Abstract
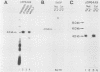
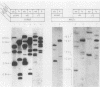
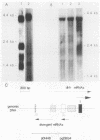
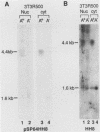
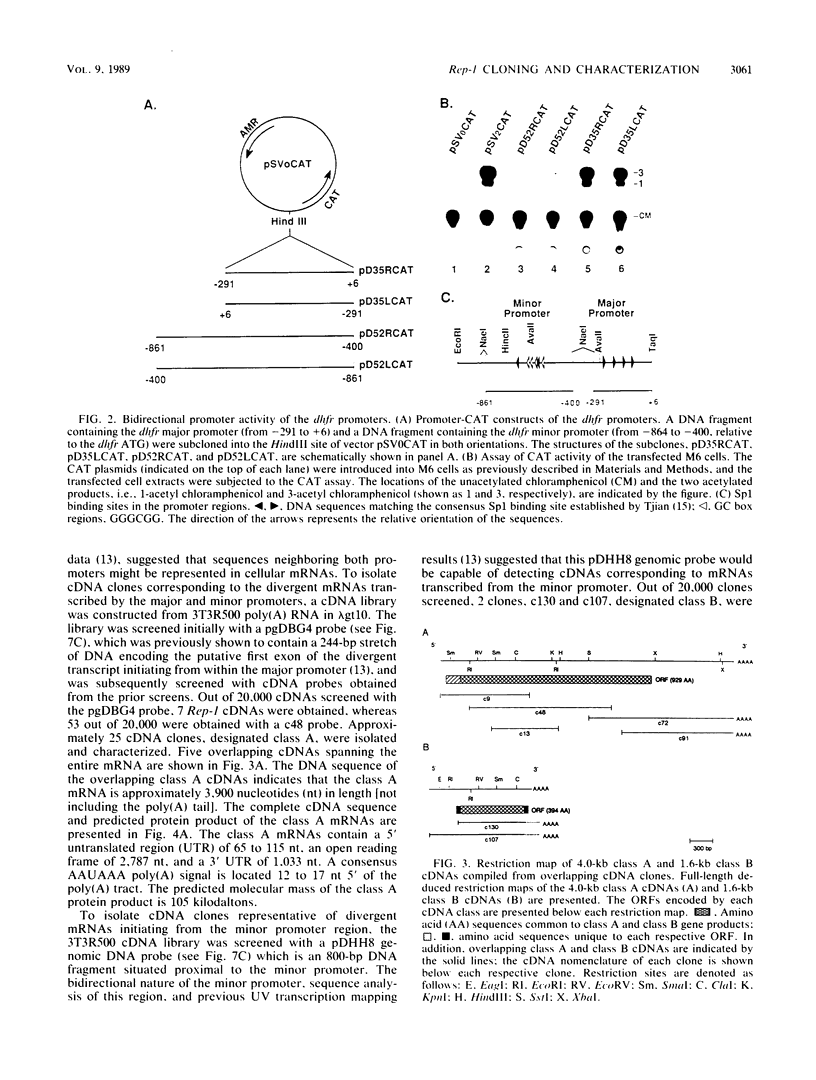
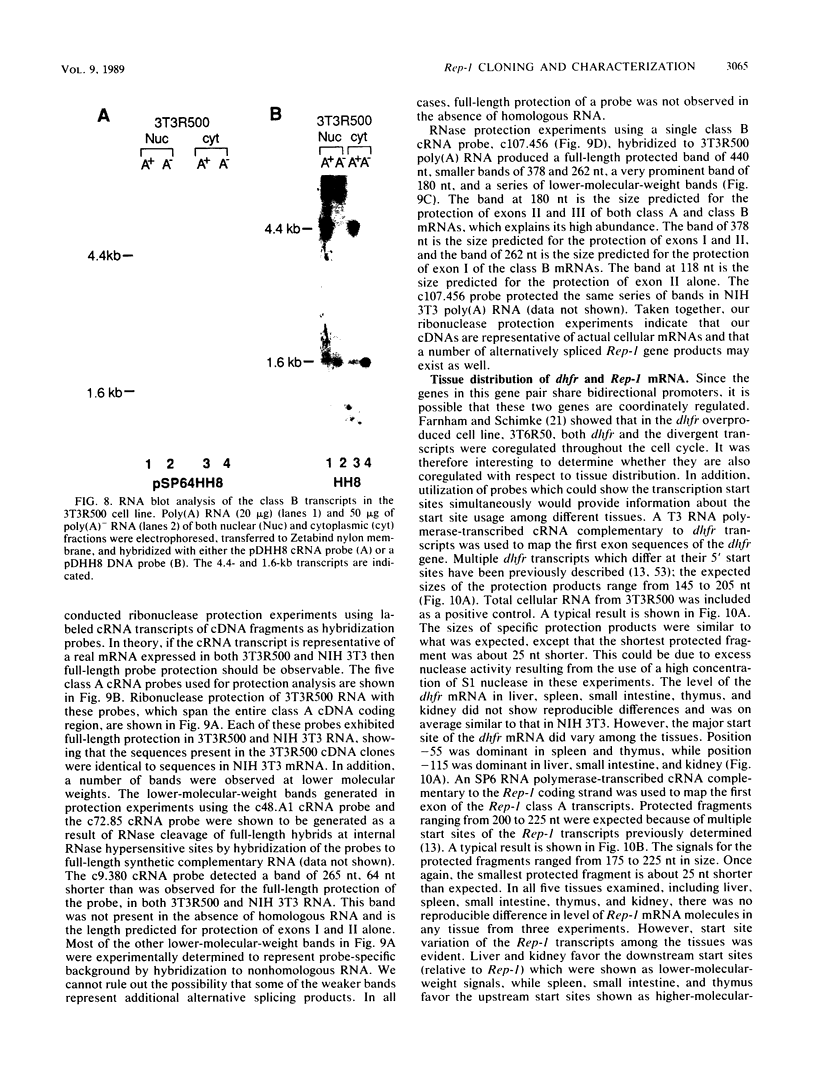
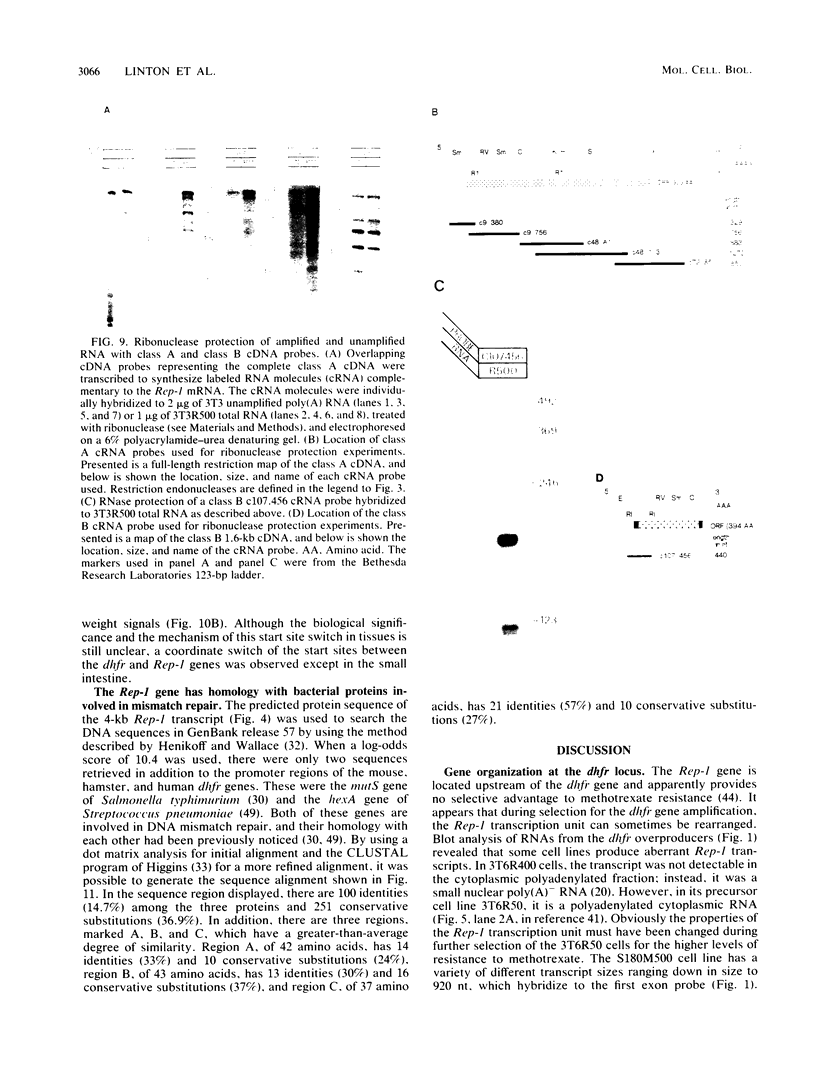
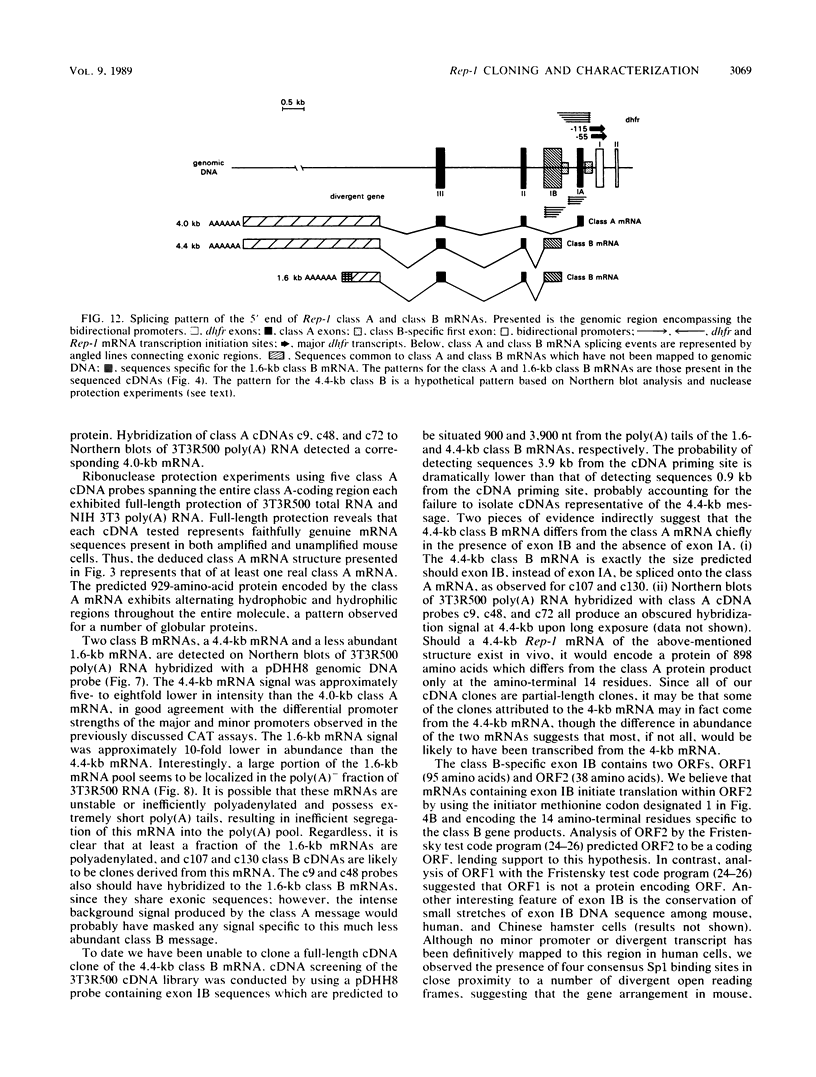
The mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene (dhfr) is a housekeeping gene expressed under the control of a promoter region embedded in a CpG island--a region rich in unmethylated CpG dinucleotides. A divergent transcription unit exists immediately upstream of the dhfr gene which is coamplified with dhfr in some but not all methotrexate-resistant cell lines. We show that the promoter region for this gene pair consists of two bidirectional promoters, a major and minor promoter, which are situated within a 660-base-pair region upstream of the dhfr ATG translation initiation codon. The major promoter controls over 90% of dhfr transcription, while the minor promoter directs the transcription of the remaining dhfr mRNAs. The major promoter functions bidirectionally, transcribing a divergent 4.0-kilobase poly(A) mRNA (class A) in the direction opposite that of dhfr transcription. The predicted protein product of this mRNA is 105 kilodaltons. The minor promoter also functions bidirectionally, directing the transcription of at least two divergent RNAs (class B). These RNAs, present in quantities approximately 1/10 to 1/50 that of the class A mRNAs, are 4.4- and 1.6-kilobase poly(A) mRNAs. cDNAs representing both class A and class B mRNAs have been cloned from a mouse fibroblast cell line which has amplified the dhfr locus (3T3R500). DNA sequence analysis of these cDNAs reveals that the class A and class B mRNAs share, for the most part, the same exons. On the basis of S1 nuclease protection analysis of RNA preparations from several mouse tissues, both dhfr and divergent genes showed similar levels of expression but did show some specificity in start site utilization. Computer homology searches have revealed sequence similarity of the divergent transcripts with bacterial genes involved in DNA mismatch repair, and we therefore have named the divergently transcribed gene Rep-1.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amasino R. M. Acceleration of nucleic acid hybridization rate by polyethylene glycol. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ares M., Jr, Chung J. S., Giglio L., Weiner A. M. Distinct factors with Sp1 and NF-A specificities bind to adjacent functional elements of the human U2 snRNA gene enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):808–817. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Applegate E. F., Yoza B. K. Identification of a promoter for transcription of the heavy strand of human mtDNA: in vitro transcription and deletion mutagenesis. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1105–1113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Precise identification of individual promoters for transcription of each strand of human mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Hixson J. E., Clayton D. A. Minor transcription initiation events indicate that both human mitochondrial promoters function bidirectionally. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Leys E. J., McEwan R. N., Frayne E. G., Kellems R. E. Analysis of the mouse dhfr promoter region: existence of a divergently transcribed gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1847–1858. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., McEwan R. N., Pearson M. L. Expression and amplification of engineered mouse dihydrofolate reductase minigenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):257–266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Simonsen C. C., McEwan R. N., Schimke R. T. Structure of amplified normal and variant dihydrofolate reductase genes in mouse sarcoma S180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7887–7897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Stivaletta L. A., Smith M. L. Analysis of gene expression using episomal mouse dihydrofolate reductase minigenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):7025–7042. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.7025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Abrams J. M., Schimke R. T. Opposite-strand RNAs from the 5' flanking region of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Murine dihydrofolate reductase transcripts through the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):365–371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federspiel N. A., Beverley S. M., Schilling J. W., Schimke R. T. Novel DNA rearrangements are associated with dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9127–9140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fickett J. W. Recognition of protein coding regions in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5303–5318. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fristensky B. Improving the efficiency of dot-matrix similarity searches through use of an oligomer table. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):597–610. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fristensky B., Lis J., Wu R. Portable microcomputer software for nucleotide sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6451–6463. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber L. T., Pang P. P., Sobell D. I., Mankovich J. A., Walker G. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Salmonella typhimurium mutS gene required for mismatch repair: homology of MutS and HexA of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):197–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.197-202.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Wallace J. C. Detection of protein similarities using nucleotide sequence databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6191–6204. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckaby C. S., Conneely O. M., Beattie W. G., Dobson A. D., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Structure of the chromosomal chicken progesterone receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8380–8384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. B., Good L., Simonetti J., Zuker M. Some simple computational methods to improve the folding of large RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):45–52. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavia P., Macleod D., Bird A. Coincident start sites for divergent transcripts at a randomly selected CpG-rich island of mouse. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2773–2779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene S. D., Zimm B. H. Separations of open-circular DNA using pulsed-field electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4054–4057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Gautron S., Hakim V., Gregori C., Mennecier F., Kahn A. Characterization of three optional promoters in the 5' region of the human aldolase A gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 5;197(3):425–438. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90556-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Simonsen C. C., Smouse D. T., Farnham P. J., Schimke R. T. Heterogeneity at the 5' termini of mouse dihydrofolate reductase mRNAs. Evidence for multiple promoter regions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2307–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Carothers A. M., Han J. H., Harding J. D., Kas E., Venolia L., Chasin L. A. Multiple transcription start sites, DNase I-hypersensitive sites, and an opposite-strand exon in the 5' region of the CHO dhfr gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):425–440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen D. A., Chou J., MacKrell A. J., Casadaban M. J., Steiner D. F. Expression of a preproinsulin-beta-galactosidase gene fusion in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5198–5202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Schimke R. T. Structure and genomic organization of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Strehler E. E., Garfinkel L. I., Gubits R. M., Ruiz-Opazo N., Nadal-Ginard B. Fast skeletal muscle myosin light chains 1 and 3 are produced from a single gene by a combined process of differential RNA transcription and splicing. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13595–13604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priebe S. D., Hadi S. M., Greenberg B., Lacks S. A. Nucleotide sequence of the hexA gene for DNA mismatch repair in Streptococcus pneumoniae and homology of hexA to mutS of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):190–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.190-196.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt J. K., Berg P. Conservation of short patches of amino acid sequence amongst proteins with a common function but evolutionarily distinct origins: implications for cloning genes and for structure-function analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):9017–9026. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.9017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Singer M. F. Transcription from SV 40-like monkey DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4769–4788. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sazer S., Schimke R. T. A re-examination of the 5' termini of mouse dihydrofolate reductase RNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4685–4690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. M., Dayhoff M. O. Origins of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Science. 1978 Jan 27;199(4327):395–403. doi: 10.1126/science.202030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweighoffer F., Maire P., Tuil D., Gautron S., Daegelen D., Bachner L., Kahn A. In vivo developmental modifications of the expression of genes encoding muscle-specific enzymes in rat. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10271–10276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Nunberg J. H., Schimke R. T. Size heterogeneity in the 3' end of dihydrofolate reductase messenger RNAs in mouse cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., McGrogan M., Schimke R. T. Nucleotide sequence surrounding multiple polyadenylation sites in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5143–5147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Pittet A. C., Schibler U. Different tissue-specific expression of the amylase gene Amy-1 in mice and rats. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4067–4076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Transcription and regulatory signals at the mating type locus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., O'Connell P., Gray M. R., Rosbash M. Drosophila maternal and embryo mRNAs transcribed from a single transcription unit use alternate combinations of exons. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1003–1013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Fried M. The MES-1 murine enhancer element is closely associated with the heterogeneous 5' ends of two divergent transcription units. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4558–4569. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Berk A. Constraints on spacing between transcription factor binding sites in a simple adenovirus promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):403–411. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen J. Y., Kellems R. E. Independent 5' and 3'-end determination of multiple dihydrofolate reductase transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3732–3739. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Garza D., Chou T. B., Goland J., Bingham P. M. Molecular cloning and genetic analysis of the suppressor-of-white-apricot locus from Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2498–2505. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]