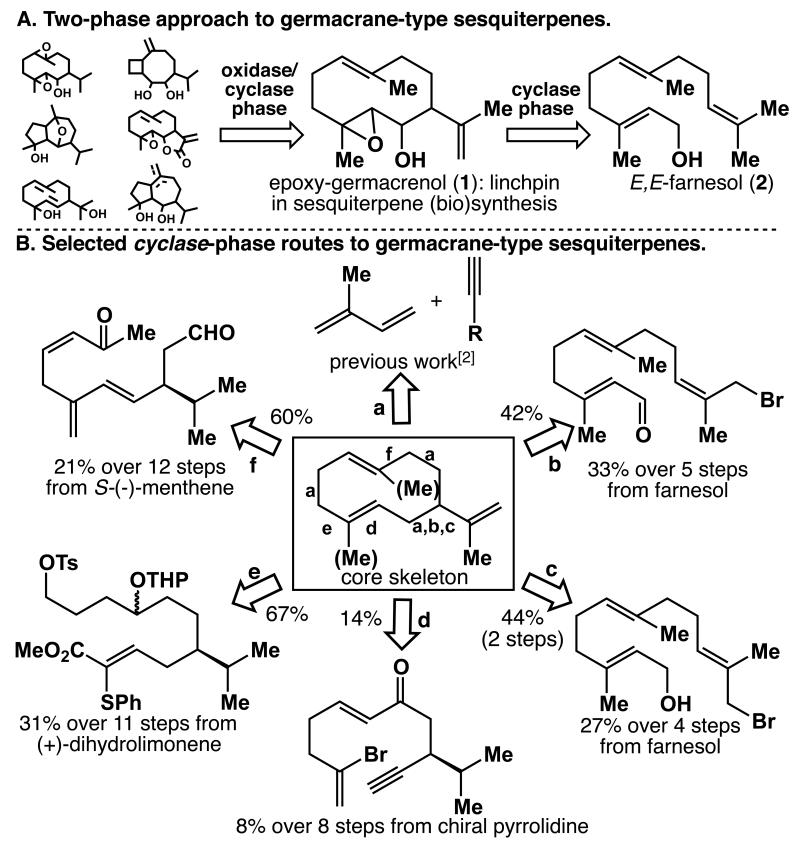
Our laboratory has a longstanding interest in harvesting new chemical knowledge by learning from terpene biosynthesis. The straightforward construction of carbocyclic terpene backbones such as epoxy-germacrenol (1, Scheme 1A) in a low oxidation state (cyclase phase) followed by regio-, chemo-, and stereoselective oxidative modifications (oxidase phase) allow Nature to access a wide variety of related family members in a divergent manner.[1] Earlier this year, we reported our initial forays into the redox-economic synthesis of terpenes that resemble 1 by oligomerization of unfunctionalized isoprene (Scheme 1B, path a).[2] These studies ultimately led us to a new approach that utilizes the more advanced, yet readily available, C15 building block farnesol (2, Scheme 1A) as a starting point. In this communication, a short, efficient, scalable, and enantioselective synthesis of 1 is described. Furthermore, we demonstrate how the key intermediate 1 can be processed not only to germacrane-type natural products by chemo- and stereoselective oxidations, but also to a variety of polycyclic sesquiterpene frameworks (like selinanes, guaianes, or elemenes) by acid-mediated transannular cyclization reactions.
Scheme 1.
(A) Retrosynthetic outline. (B) Known cyclase-phase routes (letters indicate retrosynthetic disconnections) yielding the germacrane skeleton.[5] Cyclization conditions: a) cat. Ni(cod)2, PPh3; b) CrCl3–LiAlH4, DMF, rt, 42%; c) 1. NaH, dicyclohexano-18-crown-6, PhH, 80 °C, 2 h; 2. t-BuLi, Et2O, −78 °C, 10 h, 44% over 2 steps; d) Bu3SnH, AIBN, PhH, 80 °C, 3 h, 14%; e) NaHMDS, DME, 85 °C, 50 min, 67%; f) TiCl3, Zn/Cu, DME, 0 °C, 36 h, 60%. DME = dimethoxyethane, DMF = N,N-dimethylformamide.
For the goal of establishing a scalable, divergent, and broadly applicable entry to a variety of related sesquiterpene families, the germacrenes were identified as strategic key intermediates due to the following reasons: 1) germacrenes constitute a large class of cyclic terpenes, many of which have been shown to exhibit promising bioactivities and, in addition, are of growing importance in the perfumery industry; 2) germacrenes are known to be a biosynthetic linchpin en route to various related terpene congeners; and 3) most importantly, many studies have demonstrated that germacrenes can be transformed into mono-, di-, and tricyclic sesquiterpene subclasses (e.g., the elemenes, cadinanes, eudesmanes, guaianes, and bourbonanes) with the “Achilles heel” of these approaches being the accessibility of germacrene precursors in quantity.[3]
Despite the industrial interest in terpene natural products, most of the naturally occurring germacrenes and their congeners are not easily available in bulk quantities due to a variety of challenges associated with their synthesis and/or isolation: germacrenes featuring a cyclodecadiene core are notoriously unstable to acidic and thermal conditions (leading to cyclized and/or rearranged products) and can often exist as conformationally semistable isomers at ambient temperature, thus creating complications with regard to purification and product analysis.[4]
Although the total synthesis of sesquiterpenes has been an area of intense research efforts for decades,[4] there is still no reliable synthetic pathway to rapidly forge the ten-membered germacrene carbocycle. The most effective synthetic approaches published to date (Scheme 1B) suffer from serious drawbacks such as low overall yield, poor step economy, and/or are impractical to perform on scale In addition, these syntheses either yield racemic products or start from chiral-pool starting materials. Whereas Nature’s cyclase enzymes can efficiently overcome the entropic barrier for the formation of medium-sized carbocycles, direct ring closures from acyclic precursors remain a challenge in organic synthesis and are especially difficult to perform on larger scale (e.g., due to the need for high-dilution techniques). Finally, terpenes often occur in opposite enantiomeric forms in various organisms and the programmed synthesis of either antipode of germacrenes and their congeners is a problem that has yet to be solved.
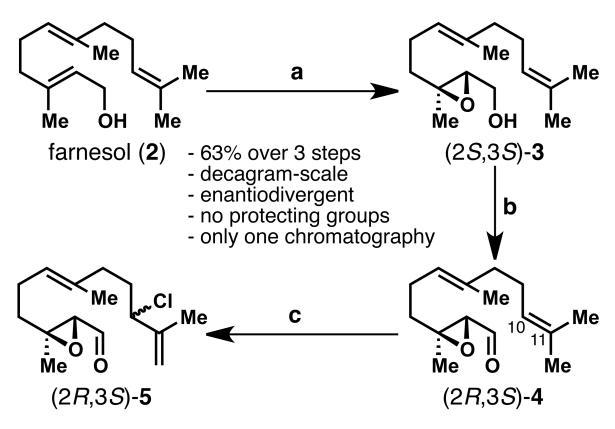
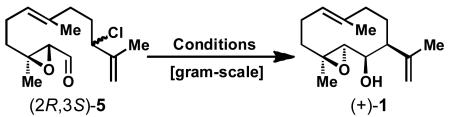
Our synthesis started with the readily available C15 building block farnesol (2, <$1.00/gram, Scheme 2), which was transformed in two known steps (Sharpless epoxidation[6] and Parikh-Doering oxidation) to epoxy aldehyde 4.[7] The crude material was used directly in the next step, a regioselective chlorination with concomitant transposition of the internal 10,11-double bond to the terminal position according to a protocol invented by Tunge et al.[8] The chlorinated epoxy aldehyde 5 was thus obtained in 63% overall yield in three steps on decagram-scale from farnesol (2), with only one chromatographic purification. The route is amenable to produce both enantiomers of 5 and the most efficient route to a cyclization precursor in the context of germacrene total synthesis.
Scheme 2.
Enantioselective synthesis of the coupling precursor 5 (shown for the (2R,3S)-enantiomer). Reagents and conditions: a) 4Å MS, Ti(OiPr)4 (0.1 equiv), (+)-DET (0.12 equiv), TBHP (2 equiv), CH2Cl2, −50 °C, then 2 (1 equiv), 2 h, ee = 90%; b) SO3.py (4 equiv), iPr2NEt (5 equiv), DMSO (10 equiv), CH2Cl2, 0 °C, 0.5 h; c) PhSeCl (0.12 equiv), NCS (1.1 equiv), CH2Cl2, rt, 1 h, 63% over 3 steps. DET = diethyl tartrate, TBHP = tert-butyl hydroperoxide, DMSO = dimethyl sulfoxide, NCS = N-chlorosuccinimide.
With the epoxy chloro aldehyde 5 in hand, cyclization conditions were explored to furnish the desired medium-sized germacrane ring system. Inspired by previous work of Shibuya et al.[5b] who performed a similar ring closure under Nozaki-Hiyama-Kishi (NHK) conditions using CrCl3–LiAlH4 (Scheme 1B, Path b), the development of a robust, scalable, and diastereoselective cyclization was pursued. While several of the attempted reductive NHK-type or Barbier-type coupling conditions using CrII, Zn0, Sn0, In0, Ba0, Ni0, or Mn0 yielded the desired cyclized product, none of them proceeded with acceptable yield or selectivity. After an extensive screening of conditions, the intramolecular coupling of aldehyde 5 succeeded via a Pd-catalyzed umpolung allylation[9] reaction. Using Pd(PPh3)4 and Et2Zn in THF, we obtained intermediate 1 in varying yields of 10–30% (see Table 1, entries 1 and 2). It was found that only 1.5 equiv. of Et2Zn (entry 2) is needed instead of 4 (entry 1). Interestingly, by switching the catalyst from Pd(PPh3)4 (20 mol %) to Pd(PPh3)2Cl2 (10 mol %) and adding K2CO3 to the reaction mixture, the reaction proceeded more cleanly, which simplified the purification of the product (entries 3–6). Finally, changing solvents from THF to DMF then to DMA gave the best yield of 42% for cyclized product 1 (entries 4 and 5). Attempts to vary the reductant from Et2Zn to Me2Zn (entry 7), Bu2Zn (entry 8), Et3B, InI or SnCl2 also failed to improve the results (see Supporting Information, Table 1 for further details).
Table 1.
Key ring closure of 5 via an umpolung allylation.
| # | catalyst | ligand | reduct. | solv. | base | 1[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pd(PPh3)4[b] | -- | Et2Zn[c] | THF | -- | 19 |
| 2 | Pd(PPh3)4[b] | -- | Et2Zn | THF | -- | 10-30 |
| 3 | PdCl2(PPh3)2 | -- | Et2Zn | THF | K2CO3 | 13-42 |
| 4 | PdCl2(PPh3)2 | -- | Et2Zn | DMF | K2CO3 | 32 |
| 5 | PdCl2(PPh3)2 | -- | Et2Zn | DMA | K2CO3 | 42 [d] |
| 6 | PdCl2(PPh3)2 | -- | Et2Zn | DMA | -- | 33 |
| 7 | PdCl2(PPh3)2 | -- | Me2Zn | DMA | K2CO3 | 0 |
| 8 | PdCl2(PPh3)2 | -- | Bu2Zn | DMA | K2CO3 | 31 |
| 9 | Pd(OAc)2 | PPh3 | Et2Zn | DMA | K2CO3 | 15 |
Standard conditions unless otherwise stated: cat. (10 mol %), ligand (20 mol %), K2CO3 (1.5 equiv), solvent (0.033 M overall), 5 (100–600 mg scale, 1.0 equiv., 0.05 M, slow addition over 1.5 h), reductant (1.5 equiv., slow addition over 1.5 h), T = 50 °C.
Isolated yield.
Cat. (20 mol %).
4 Equiv of Et2Zn.
Reproduced on six occasions, 42% was obtained for gram-scale.
THF = tetrahydrofuran, DMF = N,N,dimethylformamide, DMA = N,N-dimethylacetamide.
With optimized conditions in hand, the reaction was ultimately performed on gram-scale, by the dropwise addition of both substrate and Et2Zn to a solution of PdCl2(PPh3)2 and K2CO3 in DMA, giving (+)-1 in 42% yield, as the only diastereomer, opposite in stereoselectivity to that in the previously described conditions of Shibuya et al.[5b] Overall, this diastereoselective ring closure strategy provides efficient access to the optically active germacrane-type key intermediate 1 reproducibly on gram-scale. In retrospect, it is not surprising that this ring closure was the only method that worked well, given the pioneering findings of Trost on medium and macrocyclic ring formation via π-allyl palladium catalysis.[10]
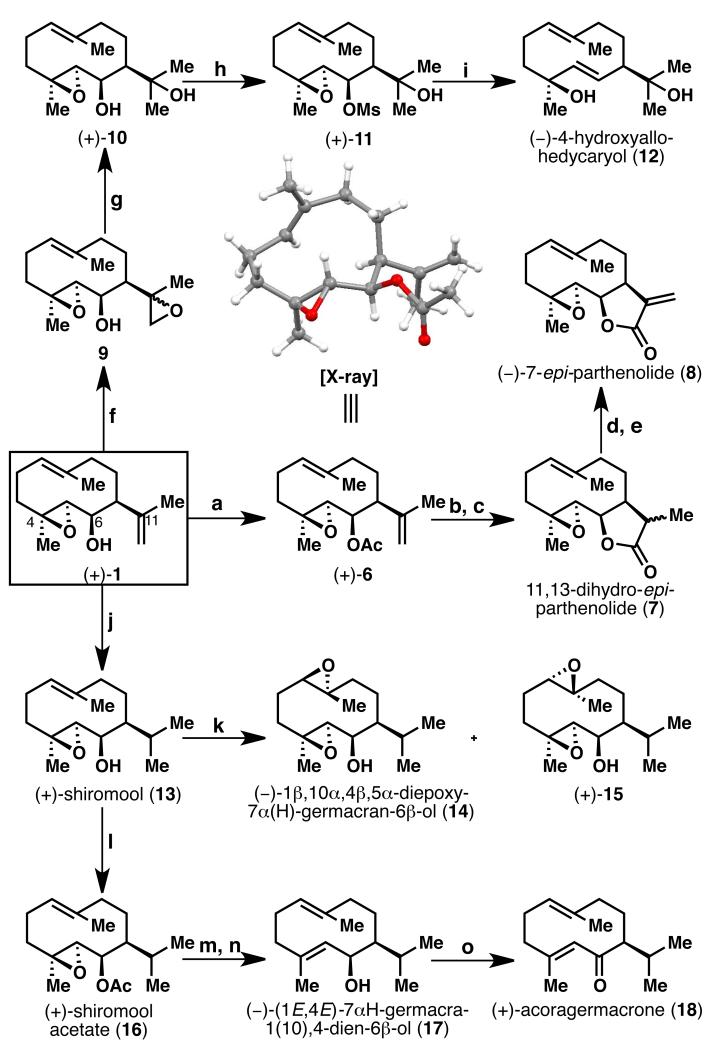
With the supply problem solved, attention turned to exploring the innate reactivity of 1 and its conversion to other natural products. Thus, acetylation of (+)-1 with DCC, DMAP and AcOH proceeded in quantitative yield to give (+)-6 (Scheme 3). The stereochemistry o f ( + )-1 was unambiguously established from the X-ray crystallographic analysis[11] of acetate 6, revealing the cis-relationship between the 6-OH group and isopropylidene group in the 7-position. Hydroboration followed by oxidative work up of acetate 6 furnished the desired diol product, which was immediately oxidized (without further purification) with TEMPO and PhI(OAc)2 to 11,13-dihydro-epi-parthenolide[12] (7) as a mixture of diastereomers. Converting 1 to acetate 6 is necessary for the hydroboration step, since a <40% conversion was observed otherwise. α-Bromination of lactone 7 with LDA and CBr4, followed by dehydrobromination with TBAF,[13] gave rise to 7-epi-parthenolide (−)-8 (60% over 2 steps), an unnatural epimer of the biologically active[14] sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide.[15] While parthenolide has been successfully isolated in quantity recently,[16] none of its epimers have been synthesized to date, and thus the biological activity of 8 has not yet been explored. (−)-4-Hydroxyallohedycaryol (12) was obtained in a four-step sequence from (+)-1 by: 1) directed epoxidation with VO(acac)2 to give bis-epoxide 9 (77% yield); 2) chemoselective reduction of the less-hindered epoxide to diol (+)-10 with LiAlH4; 3) mesylation of the 2° alcohol providing (+)-11 (44% over 2 steps); and 4) reductive elimination of the epoxy mesylate (+)-11 with lithium naphthalenide to afford (−)-12 in 65% yield, together with recovered diol 10 in 23% yield.
Scheme 3.
Synthesis of germacrane-type sesquiterpenes. Reagents and conditions: a) DCC (3 equiv), DMAP (0.5 equiv), AcOH (3 equiv), CH2Cl2, rt, quant.; b) 9-BBN (2 equiv), THF, rt, 2 h, then EtOH, 6N aq. NaOH, 35% aq. H2O2; c) TEMPO (0.5 equiv), PhI(OAc)2 (4 equiv), CH2Cl2, rt, 4 h, 77% over 2 steps; d) LDA (3.6 equiv), THF, −78 °C, 1 h, then CBr4 (4 equiv), 0.5 h; e) TBAF (3 equiv), THF, rt, 1 h, 60% over 2 steps; f) VO(acac)2 (0.27 equiv), TBHP (2.2 equiv), CH2Cl2, 0 °C, 77%; g) LiAlH4 (5 equiv), THF, 0 °C, 20 min; h) MeSO2Cl (3 equiv, as 2 portions), Et3N (3 equiv, as 2 portions), CH2Cl2, −5 °C, 0.5 h, 44% over 2 steps; i) Lithium naphthalenide (10 equiv, as 2 portions), THF, −25 °C, 20 min, 65 % of 12, 23% of 10; j) Crabtree’s cat. (7.5 mol %), 2,6-di-t-butylpyridine (1 equiv), CH2Cl2, H2 (1 atm), rt, 1 h, 65-84%; k) mCPBA (1.5 equiv), NaHCO3 (2 equiv), CH2Cl2, −5 °C, 30 min, 62% of 14, 22% of 15; l) DCC (3 equiv), AcOH (3 equiv), DMAP (0.5 equiv), CH2Cl2, rt, 2 h, quant.; m) WCl6 (1.85 equiv), n-BuLi (3.8 equiv), THF, −60 °C to rt, 86%; n) K2CO3 (10 equiv), MeOH, 50 °C, 1 h, 95%; o) IBX (4 equiv), DMSO, rt, 2 h, 90%. DCC = N,N’-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, DMAP = 4-dimethylaminopyridine, BBN = borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, TEMPO = (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl, LDA = lithium diisopropylamide, TBAF = tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride, TBHP = tert-butyl hydroperoxide, mCPBA = meta-chloroperbenzoic acid, IBX = 2-iodoxybenzoic acid.
Chemoselective hydrogenation of the isopropylidene side chain in (+)-1 using Crabtree’s catalyst[17] afforded (+)-shiromool[18] (13) in good yield (65-84%). It was found that the addition of 2,6-di-tert-butylpyridine was crucial to suppress side product formation. Epoxidation of (+)-13 with mCPBA led to a 4: 1 diastereomeric mixture of (−)-1β,10α,4β,5α-diepoxy-7α(H)-germacran-6β-ol (14) and (+)-15 in 84% combined yield, both of which are natural products.[19] Acetylation of the 6-OH of (+)-13 with AcOH, DCC and DMAP furnished (+)-shiromool acetate[20] (16) in quantitative yield. Reaction of (+)-16 with WCl6 and n-BuLi[21] effected the removal of the 4,5-epoxide, followed by saponification of the acetate group with K2CO3/MeOH at 50 °C gave (−)-(1E,4E)-7αH-germacra-1(10),4-dien-6β-ol[22] (17) in 82% yield over 2 steps. Oxidation of this natural product (−)-17 with IBX[23] gave (+)-acoragermacrone[24] (18) in 90% yield.
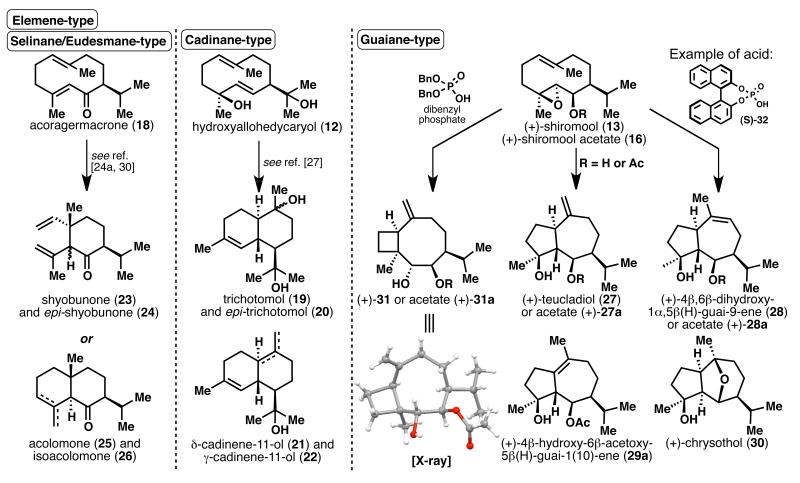
In addition to the successful syntheses of sesquiterpenes 8-18 incorporating the 10-membered carbocycle, common bicyclic sesquiterpene frameworks were also accessed by transannular cyclizations as depicted in Scheme 4. It is known that transannular cyclization of compounds such as 12, with the allohedycaryol framework, would give rise to cadinane-type sesquiterpenes. Depending on the acid used with (±)-12, trichotomol[25] (19) and its C10-epimer 20, δ-cadinene-11-ol[26] (21) and δ-cadinene-11-ol (22) were obtained in varying ratios (Scheme 4).[27] The elemene skeleton can be accessed by a Cope rearrangement of acoragermacrone (18), giving a 21: 4 mixture of shyobunone[28] (23) and its epimer 24, respectively.[24a] Alternatively, treating 18 with acid would afford selinane-type sesquiterpenes, acolamone[29] (25; 55% yield) and isoacolamone (26; 23% yield).[30] Likewise, the guaiane framework can be accessed by treating shiromool acetate (16) with dry HCl gas in Et2O at 0 °C to obtain a ~15: 5: 4 mixture of (+)-27a, (+)-28a and (+)-29a respectively, with a preference for the exocyclic olefin.[20] A similar outcome (5: 2: 1 mixture) was observed with p-TsOH (0.27 equiv) as the acid catalyst in CH2Cl2 at room temperature. The resulting major product (+)-27a was then converted to (+)-teucladiol[31] (27) by saponification. At this point, we set out to investigate whether different acids would affect the regioselectivity of this cyclization, and if the same transformation could be performed directly on (+)-shiromool (13), in order to obtain the natural products 28 and 30 selectively (see Supporting Information, Table 9 for further details). Subjecting (+)-13 to catalytic p-TsOH gave a 3: 1 mixture of (+)-28 and (+)-27, a selectivity opposite to that observed for the same reaction with acetate 16. After further screening, it was found that adding Sc(OTf)3 to (+)-13 in CH2Cl2 at 0 °C gave a >20: 1 mixture of (+)-4β,6β-dihydroxy-1α,5β(H)-guai-9-ene[32] (28) and (+)-27 in 67% yield. A separate reaction of (+)-13 with (S)-(+)-1,1′-binaphthalene-2,2′-diyl hydrogen phosphate (S)-32 as acid catalyst in CH2Cl2 at room temperature gave a 11: 5: 2 mixture of (+)-chrysothol[33] (30; 49% yield), 28 and 27 (32% yield combined) respectively. Instead of the concomitant loss of proton after the acid-induced epoxide opening, as in the case in the formation of 27 and 28, the ether linkage in (+)-30 is formed by the trapping of the cation intermediate by the 6-OH group, which is not possible when (+)-shiromool acetate (16) is used as substrate. Using the above conditions, the 4,8-ring system (as in 31) was not observed, which could potentially arise from the Markovnikov opening of the 4,5-epoxide of (+)-shiromool (13). However, when dibenzyl phosphate was used as the acid for cyclization of (+)-13, (+)-31 was obtained, albeit with poor selectivity. Gratifyingly, using (+)-16 instead of (+)-13 as substrate under the same conditions afforded acetate (+)-31a in 70% yield, whose stereochemistry was unequivocally verified by X-ray crystallographic analysis.[34] Acetate (+)-31a was subsequently converted to (+)-31 in 78% yield upon treatment with K2CO3/MeOH at 50 °C.
Scheme 4.
Transannular cyclization to cadinane-, selinane-, elemene- and guaiane-type sesquiterpenes. Reagents and conditions: for 27: a) 16 (1 equiv), p-TsOH (0.27 equiv), CH2Cl2, 40 min, 44% of 27a, 7% of 29a, 19% of 28a; b) 27a (1 equiv), K2CO3 (10 equiv), MeOH, 50 °C, 1 h, quant.; for 28: 13 (1 equiv), Sc(OTf)3 (1 equiv), CH2Cl2, 0 °C, 10 min, 67% of 28; for 30: 13 (1 equiv), 32 (0.2 equiv), CH2Cl2, rt, 1 h, 49% of 30, 32% of 27 and 28; for 31: a) 16 (1 equiv), dibenzyl phosphate (1 equiv), CH2Cl2, rt, 30 min, 70% of 31a; b) 31a (1 equiv), K2CO3 (10 equiv), MeOH, 50 °C, 1 h, 78%.
The concise, scalable, enantioselective synthesis of epoxy-germacrenol 1 via a unique Pd-catalyzed macrocyclization presents a viable solution to the longstanding problem of forming the 10-membered germacrane ring system. It has also enabled the rapid formation of a range of germacrane-type sesquiterpenes 8-18, six of which are natural products. Of these compounds, 12, 18 and 13 can be converted in one single step to give cadinane-, elemene- or selinane-, and guaiane-type frameworks respectively. In particular, we have demonstrated that the cyclization of shiromool 13 to the guaiane-type natural products 27, 28, and 30 can be performed selectively, by varying either the substrate or the acid used. Finally, the divergent pathways to sesquiterpenes illustrated here nicely complement the recent elegant studies of Winssinger and co-workers.[35]
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Prof. A. Rheingold and Dr. C. Moore for X-ray crystallographic assistance. Financial support for this work was provided by NIH/NIGMS (GM-097444) and Leo Pharmaceuticals, A*STAR (predoctoral fellowship to K. F.), Uehara Memorial Foundation (postdoctoral fellowship to I.U.), German Academic Exchange Service, DAAD (postdoctoral fellowship to D.C.G.G.) and NSF (predoctoral fellowship to D.H.).
Footnotes
Supporting information for this article is available on the WWW under http://www.angewandte.org or from the author.
References
- [1].a) Chen K, Baran PS. Nature. 2009;459:824–828. doi: 10.1038/nature08043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b) Chen K, Ishihara Y, Galán MM, Baran PS. Tetrahedron. 2010;66:4738–4744. [Google Scholar]; c) Ishihara Y, Baran PS. Synlett. 2010:1733–1745. [Google Scholar]; d) Maimone TJ, Baran PS. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007;3:396–407. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2007.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Holte D, Götz DCG, Baran PS. J. Org. Chem. 2012;77:825–842. doi: 10.1021/jo202314a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].a) Adio AM. Tetrahedron. 2009;65:1533–1552. [Google Scholar]; b) Bülow N, König WA. Phytochemistry. 2000;55:141–168. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(00)00266-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Minnaard AJ, Wijnberg JBPA, de Groot A. Tetrahedron. 1999;55:2115–2146. [Google Scholar]
- [5].a) See ref. [2]; Shibuya H, Ohashi K, Kawashima K, Hori K, Murakami N, Kitagawa I. Chem. Lett. 1986;15:85–86. Takahashi T, Nemoto H, Kanda Y, Tsuji J, Fukazawa Y, Okajima T, Fujise Y. Tetrahedron. 1987;43:5499–5520. Jonas D, Özlü Y, Parsons PJ. Synlett. 1995:255–256. Kitahara T, Mori M, Koseki K, Mori K. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986;27:1343–1346. McMurry JE, Siemers NO. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994;35:4505–4508.
- [6].a) Katsuki T, Sharpless KB. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980;102:5974–5976. [Google Scholar]; b) Marshall JA, Hann RK. J. Org. Chem. 2008;73:6753–6757. doi: 10.1021/jo801188w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c) Uyanik M, Ishibashi H, Ishihara K, Yamamoto H. Org. Lett. 2005;7:1601–1604. doi: 10.1021/ol050295r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Kotaki T, Shinada T, Kaihara K, Ohfune Y, Numata H. Org. Lett. 2009;11:5234–5237. doi: 10.1021/ol902161x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].a) Mellegaard-Waetzig SR, Wang C, Tunge JA. Tetrahedron. 2006;62:7191–7198. [Google Scholar]; b) Tunge JA, Mellegaard SR. Org. Lett. 2004;6:1205–1207. doi: 10.1021/ol036525o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].a) Masuyama Y, Takahara JP, Kurusu Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988;110:4473–4474. [Google Scholar]; b) Kimura M, Horino Y, Mukai R, Tanaka S, Tamaru Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:10401–10402. doi: 10.1021/ja011656a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c) Zhu S-F, Qiao X-C, Zhang Y-Z, Wang L-X, Zhou Q-L. Chem. Sci. 2011;2:1135–1140. [Google Scholar]
- [10].a) Trost BM. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1989;28:1173–1192. [Google Scholar]; b) Trost BM, Verhoeven TR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979;101:1595–1597. [Google Scholar]; c) Trost BM, Burns AC, Bartlett MJ, Tautz T, Weiss AH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012;134:1474–1477. doi: 10.1021/ja210986f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].CCDC 896889 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
- [12].Azarken R, Guerra FM, Moreno-Dorado FJ, Jorge ZD, Massanet GM. Tetrahedron. 2008;64:10896–10905. [Google Scholar]
- [13].a) Higuchi Y, Shimoma F, Ando M. J. Nat. Prod. 2003;66:810–817. doi: 10.1021/np020586y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b) Matsuo K, Ohtsuki K, Yoshikawa T, Shishido K, Yokotani-Tomita K, Shindo M. Tetrahedron. 2010;66:8407–8419. [Google Scholar]
- [14].a) Ogura M, Cordell GA, Farnsworth NR. Phytochemistry. 1978;17:957–961. [Google Scholar]; b) Fischer NH, Weidenhamer JD, Bradow JM. Phytochemistry. 1989;28:2315–2317. [Google Scholar]; c) Fischer NH, Weidenhamer JD, Riopel JL, Quijano L, Menelaou MA. Phytochemistry. 1990;29:2479–2483. [Google Scholar]; d) Marles RJ, Kaminski J, Arnason JT, Pazos-Sanou L, Heptinstall S, Fischer NH, Crompton CW, Kindack DG, Awang DVC. J. Nat. Prod. 1992;55:1044–1056. doi: 10.1021/np50086a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].a) Govindachari TR, Joshi BS, Kamat VN. Tetrahedron Lett. 1964;5:3927–3933. [Google Scholar]; b) Govindachari TR, Joshi BS, Kamat VN. Tetrahedron. 1965;21:1509–1519. [Google Scholar]
- [16].Zhai J-D, Li D, Long J, Zhang H-L, Lin J-P, Qiu C-J, Zhang Q, Chen Y. J. Org. Chem. 2012;77:7103–7107. doi: 10.1021/jo300888s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].a) Crabtree R. Acc. Chem. Res. 1979;12:331–337. [Google Scholar]; b) Crabtree RH, Davis MW. J. Org. Chem. 1986;51:2655–2661. [Google Scholar]
- [18].Wada K, Enomoto Y, Munakata K. Agri. Biol. Chem. 1970;34:946–953. [Google Scholar]
- [19].a) Sanz JF, Marco JA. Phytochemistry. 1991;30:2788–2790. [Google Scholar]; b) Zhu Y, Zhao Y, Huang G-D, Wu W-S. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2008;91:1894–1901. [Google Scholar]
- [20].Garcia-Granados A, Molina A, Cabrera E. Tetrahedron. 1986;42:81–87. [Google Scholar]
- [21].Sharpless KB, Umbreit MA, Nieh MT, Flood TC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972;94:6538–6540. [Google Scholar]
- [22].Stahl-Biskup E, Laakso I. Planta Med. 1990;56:464–468. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-961012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Frigerio M, Santagostino M. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994;35:8019–8022. [Google Scholar]
- [24].a) Iguchi M, Niwa M, Nishiyama A, Yamamura S. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973;14:2759–2762. [Google Scholar]; b) Niwa M, Nishiyama A, Iguchi M, Yamamura S. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1975;48:2930–2934. [Google Scholar]; c) Still WC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977;99:4186–4187. doi: 10.1021/ja00454a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d) Takahashi T, Nemoto H, Tsuji J, Miura I. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983;24:3485–3488. [Google Scholar]
- [25].Menezes JESA, Lemos TLG, Silveira ER, Braz-Filho R, Pessoa ODL. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2001;12:787–790. [Google Scholar]
- [26].Bohlmann F, Jakupovic J, Vogel W. Phytochemistry. 1982;21:1153–1154. [Google Scholar]
- [27].Kodama M, Shimada K, Takahashi T, Kabuto C, Itô S. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981;22:4271–4274. [Google Scholar]
- [28].Iguchi M, Nishiyama A, Koyama H, Yamamura S, Hirata Y. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968;9:5315–5318. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)88499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Niwa M, Nishiyama A, Iguchi M, Yamamura S. Chem. Lett. 1972;1:823–826. [Google Scholar]
- [30].Niwa M, Iguchi M, Yamamura S. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1976;49:3148–3154. [Google Scholar]
- [31].Bruno M, de la Torre MC, Rodríguez B, Omar AA. Phytochemistry. 1993;34:245–247. [Google Scholar]
- [32].Mahmoud AA. Phytochemistry. 1997;45:1633–1638. [Google Scholar]
- [33].a) Ahmed AA, Hegazy M-EF, Hassan NM, Wojcinska M, Karchesy J, Pare PW, Mabry TJ. Phytochemistry. 2006;67:1547–1553. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b) Ono M, Yamashita M, Mori K, Masuoka C, Eto M, Kinjo J, Ikeda T, Yoshimitsu H, Nohara T. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2008;14:499–508. [Google Scholar]
- [34].CCDC 896888 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.
- [35].Valot G, Garcia J, Duplan V, Serba C, Barluenga S, Winssinger N. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012;51:5391–5394. doi: 10.1002/anie.201201157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.