Abstract
Background
eHealth is an application of information and communication technologies across the whole range of functions that affect health. The benefits of eHealth (eg, improvement of health care operational efficiency and quality of patient care) have previously been documented in the literature. Health care providers (eg, medical doctors) are the key driving force in pushing eHealth initiatives. Without their acceptance and actual use, those eHealth benefits would be unlikely to be reaped.
Objective
To identify and synthesize influential factors to health care providers’ acceptance of various eHealth systems.
Methods
This systematic literature review was conducted in four steps. The first two steps facilitated the location and identification of relevant articles. The third step extracted key information from those articles including the studies’ characteristics and results. In the last step, identified factors were analyzed and grouped in accordance with the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT).
Results
This study included 93 papers that have studied health care providers’ acceptance of eHealth. From these papers, 40 factors were identified and grouped into 7 clusters: (1) health care provider characteristics, (2) medical practice characteristics, (3) voluntariness of use, (4) performance expectancy, (5) effort expectancy, (6) social influence, and (7) facilitating or inhibiting conditions.
Conclusions
The grouping results demonstrated that the UTAUT model is useful for organizing the literature but has its limitations. Due to the complex contextual dynamics of health care settings, our work suggested that there would be potential to extend theories on information technology adoption, which is of great benefit to readers interested in learning more on the topic. Practically, these findings may help health care decision makers proactively introduce interventions to encourage acceptance of eHealth and may also assist health policy makers refine relevant policies to promote the eHealth innovation.
Keywords: technology acceptance, eHealth, health care provider, adoption
Introduction
Poor health care outcomes lead to increased levels of morbidity and mortality, and obstruct countries’ prosperity and business profitability (eg, [1,2]). eHealth is an application of information and communication technologies (ICT) across health-related functions [3]. The benefits of eHealth, such as improved operational efficiency, higher quality of care, and positive return on investments have been well documented in the literature [4-6].
eHealth is an emerging field at the intersection of medical informatics, public health, and business, and refers to health services and information delivered or enhanced through the Internet and other related technologies [7,8]. Different eHealth applications have been used across countries, corresponding to their health needs and priorities. The World Health Organization (WHO) eHealth for Health Care Delivery (eHCD) program, for example, targeted primary health care in a number of countries in the Asia-Pacific region. Some of these countries have instigated telemedicine as a means of bringing specialist health care to rural communities, whereas some others have endeavoured to improve the safety and continuity of patient care through the use of electronic health records (EHR).
While there has been high interest in eHealth, the adoption and acceptance rates have not been high enough for health care systems to experience the maximal benefits eHealth has to offer [8]. Past experience of eHealth adoption in the United States, for example, informed us that the low adoption rate could be attributed to both macro-level factors (eg, supportive policies) from the perspective of the public, health care organization, and system, and micro-level barriers from the perspective of health care providers (eg, physicians’ perception about technological complexity, [9]).
A broad spectrum of research methodologies have been used to study eHealth adoption and acceptance factors based on information provided in published studies [9]. The methodologies include quantitative surveys [10], observations [11], qualitative focus groups [12], ethnographic studies [13], and personal intuition and experience [14]. According to the results of these studies, different eHealth adoption factors may have led to difficulty for decision makers to explicitly understand, measure, and decrease inhibiting factors or enhance facilitating forces [9]. Hence, there is a need to synthesize those insights and provide decision makers with a holistic view of eHealth adoption.
Health care providers are the key driving force in pushing eHealth initiatives [14]. eHealth implementation represents a disruptive change in the health care workplace. The change does not occur simply from the introduction of ICT infrastructure but may also require remodelling of the job design of interconnected health professionals to effectively and efficiently incorporate technology [15]. Without the presence of motivational forces (eg, health care providers’ dissatisfaction with the status quo), it is unlikely that the innovation process would be initiated. If health care providers resist change or do not possess attributes necessary for change (eg, adaptability and growth-orientation), the change process is less likely to proceed [16]. The objective of this paper was to identify and synthesize the factors influential to health care providers’ acceptance of various eHealth applications.
Methods
Overview
In light of the guidelines originally proposed by [17,18] and already applied in several systematic reviews (eg, [19]), we conducted a systematic literature review on eHealth adoption. For the specific objective of this study, the guidelines have been modified and 4 steps were taken: (1) identification of resources, (2) selection of relevant papers, (3) data extraction, and (4) data analysis and validation.
Identification of Resources
A literature search was conducted between October and November 2011 using 8 online databases: Medline, Cinahl, Web of Science, PubMed, PsychInfo, ERIC, ProQuest Science Journals, and EMBASE. These databases were thought to be the most likely to publish eHealth adoption related work [20]. All search fields available from each search service were used. In each database, the search was repeated 3 times using the following phrases (operators came before keywords): [“e-Health” AND “Adoption” OR “User Acceptance”] or [“eHealth” AND “Adoption” OR “User Acceptance”] or [“EMR” AND “Adoption” OR “User Acceptance”] or [“EHR" AND “Adoption” OR “User Acceptance”].
The terms “electronic medical records” (EMR) and EHR were separately used to search papers. This is because the EMR/EHR consists of patient health related information and forms the core of eHealth systems [8]. The inclusion of those papers increased the validity of the findings. Table 1 lists the number of papers found in each database using the search phrases. In summary, a total of 3315 papers were found, of which 420 papers were duplicated. The selection process excluded the repeated papers from the archive and produced a list of 2895 papers.
Table 1.
Identification of papers for review from 8 online databases.
| Keywords | Medline | Cinahl | Web of Science | PubMed | PsycInfo | ERIC | ProQuest Science Journals | EMBASE (1980+) | Total | Duplicated results |
| User acceptance AND eHealth |
2 | 3 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 73 | 2 | 100 | - |
| User acceptance AND eHealth |
6 | 0 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 45 | 2 | 71 | 20 |
| User acceptance AND EMR |
9 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 2 | 0 | 93 | 10 | 136 | 17 |
| User acceptance AND EHR |
13 | 2 | 15 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 57 | 10 | 112 | 20 |
| Adoption AND eHealth |
31 | 15 | 47 | 34 | 24 | 1 | 244 | 36 | 432 | 39 |
| Adoption AND eHealth |
29 | 9 | 29 | 44 | 28 | 1 | 155 | 30 | 325 | 74 |
| Adoption AND EMR |
89 | 30 | 67 | 97 | 12 | 3 | 395 | 101 | 794 | 87 |
| Adoption AND EHR |
165 | 83 | 106 | 187 | 17 | 1 | 607 | 179 | 1345 | 163 |
| Total unrepeated articles retrieved | 2895 | - | ||||||||
Selection of Relevant Articles
The full texts of the selected papers were reviewed for relevance. Papers with the following criteria were filtered out:
articles not written in English
articles that did not directly use the terms “adoption” and “eHealth” or related terms in the title, abstract, or entire text, with casual referencing of eHealth adoption related issues.
articles without empirical evidence
articles which discussed adoption or user acceptance of eHealth but not from the health care provider’s perspective
This examination process had two iterations. Finally, 93 relevant papers were selected.
Data Extraction
The key information was extracted from the 93 papers. The extracted data included: (1) characteristics of the study (eg, year of publication and health care settings where the studies were conducted), (2) the study results and output—eHealth adoption factors. Relevant text was extracted or retyped verbatim and was added to a database.
Data Analysis and Validation
Figure 1 illustrates the analysis process of the data collected in Step 3. Based on the terminologies or terms utilized in the papers, 49 eHealth adoption/acceptance factors were initially extracted. All citations used to identify the results were noted. The next activity was to study the definitions used in the papers. Factors with close relevance were combined, generating a list of 40 factors. For example, “time required to select, purchase, and install the eHealth system”, “time involved in learning to use the eHealth system and additionally required to become familiar with the system operation”, and “the degree to which use of the innovation is perceived as being time consuming” were all grouped to “time cost”.
Figure 1.
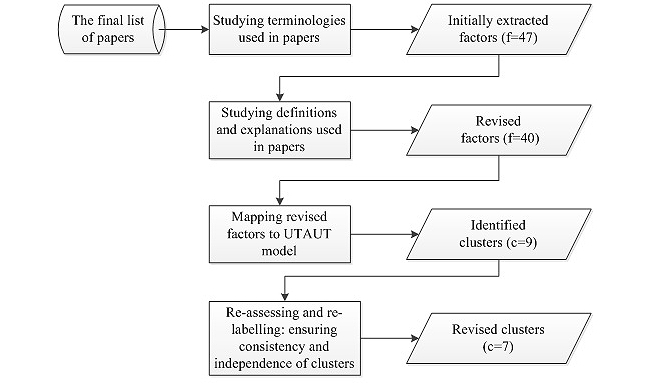
Data analysis process. f=number of factors; c=number of clusters.
Based on the perceived commonality of the themes, the 40 factors were analyzed and organized according to the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) by Venkatesh et al [21]. The UTAUT set out to integrate the fragmented theory and research on individual acceptance of information technology into a unified theoretical model, which highlights the importance of contextual analysis in developing strategies for technology implementation within organizations. This model accounts for 70% of the variance in usage intention—a substantial improvement over any of the original 8 models and their extensions. Within the UTAUT, 3 core constructs that impact on behavioral intention, and consequently use behavior, are performance expectancy, effort expectancy, and social influence, whereas the other core construct facilitating conditions has a direct impact upon use behavior. Four moderators (ie, gender, age, voluntariness of use, and experience) have also been incorporated in the UTAUT. Apart from the 4 core constructs and 4 moderators, another cluster of eHealth adoption factors, which could not be mapped against the UTAUT, was identified. Accordingly, the factors were initially grouped into 9 clusters (Figure 1).
To search for convergence among multiple sources of information and methods of data collection and analysis, a validity procedure was applied [22,23]. First, the eHealth adoption factors were reanalyzed within and across the clusters to ensure consistency and independence. The factors were regrouped into 7 clusters:
health care provider characteristics (eg, IT experience and knowledge, gender, age, and years in practice)
medical practice characteristics (eg, practice size and teaching status)
voluntariness of use
performance expectancy (eg, perceived usefulness and needs)
effort expectancy (eg, perceived ease of use)
social influence (eg, subjective norm)
facilitating or inhibiting conditions (eg, legal concerns)
The clusters were then given labels and reviewed once more for consistency. Reassessment and relabelling were performed for some papers. This step was repeated until a consensus was reached on the labels for clusters. In the final analysis, papers were reassigned to appropriate clusters. The resulting clusters represented another level of abstraction.
Results
Characteristics of Selected Studies
This section presents the results of statistical analyzes on the characteristic data extracted from the 93 papers, including: (1) the growth of publications by years, (2) distribution by geographical areas, (3) types of research methodologies employed, (4) eHealth applications studied, (5) health care settings selected, and (6) study participants.
Growth of Publications
Figure 2 shows the growth in the publications. The growth represented by the curve was not linear, with a dramatic rise in the number of papers published after 2005.
Figure 2.
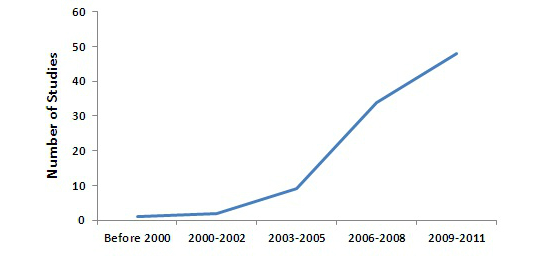
Growth of publications (based on our selected articles).
Geographical Areas
The majority of the studies (72/93, 77%) were conducted in North America, followed by Europe (9/93, 10%), and Asia (7/93, 8%).
Research Methodologies
Quantitative methodology was predominately used by 57/93 studies. The number was nearly twice as large as that of qualitative studies.
eHealth Applications
The 93 papers addressed a wide range of eHealth applications. 57 targeted the EHR/EMR, which was defined as computerized medical information systems that collect, store, and display patient information [24]. Telemedicine/Telehealth was the second most popular application studied (addressed by 7/93 studies). Telemedicine frequently referred to the use of a wide array of technologies to deliver a range of medical services to persons at some distance from a health care provider [25]. The remnant studies examined the acceptance of other eHealth applications such as Intensive Care Information System (ICIS) [26], e-discharge which helps inpatient physicians to track pending tests at hospital discharge [27], Anesthesia Information Management System (AIMS) [28], and electronic logistics information system [29].
Health Care Settings
The majority of the studies were conducted in hospitals and office-based clinics (primary care). In some studies, multiple health care settings of different types were chosen to examine the eHealth acceptance issue. For example, Jha et al used survey data from stratified random sample of all medical practices in Massachusetts in 2005 to determine rates of EHR adoption and perceived barriers to adoption [30].
Study Participants
The majority of the studies (ie, 68/93) focused on physicians. Nurses and other health workers were recruited in 25 research projects on eHealth adoption and acceptance.
eHealth Acceptance Factors
Through the data analysis and validation process, 40 factors were identified to be influential to the health care providers’ acceptance of eHealth and grouped into 7 clusters (Figure 3 and Table 2). A brief description of each cluster is provided below.
Figure 3.
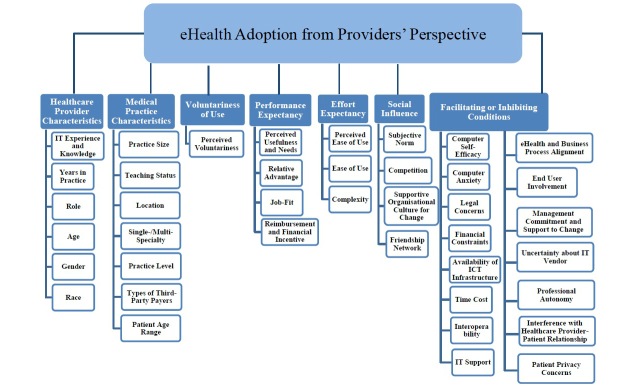
eHealth acceptance factors and clusters.
Table 2.
eHealth acceptance factors under 7 clusters.
| Cluster and factors | Definitions and citations | |
| Health care provider characteristics | ||
|
|
IT experience and knowledge | Generic IT skills (eg, typing skills) and experience [24,30-47] Those who had little experience with computers were challenged by the process of learning how to use the computer in addition to learning the software [43] Previous experience of computer use in medical practice or training in using particular eHealth systems [48-56] Respondents with an electronic health record (EHR) were more likely to e-prescribe than those who did not have an EHR, and to have patients take a computer-generated prescription to the pharmacy [55] |
|
|
Years in practice | Total years in practice since medical school graduation [32,48,57-61] Based on the comments offered by those in practice for longer than 25 years in our study, it did not make sense to invest time or money at this point in their careers [32] |
|
|
Role | Variation between physicians and other health professionals [53] Physicians use most of the advanced features more than nonphysicians [53] Variation between specialists and others [59,62,63] high-end specialists, such as obstetrician-gynecologists, are less likely to be using EHR in their practice [63] |
|
|
Age | Physical age [36,39,46,59,61,64-67] EMR use was inversely associated with physician age [65] |
|
|
Gender | Biological sex [39] Females were less likely to use PDAs [39] |
|
|
Race | A group of people of common ancestry, distinguished from others by physical characteristics [39] African American and Hispanic physicians were more likely than Caucasian to indicate routine PDA use; Asian physicians reported using email with patients significantly less frequently than their Caucasian counterparts [39] |
| Medical practice characteristics | ||
|
|
Practice size | Number of physicians in the medical practice [36,39,48,57,58,60,61,65,67-72] Physicians in practices with 11 or more physicians were most likely to use any EMR system, whereas physicians in solo practice were least likely to use EMRs [65] Number of patient visits [24,32,61,72,73] who saw fewer than ten patients per day, reviewed fewer than 20 medical records per day and handled fewer than ten calls daily, were statistically less likely to want to use a computer during a consultation; Those seeing fewer than ten patients daily were the most receptive to the use of handwriting [32] |
|
|
Teaching status | Practices affiliated with academic institutions [58,70-72] There was a statistically significant association between presence of students and residents in a practice and the practice’s use of an her [71] |
|
|
Location | The medical practice in a rural setting or urban setting [40,61,68,72-74] urban settings were significantly more likely to have adopted AIMS [72] |
|
|
Single/Multi-specialty | Difference between those in a single-specialty practice and in a multi-specialty practice [39,65,66,68,75] those in a multi-specialty group were more likely than those in a single specialty practice to routinely use EHRs [39] |
|
|
Practice level | Distinctions between Primary, Secondary and Tertiary health care [36,58,60] physicians whose practice consisted of a specialty other than primary care were more likely to use an EHR [60] |
|
|
Types of third-party payers | Proportion of patients who are privately insured, Medicaid, Medicare, or uninsured [48,66,73,76] Physicians with the highest percentage of Medicaid patients in their practices were significantly less likely to indicate using an EHR system when compared with those in the low-volume Medicaid group [76] |
|
|
Patient Age Range | The age range of served patients’ [67] doctors who treat HVE a were significantly less likely to adopt EHR [67] |
| Voluntariness of use | ||
|
|
Perceived voluntariness | The degree to which use of the innovation is perceived as being voluntary, or of free will [77] Perceived voluntariness had a negative causality on behavioral intention to use telemedicine. These findings contradict those from prior IS literature that found a positive relation between voluntariness of use and intention to adopt [77] |
| Performance expectancy | ||
|
|
Perceived usefulness and needs | The degree to which a health care provider believes that using the eHealth system would enhance his or her clinical or non-clinical job performance [24,25,28,29,33,35,36,38,41,43,46,50,56,75,77-91] Perceived needs of adopting the eHealth system [42,79,92-94] Participants from private hospitals or who owns a private practice reported that most of their patients are one-time customers and they do not expect them to come back. For private hospitals, about 30% of their patients are from out of the state (mostly from near towns and villages). Therefore, they do not keep their past medical records [93] |
|
|
Relative advantage | The degree to which using an innovation is perceived as being better than using its precursor of practices [5,45,59-61,72,93,95,96] physicians who used electronic prescribing were significantly more likely to view it as saving time than those who have not adopted the technology [5] |
|
|
Job-fit | How the capabilities of the eHealth system enhance a health care provider’s clinical job performance [24,40,97] no mechanism of alerting inpatient physicians that finalized test results were available for viewing (eg, by email or by an alert in the inpatient computer system [97] |
|
|
Reimbursement and financial incentive | The degree of a health care provider’s perception of uncertainty over return on monetary investment [5,24,26,31,40,73,86,90,91,95,98] Availability of financial reward for a health care provider’s time investment in learning and using the eHealth system [36,54,70,86,92,99] the availability of incentives for adoption of HIT were more likely to have EHRs than practices without such incentives [70] |
| Effort expectancy | ||
|
|
Perceived Ease of use | The degree to which a health care provider believes that using the eHealth system would be free of effort [5,25,28,29,38,40,46,47,52,54,56,68,74,75,81,84,87,88,90] co-existence of paper and electronic records at the transition period, as an important barrier to EMR adoption [74] |
|
|
Ease of use | The degree to which using the eHealth system is perceived as being difficult to use [5,27,28,35,41,45,46,52-54,64,77,84-86,89,91,97,100-103] a perception that technical system deficiencies reduce the quality of clinical routines can result users’ resistance [103] Location of ICT equipment for convenient use of the eHealth system [41,45,49,96,101,102] Sometimes the physician practice does not have appropriate equipment to facilitate use of the e-Prescribing system as part of the existing workflow. For example, if they do not have a handheld device or computer in the examination room, the busy clinician needs to use a PC outside the examination room, adding an extra step to the workflow [49] |
|
|
Complexity | The degree to which the eHealth system is perceived as relatively difficult to understand and use [24,26,35,37,45,46,54,79,84,86,89,93,96,100,101] this study indicated that the EMR systems are very complex and difficult to learn, and this affects their attitude towards using the EMR systems [93] |
| Social influence | ||
|
|
Subjective norm | The health care provider’s perception that most people who are important to him or her thinks he or she should or should not adopt the eHealth system in question [40,59,77,91] Patient resistance or not wanting their physicians to use EHR [40] |
|
|
Competition | Perceived competitive advantage with eHealth [48,86,94] adopt mobile technologies to gain a competitive advantage; adopting IS creates a competitive advantage by giving businesses new ways in which to outperform their rivals [94] |
|
|
Supportive organizational culture for change | Leadership and presence of champions for the eHealth system adoption within a health care setting [24,35,38,43-45,74,79,86,96,104] Health care professionals were likely to accept and participate in the process of eHealth adoption when the programs were introduced and promoted by a peer with considerable authority and influence and familiarity with the practices [79] The degree of a health care provider’s perception of organizational culture (eg, learning culture) supportive to eHealth adoption [33,105] The culture of the organization, including its supportive elements, influences both implementation and persistence of the work innovation [33] |
|
|
Friendship network | Personal intimacy and interactions with personal friends [47] Social influence affecting physician adoption of EHR was predominantly conveyed through interactions with personal friends rather than interactions in professional settings [47] |
| Facilitating or inhibiting conditions | ||
|
|
Computer self-efficacy | A health care provider’s self-judgment of his or her ability to use the eHealth system to accomplish clinical jobs or tasks [46,48,67,77,86] |
|
|
Computer anxiety | Evoking anxious or emotional reactions when it comes to adopting the eHealth system [24,33,40,77,80,92,106] They are concerned that under certain circumstances, or as time passes, the systems will reach their limitations, become obsolete and will no longer be useful [24] |
|
|
Legal concerns | The availability of the policy, regulation, and protocol supportive to using the eHealth system [31,54,74,78,79,82,93,95] Regulation regarding sharing of clinical information between the various EMR users across settings of care could represent a complex issue. During interviews, some respondents expressed concern with respect to the application of the law related to patients’ consent in the context of EMR implementation [74] |
|
|
Financial constraints | The degree of a health care provider’s perception of high monetary cost for adopting the eHealth system (ie, start-up costs and ongoing maintenance costs) and of the availability of financial resources to cover the cost [5,25,27,28,30-33,35,37,39,41,50,52,53,58,60,62,69,71-75,79,80,85-87,91,93,94,107-110] respondents noted the lack of capital to invest in EHRs as an important or very important barrier to adoption [73] |
|
|
Availability of ICT infrastructure | The degree of a health care provider’s perception of the availability of ICT infrastructure required for using the eHealth system [24,35,38,49,51,79,81,91,107] |
|
|
Time cost | Time required to select, purchase, and install the eHealth system [5,24,37,40,59,61,86,90] Implementing an EMR means switching from paper-based to electronic based systems, and this involves transferring records between the two systems [24] Time involved in learning to use the eHealth system and additionally required to become familiar with the system operation [25,28,31,32,37-39,41,44,46,50,53,55,57,60,62,71,72,74,85,87,91,92,109,110] the time and effort involved in learning to use these technologies as a significant barrier [31] The degree to which use of the innovation is perceived as being time consuming [24,35,84,86,90,93,97,99-101] takes too much time to enter data in real time [93] |
|
|
Interoperability | The degree of a health care provider’s perception of the ability of the eHealth system to exchange and use relevant clinical data within and across the health care setting [24,26,31,32,38,49,72,73,86,91,92,103,104] Lack of ability to exchange clinical data with laboratories and hospitals is a major barrier for smaller physician practices [31] |
|
|
IT support | The degree of a health care provider’s perception of the availability of experienced IT personnel for technical support (eg, troubleshooting emergent problems during actual usage of the eHealth system, and providing instructional and/or hand-on support to users before and during usage) [24,26,28,30,31,34-38,54,57,72,74,79,81,84,91,94,100] the provision of good maintenance and user support systems greatly increases user acceptance of a new system [84] The degree of a health care provider’s perception of the adequacy of training for the usage of the eHealth system [24,27,35,38,41,43,44,50,53,71,75,78,79,92,100,103,108] This study found that inadequate training limits EMR utilization [108] |
|
|
eHealth and business process alignment | The degree of a health care provider’s perception of the fitness of the eHealth system into the clinical workflow [29,32,77,96,97,99,103] |
|
|
End user involvement | The involvement of end users in the planning and implementation process of the eHealth system [24,38,75,83,84,86-88,103,104] Clinicians’ resistance was also related to whether or not they had been involved in the design and implementation process [103] |
|
|
Management commitment and support to change | The presence of management commitment and availability of management support for adoption of the eHealth system [24,33,45,75,79,81,82,87,88,91,92,103,109] the implementers’ responses were supportive and addressed the issues related to the real object of resistance; the severity of resistance decreased [109] |
|
|
Uncertainty about IT vendor | The degree of a health care provider’s perception of the availability of reputable and trustworthy external IT service providers in the market [24,29,49,52,106] |
|
|
Professional autonomy | The degree to which using the eHealth system is perceived by a health care provider as losing professional control over the conditions, processes, procedures, or content of his or her work according to the individual judgment in the application of his or her profession's body of knowledge and expertise [24,42,75,86-89,91,110,111] With the implementation of EMRs, physicians are concerned about the loss of their control of patient information and working processes since these data will be shared with and assessed by others. Physicians’ perceptions of the threat to their professional autonomy are very important in their reaction to EMR adoption [24] |
|
|
Interference with health care provider-patient relationship | The degree to which using the eHealth system is perceived as interfering the health care provider-patient relationship during their encounter [24,33,36,46,50,75,86-88,91,92,112] physicians who value a close patient relationship have less positive attitudes about the EMR [33] |
|
|
Patient privacy concerns | The degree of a health care provider’s perception of the security of patient information and protection of patient privacy [24,30,31,40,79,89,111,112] |
ahigh volume of elderly
A health care provider’s characteristics included his/her information technology (IT) experience and knowledge, years in medical practice, professional role, age, gender, and race. Characteristics in relation to a health care provider’s medical practice included the practice size, teaching status, location, single or multi-specialty, practice level, types of third party payers, and patient age range. Voluntariness of use was defined as “the degree to which use of the innovation is perceived as being voluntary or of free will” [21]. Performance expectancy was defined as the degree to which a health care provider believes that using the eHealth system will help him or her to attain gains in job performance [21]. It included the perceived usefulness and needs, relative advantage, job-fit, and reimbursement and financial incentive. Effort expectancy was defined as the degree of ease associated with the use of the eHealth system [21]. It included perceived ease of use, ease of use, and complexity. Social influence was defined as the degree to which a health care provider perceives that important others believe he or she should use the new eHealth system [21]. It included the subjective norm, competition, supportive organizational culture for change, and friendship network. Facilitating or inhibiting conditions were defined as the degree to which a health care provider believes that an organizational and technical infrastructure exists to support use of the eHealth system [21]. It included the computer self-efficacy, computer anxiety, legal concerns, financial constraints, availability of ICT infrastructure, time cost, eHealth interoperability, IT support, eHealth and business process alignment, end user involvement, management commitment and support to change, uncertainty about IT vendor, professional autonomy, interference with the health care provider and patient relationship, and patient privacy concerns.
Discussion
Comparative and Gap Analysis
Of the 93 papers, 57 examined the adoption/acceptance issue of EHR/EMR. EHR/EMR is a repository of health information in relation to a subject of care (ie, patient) in a computer processable form [113]. Li et al explained that electronic patient records form the core of any other eHealth applications and thus the success of these is very much dependent on the EHR/EMR adoption [114]. Although EHR/EMR can be utilized by all groups of health care providers (eg, physicians, nurses, and pharmacists), physicians were study participants among an overwhelmingly large number of publications.
After 2002-2004, there was a sharp increase in the number of publications. A majority of these studies were conducted in the United States. According to Burt et al [115], EHR adoption in the United States was significantly low until 2005, with less than 18% of physicians used EHR at their office. After 2005, there was a great increase in EHR adoption levels across the United States [115], making more health care settings available for eHealth acceptance research.
Most of the 93 studies used a quantitative research methodology to measure eHealth adoption/acceptance variables and test hypotheses. A small percentage applied models or theories on individual acceptance of information technology (eg, Technology Acceptance Model, TAM [116-118]). The results supported the models in predicting the adoption behavior in the health care context. The most applied model was the TAM, which proposed a method of evaluating user acceptance through his/her beliefs, attitudes, intentions, and actual technology adoption behavior. Within these studies [25,29,41,42,75,77,79,81,83-85,87,88,102], the factors influential to health care providers’ acceptance of eHealth included their perceived usefulness and needs, perceived ease of use, and all of the facilitating or inhibiting conditions.
Few studies (eg, [41]) have successfully tested the applicability of the UTAUT model by Venkatesh et al [21]. Using the definition of the UTAUT constructs, we analyzed and organized the eHealth acceptance factors that we found. The mapping work demonstrated that the UTAUT model is a useful framework for applying and organizing literature, which is of great benefit to readers interested in learning more on the topic [119]. Nevertheless, it was found that half of the health care provider characteristics (years in practice, role, and race) as well as medical practice characteristics identified from this literature review have not yet been covered in the UTAUT. Further, some studies also showed significant correlations among the identified factors. Perceived usefulness had the strongest impact on health care providers’ behavior intention [88], whereas their perceived usefulness was influenced by the perceived ease of use, eHealth and business process alignment, end user involvement, management commitment and support to change, health care provider-patient relationship, and IT experience and knowledge [25,28,33,56,77,83,86-88]. The variance of the perceived ease of use was associated with the computer self-efficacy, end user involvement, management commitment and support to change, as well as health care provider-patient relationship [77,88]. These correlations have not been incorporated in the UTAUT. Our efforts to map eHealth acceptance research results against the UTAUT model suggested that health care settings could potentially extend theories on information technology adoption due to their complex contextual dynamics.
In some of the papers, significant correlations were not necessarily found between acceptance factors on the list (particularly those of individual characteristics and medical practice characteristics) and health care providers’ usage intention or actual use of eHealth. Chavis’s study [105], for example, did not demonstrate a significant positive correlation between individual characteristics (ie, job role and age) and technology adoption. This result can be explained with the UTAUT model: the age acts as a moderator rather than a factor directly impacting upon the behavioral intention or use behavior. Russell et al found that health care providers in large practices were not more likely to use an EMR [112]. Others [24,40,57,69,120] argued against that, suggesting that larger practices tended to “have access to the potentially greater resources” (financial and human resources) required for the eHealth system delivery and adoption, and have extensive internal IT assistance and training.
Apart from the contradicting findings among these studies, some acceptance factors can also be context sensitive. Given that most of the 93 studies were conducted in the United States, the types of third-party payers (which is by definition the proportion of patients who are privately insured, Medicaid, Medicare, or uninsured), for example, reflects the health insurance scheme specifically in the United States context. In the future, further studies particularly in health care settings of other countries, are required in order to improve the understanding of eHealth adoption phenomenon in a global context, as well as to extend the theory and research on individual acceptance of information technology.
Limitations
Here are a few major limitations of this literature review. Although efforts were made to include all research papers on health care providers’ acceptance of various eHealth applications, some may not have been identified due to selected search phrases. In order to at least include those papers, which can help us increase the validity of the findings, the supplementary search keywords “EHR” and “EMR” were both used as previously discussed.
The review was limited also due to the selection of the databases. Although they are the outlets that were deemed most likely to publish eHealth acceptance-related work, some papers may have been missed. We tried to compensate for this potential loss by ensuring that all selected databases were searched to their full extent.
Mapping the identified eHealth adoption factors against the UTAUT model can be subjective. We attempted to maximize the accuracy and appropriateness of our mapping work by applying the validity procedure.
Practical Implications
To Decision Makers at Health Care Settings
The study results could help decision makers at the health care setting systematically understand facilitating forces and inhibiting factors influential to the health care providers’ acceptance of eHealth, and thus proactively introduce interventions for the adoption success. For example, health care providers may lack the adequate computer skills to use eHealth systems or had previous negative technology experiences [49,121]. IT support before, during, and after initial eHealth implementation can provide a smooth transition to their reengineered job routine and overcome their technology phobia, hence facilitating eHealth acceptance and use (eg, [27,78,81]). IT support includes, but is not limited to training, provision of guideline documents, and troubleshooting [50,123,124].
Training can take various forms such as group training or one-on-one training, which is ideal in all circumstances [122]. One-on-one training needs to set expectations, teach health care providers about the eHealth system features, customize the technology for each particular specialty, and help them to integrate the system (eg, e-Prescribing) into their medical practice workflow [49].
Guideline documents as a knowledge source promote authentic translation of domain knowledge and reduce the overall complexity of the implementation task [123]. Each care provider should be provided with a manual containing step-by-step instructions for the system’s use [124].
Real time troubleshooting (especially through internal resources) facilitates the effective use of the eHealth system and becomes essential to the system success in terms of actual usage [49,124]. Health care providers need to know how to access it when required [124]. A feedback mechanism (eg, online help) allows health care providers to document a problem that they are having with the system and then to receive prompt feedback [13,125]. Compared with external support services from the IT vendor, internal IT staff is more familiar with the work environment and related needs, and may respond more quickly to an urgent request [124].
Another example is eHealth/business process alignment. Workflow is associated with routine processes, characterized by a fixed definition of tasks and an order of execution [126]. The eHealth system needs to be designed in close collaboration with health care providers so that it truly assists their medical practice [122,127,128]. The collaboration between IT vendors and clinical sites is to understand the site's workflow and determine the most suitable IT solution [124,129]. After the workflow is analyzed thoroughly with health care providers’ involvement, their participatory process is also essential to fine-tune the system’s capabilities [128]. Extensive software testing of the vendor's claims for the baseline functionality and system adaptability to local needs is critical before the implementation, as health care providers' frustration from software problems can promptly escalate and result in resistance to continue using the system [128].
To Policy Makers at the Health Sector
By synthesizing the evidence from the literature, our study may also assist policy makers at the health sector in refining or developing relevant policies to push eHealth innovation. eHealth adoption and ongoing maintenance requires a large capital investment [131-133]. While the government in some cases funds the start-up cost of an eHealth project (eg, the EMRX system in Singapore), health care providers may still need to undertake the operation and enhancement cost of their system [8]. In small or independent medical practices, there is lack or absence of internal capacity for system maintenance; eHealth vendors alternatively provide all these services but often charge high fees. Due to financial constraints, system maintenance represents a vulnerable spot for the entire effort of eHealth and many practices underperform [130]. To address this challenge, the development of programs such as zero-interest or revolving loans that make capital available to health care provider groups at low interest rates is essential, particularly in small or independent practices [48,106,130].
Another important issue is interoperability. Bates commented that the interoperability between eHealth applications and seamless and reliable clinical information exchange is a key to making EHR use a cornerstone of practice [130]. Even if physicians started to use an EHR system, they might still be unable to seamlessly share some other patient information (such as laboratory and radiology results stored in Laboratory Information Systems, LIS, and Picture Archiving and Communication Systems, PACS) for clinical decisions [130]. According to a recent analysis, $77.8 billion USD could be saved annually by interoperable clinical information exchange among key stakeholders in the health care delivery system [131]. The government should take stronger position to create a database of eHealth vendors whose products meet certain standards and enable clinical information exchange and to certify these products [31,82]. The certification effort would also minimize health care providers’ uncertainty over the selection of a viable and sustainable product from hundreds of IT vendors in the market [68,106].
Legal and regulatory changes can be required to address eHealth adoption related issues [130,132]. For example, the Medicines Regulations (1984) and the Misuse of Drugs Regulations (1977) in New Zealand, which governs respectively the form of medication prescriptions and controlled substances, stated that indelible text and practitioners’ handwritten signature was required for a legitimate prescription. To facilitate the adoption of electronic prescribing and dispensing of medicines, the Health Department of Commonwealth has amended the National Health (Pharmaceutical Benefits) Regulations [8]. These amendments came into effect from March 1, 2007 and the electronic prescribing and dispensing process has been additional and separate to the already existing paper-based process. The states and territories have continuously been taking steps to remove any legal barriers to the adoption of the electronic process in each jurisdiction.
Concluding Remarks
In this 4-step literature review, 40 factors were identified to be influential to health care providers’ acceptance of eHealth and organized in accordance with the UTAUT model. The findings may help decision makers at health care settings and policy makers at the health sector to better understand eHealth adoption issues and take action to facilitate the eHealth innovation process. Our work also suggests further studies to extend theories on information technology adoption.
Abbreviations
- AIMS
Anesthesia Information Management System
- eHCD
eHealth for Health Care Delivery
- EHR
electronic health records
- EMR
electronic medical records
- HVE
high volume of elderly
- ICIS
Intensive Care Information System
- ICT
information and communication technologies
- IT
information technology
- LIS
Laboratory Information Systems
- PACS
Picture Archiving and Communication systems
- TAM
Technology Acceptance Model
- UTAUT
Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology
- WHO
World Health Organization
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.World Health Organization. [2013-03-21]. Global tuberculosis control: surveillance, planning, financing: WHO report 2008 http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/2008/en/index.html.
- 2.New Delhi: Central TB Division, DGHS, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. [2013-03-21]. RNTCP Status report 2010 http://tbcindia.nic.in/pdfs/TB%20India%202010.pdf.
- 3.Silber D. European Commission, Information Society, eHealth Conference. Atlanta, Belgium: 2003. [2013-03-21]. The case for ehealth http://ec.europa.eu/information_society/eeurope/ehealth/conference/2003/doc/the_case_for_eHealth.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Grieger DL, Cohen SH, Krusch DA. A pilot study to document the return on investment for implementing an ambulatory electronic health record at an academic medical center. J Am Coll Surg. 2007 Jul;205(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.02.074. http://www.sciencedirect.com.viviena.library.unsw.edu.au/science/journal/10727515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schade CP, Sullivan FM, de Lusignan S, Madeley J. e-Prescribing, efficiency, quality: lessons from the computerization of UK family practice. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006;13(5):470–5. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M2041. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16799129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Thakkar M, Davis DC. Risks, barriers, and benefits of EHR systems: a comparative study based on size of hospital. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2006;3:5. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/18066363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Eysenbach G. What is e-health? J Med Internet Res. 2001;3(2):E20. doi: 10.2196/jmir.3.2.e20. http://www.jmir.org/2001/2/e20/ [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li J, Land L, Ray P. Humanitarian Technology Challenge (HTC)-electronic health records perspective. A Report of Joint Project of IEEE and United Nations Foundation. 2008 [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vishwanath A, Scamurra SD. Barriers to the adoption of electronic health records: using concept mapping to develop a comprehensive empirical model. Health Informatics J. 2007 Jun;13(2):119–34. doi: 10.1177/1460458207076468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.O'Connell RT, Cho C, Shah N, Brown K, Shiffman RN. Take note(s): differential EHR satisfaction with two implementations under one roof. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2004;11(1):43–9. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1409. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=14527978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Patterson ES, Nguyen AD, Halloran JP, Asch SM. Human factors barriers to the effective use of ten HIV clinical reminders. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2004;11(1):50–9. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1364. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=14527974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wallis K, Rice RE. Technology and health information privacy: consumers and the adoption of digital medical records technology. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Saleem JJ, Patterson ES, Militello L, Render ML, Orshansky G, Asch SM. Exploring barriers and facilitators to the use of computerized clinical reminders. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2005;12(4):438–47. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1777. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15802482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wickramasinghe NS, Fadlalla AMA, Geisler E, Schaffer JL. A framework for assessing e-health preparedness. Int J Electron Healthc. 2005;1(3):316–34. doi: 10.1504/IJEH.2005.006478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ford EW, Menachemi N, Phillips MT. Predicting the adoption of electronic health records by physicians: when will health care be paperless? J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006;13(1):106–12. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1913. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16221936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lehman WE, Greener JM, Simpson DD. Assessing organizational readiness for change. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2002 Jun;22(4):197–209. doi: 10.1016/s0740-5472(02)00233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kitchenham B. 2004. [2013-03-27]. Procedures for performing systematic reviews http://www.researchgate.net/publication/228756057_Procedures_for_performing_systematic_reviews.
- 18.Kitchenham B, Pearl Brereton O, Budgen D, Turner M, Bailey J, Linkman S. Systematic literature reviews in software engineering - A systematic literature review. Information and Software Technology. 2009;51:7–15. doi: 10.1016/j.infsof.2008.09.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ghapanchi AH, Aurum A. Antecedents to IT personnel's intentions to leave: A systematic literature review. J Syst Softw. 2011;84:238–249. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.09.022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li J, Land L, Ray P. Evaluation criteria for frameworks in e-health domain. The 15th American Conference on Information Systems; 2009 6-9 August; San Francisco, California United States. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Venkatesh V, Morris MG, Davis GB, Davis FD. User acceptance of information technology: toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly. 2003;27:425–478. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Patton MQ. Qualitative research and evaluation methods. Thousand Oaks, Calif: Sage Publications; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Creswell JW, Miller DL. Determining validity in qualitative inquiry. Theory into Practice. 2000;39(3):124–131. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Boonstra A, Broekhuis M. Barriers to the acceptance of electronic medical records by physicians from systematic review to taxonomy and interventions. BMC Health Serv Res. 2010;10:231. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-10-231. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6963/10/231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Djamasbi S, Fruhling AL, Loiacono ET. The influence of affect, attitude and usefulness in the acceptance of telemedicine systems. Journal of Information Technology Theory and Application. 2009;10(1):41–58. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Colpaert K, Vanbelleghem S, Danneels C, Benoit D, Steurbaut K, Van Hoecke S, De Turck F, Decruyenaere J. Has information technology finally been adopted in Flemish intensive care units? BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010;10:62. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-62. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6947/10/62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pagliari C, Donnan P, Morrison J, Ricketts I, Gregor P, Sullivan F. Adoption and perception of electronic clinical communications in Scotland. Inform Prim Care. 2005;13(2):97–104. doi: 10.14236/jhi.v13i2.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tsiknakis M, Kouroubali A. Organizational factors affecting successful adoption of innovative eHealth services: a case study employing the FITT framework. Int J Med Inform. 2009 Jan;78(1):39–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tung FC, Chang SC, Chou CM. An extension of trust and TAM model with IDT in the adoption of the electronic logistics information system in HIS in the medical industry. Int J Med Inform. 2008 May;77(5):324–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2007.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jha AK, Bates DW, Jenter C, Orav EJ, Zheng J, Cleary P, Simon SR. Electronic health records: use, barriers and satisfaction among physicians who care for black and Hispanic patients. J Eval Clin Pract. 2009 Feb;15(1):158–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2008.00975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Anderson JG. Social, ethical and legal barriers to e-health. Int J Med Inform. 2007;76(5-6):480–3. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2006.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Arvary G. A primary care physician perspective survey on the limited use of handwriting and pen computing in the electronic medical record. Informatics in Primary Care. 2002;10(3):161–72. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dansky KH, Gamm LD, Vasey JJ, Barsukiewicz CK. Electronic medical records: are physicians ready? J Healthc Manag. 1999;44(6):440–54; discussion 454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Guida K, LaVenture M. EHR adoption and use. Results from the 2010 Minnesota ambulatory clinic survey. Minn Med. 2011 Apr;94(4):33–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Holden RJ. Dissertation International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering. Ann Arbor, MI, USA: Proquest, Umi Dissertation Publishing; 2010. Beliefs about health information technology: an investigation of hospital physicians' beliefs about and experiences with using electronic medical records; p. 4413. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kaushal R, Bates DW, Jenter CA, Mills SA, Volk LA, Burdick E, Tripathi M, Simon SR. Imminent adopters of electronic health records in ambulatory care. Inform Prim Care. 2009;17(1):7–15. doi: 10.14236/jhi.v17i1.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ludwick DA, Doucette J. Primary care physicians' experience with electronic medical records: barriers to implementation in a fee-for-service environment. International Journal of Telemedicine and Applications. 2009 doi: 10.1155/2009/853524. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2593889/pdf/IJTA2009-853524.pdf. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.McAlearney AS, Schweikhart SB, Medow MA. Organizational and physician perspectives about facilitating handheld computer use in clinical practice: results of a cross-site qualitative study. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2005 May;12(5):568–75. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1816. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15905482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Menachemi N, Brooks RG. EHR and other IT adoption among physicians: results of a large-scale statewide analysis. J Healthc Inf Manag. 2006;20(3):79–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Menachemi N, Langley A, Brooks RG. The Use of Information Technologies Among Rural and Urban Physicians in Florida. J Med Syst. 2007 Aug 2007;31(6):483–488. doi: 10.1007/s10916-007-9088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ruxwana NL, Herselman ME, Conradie DP. ICT applications as e-health solutions in rural healthcare in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. HIM J. 2010;39(1):17–26. doi: 10.1177/183335831003900104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tamblyn R, Huang A, Kawasumi Y, Bartlett G, Grad R, Jacques A, Dawes M, Abrahamowicz M, Perreault R, Taylor L, Winslade N, Poissant L, Pinsonneault A. The development and evaluation of an integrated electronic prescribing and drug management system for primary care. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006;13(2):148–59. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1887. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16357357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Terry AL, Thorpe CF, Giles G, Brown JB, Harris SB, Reid GJ, Thind A, Stewart M. Implementing electronic health records: Key factors in primary care. Can Fam Physician. 2008 May;54(5):730–6. http://www.cfp.ca/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18474707. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Terry AL, Giles G, Brown JB, Thind A, Stewart M. Adoption of electronic medical records in family practice: the providers' perspective. Fam Med. 2009;41(7):508–12. http://www.stfm.org/fmhub/fm2009/July/Amanda508.pdf. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Whittaker AA, Aufdenkamp M, Tinley S. Barriers and facilitators to electronic documentation in a rural hospital. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2009;41(3):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1547-5069.2009.01278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Whittaker L, Van Zyl J, Soicher AS. What is the point of the point-of-care? A case study of user resistance to an e-health system. Telemed J E Health. 2011;17(1):55–61. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2010.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zheng K, Padman R, Krackhardt D, Johnson MP, Diamond HS. Social networks and physician adoption of electronic health records: insights from an empirical study. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010;17(3):328–36. doi: 10.1136/jamia.2009.000877. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=20442152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Abdolrasulnia M, Menachemi N, Shewchuk RM, Ginter PM, Duncan WJ, Brooks RG. Market effects on electronic health record adoption by physicians. Health Care Manage Rev. 2008;33(3):243–52. doi: 10.1097/01.HMR.0000324904.19272.c2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Halamka J, Aranow M, Ascenzo C, Bates DW, Berry K, Debor G, Fefferman J, Glaser J, Heinold J, Stanley J, Stone DL, Sullivan TE, Tripathi M, Wilkinson B. E-Prescribing collaboration in Massachusetts: early experiences from regional prescribing projects. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006;13(3):239–44. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M2028. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16501174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ludwick D, Manca D, Doucette J. Primary care physicians' experiences with electronic medical records: implementation experience in community, urban, hospital, and academic family medicine. Can Fam Physician. 2010 Jan;56(1):40–7. http://www.cfp.ca/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=20090083. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Marques A, Oliveira T, Martins MFO. Adoption of medical records management system in European hospitals. ECIME; September 9-10; Lisbon, Portugal. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Randeree E. Exploring physician adoption of EMRs: a multi-case analysis. J Med Syst. 2007 Dec;31(6):489–96. doi: 10.1007/s10916-007-9089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rockswold PD, Finnell VW. Predictors of tool usage in the military health system's electronic health record, the Armed Forces Health Longitudinal Technology Application. Mil Med. 2010 May;175(5):313–6. doi: 10.7205/milmed-d-09-00286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Samoutis G, Soteriades ES, Kounalakis DK, Zachariadou T, Philalithis A, Lionis C. Implementation of an electronic medical record system in previously computer-naïve primary care centres: a pilot study from Cyprus. Inform Prim Care. 2007;15(4):207–16. doi: 10.14236/jhi.v15i4.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Siracuse M, Galt K, Drincic A, Bramble J, Fuji K, Paschal K. E-prescribing: Are Medicare incentive payments enough to encourage adoption by physicians? Journal of the American Pharmacists Association. 2010;50(2):249–250. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Vogel EW, Gracely EJ, Kwon Y, Maulitz RC. Factors determining the use of personal digital assistants among physicians. Telemed J E Health. 2009 Apr;15(3):270–6. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2008.0112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bramble JD, Galt KA, Siracuse MV, Abbott AA, Drincic A, Paschal KA, Fuji KT. The relationship between physician practice characteristics and physician adoption of electronic health records. Health Care Manage Rev. 2010;35(1):55–64. doi: 10.1097/HMR.0b013e3181c3f9ad. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Grant RW, Campbell EG, Gruen RL, Ferris TG, Blumenthal D. Prevalence of basic information technology use by U.S. physicians. J Gen Intern Med. 2006 Nov;21(11):1150–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.00571.x. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/16879417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Pizzi LT, Suh DC, Barone J, Nash DB. Factors related to physicians' adoption of electronic prescribing: results from a national survey. Am J Med Qual. 2005;20(1):22–32. doi: 10.1177/1062860604273775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Simon SR, Kaushal R, Cleary PD, Jenter CA, Volk LA, Orav EJ, Burdick E, Poon EG, Bates DW. Physicians and electronic health records: a statewide survey. Arch Intern Med. 2007 Mar 12;167(5):507–12. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.5.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tucker MT. Dissertation International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering. 2009. [2013-03-27]. Application of the diffusion of innovations theory and the health belief model to describe EMR use among Alabama family medicine physicians: A rural and urban analysis http://free-doc-lib.com/book/application-of-the-diffusion-of-innovations-theory-among-alabama.pdf.
- 62.Hoffman T. Computerworld. 2007. Mar 26, [2013-03-27]. What's Plaguing E-health? http://www.wpmassociates.com/healthcare/articles/plaguing_hit.html.
- 63.Menachemi N, Lee SC, Shepherd JE, Brooks RG. Proliferation of electronic health records among obstetrician-gynecologists. Qual Manag Health Care. 2006;15(3):150–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chiu TM, Eysenbach G. Stages of use: consideration, initiation, utilization, and outcomes of an internet-mediated intervention. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010;10:73. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-73. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6947/10/73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hing E, Hsiao CJ. Electronic medical record use by office-based physicians and their practices: United States, 2007. Natl Health Stat Report. 2010 Mar 31;(23):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Menachemi N, Powers TL, Brooks RG. Physician and practice characteristics associated with longitudinal increases in electronic health records adoption. J Healthc Manag. 2011;56(3):183–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Yeager VA, Menachemi N, Brooks RG. EHR adoption among doctors who treat the elderly. J Eval Clin Pract. 2010 Dec;16(6):1103–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2009.01277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Menachemi N. Barriers to ambulatory EHR: who are 'imminent adopters' and how do they differ from other physicians? Inform Prim Care. 2006;14(2):101–8. doi: 10.14236/jhi.v14i2.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Simon JS, Rundall TG, Shortell SM. Drivers of electronic medical record adoption among medical groups. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2005 Nov;31(11):631–9. doi: 10.1016/s1553-7250(05)31081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Simon SR, Kaushal R, Cleary PD, Jenter CA, Volk LA, Poon EG, Orav EJ, Lo HG, Williams DH, Bates DW. Correlates of electronic health record adoption in office practices: a statewide survey. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2007;14(1):110–7. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M2187. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17068351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Stream GR. Trends in adoption of electronic health records by family physicians in Washington State. Inform Prim Care. 2009;17(3):145–52. doi: 10.14236/jhi.v17i3.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Trentman TL, Mueller JT, Ruskin KJ, Noble BN, Doyle CA. Adoption of anesthesia information management systems by US anesthesiologists. J Clin Monit Comput. 2011 Apr;25(2):129–35. doi: 10.1007/s10877-011-9289-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Shields AE, Shin P, Leu MG, Levy DE, Betancourt RM, Hawkins D, Proser M. Adoption of health information technology in community health centers: results of a national survey. Health Aff (Millwood) 2007;26(5):1373–83. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.26.5.1373. http://content.healthaffairs.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17848448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Gagnon MP, Desmartis M, Labrecque M, Légaré F, Lamothe L, Fortin JP, Rancourt JF, Duplantie J. Implementation of an electronic medical record in family practice: a case study. Inform Prim Care. 2010;18(1):31–40. doi: 10.14236/jhi.v18i1.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Morton ME, Wiedenbeck S. EHR acceptance factors in ambulatory care: a survey of physician perceptions. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2010;7:1c. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/20697466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Menachemi N, Matthews MC, Ford EW, Brooks RG. The influence of payer mix on electronic health record adoption by physicians. Health Care Manage Rev. 2007;32(2):111–8. doi: 10.1097/01.HMR.0000267791.02062.3f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Kifle M, Payton FC, Mbarika V, Meso P. Transfer and adoption of advanced information technology solutions in resource-poor environments: the case of telemedicine systems adoption in Ethiopia. Telemed J E Health. 2010 Apr;16(3):327–43. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2009.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Cherry B, Carter M, Owen D, Lockhart C. Factors affecting electronic health record adoption in long-term care facilities. J Healthc Qual. 2008;30(2):37–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1945-1474.2008.tb01133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Baroud RM. Dissertation International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering. 2008. [2013-03-27]. How ready are the stakeholders in the Palestinian healthcare system in the Gaza strip to adopt e-health? http://dspace.ucalgary.ca/jspui/bitstream/1880/46329/1/Baroud_Thesis_2008.pdf.
- 80.Bennani A, Belalia M, Oumlil R. As a human factor, the attitude of healthcare practitioners is the primary step for the e-health: First outcome of an ongoing study in Morocco. Communications of the IBIMA. 2008;3(4):1943–7765. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Bhattacherjee A, Hikmet N. Reconceptualizing organizational support and its effect on information technology usage: evidence from the health care sector. Journal of Computer Information Systems. 2008;48(4):69–76. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Chang IC, Hwang H, Yen DC, Lian JW. Critical factors for adopting PACS in Taiwan: Views of radiology department directors. Decision Support Systems. 2006;42:1042–1053. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2005.08.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Ernstmann N, Ommen O, Neumann M, Hammer A, Voltz R, Pfaff H. Primary care physician's attitude towards the German e-health card project--determinants and implications. J Med Syst. 2009 Jun;33(3):181–8. doi: 10.1007/s10916-008-9178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Handy J, Hunter I, Whiddett R. Erratum. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2012 Sep;5(5):371–107. doi: 10.1177/1756283X10363751. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22973420. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Hewitt B. Exploring how security features affect the use of electronic health records. IJHTM. 2010;11(1/2):31–49. doi: 10.1504/IJHTM.2010.033273. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 86.McGinn CA, Grenier S, Duplantie J, Shaw N, Sicotte C, Mathieu L, Leduc Y, Légaré F, Gagnon MP. Comparison of user groups' perspectives of barriers and facilitators to implementing electronic health records: a systematic review. BMC Med. 2011;9:46. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-46. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1741-7015/9/46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Morton ME, Wiedenbeck S. A framework for predicting EHR adoption attitudes: a physician survey. Perspect Health Inf Manag. 2009;6:1a. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/20169013. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Morton ME. Dissertation International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA: Drexel University; 2009. [2013-03-28]. Use and acceptance of an electronic health record: factors affecting physician attitudes http://idea.library.drexel.edu/bitstream/1860/2905/1/Morton_Mary.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Rudin RS, Simon SR, Volk LA, Tripathi M, Bates D. Understanding the decisions and values of stakeholders in health information exchanges: experiences from Massachusetts. Am J Public Health. 2009 May;99(5):950–5. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.144873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Gans D, Kralewski J, Hammons T, Dowd B. Medical groups' adoption of electronic health records and information systems. Health Aff (Millwood) 2005;24(5):1323–33. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.24.5.1323. http://content.healthaffairs.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16162580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Vishwanath A, Scamurra SD. Barriers to the adoption of electronic health records: using concept mapping to develop a comprehensive empirical model. Health Informatics J. 2007 Jun;13(2):119–34. doi: 10.1177/1460458207076468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Fitzgerald G, Piris L, Serrano A. Identification of benefits and barriers for the adoption of e-health information systems using a socio-technical approach. 30th International Conference on Information Technology Interfaces; 2008 Jun 23-26; Cavtat/Dubrovnik, Croatia. 2008. pp. 601–606. [Google Scholar]
- 93.Gómez Reynoso JM, Tulu B. Electronic Medical Records Adoption Challenges in Mexico. AMIA 2007 Symposium Proceedings; 2007 Nov 10-14; CHICAGO IL, United States. 2007. p. 1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Hsiao S, Li Y, Chen Y, Ko H. Critical factors for the adoption of mobile nursing information systems in Taiwan: the nursing department administrators’ perspective. J Med Syst. 2008 Aug 2008;33(5):369–377. doi: 10.1007/s10916-008-9199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Al-Qirim NA. Teledermatology: the case of adoption and diffusion of telemedicine health Waikato in New Zealand. Telemed J E Health. 2003 Jun;9(2):167–77. doi: 10.1089/153056203766437507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Helitzer D, Heath D, Maltrud K, Sullivan E, Alverson D. Assessing or predicting adoption of telehealth using the diffusion of innovations theory: a practical example from a rural program in New Mexico. Telemed J E Health. 2003;9(2):179–87. doi: 10.1089/153056203766437516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Dalal AK, Poon EG, Karson AS, Gandhi TK, Roy CL. Lessons learned from implementation of a computerized application for pending tests at hospital discharge. J Hosp Med. 2011 Jan;6(1):16–21. doi: 10.1002/jhm.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Grigsby B, Brega AG, Bennett RE, Devore PA, Paulich MJ, Talkington SG, Floersch NR, Barton PL, Neal S, Araya TM, Loker JL, Krohn N, Grigsby J. The slow pace of interactive video telemedicine adoption: the perspective of telemedicine program administrators on physician participation. Telemed J E Health. 2007 Dec;13(6):645–56. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2007.0090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Halifax NV, Cafazzo JA, Irvine MJ, Hamill M, Rizo CA, McIssac WJ, Rossos PG, Logan AG. Telemanagement of hypertension: a qualitative assessment of patient and physician preferences. Can J Cardiol. 2007 May 15;23(7):591–4. doi: 10.1016/s0828-282x(07)70807-3. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/17534469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Granlien MF, Hertzum M, Gudmundsen J. The gap between actual and mandated use of an electronic medication record three years after deployment. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2008;136:419–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Hier DB, Rothschild A, LeMaistre A, Keeler J. Differing faculty and housestaff acceptance of an electronic health record. Int J Med Inform. 2005 Aug;74(7-8):657–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2005.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Ilie V, Slyke CV, Parikh MA, Courtney JF. Paper versus electronic medical records: the effects of access on physicians' decisions to use complex information technologies. Decision Sciences. 2009;40(2) doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5915.2009.00227.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Rahimi B, Vimarlund V, Timpka T. Health information system implementation: a qualitative meta-analysis. J Med Syst. 2008 Aug 2008;33(5):359–368. doi: 10.1007/s10916-008-9198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Sicotte C, Paré G, Moreault MP, Paccioni A. A risk assessment of two interorganizational clinical information systems. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006;13(5):557–66. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M2012. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16799130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Chavis VD. Dissertation International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences. 2010. [2013-03-27]. Organizational learning and large-scale change: adoption of electronic medical records http://udini.proquest.com/view/organizational-learning-and-large-goid:520286516/
- 106.Rao SR, Desroches CM, Donelan K, Campbell EG, Miralles PD, Jha AK. Electronic health records in small physician practices: availability, use, and perceived benefits. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2011 May 1;18(3):271–5. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2010-000010. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=21486885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Chattopadhyay S. A framework for studying perceptions of rural healthcare staff and basic ICT support for e-health use: an Indian experience. Telemed J E Health. 2010;16(1):80–8. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2009.0081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Elekwachi AO. Dissertation International Section A: Humanities and Social Sciences. Ann Arbor, MI, USA: ProQuest; 2008. Limitations to the utilization of electronic medical records by healthcare professionals: a case study of small medical practices; p. 793. [Google Scholar]
- 109.Lapointe L, Rivard S. Getting physicians to accept new information technology: insights from case studies. CMAJ. 2006;174(11) doi: 10.1503/cmaj.050281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Ross S. Results of a survey of an online physician community regarding use of electronic medical records in office practices. J Med Pract Manage. 2009;24(4):254–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Nash K. Urologists wary of mandatory EMR system. Urology times. 2009;37(5):34. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Russell SC, Spooner SA. Barriers to EMR adoption in internal medicine and pediatric outpatient practices. Tenn Med. 2004 Oct;97(10):457–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.ISO Technical Report. 2004. [2013-03-21]. Health informatics - Electronic health record – Definition, scope and context http://sl.infoway-inforoute.ca/downloads/infostand_V0.4_ISO_DTR_Defn_Scope_Context_e.pdf.
- 114.Li J, Land L, Ray P, Chattopadhyaya S. E-Health readiness framework from Electronic Health Records perspective. IJIEM. 2010;6(4):326. doi: 10.1504/IJIEM.2010.035626. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Burt CW, Hing E. Use of computerized clinical support systems in medical settings: United States, 2001-03. Adv Data. 2005 Mar 2;(353):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Davis F. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Quarterly. 1989;13:319–40. doi: 10.2307/249008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Davis FD, Bagozzi RP, Warshaw PR. User Acceptance of Computer Technology: A Comparison of Two Theoretical Models. Management Science. 1989 Aug 1989;35(8):982–1003. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.35.8.982. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Davis FD. User acceptance of information technology: system characteristics, user perceptions and behavioral impacts. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies. 1993 Mar 1993;38(3):475–487. doi: 10.1006/imms.1993.1022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Hennington AH, Janz BD. Information systems and healthcare XVI: physician adoption of electronic medical records: applying the UTAUT model in a healthcare context. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2007;19:60–80. [Google Scholar]
- 120.Mattocks K, Lalime K, Tate JP, Giannotti TE, Carr K, Carrabba A, Blum T, Meehan TP. The state of physician office-based health information technology in Connecticut: current use, barriers and future plans. Conn Med. 2007 Jan;71(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Kemper AR, Uren RL, Clark SJ. Adoption of electronic health records in primary care pediatric practices. Pediatrics. 2006 Jul;118(1):e20–4. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-3000. http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16818534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Ash JS, Bates DW. Factors and forces affecting EHR system adoption: report of a 2004 ACMI discussion. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2005;12(1):8–12. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1684. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15492027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Shiffman RN, Michel G, Essaihi A, Thornquist E. Bridging the guideline implementation gap: a systematic, document-centered approach to guideline implementation. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2004;11(5):418–26. doi: 10.1197/jamia.M1444. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15187061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Fullerton C, Aponte P, Hopkins R III, Bragg D, Ballard DJ. Lessons learned from pilot site implementation of an ambulatory electronic health record. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2006 Oct;19(4):303–10. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2006.11928188. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/17106488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Lee F, Teich JM, Spurr CD, Bates DW. Implementation of physician order entry: user satisfaction and self-reported usage patterns. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 1996;3(1):42–55. doi: 10.1136/jamia.1996.96342648. http://jamia.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=8750389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Xu L, Liu H, Wang S, Wang K. Modelling and analysis techniques for cross-organizational workflow systems. Syst. Res. 2009 May 2009;26(3):367–389. doi: 10.1002/sres.978. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Kamadjeu EM, Tapang EM, Moluh RN. Designing and implementing an electronic health record system in primary care practice in sub-Saharan Africa: a case study from Cameroon. Inform Prim Care. 2005;13(3):179–86. doi: 10.14236/jhi.v13i3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Scott JT, Rundall TG, Vogt TM, Hsu J. Kaiser Permanente's experience of implementing an electronic medical record: a qualitative study. BMJ. 2005 Dec 3;331(7528):1313–6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38638.497477.68. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/16269467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Darroch K, Ellis B. Development and use of integrated electronic records. Community Practitioner. 2003;76(2):53–5. [Google Scholar]
- 130.Bates DW. Physicians and ambulatory electronic health records. Health Aff (Millwood) 2005;24(5):1180–9. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.24.5.1180. http://content.healthaffairs.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16162561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Walker J, Pan E, Johnston D, Adler-Milstein J, Bates DW, Middleton B. The value of health care information exchange and interoperability. Health Aff (Millwood) 2005;Suppl Web Exclusives:W5–10. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.w5.10. http://content.healthaffairs.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15659453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Jha AK, Ferris TG, Donelan K, DesRoches C, Shields A, Rosenbaum S, Blumenthal D. How common are electronic health records in the United States? A summary of the evidence. Health Aff (Millwood) 2006;25(6):w496–507. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.25.w496. http://content.healthaffairs.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17035341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


