Abstract
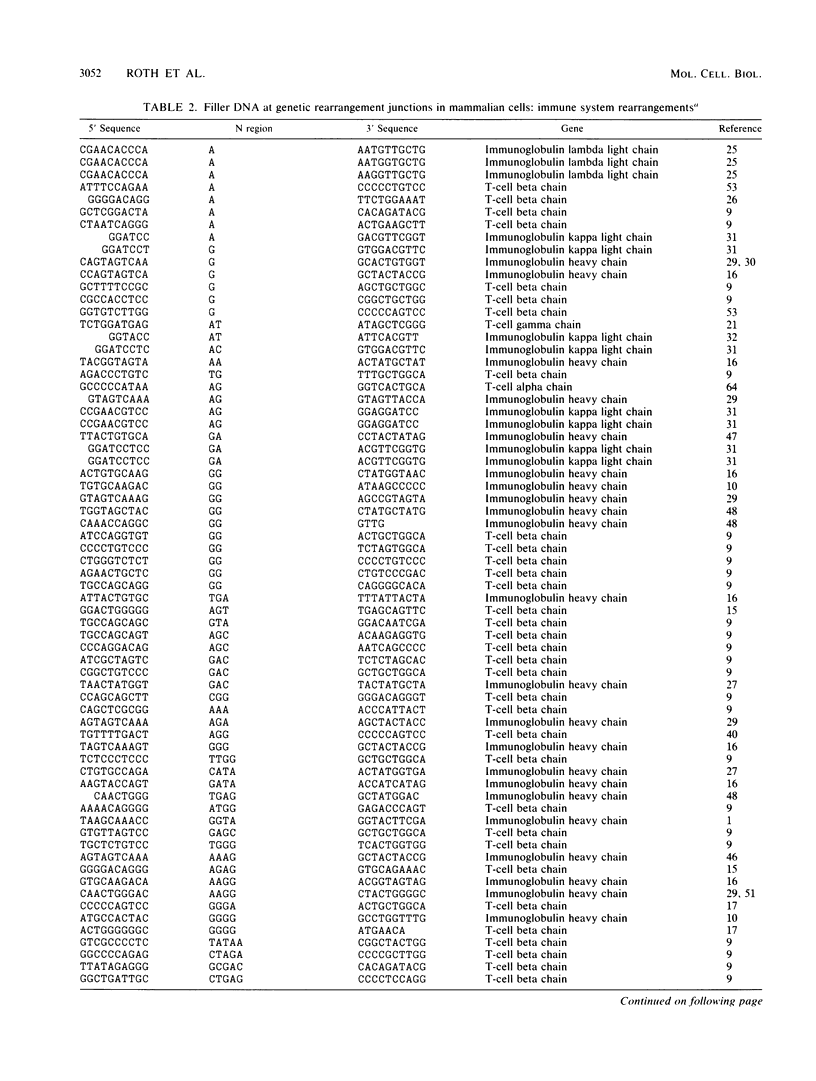
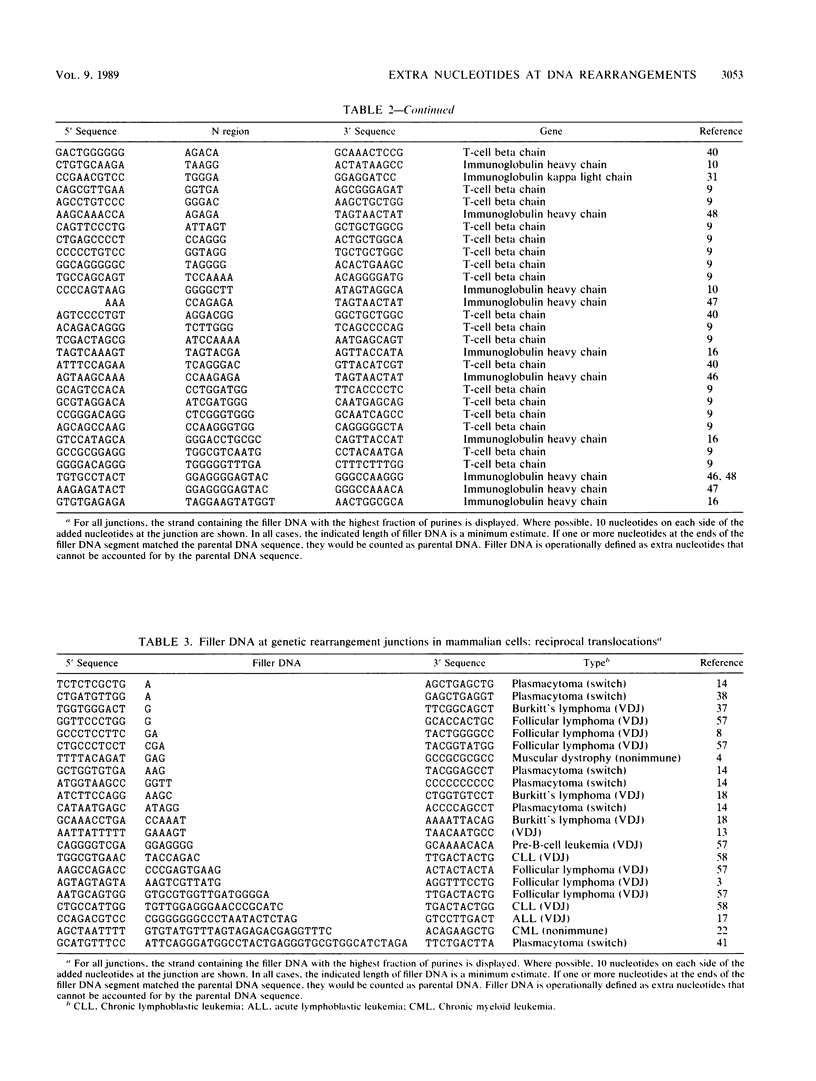
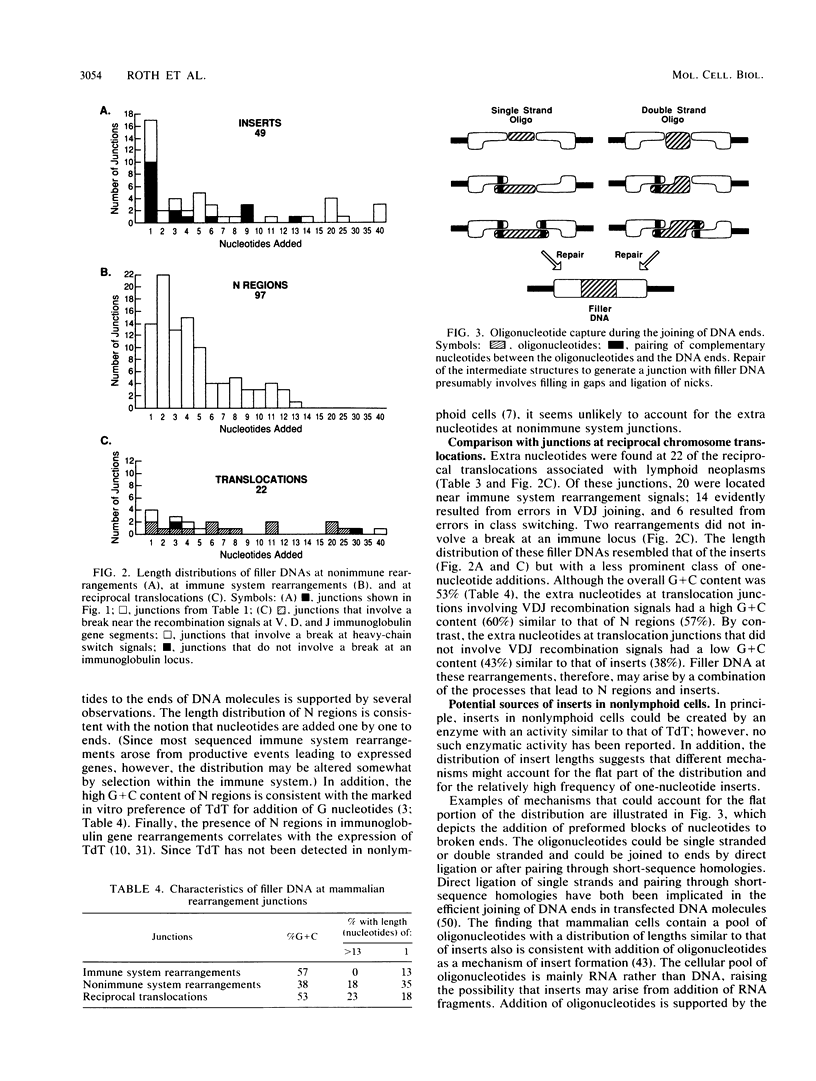
Extra nucleotides (termed filler DNA) are commonly found at the junctions of genetic rearrangements in mammalian cells. The filler DNA at immune system rearrangements, which are called N regions, are generated at VDJ joints primarily by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. However, the origin of filler DNA at genetic rearrangements in nonlymphoid cells is uncertain. In an analysis of more than 200 junctions that arose by circularization of transfected linear DNA (D. B. Roth and J. H. Wilson, Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:4295-4304, 1986), we found 18 junctions with extra nucleotides exactly at the point of circularization. Analysis of these 18 junctions indicated that nonlymphoid cells could add extra nucleotides to the ends of duplex DNA. The characteristics of the extra nucleotides at these junctions and at 31 other rearrangement junctions from nonlymphoid cells were quite similar, suggesting that many genetic rearrangements may pass through a stage with free DNA ends. A comparison of the filler DNA at these 49 nonimmune system rearrangements with 97 N regions derived from immune system rearrangements suggested that lymphoid and nonlymphoid cells use different mechanisms for insertion of filler DNA, as expected from the absence of detectable terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase in cells from nonlymphoid tissues. The filler DNAs at a smaller group of 22 translocations associated with cancer had features in common with both immune and nonimmune system rearrangements and therefore may represent a mixture of these two processes. Mechanisms that might account for the presence of filler DNA in nonlymphoid cells are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Kato S., Camerini-Otero R. D. A pattern of partially homologous recombination in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):206–210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshi A., Wright J. J., Graninger W., Seto M., Owens J., Cossman J., Jensen J. P., Goldman P., Korsmeyer S. J. Mechanism of the t(14;18) chromosomal translocation: structural analysis of both derivative 14 and 18 reciprocal partners. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodrug S. E., Ray P. N., Gonzalez I. L., Schmickel R. D., Sylvester J. E., Worton R. G. Molecular analysis of a constitutional X-autosome translocation in a female with muscular dystrophy. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1620–1624. doi: 10.1126/science.3629260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Stringer J., Mitchison T., Sambrook J. Integration and excision of SV40 DNA from the chromosome of a transformed cell. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Lebkowski J. S., Botchan M. R. High mutation frequency in DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M. Development of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity in embryonic calf thymus gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):124–131. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Sklar J. Nucleotide sequence of a t(14;18) chromosomal breakpoint in follicular lymphoma and demonstration of a breakpoint-cluster region near a transcriptionally active locus on chromosome 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7439–7443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concannon P., Pickering L. A., Kung P., Hood L. Diversity and structure of human T-cell receptor beta-chain variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6598–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio S. V., Yancopoulos G. D., Paskind M., Thomas E., Boss M. A., Landau N., Alt F. W., Baltimore D. Insertion of N regions into heavy-chain genes is correlated with expression of terminal deoxytransferase in B cells. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):752–755. doi: 10.1038/311752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Cold-sensitive regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):129–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W., Gahlmann R., Stabel S., Deuring R., Lichtenberg U., Schulz M., Eick D., Leisten R. On the mechanism of recombination between adenoviral and cellular DNAs: the structure of junction sites. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;109:193–228. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69460-8_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger L. R., Harvey R. C., Moore R. C., Showe L. C., Croce C. M. A common mechanism of chromosomal translocation in T- and B-cell neoplasia. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):982–985. doi: 10.1126/science.3490692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerondakis S., Cory S., Adams J. M. Translocation of the myc cellular oncogene to the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in murine plasmacytomas is an imprecise reciprocal exchange. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. A., Nguyen P. N., McBride L. J., Koepf S. M., Caskey C. T. Identification of mutations leading to the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome by automated direct DNA sequencing of in vitro amplified cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1919–1923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiya M., Davis D. D., Shultz L. D., Sakano H. Non-germ-line elements (NGE) are present in the T cell receptor beta-chain genes isolated from the mutant mouse, motheaten (me/me). J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2697–2700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiya M., Davis D. D., Takahashi T., Okuda K., Raschke W. C., Sakano H. Two types of immunoglobulin-negative Abelson murine leukemia virus-transformed cells: implications for B-lymphocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):145–149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haluska F. G., Finver S., Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. The t(8; 14) chromosomal translocation occurring in B-cell malignancies results from mistakes in V-D-J joining. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):158–161. doi: 10.1038/324158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haluska F. G., Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. The t(8;14) chromosome translocation of the Burkitt lymphoma cell line Daudi occurred during immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and involved the heavy chain diversity region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6835–6839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser J., Levine A. S., Dixon K. Unique pattern of point mutations arising after gene transfer into mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):63–67. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04719.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser J., Seidman M. M., Sidur K., Dixon K. Sequence specificity of point mutations induced during passage of a UV-irradiated shuttle vector plasmid in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):277–285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayday A. C., Saito H., Gillies S. D., Kranz D. M., Tanigawa G., Eisen H. N., Tonegawa S. Structure, organization, and somatic rearrangement of T cell gamma genes. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):259–269. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Stam K., Groffen J., de Klein A., Grosveld G. Structural organization of the bcr gene and its role in the Ph' translocation. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):758–761. doi: 10.1038/315758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope T. J., Aguilera R. J., Minie M. E., Sakano H. Endonucleolytic activity that cleaves immunoglobulin recombination sequences. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1141–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.3003919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. W., Jones R. W., Wood W. G., Weatherall D. J. Analysis of an inversion within the human beta globin gene cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2897–2906. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen K., Coleclough C. An unusual type of V-J joining diversifies the primary repertoire of mouse lambda 1 light chains. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):544–546. doi: 10.1038/314544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavaler J., Davis M. M., Chien Y. Localization of a T-cell receptor diversity-region element. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):421–423. doi: 10.1038/310421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinfield R., Hardy R. R., Tarlinton D., Dangl J., Herzenberg L. A., Weigert M. Recombination between an expressed immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene and a germline variable gene segment in a Ly 1+ B-cell lymphoma. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):843–846. doi: 10.1038/322843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Alexander P. S. The base substitution fidelity of eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Mispairing frequencies, site preferences, insertion preferences, and base substitution by dislocation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., Tonegawa S. Organization, structure, and assembly of immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity DNA segments. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):201–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., von Boehmer H., Haas W., Sakano H., Trauneker A., Tonegawa S. Identification of D segments of immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes and their rearrangement in T lymphocytes. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):565–570. doi: 10.1038/290565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Schatz D. G., Rosa M., Baltimore D. Increased frequency of N-region insertion in a murine pre-B-cell line infected with a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase retroviral expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3237–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Gifford A., Baltimore D. DNA elements are asymmetrically joined during the site-specific recombination of kappa immunoglobulin genes. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):677–685. doi: 10.1126/science.3158075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling L. E., Manos M. M., Gluzman Y. Sequence of the junction in adenovirus 2-SV40 hybrids: examples of illegitimate recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8099–8112. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager D. L., Henthorn P. S., Smithies O. A Chinese G gamma + (A gamma delta beta)zero thalassemia deletion: comparison to other deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster and sequence analysis of the breakpoints. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6559–6575. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munz P. L., Young C. S. The creation of adenovirus genomes with viable, stable, internal redundancies centered about the E2b region. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):52–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90237-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Phear G., Meuth M. DNA sequence analysis of spontaneous mutations at the aprt locus of hamster cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1445–1449. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri A., Barriga F., Knowles D. M., Magrath I. T., Dalla-Favera R. Different regions of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus are involved in chromosomal translocations in distinct pathogenetic forms of Burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2748–2752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Calabi F. Reciprocal chromosome translocation between c-myc and immunoglobulin gamma 2b genes. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):240–243. doi: 10.1038/305240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Fischel-Ghodsian N., Higgs D. R. Recombination at the human alpha-globin gene cluster: sequence features and topological constraints. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Davis D. D., Sakano H. T cell receptor beta gene sequences in the circular DNA of thymocyte nuclei: direct evidence for intramolecular DNA deletion in V-D-J joining. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90450-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli S. P., Caimi P. G., Cole M. D. A conserved sequence at c-myc oncogene chromosomal translocation breakpoints in plasmacytomas. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):327–330. doi: 10.1038/310327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plesner P., Goodchild J., Kalckar H. M., Zamecnik P. C. Oligonucleotides with rapid turnover of the phosphate groups occur endogenously in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1936–1939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin S. D., Moore P. D., Strauss B. S. In vitro bypass of UV-induced lesions by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I: specificity of nucleotide incorporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1541–1545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razzaque A., Chakrabarti S., Joffee S., Seidman M. Mutagenesis of a shuttle vector plasmid in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. G., Alt F. W. Novel immunoglobulin heavy chains are produced from DJH gene segment rearrangements in lymphoid cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):418–423. doi: 10.1038/312418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. G., Jackson S., Alt F. W. VHDJH formation and DJH replacement during pre-B differentiation: non-random usage of gene segments. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Gehrmann P., Petrac E., Wiese P. A novel VH to VHDJH joining mechanism in heavy-chain-negative (null) pre-B cells results in heavy-chain production. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):840–842. doi: 10.1038/322840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Porter T. N., Wilson J. H. Mechanisms of nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Nonhomologous recombination in mammalian cells: role for short sequence homologies in the joining reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4295–4304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Kurosawa Y., Weigert M., Tonegawa S. Identification and nucleotide sequence of a diversity DNA segment (D) of immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):562–565. doi: 10.1038/290562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheflin L., Celeste A., Woodworth-Gutai M. Recombination in simian virus 40-infected cells. Structure of naturally arising variants ev-2114, ev-2102, and ev-1110. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14315–14321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu G., Kronenberg M., Strauss E., Haars R., Mak T. W., Hood L. The structure, rearrangement and expression of D beta gene segments of the murine T-cell antigen receptor. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):344–350. doi: 10.1038/311344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spritz R. A., Orkin S. H. Duplication followed by deletion accounts for the structure of an Indian deletion beta (0)-thalassemia gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8025–8029. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W. Roles of double-strand breaks in generalized genetic recombination. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:169–194. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Gorham J., Cossman J., Jaffe E., Croce C. M. The t(14;18) chromosome translocations involved in B-cell neoplasms result from mistakes in VDJ joining. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1390–1393. doi: 10.1126/science.3929382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Jaffe E., Cossman J., Gorham J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Clustering of breakpoints on chromosome 11 in human B-cell neoplasms with the t(11;14) chromosome translocation. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):340–343. doi: 10.1038/315340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Vernaleone F., Wilson J. H. Topological requirements for homologous recombination among DNA molecules transfected into mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2080–2089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss U., Wilson J. H. Heteroduplex-induced mutagenesis in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2313–2322. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie T. M., Palmiter R. D. Analysis of the integrant in MyK-103 transgenic mice in which males fail to transmit the integrant. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1646–1655. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Fried M. Inverted duplication-transposition event in mammalian cells at an illegitimate recombination join. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2179–2184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Berget P. B., Pipas J. M. Somatic cells efficiently join unrelated DNA segments end-to-end. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winoto A., Mjolsness S., Hood L. Genomic organization of the genes encoding mouse T-cell receptor alpha-chain. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):832–836. doi: 10.1038/316832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth-Gutai M. Recombination in SV40-infected cells: viral DNA sequences at sites of circularization of transfecting linear DNA. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


