Abstract
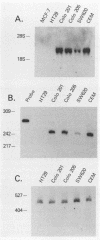
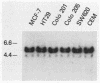
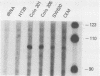
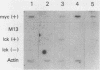
The lck protein tyrosine kinase is normally expressed in a cell type-specific fashion, with mRNA being confined to cells of lymphoid lineage. Despite this highly specific pattern of expression in normal tissues, lck mRNA has also been detected in selected cell lines derived from human nonlymphoid neoplasms. In this study we explored the mechanisms underlying the expression of lck mRNA within human nonlymphoid neoplastic cell lines. We determined that lck mRNA expression was correlated with transcriptional activation and that there was no evidence for genomic rearrangement or amplification within the lck coding region to account for the expression of lck mRNA in the nonlymphoid neoplastic cell lines. The lck gene has previously been shown to contain two distinct promoter elements. In this study, we demonstrated that lck-producing cell lines derived from human nonlymphoid neoplasms expressed transcripts initiated exclusively from the 3'-most promoter element (3' promoter). In contrast, lymphoid cell lines derived from nonmalignant sources expressed lck transcripts exclusively initiated from the 5'-most promoter element (5' promoter). Most cell lines derived from human lymphoid neoplasms express lck transcripts initiated from both the 5' and 3' promoters in various ratios. Thus, lck expression in a variety of malignant cell lines results from a selective induction of transcription from the 3' promoter.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. T., Reynolds P. J., Kelley C. M., Sefton B. M. Transcriptional activation of lck by retrovirus promoter insertion between two lymphoid-specific promoters. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4113–4122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4113-4122.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama Y., Miller P. J., Thurman G. B., Neubauer R. H., Oliver C., Favilla T., Beman J. A., Oldham R. K., Stevenson H. C. Characterization of a human blood monocyte subset with low peroxidase activity. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):1093–1105. doi: 10.1172/JCI111034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrein K. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of a site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase, p56lck, reveals its oncogenic potential in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4247–4251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Kaplan P. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Altered sites of tyrosine phosphorylation in pp60c-src associated with polyomavirus middle tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1562–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E. Sites of in vivo phosphorylation of the T cell tyrosine protein kinase in LSTRA cells and their alteration by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9859–9864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny C. T., Hollis G. F., Magrath I. T., Kirsch I. R. Burkitt lymphoma cell line carrying a variant translocation creates new DNA at the breakpoint and violates the hierarchy of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3199–3207. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin A. M., Pawar S., Marth J. D., Perlmutter R. M. Structure of the murine lck gene and its rearrangement in a murine lymphoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3058–3064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga Y., Caccia N., Toyonaga B., Spolski R., Yanagi Y., Yoshikai Y., Mak T. W. A human T cell-specific cDNA clone (YT16) encodes a protein with extensive homology to a family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1643–1646. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G., Birrer M., Way J., Nau M., Sausville E., Thompson C., Minna J., Battey J. Multiple mechanisms for transcriptional regulation of the myc gene family in small-cell lung cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3373–3381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Cooper J. A., King C. S., Ziegler S. F., Tinker D. A., Overell R. W., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Neoplastic transformation induced by an activated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (pp56lck). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):540–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Lewis D. B., Wilson C. B., Gearn M. E., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Regulation of pp56lck during T-cell activation: functional implications for the src-like protein tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2727–2734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Overell R. W., Meier K. E., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Translational activation of the lck proto-oncogene. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):171–173. doi: 10.1038/332171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Peet R., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. A lymphocyte-specific protein-tyrosine kinase gene is rearranged and overexpressed in the murine T cell lymphoma LSTRA. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray D., Meneceur P., Tavitian A., Robert-Lezenes J. Presence of a c-myc transcript initiated in intron 1 in Friend erythroleukemia cells and in other murine cell types with no evidence of c-myc gene rearrangement. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):940–945. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Foss F. M., Sausville E. A., Bolen J. B., Rosen N. Expression of the lck tyrosine kinase gene in human colon carcinoma and other non-lymphoid human tumor cell lines. Oncogene Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;1(4):357–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Horak E. M., Bookman M. A., Bolen J. B. Alterations of the lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (p56lck) during T-cell activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4353–4361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Adler H. T., Sefton B. M. Two lck transcripts containing different 5' untranslated regions are present in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4407–4413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Sefton B. M. Expression of a new tyrosine protein kinase is stimulated by retrovirus promoter insertion. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):682–685. doi: 10.1038/319682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Gene amplification causes overproduction of the first three enzymes of UMP synthesis in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8679–8689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajac-Kaye M., Gelmann E. P., Levens D. A point mutation in the c-myc locus of a Burkitt lymphoma abolishes binding of a nuclear protein. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1776–1780. doi: 10.1126/science.2454510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]