Abstract
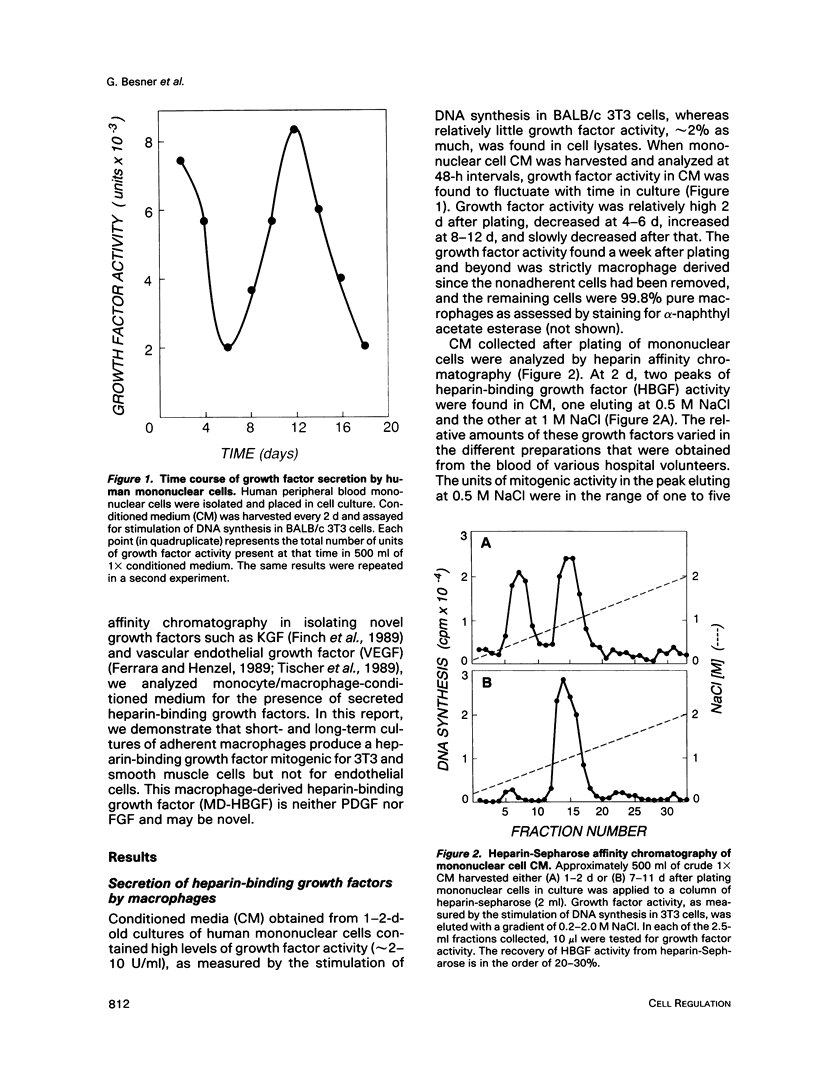
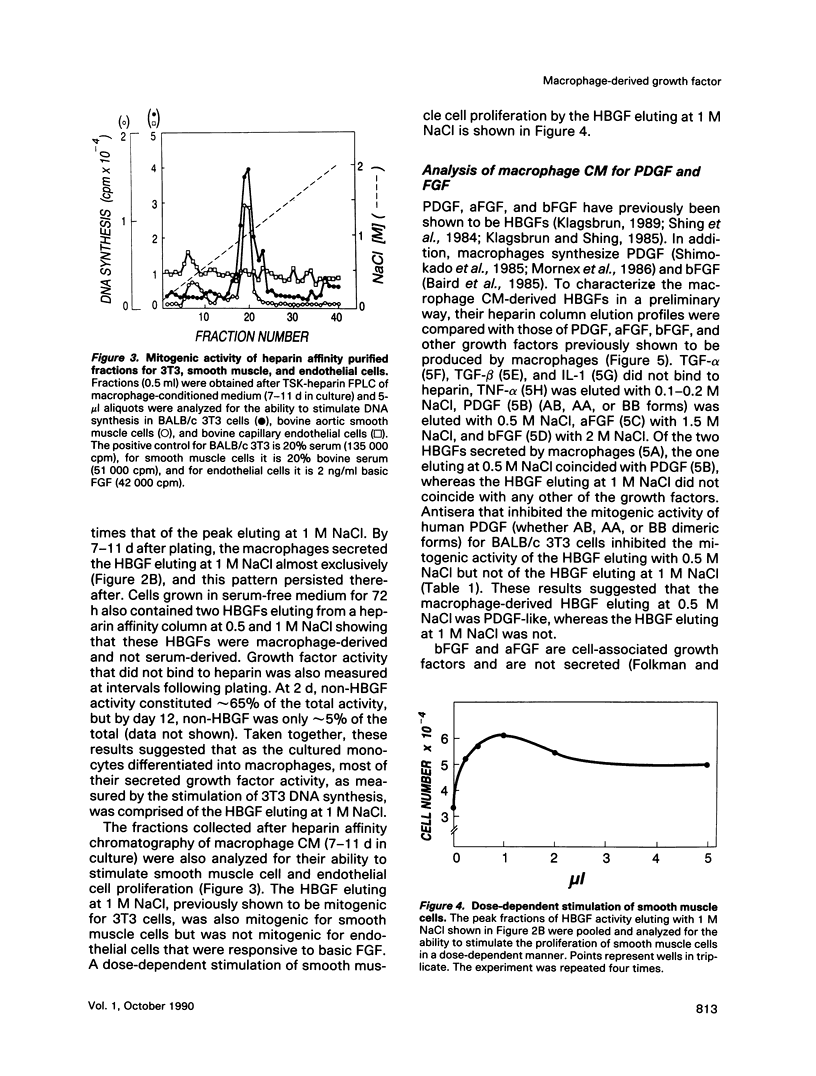
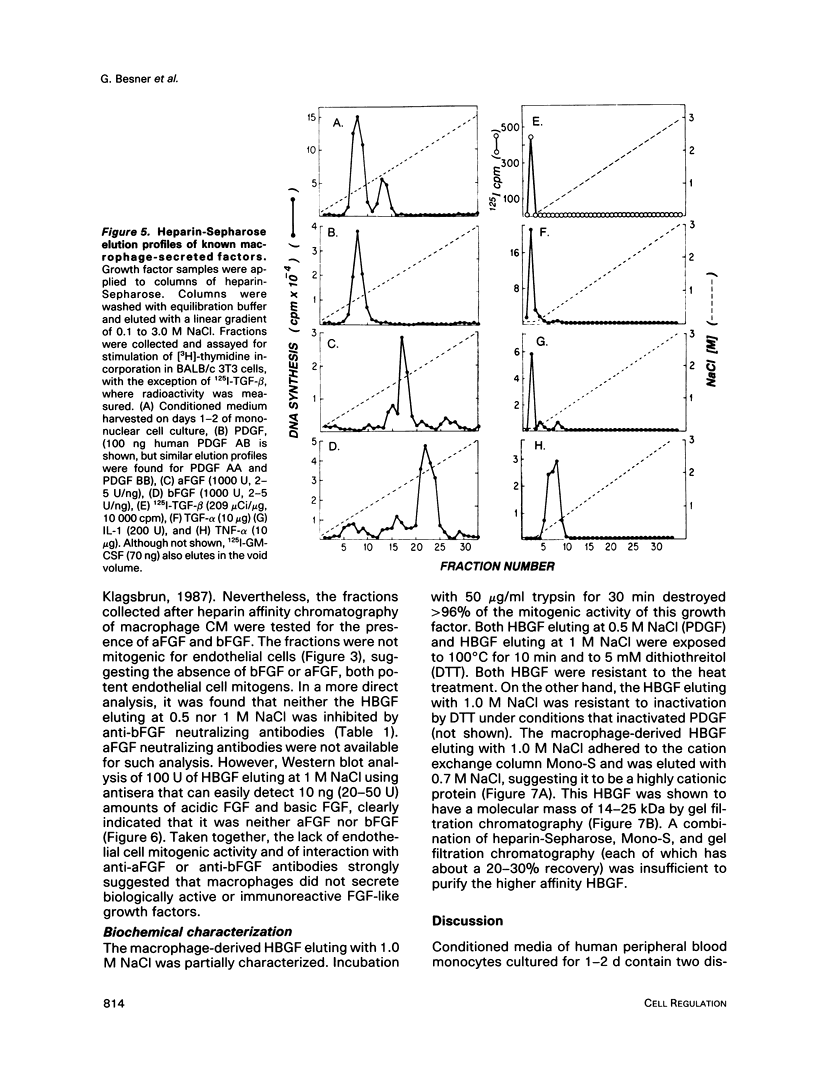
Human mononuclear cells were plated in culture, and the conditioned media of these cells were analyzed by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography. The fractions were tested for growth factor activity as measured by the stimulation of DNA synthesis in BALB/c 3T3 cells. After 2 d in culture, two peaks of heparin-binding growth factor (HBGF) activity were detected, one eluting with 0.5 M NaCl, which could be shown to be platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-like, and the other eluting with 1.0 M NaCl. After 7-11 d in culture, when monocytes had clearly differentiated into macrophages, greater than 95% of the HBGF activity in conditioned medium consisted of the 1.0 M NaCl elution peak. This activity, which was designated macrophage-derived HBGF (MD-HBGF), was found to be a cationic heat-resistant polypeptide with a molecular weight in the range of 14-25 kDa. Analysis using Western blots and specific neutralizing antisera, as well as comparative heparin affinity analysis, indicated that MD-HBGF was not identical to other heparin-binding 3T3 cell growth factors known to be produced by macrophages, such as PDGF (AB, AA, and BB forms), acidic fibroblast growth factor, and basic fibroblast growth factor. In addition to stimulating mitogenesis in 3T3 cells, MD-HBGF also stimulated the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells, but did not stimulate the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assoian R. K., Fleurdelys B. E., Stevenson H. C., Miller P. J., Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Ross R., Sporn M. B. Expression and secretion of type beta transforming growth factor by activated human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6020–6024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Durkin T. Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by type beta-transforming growth factor: interactions with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 16;138(1):476–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Mormède P., Böhlen P. Immunoreactive fibroblast growth factor in cells of peritoneal exudate suggests its identity with macrophage-derived growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):358–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90614-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashkin P., Doctrow S., Klagsbrun M., Svahn C. M., Folkman J., Vlodavsky I. Basic fibroblast growth factor binds to subendothelial extracellular matrix and is released by heparitinase and heparin-like molecules. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1737–1743. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., Klagsbrun M., Hill K. E., Buckley A., Sullivan R., Brewer P. S., Woodward S. C. Accelerated wound repair, cell proliferation, and collagen accumulation are produced by a cartilage-derived growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1219–1227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delli-Bovi P., Curatola A. M., Newman K. M., Sato Y., Moscatelli D., Hewick R. M., Rifkin D. B., Basilico C. Processing, secretion, and biological properties of a novel growth factor of the fibroblast growth factor family with oncogenic potential. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2933–2941. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Henzel W. J. Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):851–858. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Rubin J. S., Miki T., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Human KGF is FGF-related with properties of a paracrine effector of epithelial cell growth. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):752–755. doi: 10.1126/science.2475908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fràter-Schröder M., Risau W., Hallmann R., Gautschi P., Böhlen P. Tumor necrosis factor type alpha, a potent inhibitor of endothelial cell growth in vitro, is angiogenic in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5277–5281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazuda D. J., Lee J. C., Young P. R. The kinetics of interleukin 1 secretion from activated monocytes. Differences between interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8473–8479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Twardzik D. R., Schwartz S. M. Inhibition of endothelial regeneration by type-beta transforming growth factor from platelets. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1078–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.3461562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iberg N., Rogelj S., Fanning P., Klagsbrun M. Purification of 18- and 22-kDa forms of basic fibroblast growth factor from rat cells transformed by the ras oncogene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19951–19955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Miyazono K., Hellman U., Drexler H., Wernstedt C., Hagiwara K., Usuki K., Takaku F., Risau W., Heldin C. H. Identification of angiogenic activity and the cloning and expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):557–562. doi: 10.1038/338557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Shing Y. Heparin affinity of anionic and cationic capillary endothelial cell growth factors: analysis of hypothalamus-derived growth factors and fibroblast growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M. The fibroblast growth factor family: structural and biological properties. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(4):207–235. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa M., Doctrow S. R., Klagsbrun M. Neutralizing antibodies inhibit the binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to its receptor but not to heparin. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7686–7691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Polverini P. J., Shepard H. M., Wiseman D. M., Shively V., Nuseir N. Macrophage-induced angiogenesis is mediated by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):630–632. doi: 10.1038/329630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Sakariassen K. S., Assoian R. K., Sporn M. B., Bell G. I., Ross R. Induction of transforming growth factor-alpha in activated human alveolar macrophages. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornex J. F., Martinet Y., Yamauchi K., Bitterman P. B., Grotendorst G. R., Chytil-Weir A., Martin G. R., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous expression of the c-sis gene and release of a platelet-derived growth factorlike molecule by human alveolar macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):61–66. doi: 10.1172/JCI112574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. Metabolism of receptor-bound and matrix-bound basic fibroblast growth factor by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):753–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Behrens J., Nussbaumer U., Böhlen P., Birchmeier W. Inhibitory action of transforming growth factor beta on endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5600–5604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Oliver C. N., Lepe-Zuniga J. L., Green I., Gery I. Silica-stimulated monocytes release fibroblast proliferation factors identical to interleukin 1. A potential role for interleukin 1 in the pathogenesis of silicosis. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1462–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI111350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Winkler M. E., Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: a more potent angiogenic mediator than epidermal growth factor. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1250–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.2422759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Reidy M. A. Common mechanisms of proliferation of smooth muscle in atherosclerosis and hypertension. Hum Pathol. 1987 Mar;18(3):240–247. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Malerstein B., Gospodarowicz D. Tumor necrosis factor inhibits the proliferation of cultured capillary endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 30;143(3):997–1004. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokado K., Raines E. W., Madtes D. K., Barrett T. B., Benditt E. P., Ross R. A significant part of macrophage-derived growth factor consists of at least two forms of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Haudenschild C., Lund D., Crum R., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenesis is stimulated by a tumor-derived endothelial cell growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(4):275–287. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240290402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh J. P., Bonin P. D. Purification and biochemical properties of a human monocyte-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6374–6378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischer E., Gospodarowicz D., Mitchell R., Silva M., Schilling J., Lau K., Crisp T., Fiddes J. C., Abraham J. A. Vascular endothelial growth factor: a new member of the platelet-derived growth factor gene family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1198–1206. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92729-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Fridman R., Ishai-Michaeli R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2292–2296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadzinski M. G., Folkman J., Sasse J., Devey K., Ingber D., Klagsbrun M. Heparin-binding angiogenesis factors: detection by immunological methods. Clin Physiol Biochem. 1987;5(3-4):200–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpe S. D., Davatelis G., Sherry B., Beutler B., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Moldawer L. L., Nathan C. F., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Macrophages secrete a novel heparin-binding protein with inflammatory and neutrophil chemokinetic properties. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):570–581. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpe S. D., Sherry B., Juers D., Davatelis G., Yurt R. W., Cerami A. Identification and characterization of macrophage inflammatory protein 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):612–616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan X., Bates B., Hu X. G., Goldfarb M. The human FGF-5 oncogene encodes a novel protein related to fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3487–3495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]