Abstract
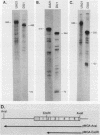
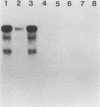
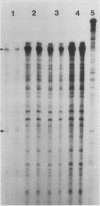
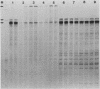
Steady-state dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) mRNA levels were decreased as a result of nonsense mutations in the dhfr gene. Thirteen DHFR-deficient mutants were isolated after treatment of Chinese hamster ovary cells with UV irradiation. The positions of most point mutations were localized by RNA heteroduplex mapping, the mutated regions were isolated by cloning or by enzymatic amplification, and base changes were determined by DNA sequencing. Two of the mutants suffered large deletions that spanned the entire dhfr gene. The remaining 11 mutations consisted of nine single-base substitutions, one double-base substitution, and one single-base insertion. All of the single-base substitutions took place at the 3' position of a pyrimidine dinucleotide, supporting the idea that UV mutagenesis proceeds through the formation of pyrimidine dimers in mammalian cells. Of the 11 point mutations, 10 resulted in nonsense codons, either directly or by a frameshift, suggesting that the selection method favored a null phenotype. An examination of steady-state RNA levels in cells carrying these mutations and a comparison with similar data from other dhfr mutants (A. M. Carothers, R. W. Steigerwalt, G. Urlaub, L. A. Chasin, and D. Grunberger, J. Mol. Biol., in press) showed that translation termination mutations in any of the internal exons of the gene gave rise to a low-RNA phenotype, whereas missense mutations in these exons or terminations in exon 6 (the final exon) did not affect dhfr mRNA levels. Nuclear run-on experiments showed that transcription of the mutant genes was normal. The stability of mature dhfr mRNA also was not affected, since (i) decay rates were the same in wild-type and mutant cells after inhibition of RNA synthesis with actinomycin D and (ii) intronless minigene versions of cloned wild-type and nonsense mutant genes were expressed equally after stable transfection. We conclude that RNA processing has been affected by these nonsense mutations and present a model in which both splicing and nuclear transport of an RNA molecule are coupled to its translation. Curiously, the low-RNA mutant phenotype was not exhibited after transfer of the mutant genes, suggesting that the transcripts of transfected genes may be processed differently than are those of their endogenous counterparts.
Full text
PDF
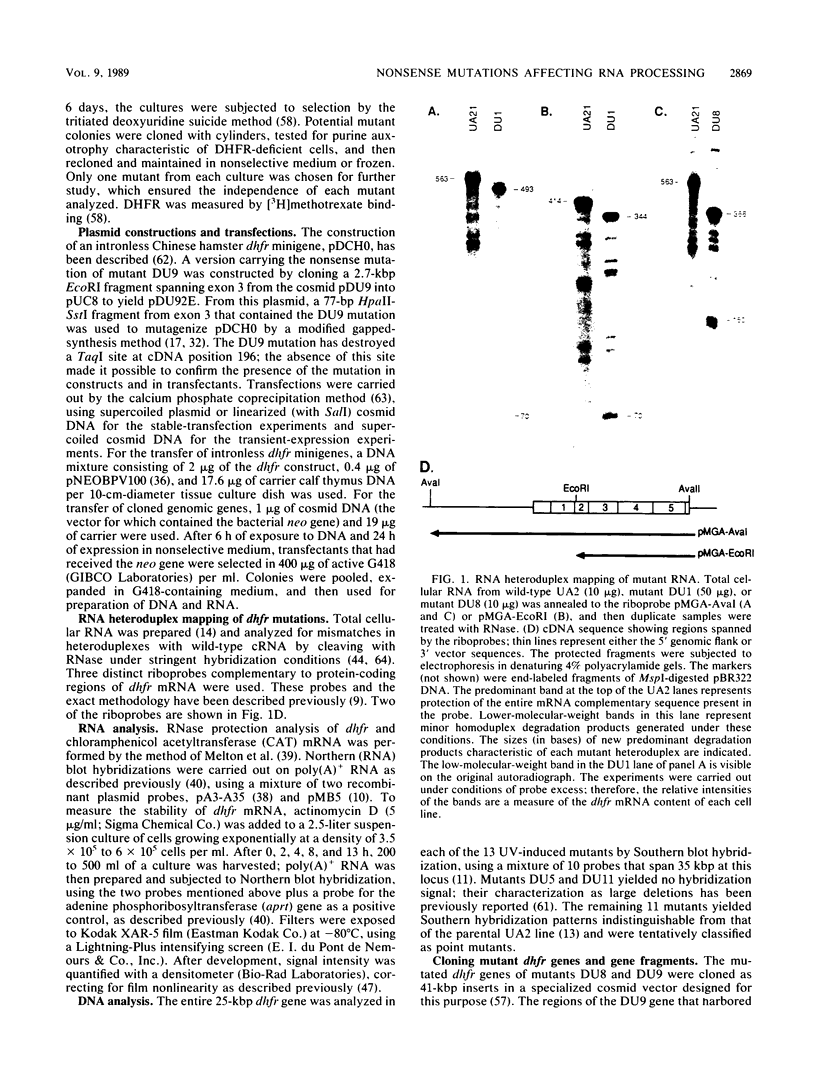

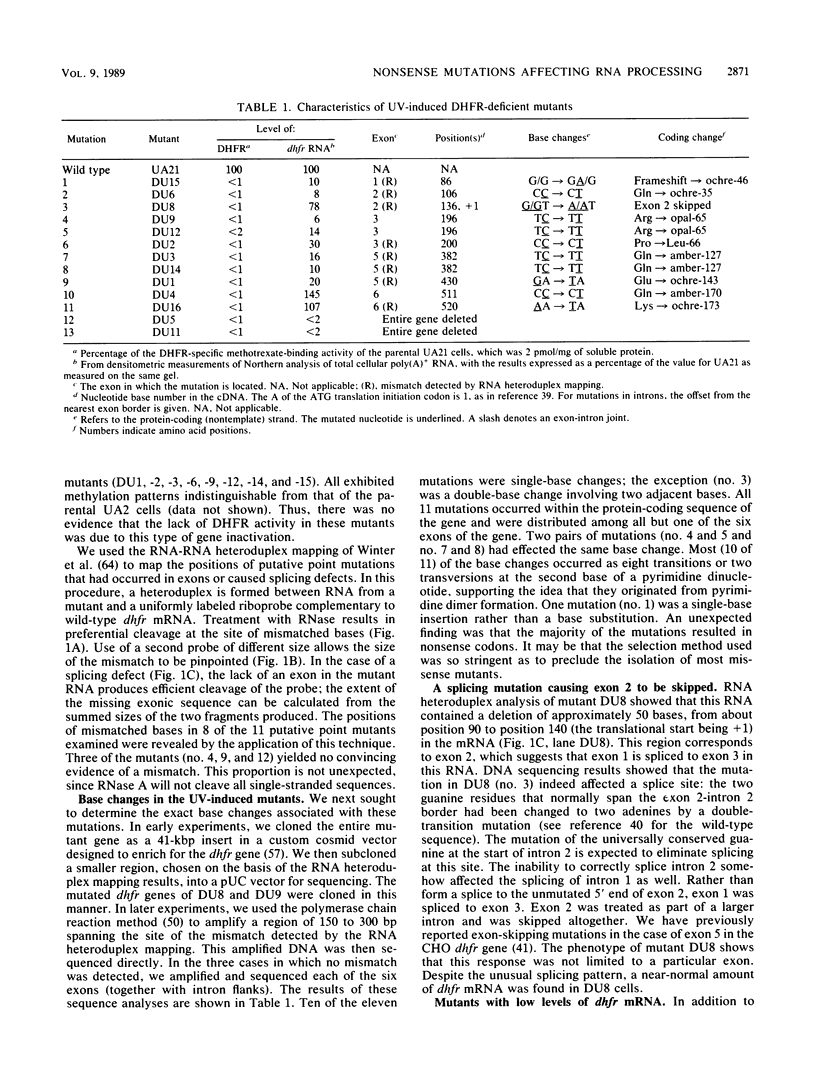

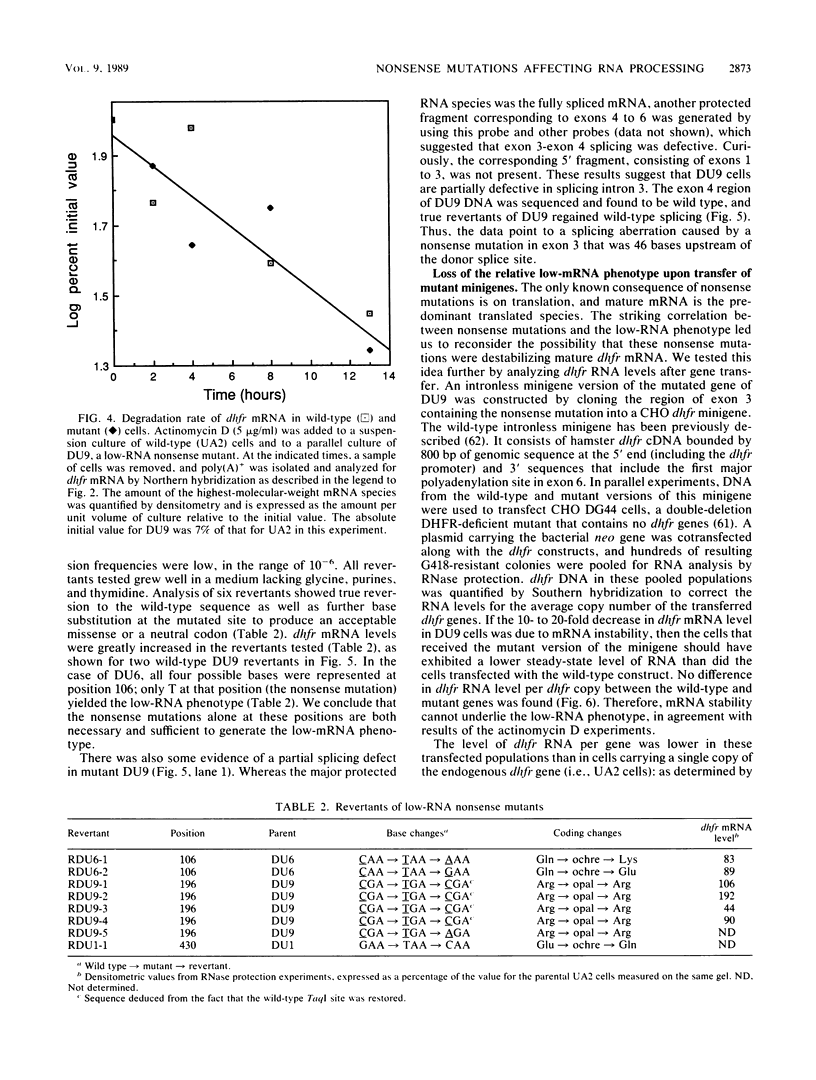
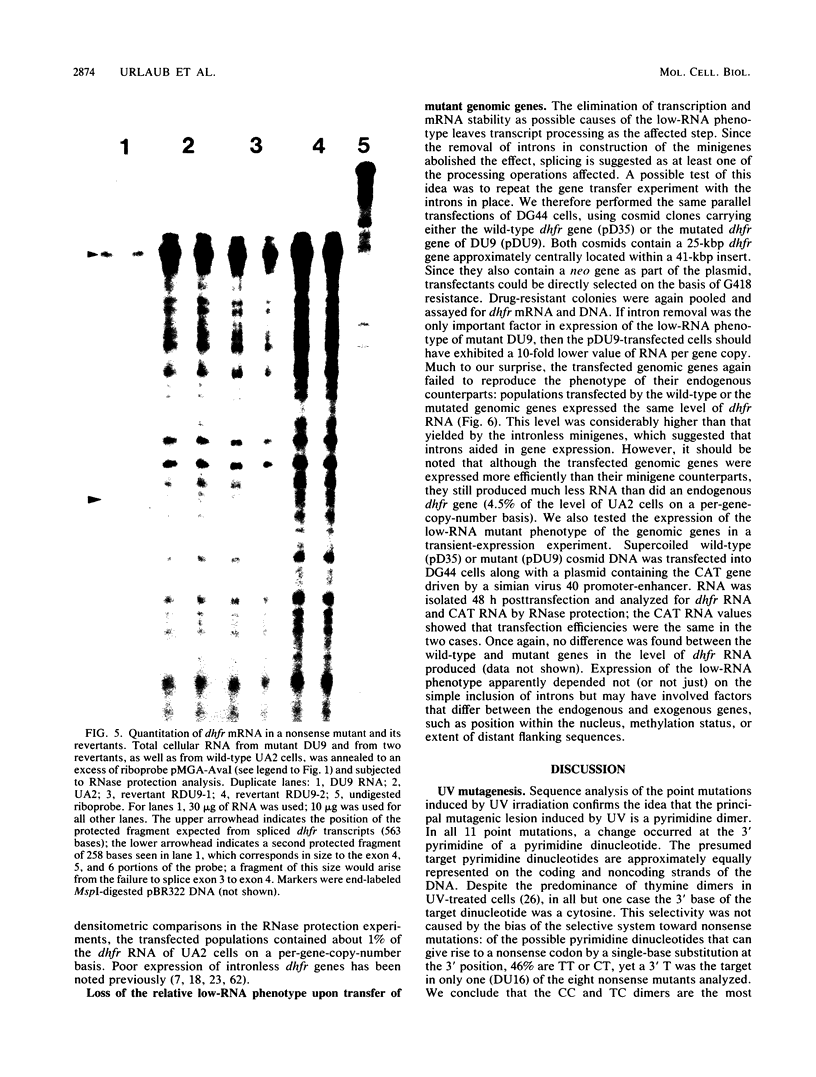




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M. A protein required for splicing group I introns in Neurospora mitochondria is mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase or a derivative thereof. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh G. F., Brickner H. E., Zhu X. X., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Forget B. G. New amber mutation in a beta-thalassemic gene with nonmeasurable levels of mutant messenger RNA in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):557–561. doi: 10.1172/JCI113632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga S. J., Benz E. J., Jr Nonsense mutations in the human beta-globin gene affect mRNA metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2056–2060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann B., Potash M. J., Köhler G. Consequences of frameshift mutations at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus of the mouse. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):351–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Gene gating: a hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8527–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Berg P. Comparison of intron-dependent and intron-independent gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4395–4405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Wagar M. A., Atkinson M. R. Calcium-dependent priming of DNA synthesis in isolated rat liver nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 24;39(2):254–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90786-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers A. M., Urlaub G., Ellis N., Chasin L. A. Structure of the dihydrofolate reductase gene in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):1997–2012. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers A. M., Urlaub G., Grunberger D., Chasin L. A. Mapping and characterization of mutations induced by benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide at dihydrofolate reductase locus in CHO cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Mar;14(2):169–183. doi: 10.1007/BF01534402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers A. M., Urlaub G., Steigerwalt R. W., Chasin L. A., Grunberger D. Characterization of mutations induced by 2-(N-acetoxy-N-acetyl)aminofluorene in the dihydrofolate reductase gene of cultured hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6519–6523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciudad C. J., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Deletion analysis of the Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16274–16282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. F., Harrelson A. L., Darnell J. E., Jr Dependence of liver-specific transcription on tissue organization. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2623–2632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courage-Tebbe U., Kemper B. Construction of gapped circular DNA from phage M13 by in vitro hybridization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 26;697(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., McEwan R. N., Pearson M. L. Expression and amplification of engineered mouse dihydrofolate reductase minigenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):257–266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I. O., Maquat L. E. Premature translation termination mediates triosephosphate isomerase mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):802–813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drobetsky E. A., Grosovsky A. J., Glickman B. W. The specificity of UV-induced mutations at an endogenous locus in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9103–9107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworetzky S. I., Feldherr C. M. Translocation of RNA-coated gold particles through the nuclear pores of oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):575–584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser C. S., Simonsen C. C., Schilling J. W., Schimke R. T. Expression of abbreviated mouse dihydrofolate reductase genes in cultured hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer P. M., Sarkar S. N., Summers W. C. Detection and analysis of UV-induced mutations in mammalian cell DNA using a lambda phage shuttle vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1041–1044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyllensten U. B., Erlich H. A. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of the HLA-DQA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7652–7656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser J., Seidman M. M., Sidur K., Dixon K. Sequence specificity of point mutations induced during passage of a UV-irradiated shuttle vector plasmid in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):277–285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson S. L., Wu J. S., Johnson L. F. Cell cycle regulation of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA metabolism in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes D. H., Steitz J. A. Correct in vivo splicing of the mouse immunoglobulin kappa light-chain pre-mRNA is dependent on 5' splice-site position even in the absence of transcription. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1448–1459. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käs E., Chasin L. A. Anchorage of the Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene to the nuclear scaffold occurs in an intragenic region. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 20;198(4):677–692. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Clancy S., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. The lacI shuttle: rapid analysis of the mutagenic specificity of ultraviolet light in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8606–8610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Lacroute F. Interference of nonsense mutations with eukaryotic messenger RNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5134–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowery D. E., Van Ness B. G. Comparison of in vitro and in vivo splice site selection in kappa-immunoglobulin precursor mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2610–2619. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Characterization of the bovine papilloma virus plasmid maintenance sequences. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melera P. W., Davide J. P., Hession C. A., Scotto K. W. Phenotypic expression in Escherichia coli and nucleotide sequence of two Chinese hamster lung cell cDNAs encoding different dihydrofolate reductases. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):38–48. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Carothers A. M., Han J. H., Harding J. D., Kas E., Venolia L., Chasin L. A. Multiple transcription start sites, DNase I-hypersensitive sites, and an opposite-strand exon in the 5' region of the CHO dhfr gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):425–440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Urlaub G., Chasin L. Spontaneous splicing mutations at the dihydrofolate reductase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1926–1935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moschonas N., de Boer E., Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., Wright S., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. Structure and expression of a cloned beta o thalassaemic globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4391–4401. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muralidhar M. G., Johnson L. F. Delayed processing/export of messenger RNA under conditions of reduced protein synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Apr;135(1):115–121. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Larin Z., Maniatis T. Detection of single base substitutions by ribonuclease cleavage at mismatches in RNA:DNA duplexes. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1242–1246. doi: 10.1126/science.4071043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Belasco J. G., Cohen S. N., von Gabain A. Effect of premature termination of translation on mRNA stability depends on the site of ribosome release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4890–4894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Goff S. C. Nonsense and frameshift mutations in beta 0-thalassemia detected in cloned beta-globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9782–9784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlofsky A., Chasin L. A. A domain of methylation change at the albumin locus in rat hepatoma cell variants. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):214–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter J. S., Yen T. J., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulation of tubulin expression is achieved through specific degradation of polysomal tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltz S. W., Ross J. Autogenous regulation of histone mRNA decay by histone proteins in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4345–4356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Nienhuis A. W. Only the promoter region of the constitutively expressed normal and amplified human dihydrofolate reductase gene is DNase I hypersensitive and undermethylated. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2468–2474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Simon M., Boulet A., Faye G. Mitochondrial splicing requires a protein from a novel helicase family. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):84–87. doi: 10.1038/337084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita K., Forget B. G., Scarpa A., Benz E. J., Jr Intranuclear defect in beta-globin mRNA accumulation due to a premature translation termination codon. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Milligan R. A. A large particle associated with the perimeter of the nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):63–75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Carothers A. M., Chasin L. A. Efficient cloning of single-copy genes using specialized cosmid vectors: isolation of mutant dihydrofolate reductase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1189–1193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Käs E., Carothers A. M., Chasin L. A. Deletion of the diploid dihydrofolate reductase locus from cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90422-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Landzberg M., Chasin L. A. Selective killing of methotrexate-resistant cells carrying amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):1594–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Mitchell P. J., Kas E., Chasin L. A., Funanage V. L., Myoda T. T., Hamlin J. Effect of gamma rays at the dihydrofolate reductase locus: deletions and inversions. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Nov;12(6):555–566. doi: 10.1007/BF01671941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venolia L., Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Polyadenylation of Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase genomic genes and minigenes after gene transfer. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Sep;13(5):491–504. doi: 10.1007/BF01534491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Yamamoto F., Almoguera C., Perucho M. A method to detect and characterize point mutations in transcribed genes: amplification and overexpression of the mutant c-Ki-ras allele in human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7575–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. tRNA transport from the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell: carrier-mediated translocation process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6436–6440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]