Abstract
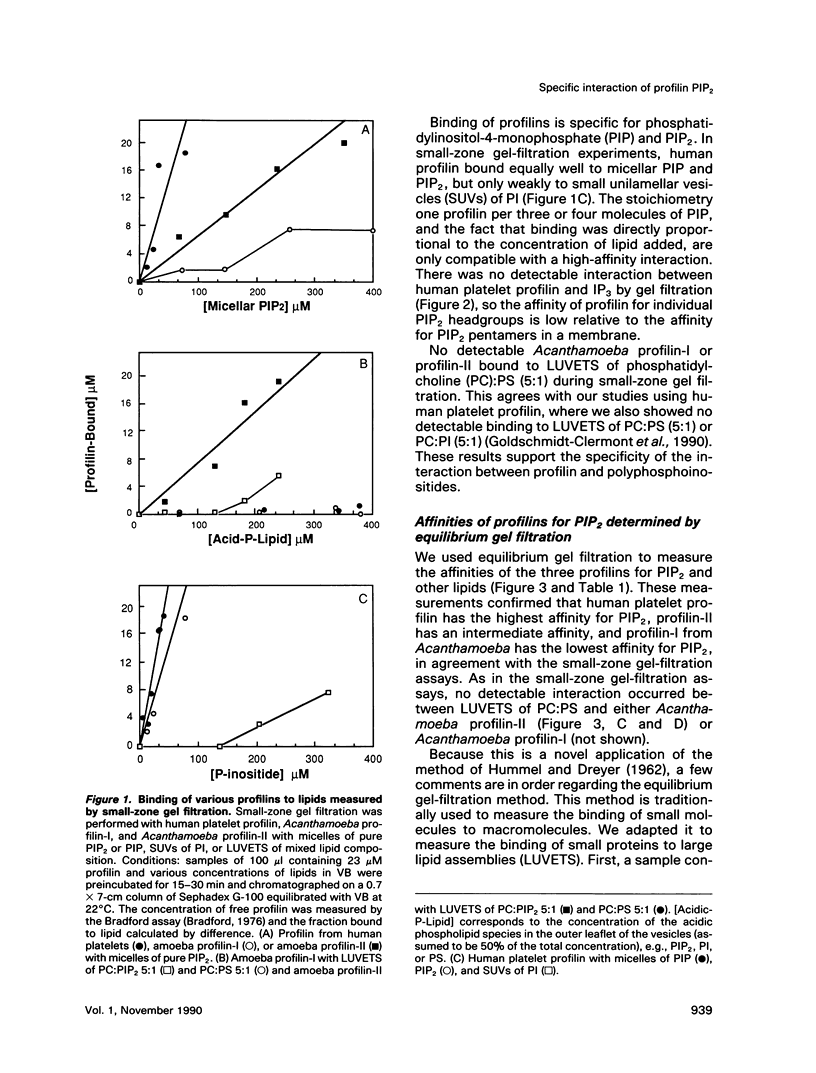
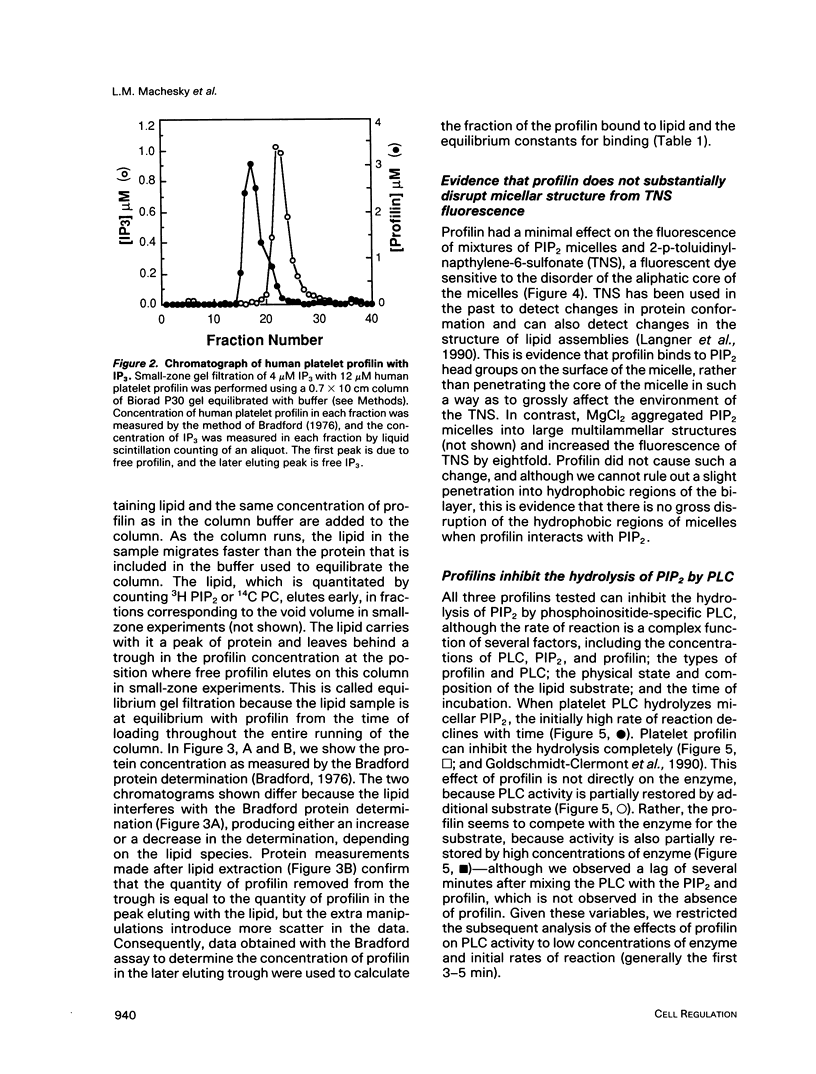
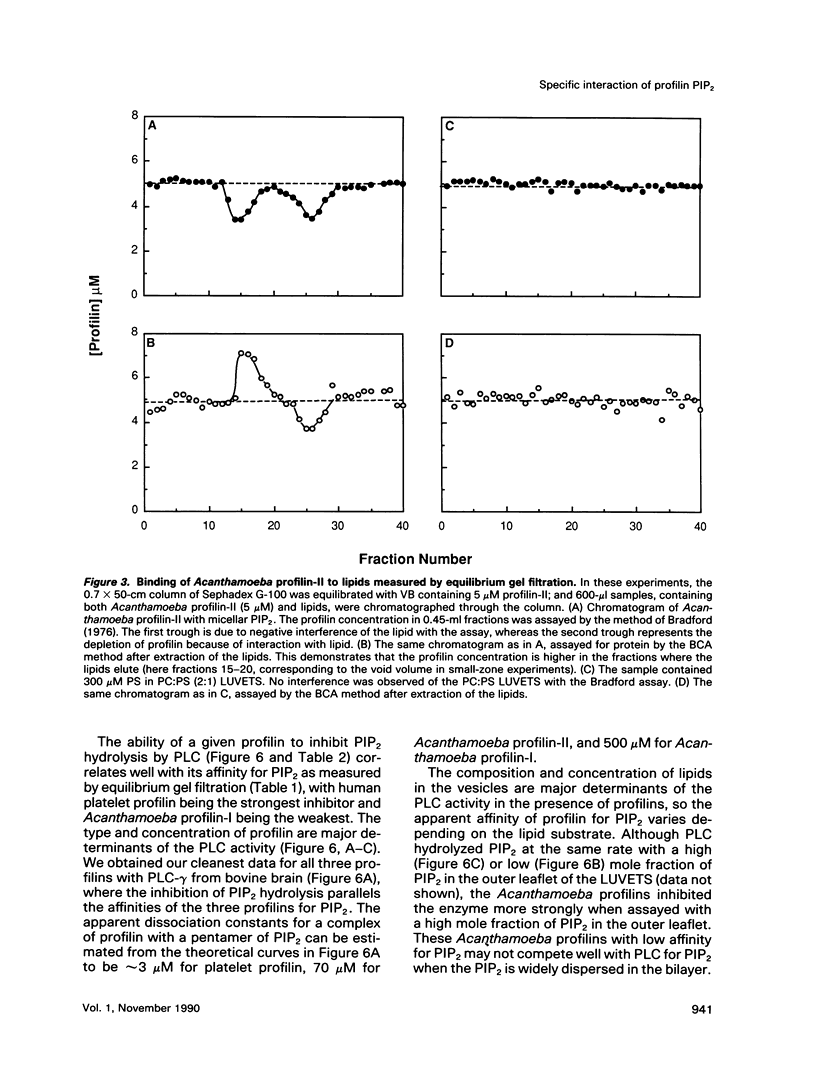
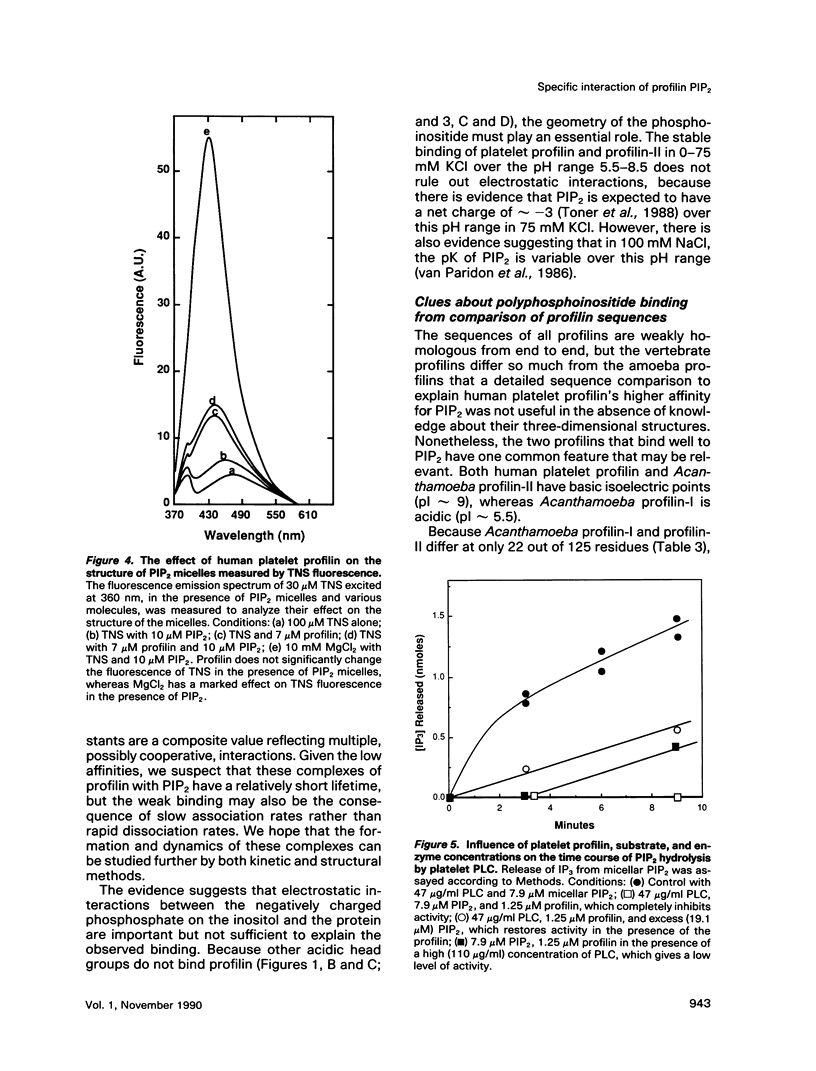
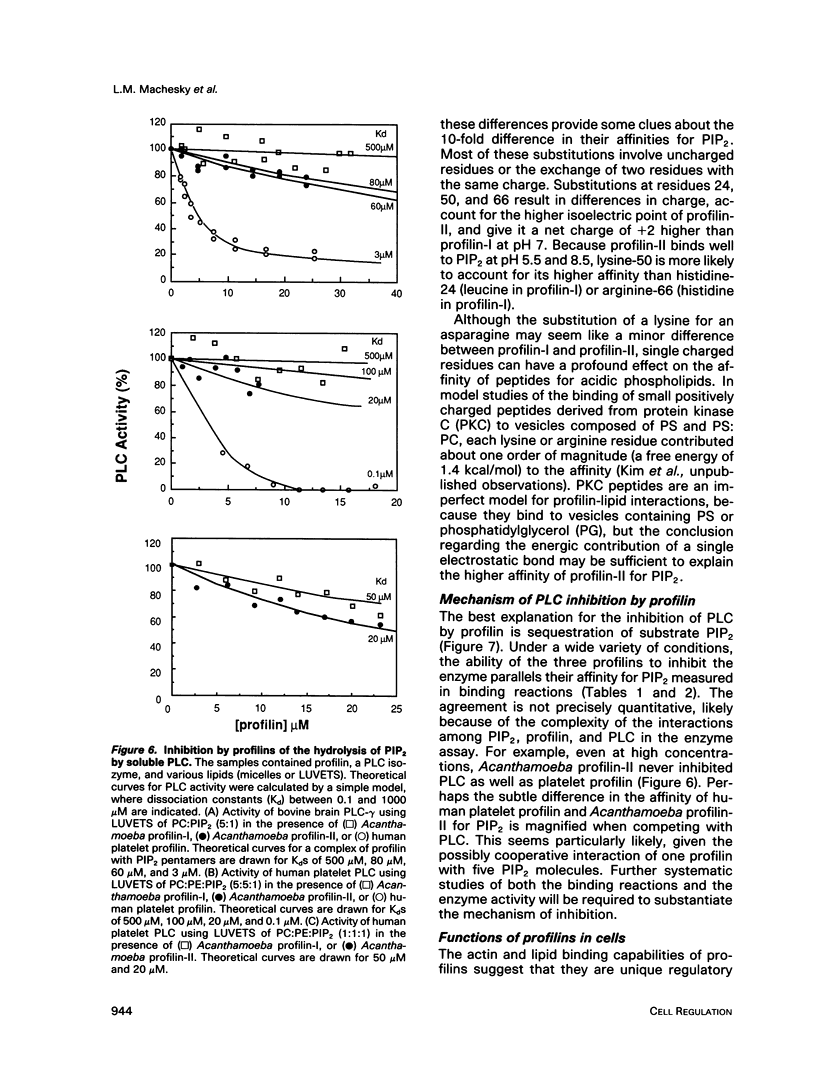
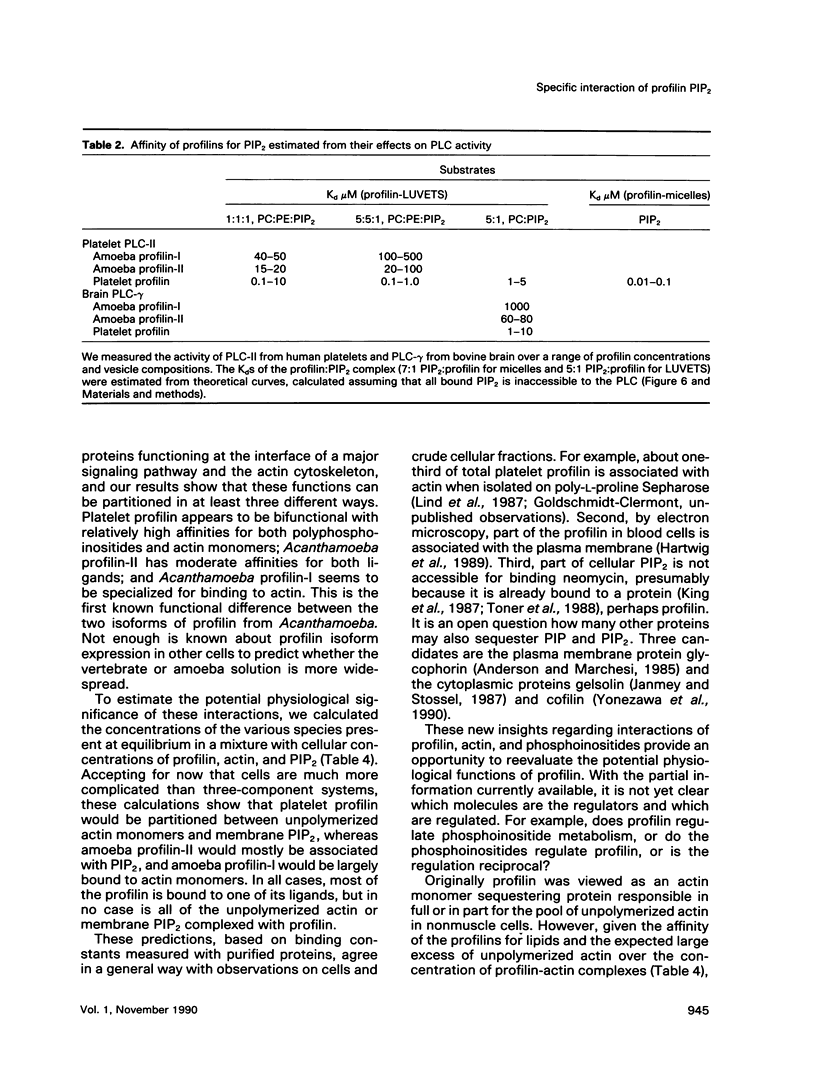
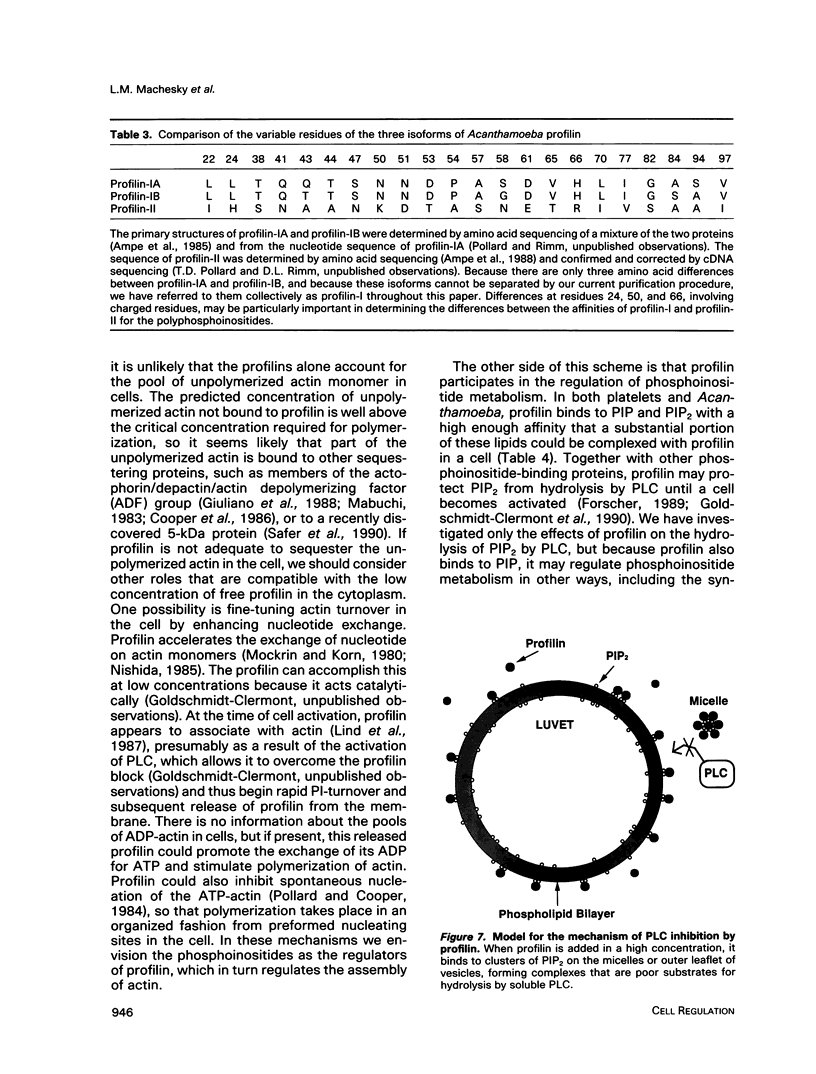
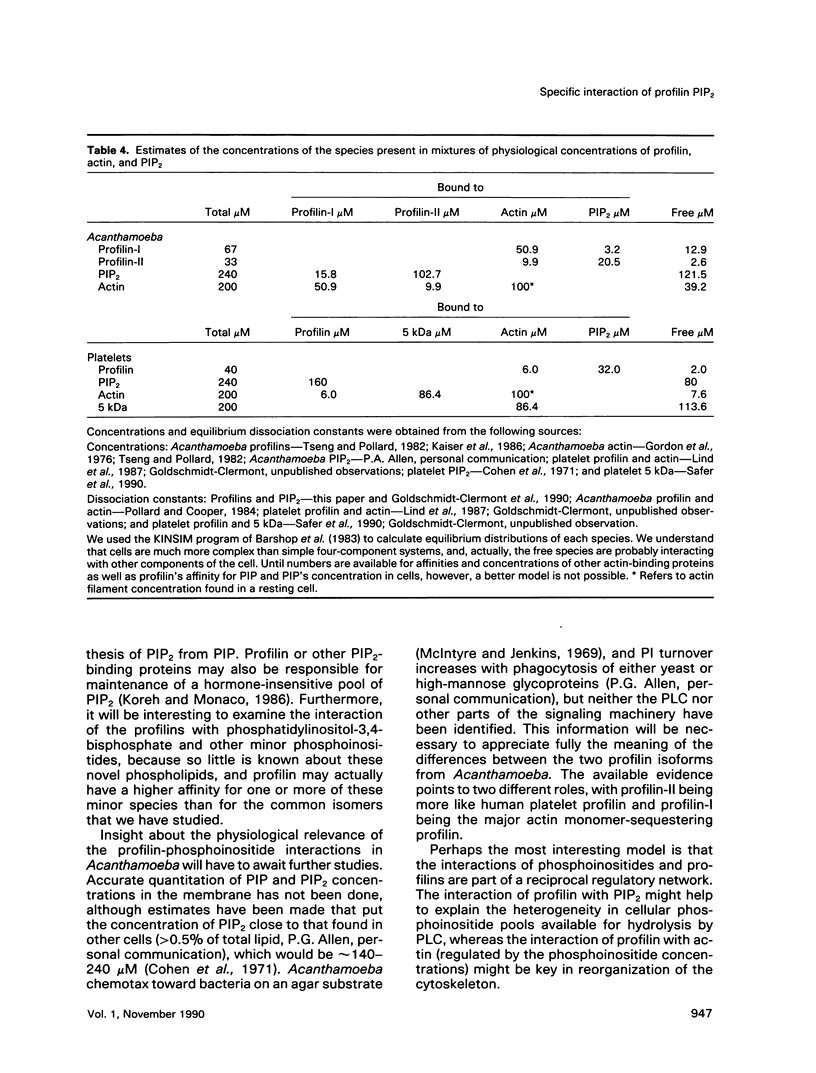
In light of recent work implicating profilin from human platelets as a possible regulator of both cytoskeletal dynamics and inositol phospholipid-mediated signaling, we have further characterized the interaction of platelet profilin and the two isoforms of Acanthamoeba profilin with inositol phospholipids. Profilin from human platelets binds to phosphatidylinositol-4-monophosphate (PIP) and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) with relatively high affinity (Kd approximately 1 microM for PIP2 by equilibrium gel filtration), but interacts only weakly (if at all) with phosphatidylinositol (PI) or inositol trisphosphate IP3) in small-zone gel-filtration assays. The two isoforms of Acanthamoeba profilin both have a lower affinity for PIP2 than does human platelet profilin, but the more basic profilin isoform from Acanthamoeba (profilin-II) has a much higher (approximately 10-microM Kd) affinity than the acidic isoform (profilin-I, 100 to 500-microM Kd). None of the profilins bind to phosphatidylserine (PS) or phosphatidylcholine (PC) in small-zone gel-filtration experiments. The differences in affinity for PIP2 parallel the ability of these three profilins to inhibit PIP2 hydrolysis by soluble phospholipase C (PLC). The results show that the interaction of profilins with PIP2 is specific with respect to both the lipid and the proteins. In Acanthamoeba, the two isoforms of profilin may have specialized functions on the basis of their identical (approximately 10 microM) affinities for actin monomers and different affinities for PIP2.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ampe C., Sato M., Pollard T. D., Vandekerckhove J. The primary structure of the basic isoform of Acanthamoeba profilin. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 4;170(3):597–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J., Brenner S. L., Tobacman L., Korn E. D. The amino acid sequence of Acanthamoeba profilin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):834–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Marchesi V. T. Regulation of the association of membrane skeletal protein 4.1 with glycophorin by a polyphosphoinositide. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):295–298. doi: 10.1038/318295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassare J. J., Fisher G. J. Regulation of membrane-associated and cytosolic phospholipase C activities in human platelets by guanosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11942–11944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassare J. J., Henderson P. A., Fisher G. J. Isolation and characterization of one soluble and two membrane-associated forms of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from human platelets. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):6010–6016. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barshop B. A., Wrenn R. F., Frieden C. Analysis of numerical methods for computer simulation of kinetic processes: development of KINSIM--a flexible, portable system. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 1;130(1):134–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90660-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson L., Nyström L. E., Sundkvist I., Markey F., Lindberg U. Actin polymerizability is influenced by profilin, a low molecular weight protein in non-muscle cells. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Broekman M. J., Verkley A., Lisman J. W., Derksen A. Quantification of human platelet inositides and the influence of ionic environment on their incorporation of orthophosphate-32P. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):762–772. doi: 10.1172/JCI106547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Blum J. D., Williams R. C., Jr, Pollard T. D. Purification and characterization of actophorin, a new 15,000-dalton actin-binding protein from Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):477–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M. 'Phosphatido-peptide'-like complexes formed by the interaction of calcium triphosphoinositide with protein. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):134–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0970134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiNubile M. J., Southwick F. S. Effects of macrophage profilin on actin in the presence and absence of acumentin and gelsolin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7402–7409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forscher P. Calcium and polyphosphoinositide control of cytoskeletal dynamics. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):468–474. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano K. A., Khatib F. A., Hayden S. M., Daoud E. W., Adams M. E., Amorese D. A., Bernstein B. W., Bamburg J. R. Properties of purified actin depolymerizing factor from chick brain. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):8931–8938. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Baldassare J. J., Pollard T. D. The actin-binding protein profilin binds to PIP2 and inhibits its hydrolysis by phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2157283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Williams M. H., Galbraith R. M. Altered conformation of Gc (vitamin D-binding protein) upon complexing with cellular actin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):611–617. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90572-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Eisenberg E., Korn E. D. Characterization of cytoplasmic actin isolated from Acanthamoeba castellanii by a new method. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4778–4786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Chambers K. A., Hopcia K. L., Kwiatkowski D. J. Association of profilin with filament-free regions of human leukocyte and platelet membranes and reversible membrane binding during platelet activation. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1571–1579. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Stossel T. P. Modulation of gelsolin function by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):362–364. doi: 10.1038/325362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. A., Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Levine B. A., Pollard T. D. Characterization of renatured profilin purified by urea elution from poly-L-proline agarose columns. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;14(2):251–262. doi: 10.1002/cm.970140211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. A., Sato M., Ebert R. F., Pollard T. D. Purification and characterization of two isoforms of Acanthamoeba profilin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):221–226. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. E., Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Guy G. R., Michell R. H. Multiple metabolic pools of phosphoinositides and phosphatidate in human erythrocytes incubated in a medium that permits rapid transmembrane exchange of phosphate. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):209–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2440209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koréh K., Monaco M. E. The relationship of hormone-sensitive and hormone-insensitive phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in the WRK-1 cell. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):88–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Bruns G. A. Human profilin. Molecular cloning, sequence comparison, and chromosomal analysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5910–5915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langner M., Cafiso D., Marcelja S., McLaughlin S. Electrostatics of phosphoinositide bilayer membranes. Theoretical and experimental results. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):335–349. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82535-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassing I., Lindberg U. Specific interaction between phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and profilactin. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):472–474. doi: 10.1038/314472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassing I., Lindberg U. Specificity of the interaction between phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and the profilin:actin complex. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Jul;37(3):255–267. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240370302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind S. E., Janmey P. A., Chaponnier C., Herbert T. J., Stossel T. P. Reversible binding of actin to gelsolin and profilin in human platelet extracts. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):833–842. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi I. An actin-depolymerizing protein (depactin) from starfish oocytes: properties and interaction with actin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1612–1621. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. D., Hope M. J., Cullis P. R. Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 13;858(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. O., Edelman G. M. Fluorescent probes for conformational states of proteins. I. Mechanism of fluorescence of 2-p-toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate, a hydrophobic probe. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):1908–1919. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre J., Jenkin C. R. Chemotaxis in the free living amoeba (Hartmannella rhysodes). Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1969 Oct;47(5):625–632. doi: 10.1038/icb.1969.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mockrin S. C., Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba profilin interacts with G-actin to increase the rate of exchange of actin-bound adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5359–5362. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E. Opposite effects of cofilin and profilin from porcine brain on rate of exchange of actin-bound adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 26;24(5):1160–1164. doi: 10.1021/bi00326a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström L. E., Lindberg U., Kendrick-Jones J., Jakes R. The amino acid sequence of profilin from calf spleen. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oechsner U., Magdolen V., Bandlow W. The cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of profilin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9078–9078. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Quantitative analysis of the effect of Acanthamoeba profilin on actin filament nucleation and elongation. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6631–6641. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raben D. M., Yasuda K., Cunningham D. D. Modulation of thrombin-stimulated lipid responses in cultured fibroblasts. Evidence for two coupling mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2759–2765. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichstein E., Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba profilin. A protein of low molecular weight from Acanpthamoeba castellanii that inhibits actin nucleation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6174–6179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Suh P. G., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Bovine brain cytosol contains three immunologically distinct forms of inositolphospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6649–6653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer D., Golla R., Nachmias V. T. Isolation of a 5-kilodalton actin-sequestering peptide from human blood platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2536–2540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Bonder E. M., Coluccio L. M., Mooseker M. S. Actin from Thyone sperm assembles on only one end of an actin filament: a behavior regulated by profilin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):112–124. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobacman L. S., Korn E. D. The regulation of actin polymerization and the inhibition of monomeric actin ATPase activity by Acanthamoeba profilin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4166–4170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toner M., Vaio G., McLaughlin A., McLaughlin S. Adsorption of cations to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7435–7443. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng P. C., Pollard T. D. Mechanism of action of Acanthamoeba profilin: demonstration of actin species specificity and regulation by micromolar concentrations of MgCl2. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):213–218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng P. C., Runge M. S., Cooper J. A., Williams R. C., Jr, Pollard T. D. Physical, immunochemical, and functional properties of Acanthamoeba profilin. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):214–221. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa N., Nishida E., Iida K., Yahara I., Sakai H. Inhibition of the interactions of cofilin, destrin, and deoxyribonuclease I with actin by phosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8382–8386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Paridon P. A., de Kruijff B., Ouwerkerk R., Wirtz K. W. Polyphosphoinositides undergo charge neutralization in the physiological pH range: a 31P-NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 11;877(1):216–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



