Abstract
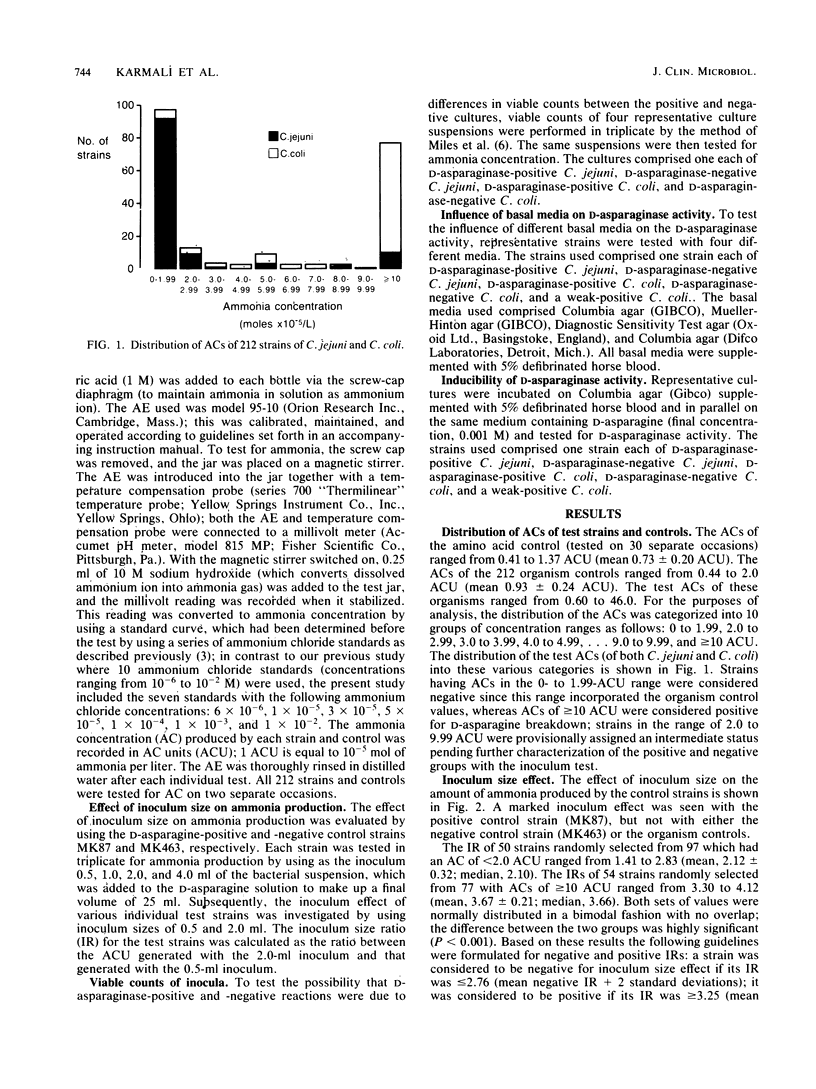
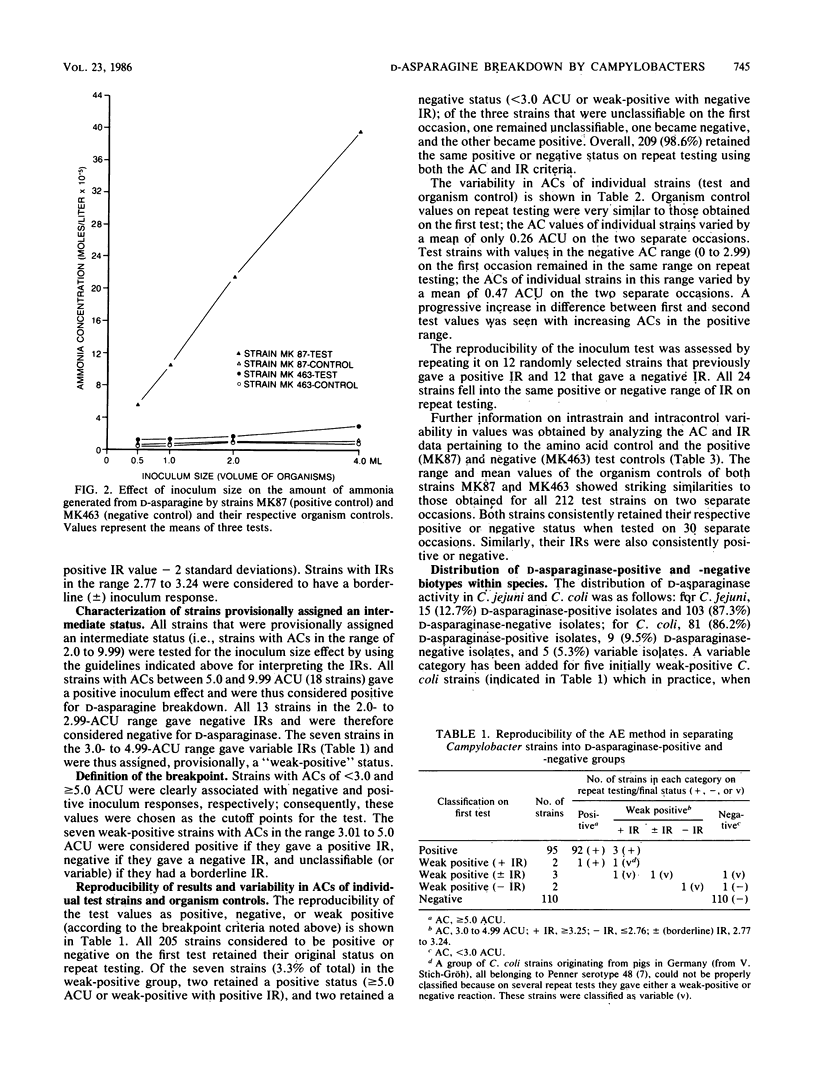
An ammonia electrode method has been developed for investigating the deamination of amino acids by bacteria. It consists of incubating a standard inoculum of organisms in an amino acid solution and then measuring the amount of ammonia evolved by the electrode. Two hundred and twelve Campylobacter strains (118 C. jejuni and 94 C. coli) were tested for their ability to break down D-asparagine by this method. Organism control (bacterial suspension in buffer alone) values ranged from 0.44 to 2.0 (mean 0.93 +/- 0.24) ammonia concentration (AC) units (one AC unit is equal to 10(-5) mol of ammonia per liter), whereas test values ranged from 0.60 to 46.0 units. Test ACs of less than 2 units (97 strains) were considered negative, whereas ACs of greater than or equal to 10 (77 strains) were considered positive for D-asparaginase; 38 (18%) strains with ACs between 2 and 10 units were provisionally assigned an intermediate status. The amount of ammonia produced by strains with ACs of greater than or equal to 10 increased greatly when the inoculum size was increased, whereas this was not a feature of strains with ACs of less than 2 units. The presence or absence of an inoculum effect was instrumental in classifying strains with intermediate ACs and allowed a breakpoint to be defined. When the ammonia electrode method was repeated, 97.6% of the 212 strains gave the same positive or negative reaction that they did on the first occasion. Thus the test was highly reproducible. Five strains (all porcine C. coli from Germany) were unclassifiable because they repeatedly gave either a weak-positive or negative reaction. Overall, 12.7% of C. jejuni strains and 86.2% of C. coli strains were positive for D-asparaginase. The ammonia electrode method was found to be simple and reliable for separating strains on the basis of D-asparaginase activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hwang M. N., Ederer G. M. Rapid hippurate hydrolysis method for presumptive identification of group B streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):114–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.114-115.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Williams A., Fleming P. C., Krishnan C., Wood M. M. Use of an ammonia electrode to study bacterial deamination of amino acids with special reference to D-asparagine breakdown by campylobacters. J Hyg (Lond) 1984 Oct;93(2):189–196. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400064706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lior H. New, extended biotyping scheme for Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and "Campylobacter laridis". J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):636–640. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.636-640.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Warren J. R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet. 1984 Jun 16;1(8390):1311–1315. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91816-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner J. L., Hennessy J. N. Passive hemagglutination technique for serotyping Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Dec;12(6):732–737. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.6.732-737.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop R. M., 2nd, Smibert R. M., Johnson J. L., Krieg N. R. Differential characteristics of catalase-positive campylobacters correlated with DNA homology groups. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Jul;30(7):938–951. doi: 10.1139/m84-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop R. M., 2nd, Smibert R. M., Krieg N. R. Improved biotyping schemes for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Nov;20(5):990–992. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.5.990-992.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B., Benjamin J. Differentiation of enteropathogenic Campylobacter. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;33(11):1122–1122. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.11.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totten P. A., Fennell C. L., Tenover F. C., Wezenberg J. M., Perine P. L., Stamm W. E., Holmes K. K. Campylobacter cinaedi (sp. nov.) and Campylobacter fennelliae (sp. nov.): two new Campylobacter species associated with enteric disease in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):131–139. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



