Abstract
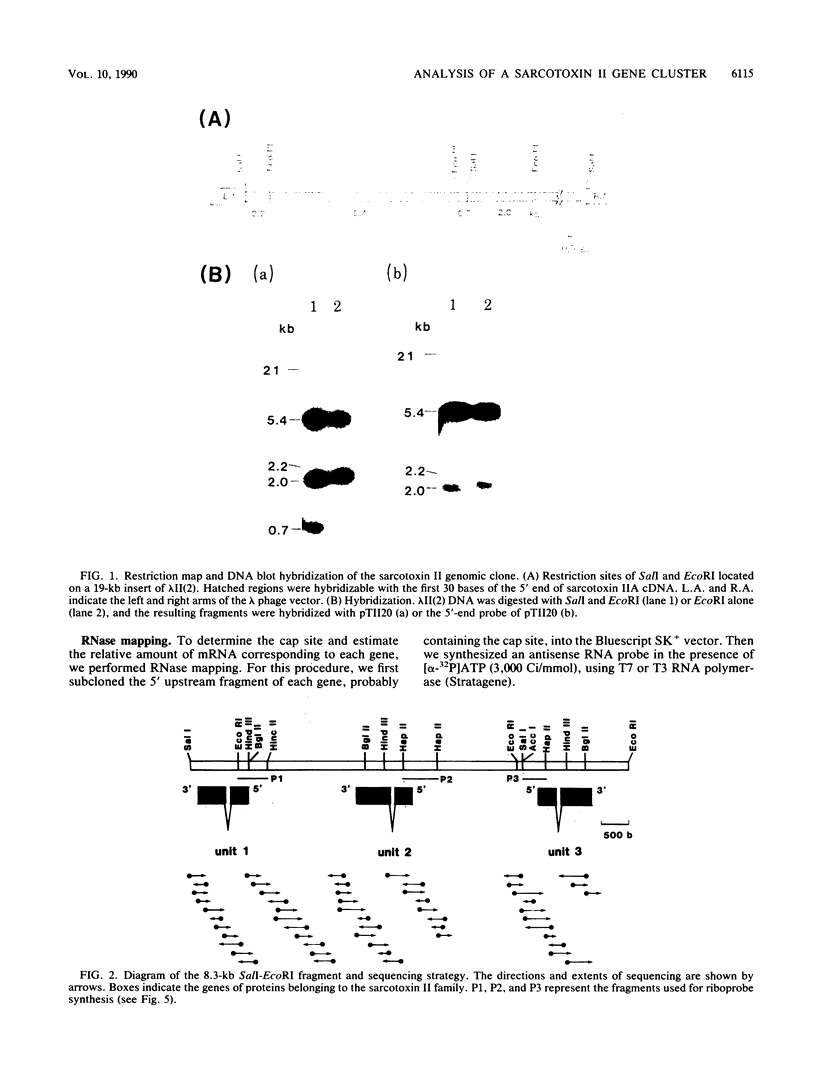
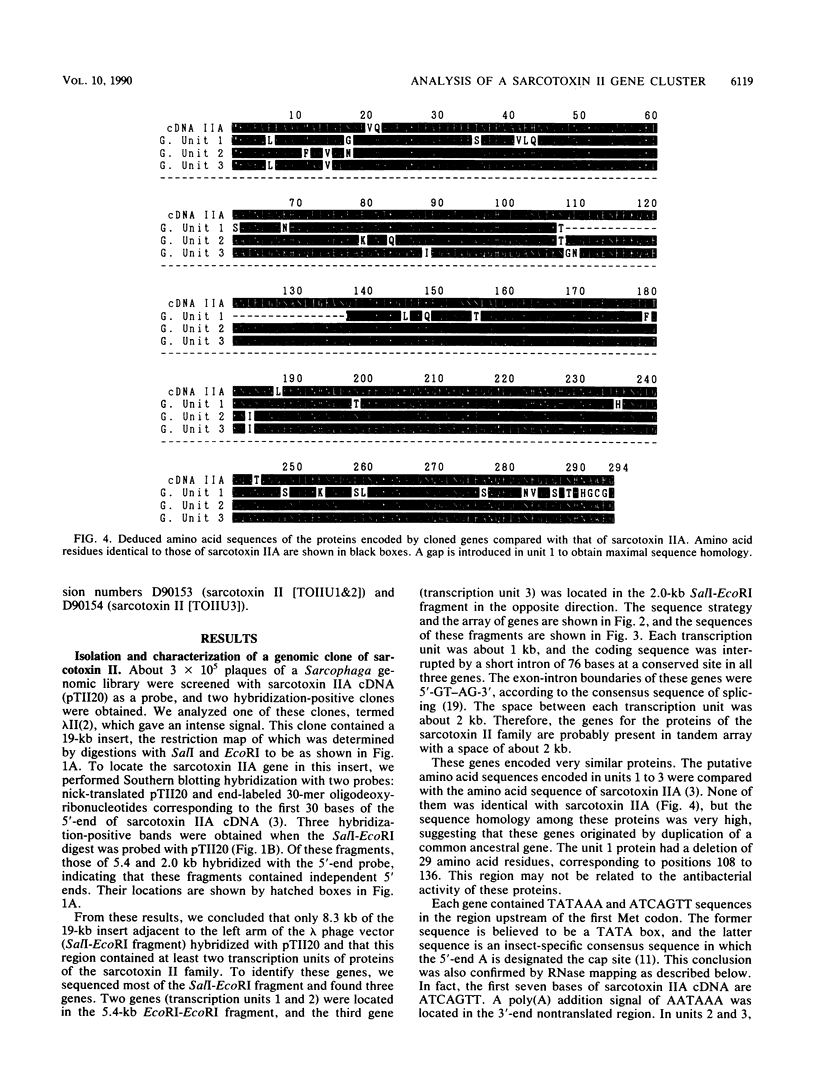
Sarcotoxin II is a group of antibacterial proteins of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) with related primary structures. We have cloned three genes in this family. These genes formed a tandem array with about 2-kb intervals, and one of them was present in the opposite strand. The putative amino acid sequences of the proteins encoded by these genes were very similar except for a deletion in one of them. All of the genes were found to be activated transiently in the same way when the larval body wall was injured, suggesting that the encoded proteins are acute-phase-responsive proteins for protecting the insect from bacterial infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando K., Natori S. Inhibitory effect of sarcotoxin IIA, an antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina, on growth of Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1988 Apr;103(4):735–739. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando K., Natori S. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and characterization of cDNA for sarcotoxin IIA, an inducible antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1715–1721. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando K., Okada M., Natori S. Purification of sarcotoxin II, antibacterial proteins of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 13;26(1):226–230. doi: 10.1021/bi00375a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba K., Okada M., Kawano T., Komano H., Natori S. Purification of sarcotoxin III, a new antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biochem. 1987 Jul;102(1):69–74. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels P., Ampe C., Riviere L., Van Damme J., Elicone C., Fleming M., Jacobs F., Tempst P. Isolation and characterization of abaecin, a major antibacterial response peptide in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 26;187(2):381–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimarcq J. L., Keppi E., Dunbar B., Lambert J., Reichhart J. M., Hoffmann D., Rankine S. M., Fothergill J. E., Hoffmann J. A. Insect immunity. Purification and characterization of a family of novel inducible antibacterial proteins from immunized larvae of the dipteran Phormia terranovae and complete amino-acid sequence of the predominant member, diptericin A. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):17–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Engström A., Andersson K., Steiner H., Bennich H., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Attacins, a family of antibacterial proteins from Hyalophora cecropia. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):571–576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Engström A., Bennich H., Kapur R., Boman H. G. Insect immunity: isolation and structure of cecropin D and four minor antibacterial components from Cecropia pupae. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep;127(1):207–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Translational and transcriptional control elements in the untranslated leader of the heat-shock gene hsp22. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Steiner H., Rasmuson T., Boman H. G. Insect immunity. Purification and properties of three inducible bactericidal proteins from hemolymph of immunized pupae of Hyalophora cecropia. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):7–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb05991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai A., Natori S. Cloning of gene cluster for sarcotoxin I, antibacterial proteins of Sarcophaga peregrina. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 4;258(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81652-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kylsten P., Samakovlis C., Hultmark D. The cecropin locus in Drosophila; a compact gene cluster involved in the response to infection. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):217–224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J., Keppi E., Dimarcq J. L., Wicker C., Reichhart J. M., Dunbar B., Lepage P., Van Dorsselaer A., Hoffmann J., Fothergill J. Insect immunity: isolation from immune blood of the dipteran Phormia terranovae of two insect antibacterial peptides with sequence homology to rabbit lung macrophage bactericidal peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama K., Natori S. Purification of three antibacterial proteins from the culture medium of NIH-Sape-4, an embryonic cell line of Sarcophaga peregrina. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17112–17116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Primary structure of sarcotoxin I, an antibacterial protein induced in the hemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7174–7177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Natori S. Purification and characterization of an antibacterial protein from haemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh-fly) larvae. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 1;211(3):727–734. doi: 10.1042/bj2110727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]