Abstract
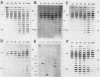
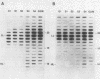
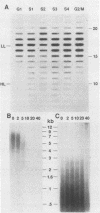
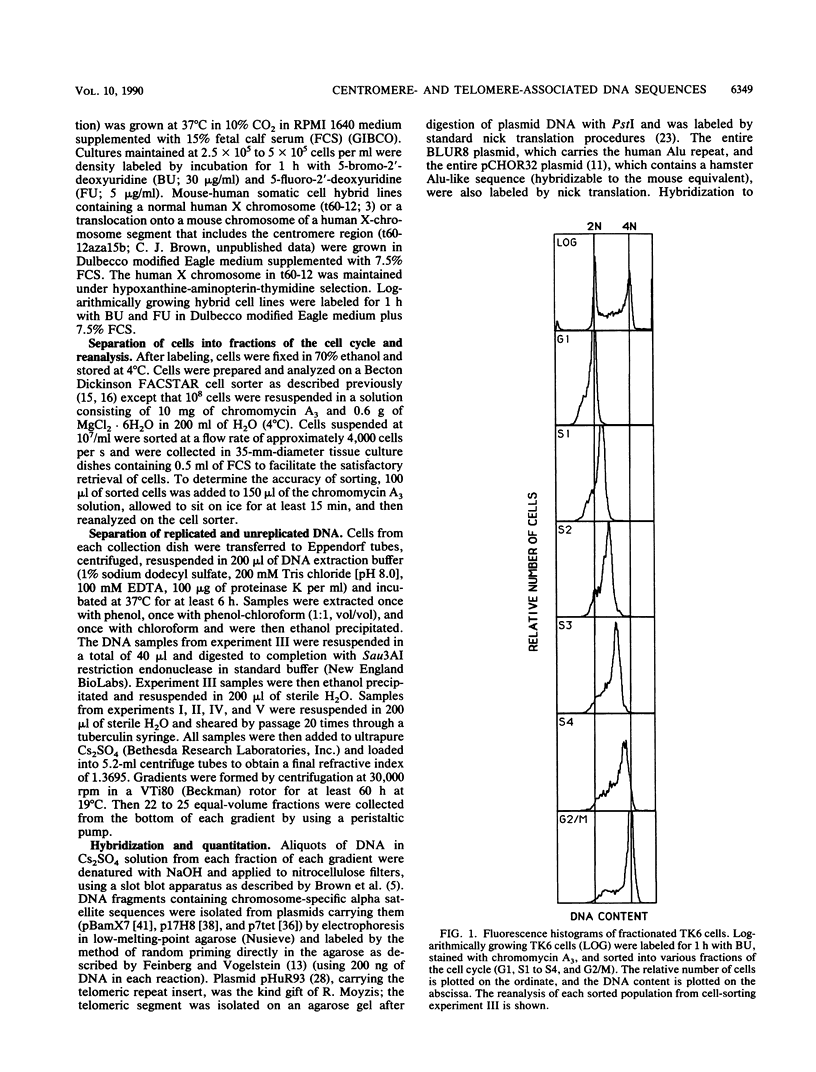
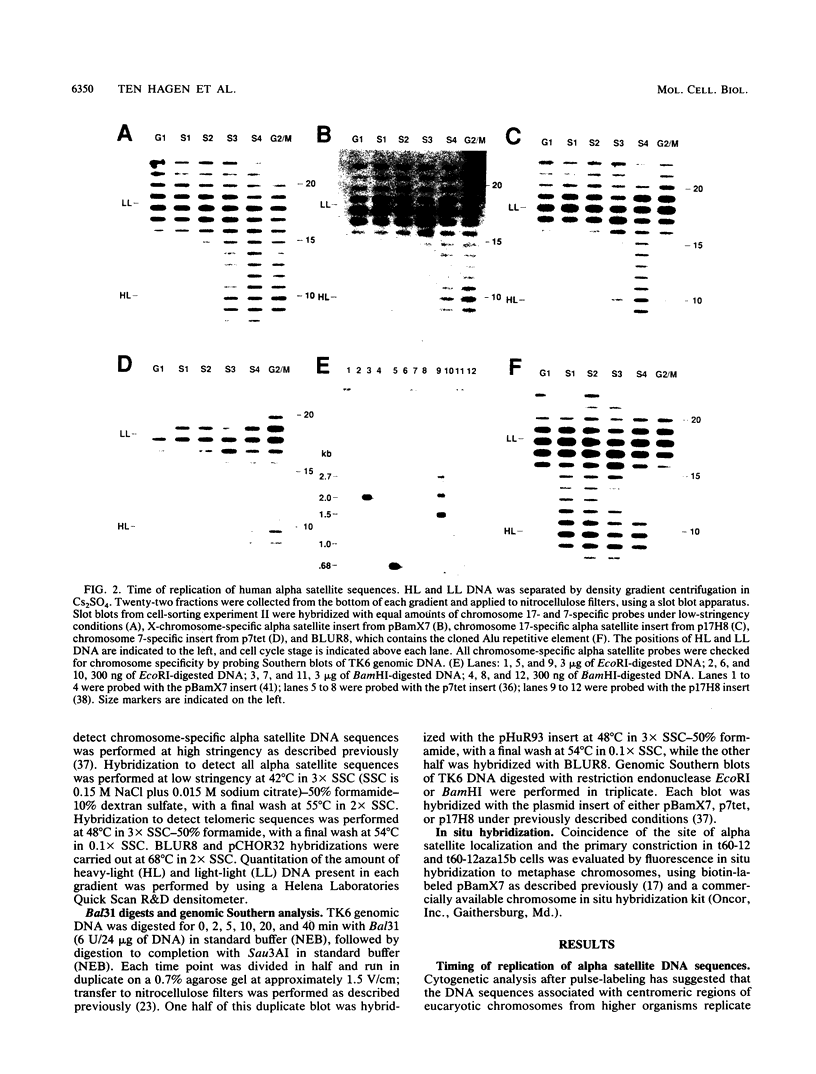
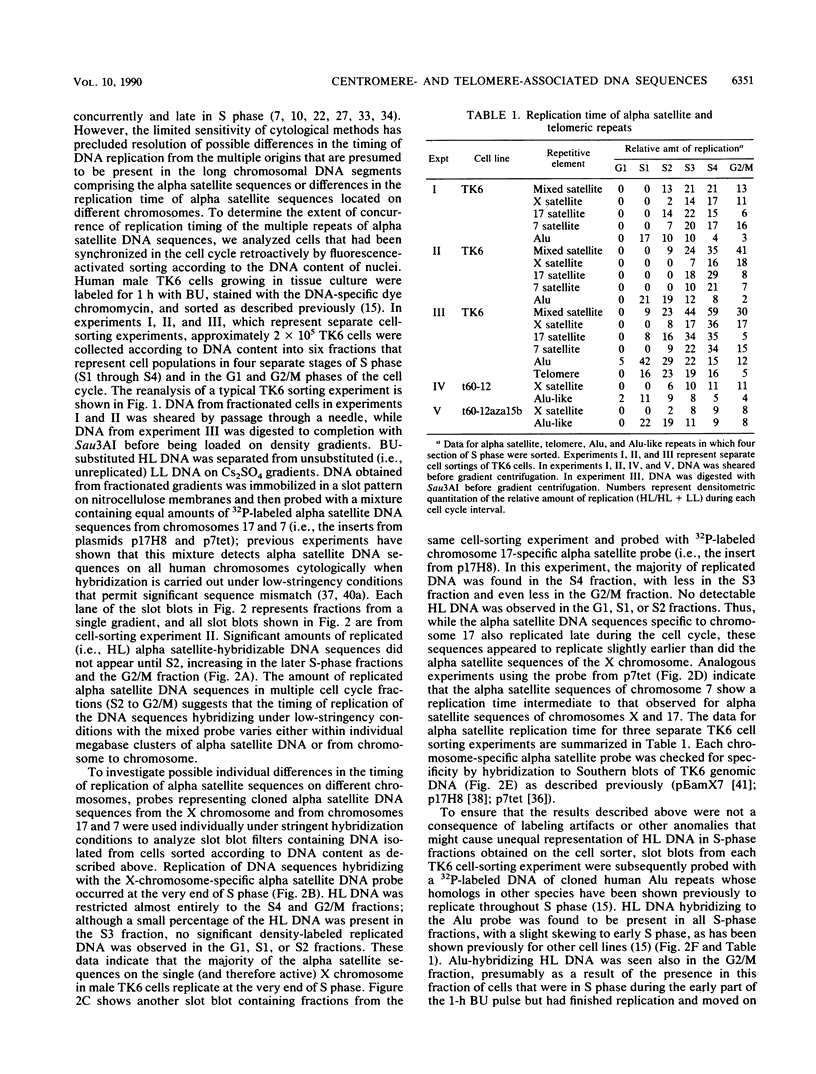
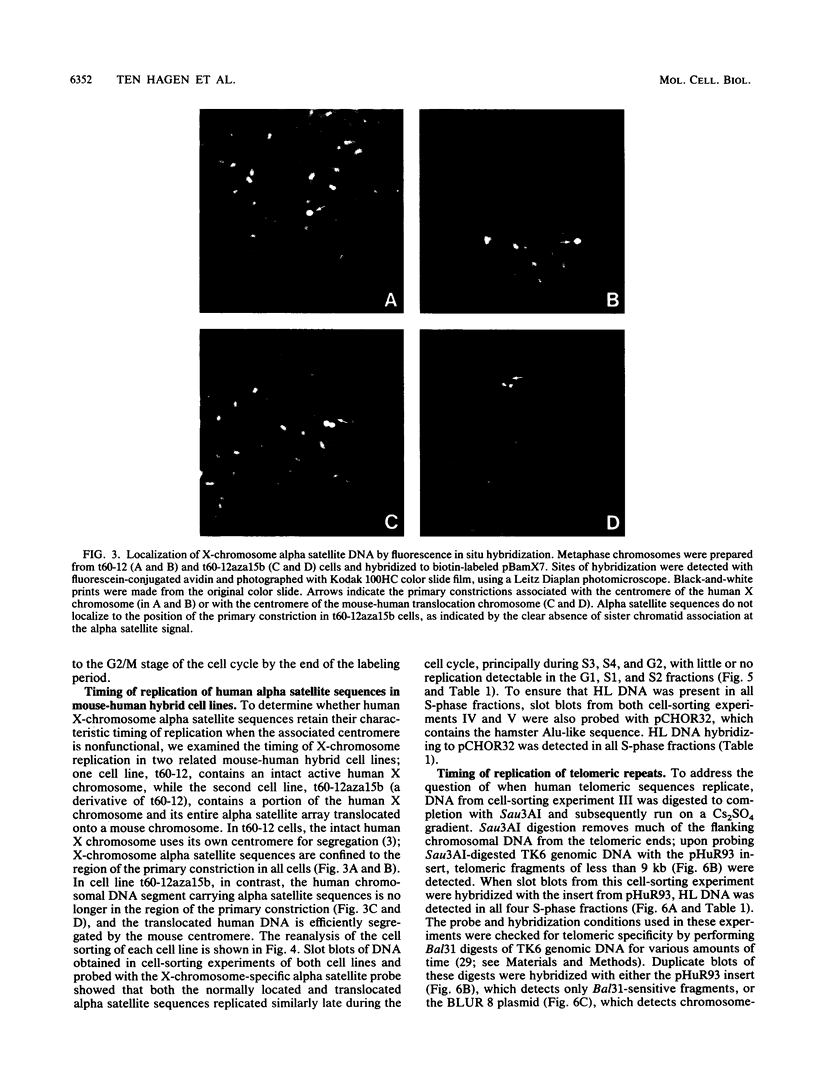
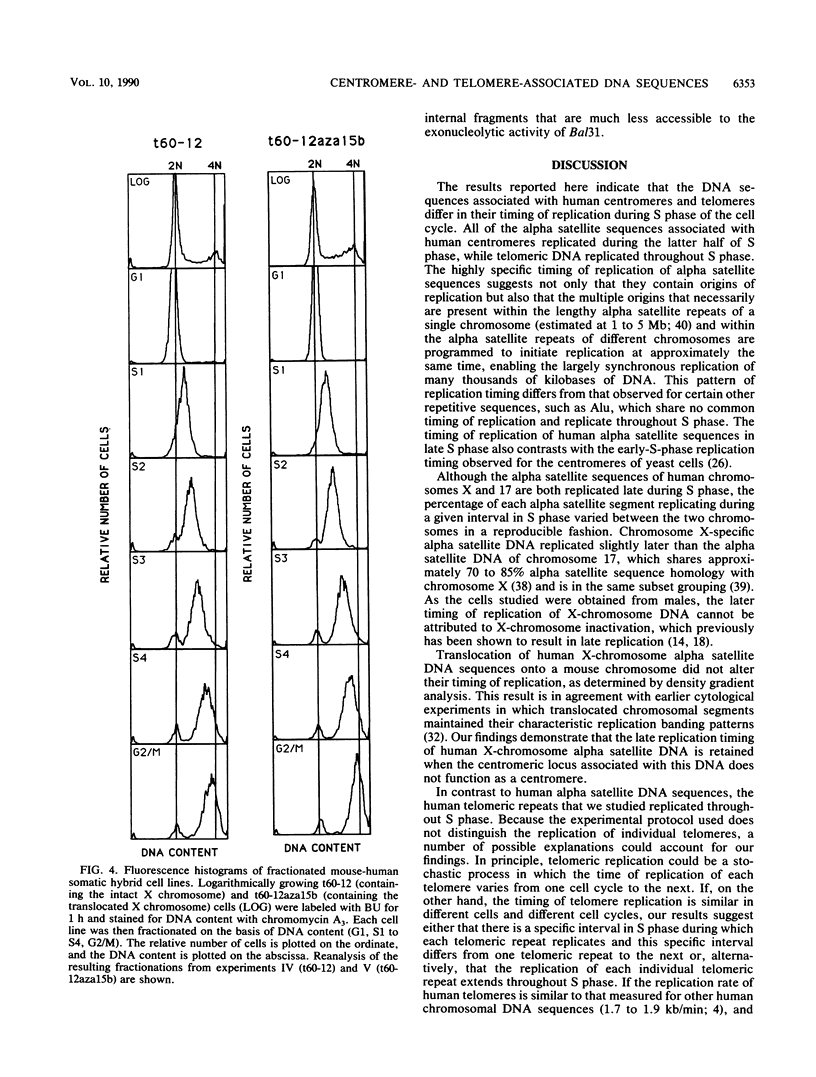
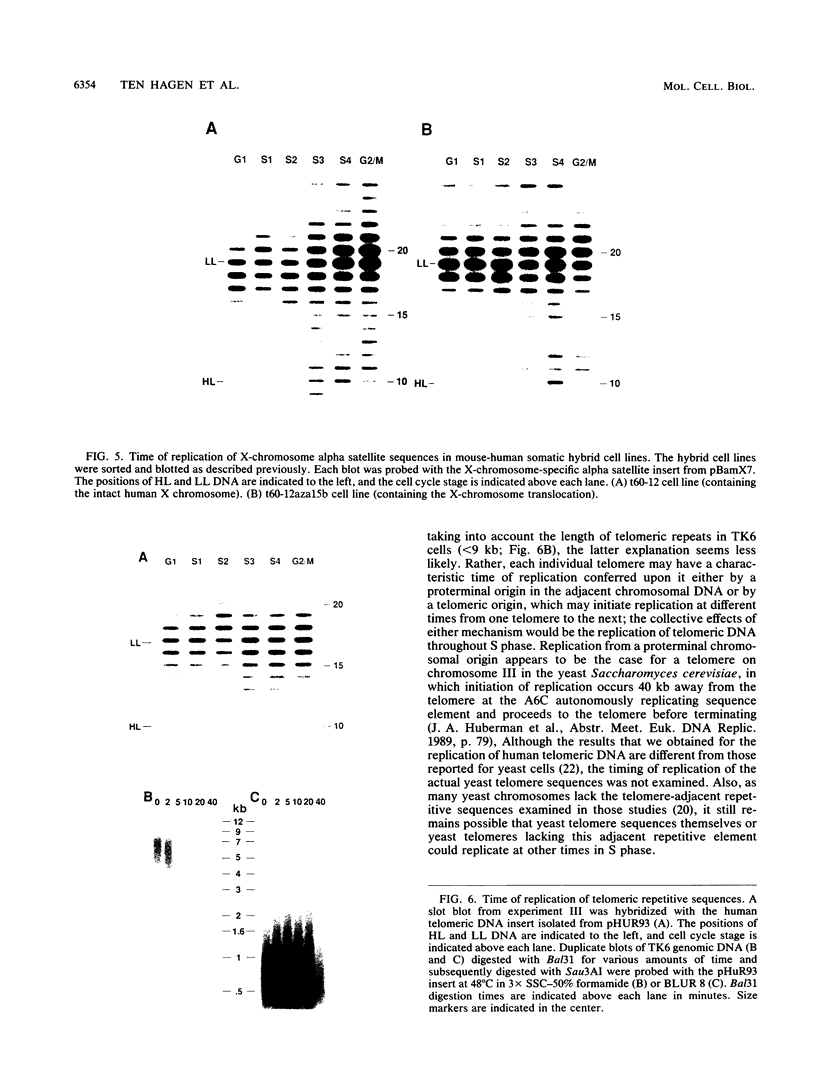
The timing of replication of centromere-associated human alpha satellite DNA from chromosomes X, 17, and 7 as well as of human telomeric sequences was determined by using density-labeling methods and fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Alpha satellite sequences replicated late in S phase; however, the alpha satellite sequences of the three chromosomes studied replicated at slightly different times. Human telomeres were found to replicate throughout most of S phase. These results are consistent with a model in which multiple initiations of replication occur at a characteristic time within the alpha satellite repeats of a particular chromosome, while the replication timing of telomeric sequences is determined by either telomeric origins that can initiate at different times during S phase or by replication origins within the flanking chromosomal DNA sequences.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adegoke J. A., Taylor J. H. Sequence programming of DNA replication over the S phase of Chinese hamster cells. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Jan;104(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allshire R. C., Gosden J. R., Cross S. H., Cranston G., Rout D., Sugawara N., Szostak J. W., Fantes P. A., Hastie N. D. Telomeric repeat from T. thermophila cross hybridizes with human telomeres. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):656–659. doi: 10.1038/332656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Powers V. E., Munroe D. L., Sheinin R., Willard H. F. Gene on short arm of human X chromosome complements murine tsA1S9 DNA synthesis mutation. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1989 Mar;15(2):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01535079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. H., Iqbal M. A., Stuart S., Hatton K. S., Valinsky J., Schildkraut C. L. Rate of replication of the murine immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus: evidence that the region is part of a single replicon. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):450–457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. C., Tlsty T. D., Schimke R. T. Enhancement of methotrexate resistance and dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification by treatment of mouse 3T6 cells with hydroxyurea. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1097–1107. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R. Molecular cloning of human telomeres in yeast. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):774–776. doi: 10.1038/338774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo M., Cervenka J. Patterns of DNA replication of human chromosomes. II. Replication map and replication model. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Sep;34(5):757–780. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. The structure and function of yeast centromeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:29–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. H., Allshire R. C., McKay S. J., McGill N. I., Cooke H. J. Cloning of human telomeres by complementation in yeast. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):771–774. doi: 10.1038/338771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossen P. E., Pathak S., Arrighi F. E. A high resolution study of the DNA replication patterns of chinese hamster chromosomes using sister chromatid differential staining technique. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 11;52(4):339–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00364018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Simonsen C. C., McEwan R. N., Schimke R. T. Structure of amplified normal and variant dihydrofolate reductase genes in mouse sarcoma S180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7887–7897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPraw E. J. Macromolecular organization of nuclei and chromosomes: a folded fibre model based on whole-mount electron microscopy. Nature. 1965 Apr 24;206(982):338–343. doi: 10.1038/206338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. M., Cohen S. N. Bovine papilloma virus plasmids replicate randomly in mouse fibroblasts throughout S phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90662-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. W., Coffino P. Cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:233–248. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig G. M., England S. B., Bedford H. M., Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA from the centromere of human chromosome 16. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;45(6):862–872. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumbach M. M., Morishima A., Taylor J. H. HUMAN SEX CHROMOSOME ABNORMALITIES IN RELATION TO DNA REPLICATION AND HETEROCHROMATINIZATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):581–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäger D., Philippsen P. Many yeast chromosomes lack the telomere-specific Y' sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5754–5757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Harland R. M. Replication origins in the eucaryotic chromosome. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):283–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masumoto H., Masukata H., Muro Y., Nozaki N., Okazaki T. A human centromere antigen (CENP-B) interacts with a short specific sequence in alphoid DNA, a human centromeric satellite. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):1963–1973. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masumoto H., Sugimoto K., Okazaki T. Alphoid satellite DNA is tightly associated with centromere antigens in human chromosomes throughout the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Mar;181(1):181–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90192-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarroll R. M., Fangman W. L. Time of replication of yeast centromeres and telomeres. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):505–513. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90072-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meer B., Hameister H., Cerrillo M. Early and later replication patterns of increased resolution in human lymphocyte chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):315–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00286114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller G. C., Kajiwara K. Early- and late-replicating deoxyribonucleic acid complexes in HeLa nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):108–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Cooke C. A., Earnshaw W. C. Structure of the human centromere at metaphase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E. Analysis of the replication pattern of Chinese hamster chromosomes using 5-bromodeoxyuridine suppression of 33258 Hoechst fluorescence. Chromosoma. 1975 Dec 10;53(3):209–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00329172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E. Mammalian chromosomes in vitro. XIX. Chromosomes of Don-C, a Chinese hamster fibroblast strain with a part of autosome 1b translocated to the Y chromosome. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Dec;37(6):799–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. H. Asynchronous duplication of chromosomes in cultured cells of Chinese hamster. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jun;7:455–464. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.3.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Copy number control by a yeast centromere. Gene. 1983 Aug;23(2):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., England S. B., Willard H. F. Genomic organization of alpha satellite DNA on human chromosome 7: evidence for two distinct alphoid domains on a single chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):349–356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Mitchell A. R., Willard H. F. Organization and genomic distribution of "82H" alpha satellite DNA. Evidence for a low-copy or single-copy alphoid domain located on human chromosome 14. Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;78(1):27–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00291229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Nucleotide sequence heterogeneity of alpha satellite repetitive DNA: a survey of alphoid sequences from different human chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7549–7569. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Structure, organization, and sequence of alpha satellite DNA from human chromosome 17: evidence for evolution by unequal crossing-over and an ancestral pentamer repeat shared with the human X chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3156–3165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wevrick R., Willard H. F. Long-range organization of tandem arrays of alpha satellite DNA at the centromeres of human chromosomes: high-frequency array-length polymorphism and meiotic stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9394–9398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Smith K. D., Sutherland J. Isolation and characterization of a major tandem repeat family from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):2017–2033. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]