Abstract
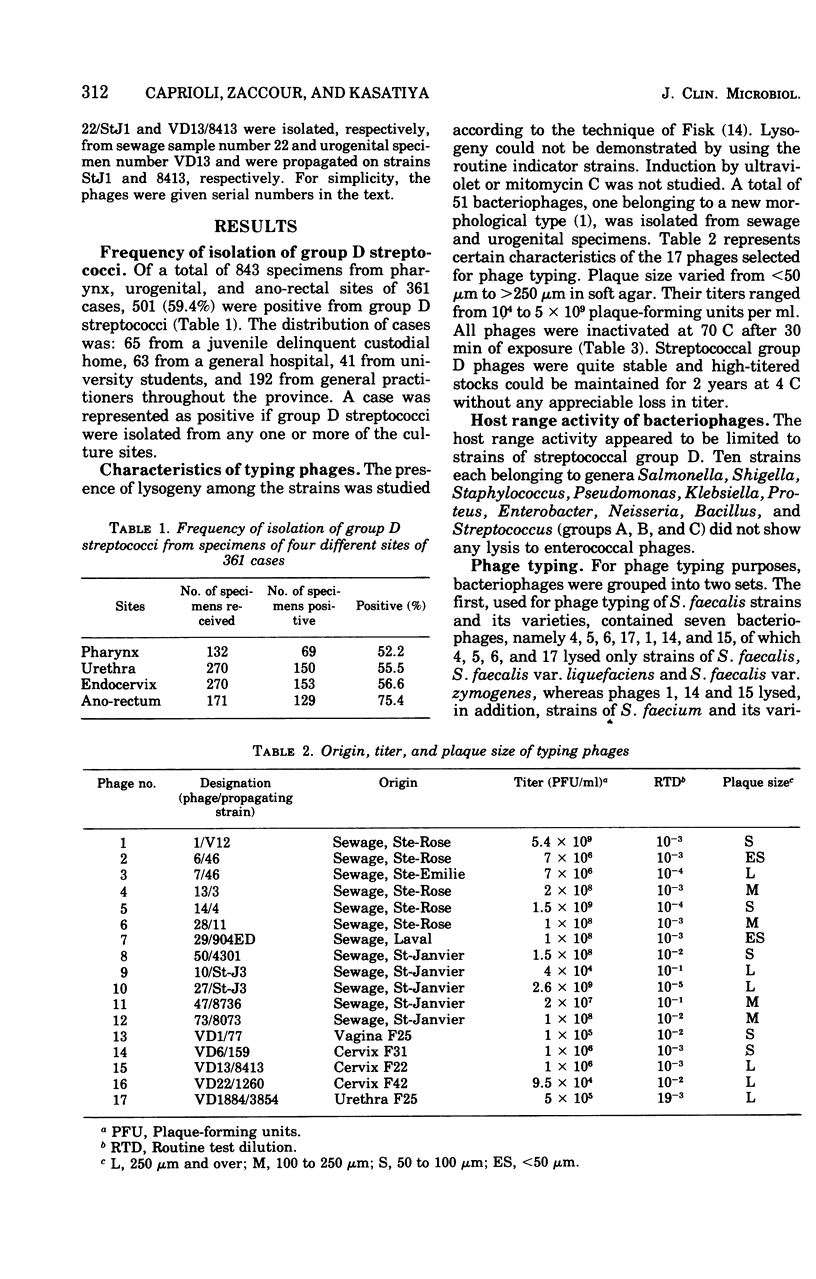
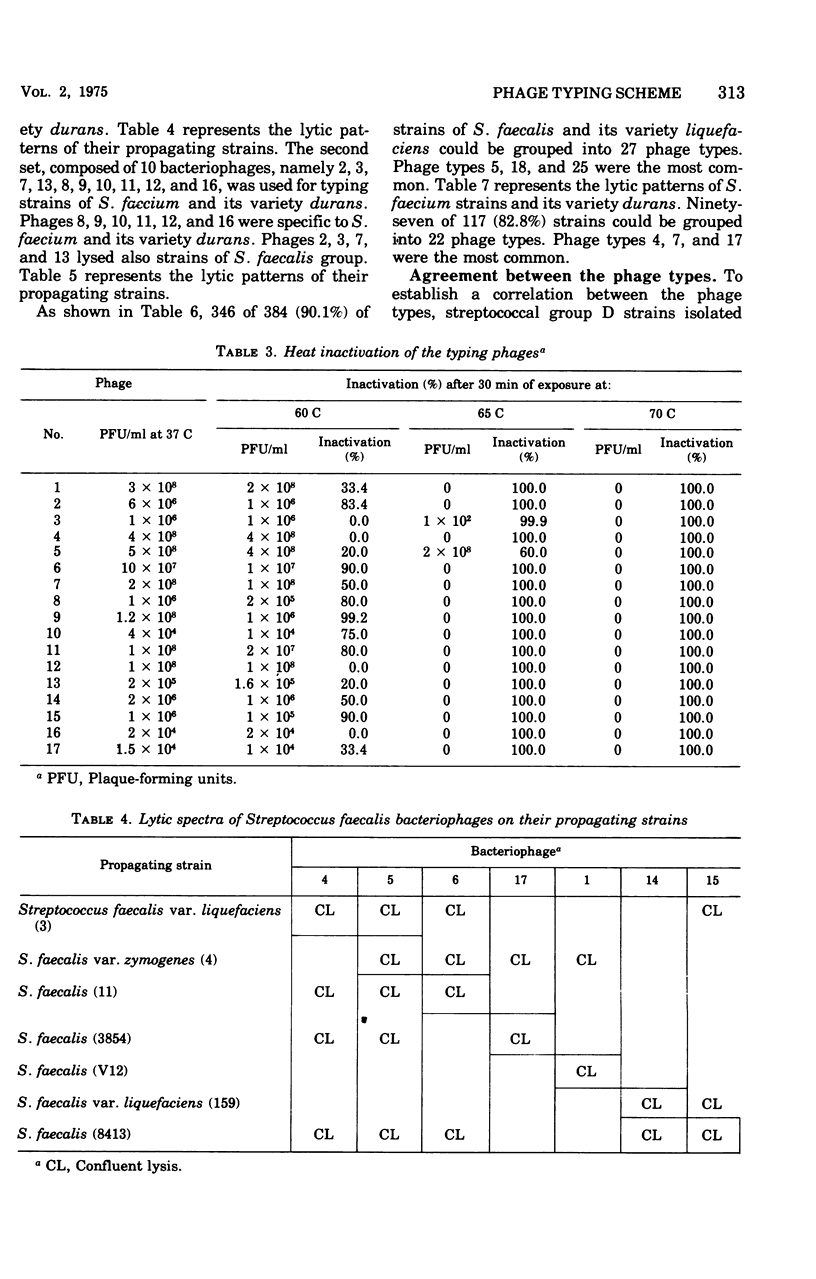
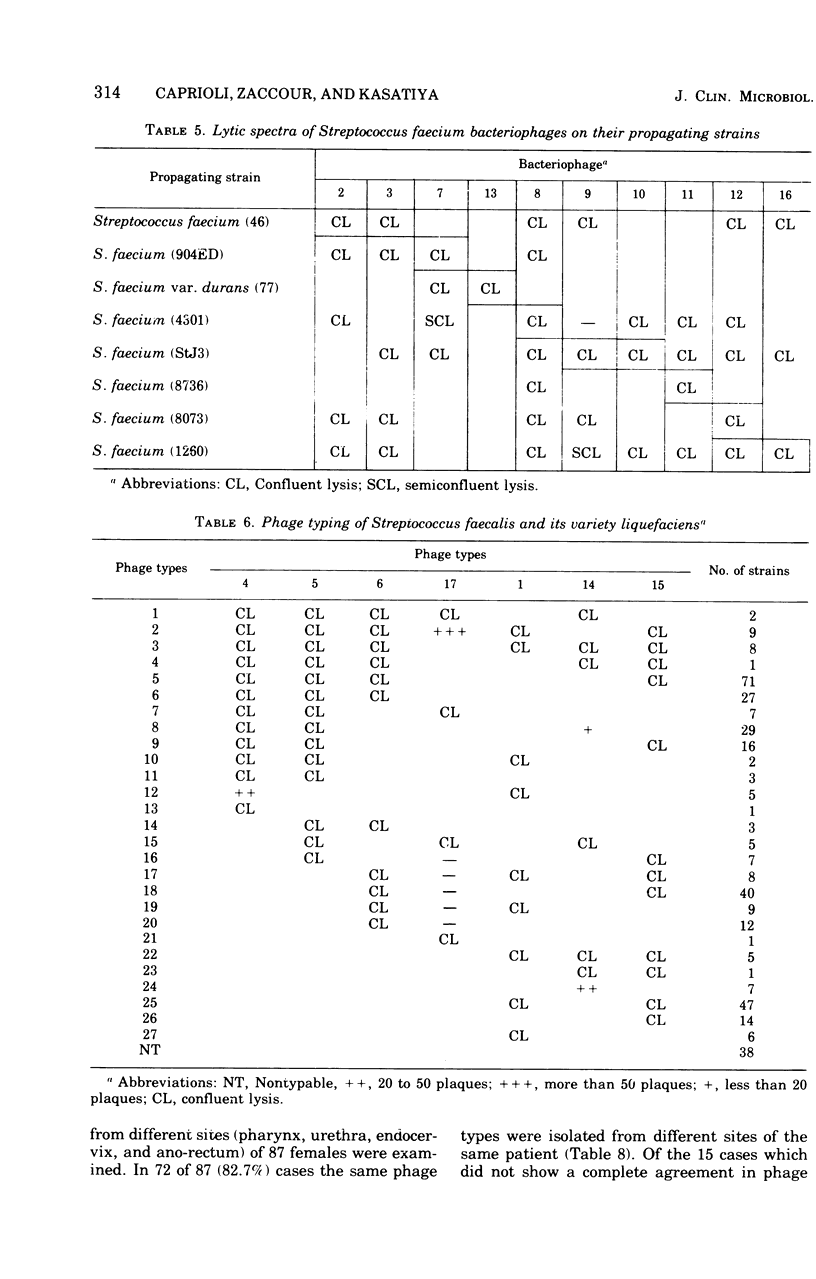
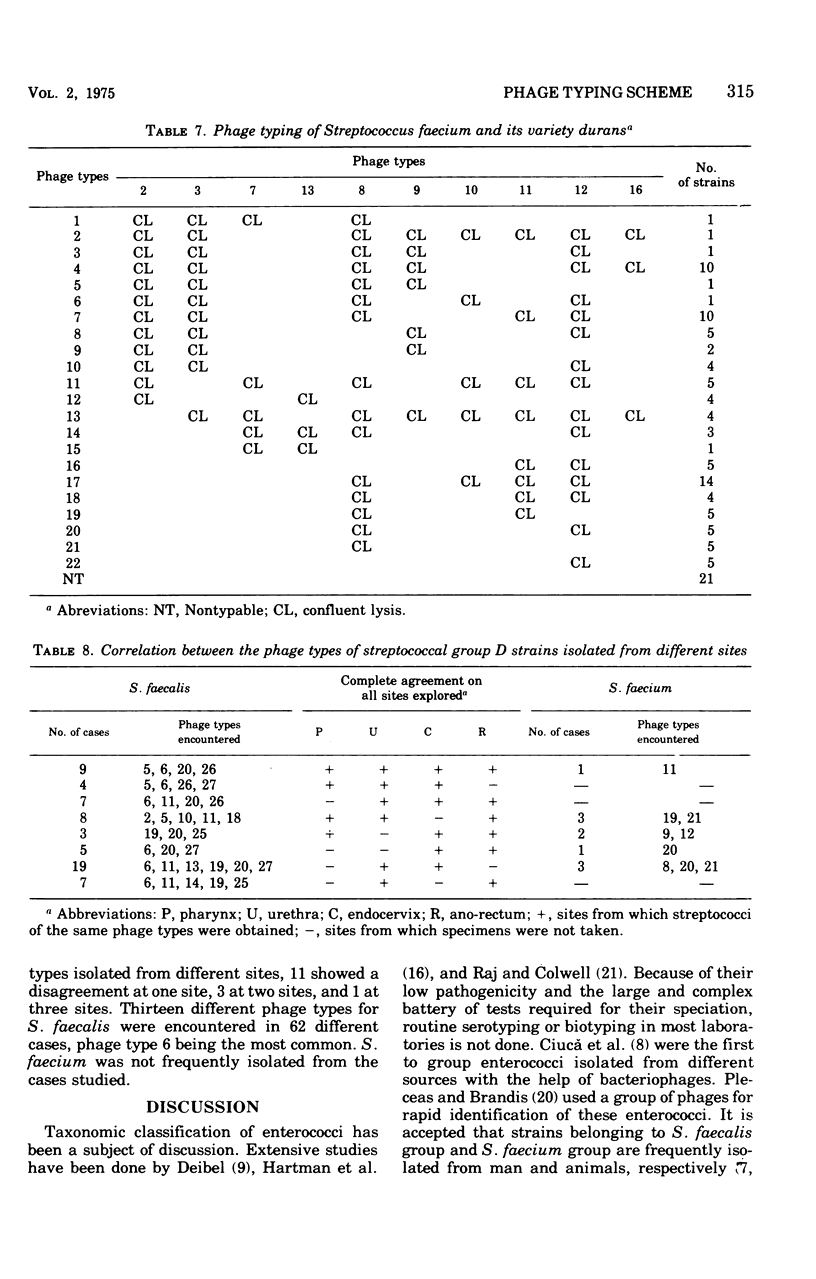
Streptococci of Lancefield group D were isolated from 52.2% of pharyngeal, 55.5% of urethral, 56.6% of endocervical, and 75.4% of ano-rectal specimens. Seventeen phages isolated from sewage and urogenital specimens were selected for phage typing. Four of these lysed only the strains of Streptococcus faecalis and its variety liquefaciens. Another six phages lysed only the strains of Streptococcus faecium and its variety durans. With the help of seven bacteriophages, 346 of 384 (90.1%) strains of S. faecalis and its variety liquefaciens could be classified into 27 types. Similarly, with the help of 10 other bacteriophages, 97 of 117 (82.9%) strains of S. faecium and its variety durans could be grouped into 22 types. In 72 of 87 (82.7%) cases, similar phage types were obtained at different culture sites of the same individual.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann H. W., Caprioli T., Kasatiya S. S. A large new Streptococcus bacteriophage. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Apr;21(4):571–574. doi: 10.1139/m75-080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D. HOST RANGE OF CERTAIN VIRULENT AND TEMPERATE BACTERIOPHAGES ATTACKING GROUP D STREPTOCOCCI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:165–171. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.165-171.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTTIAUX R. Les streptocoques fécaux des intestins humains et animaux. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Jun;94(6):778–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce A. W., Chadwick P., Hassan A., VanCott G. F. Recurrent urethritis in women. Can Med Assoc J. 1973 Apr 21;108(8):973–976. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEIBEL R. H. THE GROUP D STREPTOCOCCI. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:330–366. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.330-366.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkins I. B., Cox C. E. Perineal, vaginal and urethral bacteriology of young women. I. Incidence of gram-negative colonization. J Urol. 1974 Jan;111(1):88–92. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59896-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. C., Sockrider E. M. Another Serologic Type of Streptococcic Bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1942 Aug;44(2):211–214. doi: 10.1128/jb.44.2.211-214.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch V., Hérmán G. Phage typing of D-group streptococci. I. Typing of enterococci with Roumanian phages. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1971;18(2):95–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KJEMS E. Studies on streptococcal bacteriophages. I. Technique of isolating phage-producing strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1955;36(5):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleceas P., Brandis H. Rapid group and species identification of enterococci by means of tests with pooled phages. J Med Microbiol. 1974 Nov;7(4):529–533. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-4-529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj H., Colwell R. R. Taxonomy of enterococci by computer analysis. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Apr;12(2):353–362. doi: 10.1139/m66-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWANSTROM M., ADAMS M. H. Agar layer method for production of high titer phage stocks. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Nov;78(2):372–375. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-19076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTENBURY R. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS AND S. FAECIUM. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Feb;38:279–287. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S. Enterococcal endocarditis. JAMA. 1968 Jun 3;204(10):916–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



