Abstract
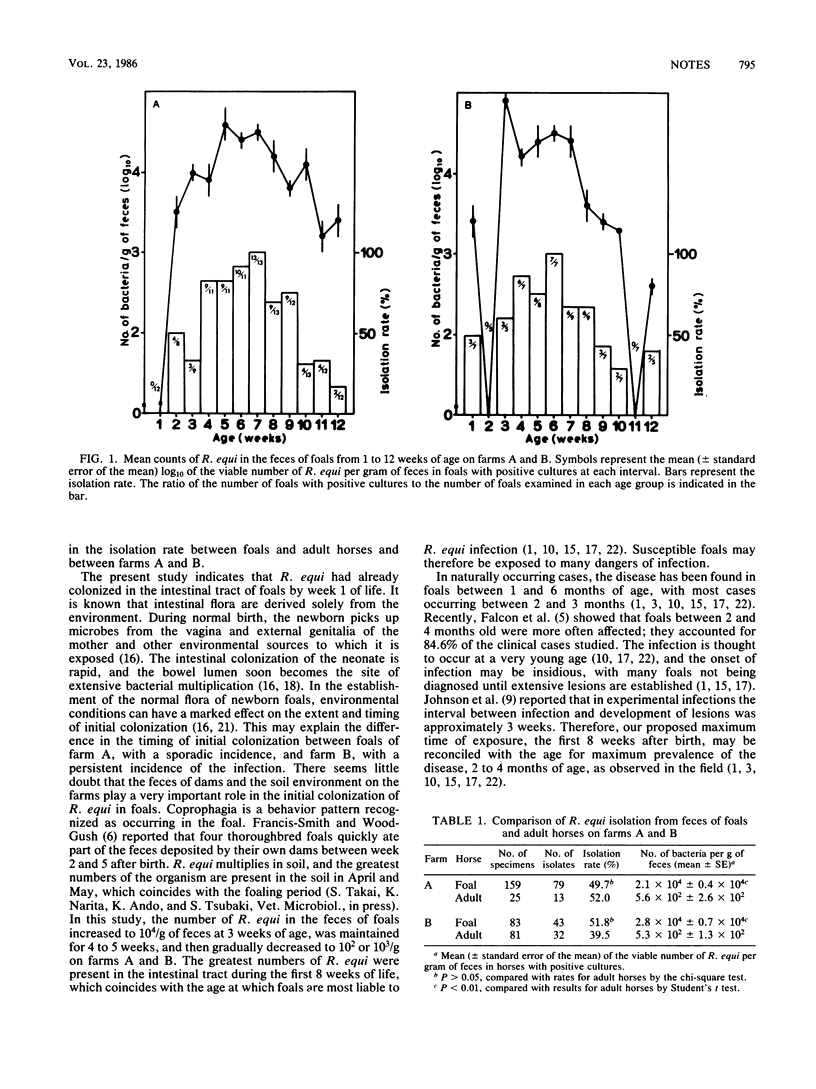
Quantitative aspects of fecal Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi in newborn foals for 12 weeks after birth were investigated on two horse breeding farms. R. equi was found in the feces of foals during week 1 of life. The greatest numbers of R. equi were present in the feces of foals during the first 8 weeks of their lives, which coincides with the age when foals are most liable to be exposed to R. equi.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton M. D., Hughes K. L. Ecology of Rhodococcus equi. Vet Microbiol. 1984 Feb;9(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(84)90079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimprich R. E., Rooney J. R. Corynebacterium equi enteritis in foals. Vet Pathol. 1977 Mar;14(2):95–102. doi: 10.1177/030098587701400201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger M. A., Kaeberle M. L., Roth J. A. Equine humoral immune response to Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2428–2430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcon J., Smith B. P., O'Brien T. R., Carlson G. P., Biberstein E. Clinical and radiographic findings in Corynebacterium equi pneumonia of foals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1985 Mar 15;186(6):593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis-Smith K., Wood-Gush D. G. Coprophagia as seen in thoroughbred foals. Equine Vet J. 1977 Jul;9(3):155–157. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1977.tb04010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hietala S. K., Ardans A. A., Sansome A. Detection of Corynebacterium equi-specific antibody in horses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jan;46(1):13–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Prescott J. F., Markham R. J. The pathology of experimental Corynebacterium equi infection in foals following intrabronchial challenge. Vet Pathol. 1983 Jul;20(4):440–449. doi: 10.1177/030098588302000407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Prescott J. F., Markham R. J. The pathology of experimental Corynebacterium equi infection in foals following intragastric challenge. Vet Pathol. 1983 Jul;20(4):450–459. doi: 10.1177/030098588302000408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight H. D. Corynebacterial infections in the horse: problems of prevention. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1969 Jul 15;155(2):446–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Sugimoto C., Isayama Y. Quantitative culture of Rhodococcus equi from the feces of horse. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1983 Summer;23(2):67–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Ogilvie T. H., Markham R. J. Lymphocyte immunostimulation in the diagnosis of Corynebacterium equi pneumonia of foals. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Dec;41(12):2073–2075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Travers M., Yager-Johnson J. A. Epidemiological survey of Corynebacterium equi infections on five Ontario horse farms. Can J Comp Med. 1984 Jan;48(1):10–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:107–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel W. L., Keahey E. E., Bullard T. L. Corynebacterium infection in foals: etiology, pathogenesis, and laboratory diagnosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1968 Dec 15;153(12):1610–1613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. The development of the flora of the alimentary tract in young animals. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(2):495–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Kawazu S., Tsubaki S. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of Corynebacterium (Rhodococcus) equi infection in foals. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Oct;46(10):2166–2170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Tsubaki S. The incidence of Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi in domestic animals and soil. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985 Jun;47(3):493–496. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.47.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Savage D. C. Influences of dietary and environmental stress on microbial populations in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):591–598. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.591-598.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock J. B., Farmer A. M., Mutimer M. D. Selective medium for Corynebacterium equi isolation. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):640–642. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.640-642.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock J. B., Mutimer M. D., Farmer A. M. Epidemiology of Corynebacterium equi in horses. Res Vet Sci. 1980 Jan;28(1):87–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



