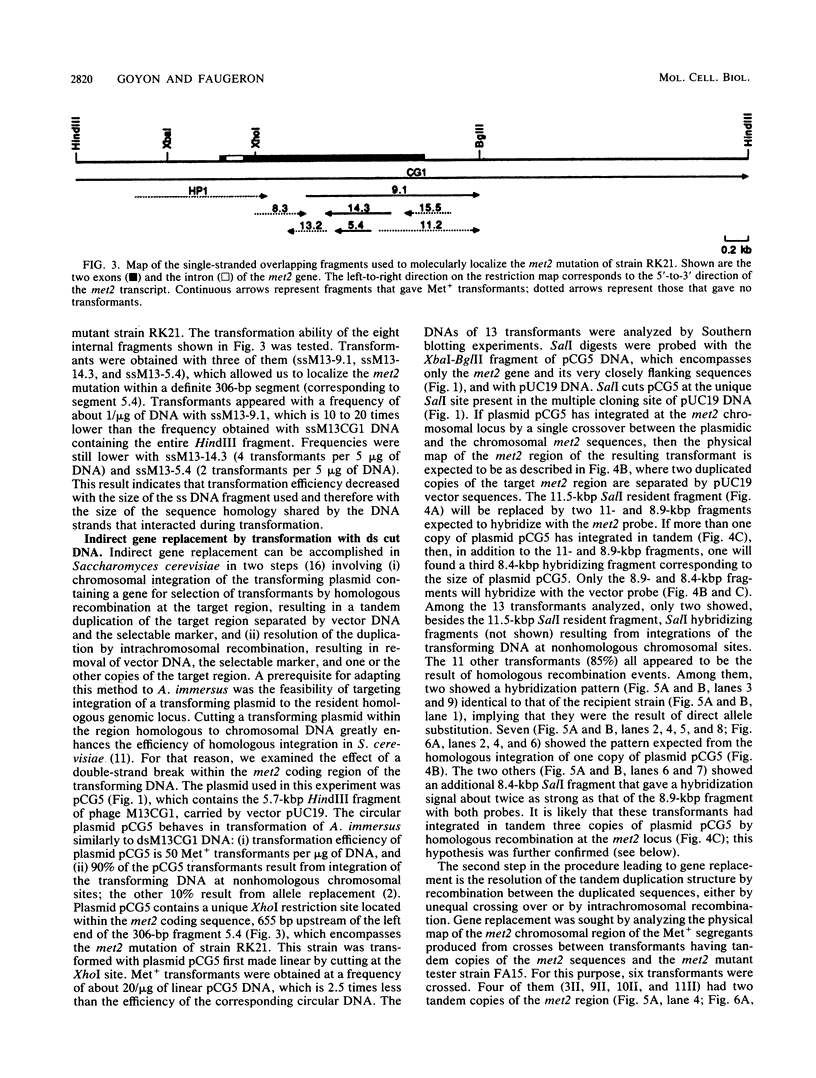
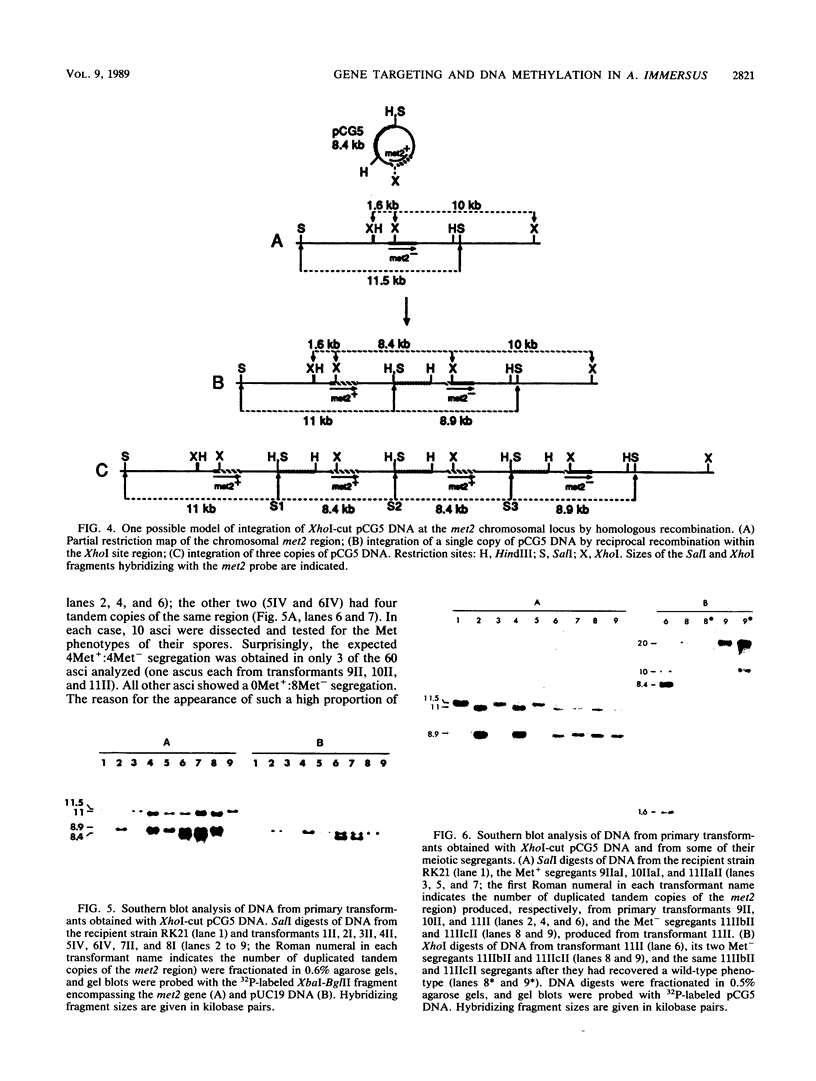
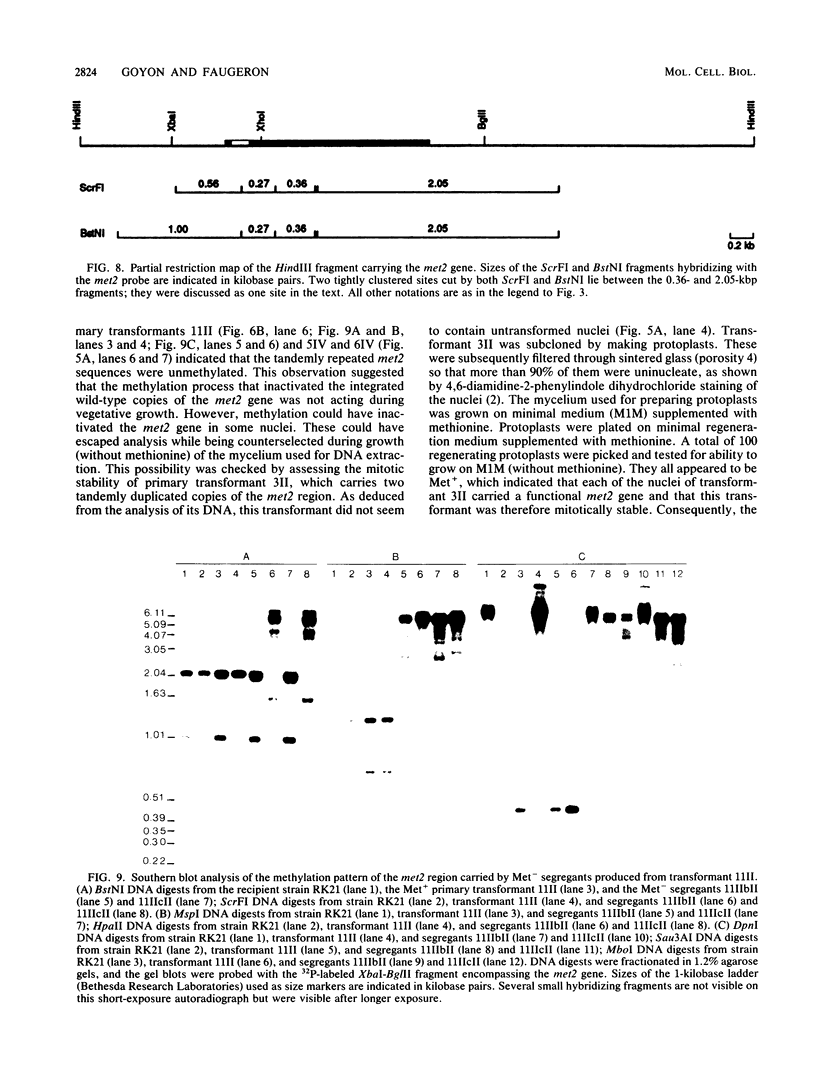
To develop a method to modify genomic sequences in Ascobolus immersus by precisely reintroducing defined DNA segments previously manipulated in vitro, we investigated the effect of transforming DNA conformation on recombination with chromosomal sequences. Circular single-stranded DNA carrying the met2 gene and double-stranded DNA linearized by cutting within the met2 gene both transformed protoplasts of a met2 mutant strain of A. immersus to prototrophy. In contrast to the equivalent circular double-stranded DNA, which chiefly integrated at nonhomologous chromosomal sites, single-stranded and double-stranded cut DNAs recombined primarily with the homologous chromosomal met2 sequence. Of the single-stranded DNA transformants, 65% resulted from replacement of the resident met2 mutation by the exogenous wild-type allele. In 70% of the double-stranded-cut DNA transformants, one or more copies of the transforming DNA had integrated at the met2 locus, leading to tandem duplications of the met2 target region separated by plasmid DNA. These duplicated sequences could recombine, leading to progeny containing only one copy of the met2 region. This resulted in a precise gene replacement if the wild-type allele had been retained. In addition, we show that newly duplicated sequences were most often de novo methylated at the cytosine residues during the sexual phase. Cytosine methylation was associated with inactivation of the integrated met2 gene(s) in segregants of crosses. However, methylation was not accurately maintained at each DNA replication cycle, so that Met- segregants recovered a wild-type phenotype through successive mitotic divisions. This finding indicated that met2 genes were silenced by methylation alone.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faugeron G., Goyon C., Grégoire A. Stable allele replacement and unstable non-homologous integration events during transformation of Ascobolus immersus. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyon C., Faugeron G., Rossignol J. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of the met2 gene from Ascobolus immersus. Gene. 1988 Mar 31;63(2):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90533-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Taylor S. M. Cellular differentiation, cytidine analogs and DNA methylation. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Nelson M. The effect of site specific methylation on restriction endonuclease digestion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13 (Suppl):r201–r207. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.suppl.r201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. L., Miller K. Y., Timberlake W. E. Direct and indirect gene replacements in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1714–1721. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIZET G., ENGELMANN N., LEFORT C., LISSOUBA P., MOUSSEAU J. [On an Ascomycete of interest for the study of certain aspects of the problem of gene structure]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1960 Mar 14;250:2050–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol J. L., Paquette N. Disparity of gene conversion in frameshift mutants located in locus b2 of Ascobolus immersus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2871–2875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A. Direct cloning and sequence analysis of enzymatically amplified genomic sequences. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.3461561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Davis R. W. Replacement of chromosome segments with altered DNA sequences constructed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4951–4955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Cambareri E. B., Jensen B. C., Haack K. R. Rearrangement of duplicated DNA in specialized cells of Neurospora. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Garrett P. W. DNA sequence duplications trigger gene inactivation in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6870–6874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Stevens J. N. DNA methylation at asymmetric sites is associated with numerous transition mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8114–8118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. R., Moore P. D. Homologous recombination between single-stranded DNA and chromosomal genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2329–2334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]