Abstract
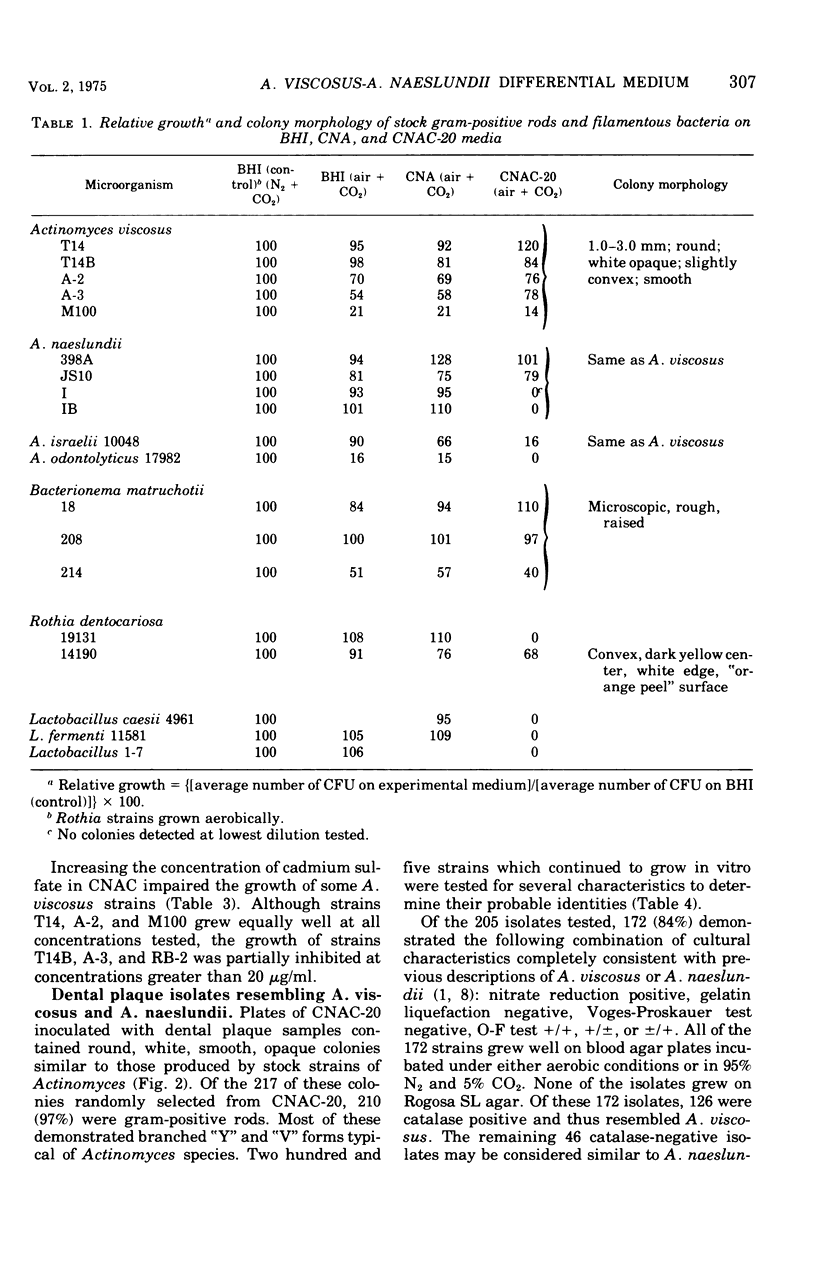
A medium for detecting colonies of Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces naeslundii in dental plaque samples was developed. The medium (CNAC-20) contains 20.0 mug of 3CdSO4-8H2O per ml of Columbia CNA agar base. Laboratory strains of A. viscosus grew on CNAC-20 in characteristic round, white, smooth, opaque colonies. Increasing the cadmium concentration impaired the growth of some A. viscosus strains. Stock strains of A. naeslundii and A. israelii grew in colonies of similar white, opaque morphology. The few strains of other gram-positive plaque bacteria that grew on CNAC-20 had colonies easily distinguished from those of A. viscosus. Most of the bacterial strains freshly isolated from Actinomyces-like colonies on CNAC-20 that had been inoculated with human dental plaque samples were found to have cultural characteristics consistent with previous descriptions of A. viscosus or A. naeslundii. CNAC-20 may facilitate investigations into the relationship of microaerophilic Actinomyces with the etiology of dental diseases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlsson J. A medium for isolation of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1657–1658. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton S. L., Chipps D. D., Blasi D., Smith R. F. Evaluation of three media for selective isolation of gram-positive bacteria from burn wounds. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):420–422. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.420-422.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner P. D., Stoessel C. J., Drakeford E., Vasi F. A new culture medium for medical bacteriology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):502–504. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/45.4_ts.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour M. N., Turner G. Culture purity assessments and morphological dissociation in the pleomorphic microorganism Bacterionema matruchotii. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1134–1141. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1134-1141.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold O. G., Jordan H. V., Van Houte J. A selective medium for Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Nov;18(11):1357–1364. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90109-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGH R., LEIFSON E. The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):24–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.24-26.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg K., Hallander H. O. Numerical taxonomy and laboratory identification of Bacterionema matruchotii, Rothia dentocariosa, Actinomyces naeslundii, Actinomyces viscosus, and some related bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):43–63. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell A., Jr, Jordan H. V., Georg L. K., Pine L. Odontomyces viscosus, gen. nov., spec. nov., a filamentous microorganism isolated from periodontal plaque in hamsters. Sabouraudia. 1965 Jun;4(2):65–68. doi: 10.1080/00362176685190181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T., Sandham H. J. A high-sucrose medium for the identification of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Apr;17(4):781–783. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving J. T., Socransky S. S., Heeley J. D. Histological changes in experimental periodontal disease in gnotobiotic rats and conventional hamsters. J Periodontal Res. 1974;9(2):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1974.tb00656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN H. V., KEYES P. H. AEROBIC, GRAM-POSITIVE, FILAMENTOUS BACTERIA AS ETIOLOGIC AGENTS OF EXPERIMENTAL PERIODONTAL DISEASE IN HAMSTERS. Arch Oral Biol. 1964 Jul-Aug;9:401–414. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(64)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Hammond B. F. Filamentous bacteria isolated from human root surface caries. Arch Oral Biol. 1972 Sep;17(9):1333–1342. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(72)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V., Keyes P. H., Bellack S. Periodontal lesions in hamsters and gnotobiotic rats infected with actinomyces of human origin. J Periodontal Res. 1972;7(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1972.tb00627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan H. V. Rodent model systems in periodontal disease research. J Dent Res. 1971 Mar-Apr;50(2):236–242. doi: 10.1177/00220345710500021301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYES P. H., JORDAN H. V. PERIODONTAL LESIONS IN THE SYRIAN HAMSTER. III. FINDINGS RELATED TO AN INFECTIOUS AND TRANSMISSIBLE COMPONENT. Arch Oral Biol. 1964 Jul-Aug;9:377–400. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(64)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOSA M., MITCHELL J. A., WISEMAN R. F. A selective medium for the isolation and enumeration of oral lactobacilli. J Dent Res. 1951 Oct;30(5):682–689. doi: 10.1177/00220345510300051201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Hubersak C., Propas D. Induction of periodontal destruction in gnotobiotic rats by a human oral strain of Actinomyces naeslundii. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Oct;15(10):993–995. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Relationship of bacteria to the etiology of periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1970 Mar-Apr;49(2):203–222. doi: 10.1177/00220345700490020401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumney D. L., Jordan H. V. Characterization of bacteria isolated from human root surface carious lesions. J Dent Res. 1974 Mar-Apr;53(2):343–351. doi: 10.1177/00220345740530022701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A., Loesche W. J., Pape H. L., Jr, grenier E. Predominant cultivable flora isolated from human root surface caries plaque. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):727–731. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.727-731.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. Survival of human dental plaque flora in various transport media. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):638–644. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.638-644.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]