Abstract
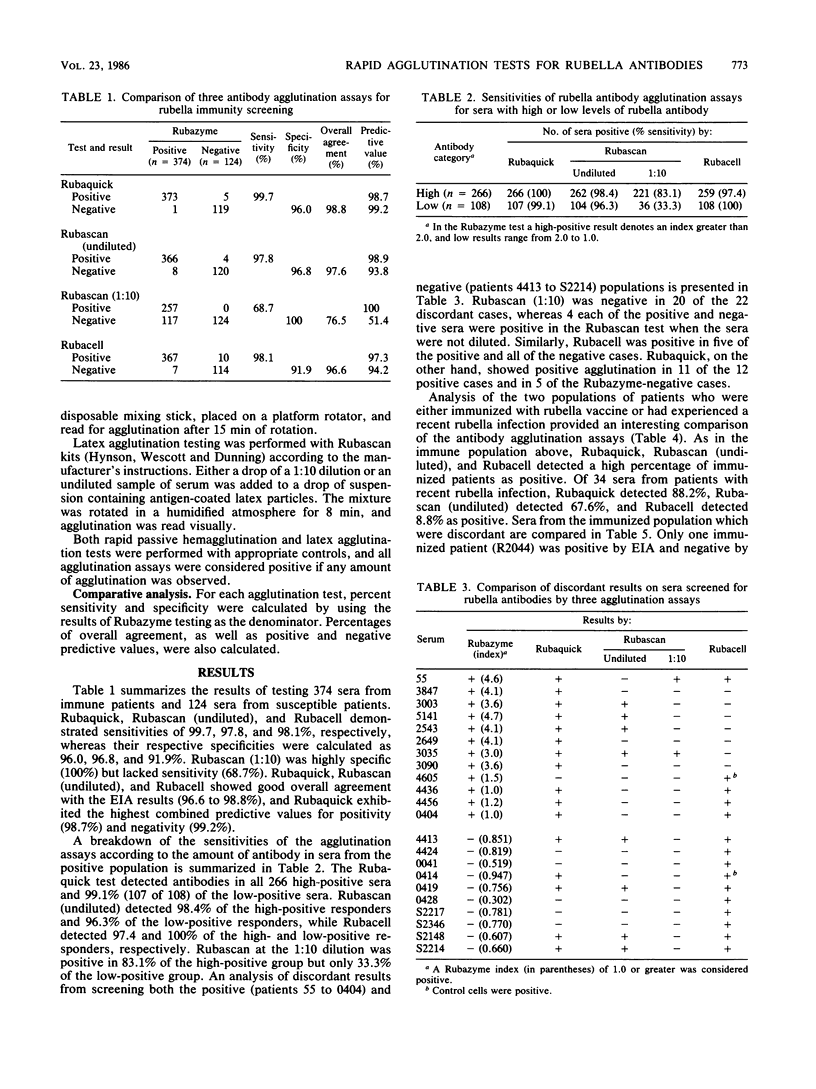
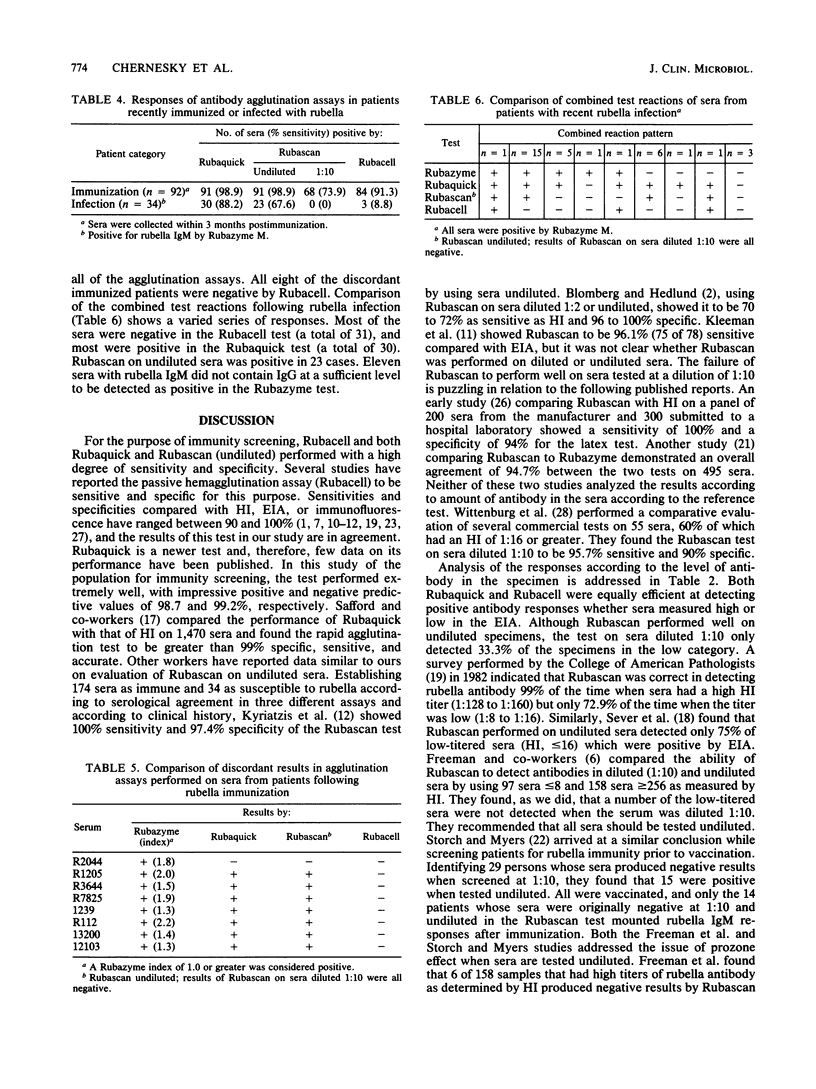
Rapid agglutination tests (Rubaquick, Rubascan, and Rubacell) were used to screen sera (374 from immune and 124 from susceptible patients) for rubella immunity. Compared with enzyme immunoassay (Rubazyme) the erythrocyte agglutination assays (Rubaquick and Rubacell) were greater than 98% sensitive and 92 to 96% specific. The latex test (Rubascan) was sensitive (97.8%) and specific (96.8%) on undiluted serum but only 68.7% sensitive on serum diluted 1:10. Although the three rapid assays detected a substantial number of positive sera within 3 months of rubella immunization, a large number of variable responses were seen after infection with rubella. Analysis of discordant results suggests that these tests may be effectively used for immunity screening. The different individual assay results observed on low-titered sera or blood collected shortly after infection or immunization may not be comparable, because each assay has a different antigenic component on the agglutinin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birch C. J., Glaun B. P., Hunt V., Irving L. G., Gust I. D. Comparison of passive haemagglutination and haemagglutination-inhibition techniques for detection of antibodies to rubella virus. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Feb;32(2):128–131. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg J., Hedlund T. Determination of rubella immunity by latex agglutination: its place in clinical routines. Scand J Infect Dis. 1984;16(4):327–333. doi: 10.3109/00365548409073956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody J. P., Binkley J. H., Harding S. A. Evaluation and comparison of two assays for detection of immunity to rubella infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):708–711. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.708-711.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellano G. A., Madden D. L., Hazzard G. T., Cleghorn C. S., Vails D. V., Ley A. C., Tzan N. R., Sever J. L. Evaluation of commercially available diagnostic test kits for rubella. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):578–584. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman S., Clark L., Dumas N. Evaluation of a latex agglutination test for detection of antibodies to rubella virus in selected sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):197–198. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.197-198.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haukenes G. Experience with an indirect (passive) haemagglutination test for the demonstration of rubella virus antibody. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Apr;88(2):85–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho-Terry L., Cohen A. Degradation of rubella virus envelope components. Arch Virol. 1980;65(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF01340535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katow S., Sugiura A. Antibody response to individual rubella virus proteins in congenital and other rubella virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):449–451. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.449-451.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilgore J. M. Clinical evaluation of a rubella passive hemagglutination test system. J Med Virol. 1979;3(3):231–236. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890030309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleeman K. T., Kiefer D. J., Halbert S. P. Rubella antibodies detected by several commercial immunoassays in hemagglutination inhibition-negative sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1131–1137. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1131-1137.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M., Evans B. K., Horstmann D. M. Comparison of the latex agglutination test with the hemagglutination inhibition test, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and neutralization test for detection of antibodies to rubella virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):644–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.644-649.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M., Evans B. K., Horstmann D. M. Use of enzyme immunoassays and the latex agglutination test to measure the temporal appearance of immunoglobulin G and M antibodies after natural infection or immunization with rubella virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):745–748. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.745-748.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oker-Blom C., Kalkkinen N., Käriäinen L., Pettersson R. F. Rubella virus contains one capsid protein and three envelope glycoproteins, E1, E2a, and E2b. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):964–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.964-973.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen P., Seppänen H., Suni J., Vaheri A. Selective reactivity of antibodies to human immunoglobulins G, M, and A with rubella virus proteins. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):800–802. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.800-802.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safford J. W., Abbott G. G., Deimler C. M. Evaluation of a rapid passive hemagglutination assay for anti-rubella antibody: comparison to hemagglutination inhibition and a vaccine challenge study. J Med Virol. 1985 Nov;17(3):229–236. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sever J. L., Tzan N. R., Shekarchi I. C., Madden D. L. Rapid latex agglutination test for rubella antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):52–54. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.52-54.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skendzel L. P., Wilcox K. R., Edson D. C. Evaluation of assays for the detection of antibodies to rubella. A report based on data from the College of American Pathologists Surveys of 1982. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4 Suppl):594–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steece R. S., Talley M. S., Skeels M. R., Lanier G. A. Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, hemagglutination inhibition, and passive latex agglutination for determination of rubella immune status. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):140–142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.140-142.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steece R. S., Talley M. S., Skeels M. R., Lanier G. A. Problems in determining immune status in borderline specimens in an enzyme immunoassay for rubella immunoglobulin G antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):923–925. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.923-925.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch G. A., Myers N. Latex-agglutination test for rubella antibody: validity of positive results assessed by response to immunization and comparison with other tests. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):459–464. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truant A. L., Barksdale B. L., Huber T. W., Elliott L. B. Comparison of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with indirect hemagglutination and hemagglutination inhibition for determination of rubella virus antibody: evaluation of immune status with commercial reagents in a clinical laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jan;17(1):106–108. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.1.106-108.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vänänen P., Häivä V. M., Koskela P., Meurman O. Comparison of a simple latex agglutination test with hemolysis-in-gel, hemagglutination inhibition, and radioimmunoassay for detection of rubella virus antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 May;21(5):793–795. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.5.793-795.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxham M. N., Wolinsky J. S. Immunochemical identification of rubella virus hemagglutinin. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):194–203. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90471-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissfeld A. S., Sonnenwirth A. C. New latex agglutination test for rapid determination of rubella immune status. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):971–972. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.971-972.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West D. J., Manty A. M., Siem R. A. Evaluation of a passive hemagglutination test kit for the detection of rubella antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Apr;77(4):462–464. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.4.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenburg R. A., Roberts M. A., Elliott L. B., Little L. M. Comparative evaluation of commercial rubella virus antibody kits. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):161–163. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.161-163.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



