Abstract
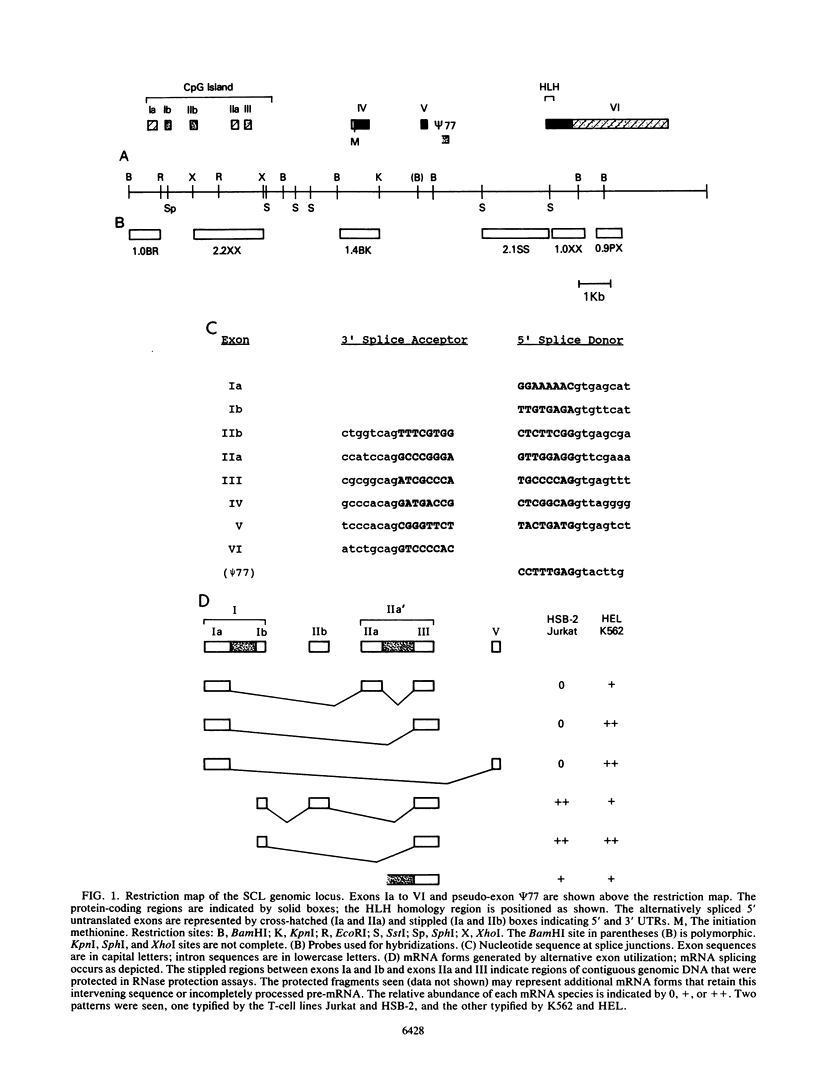
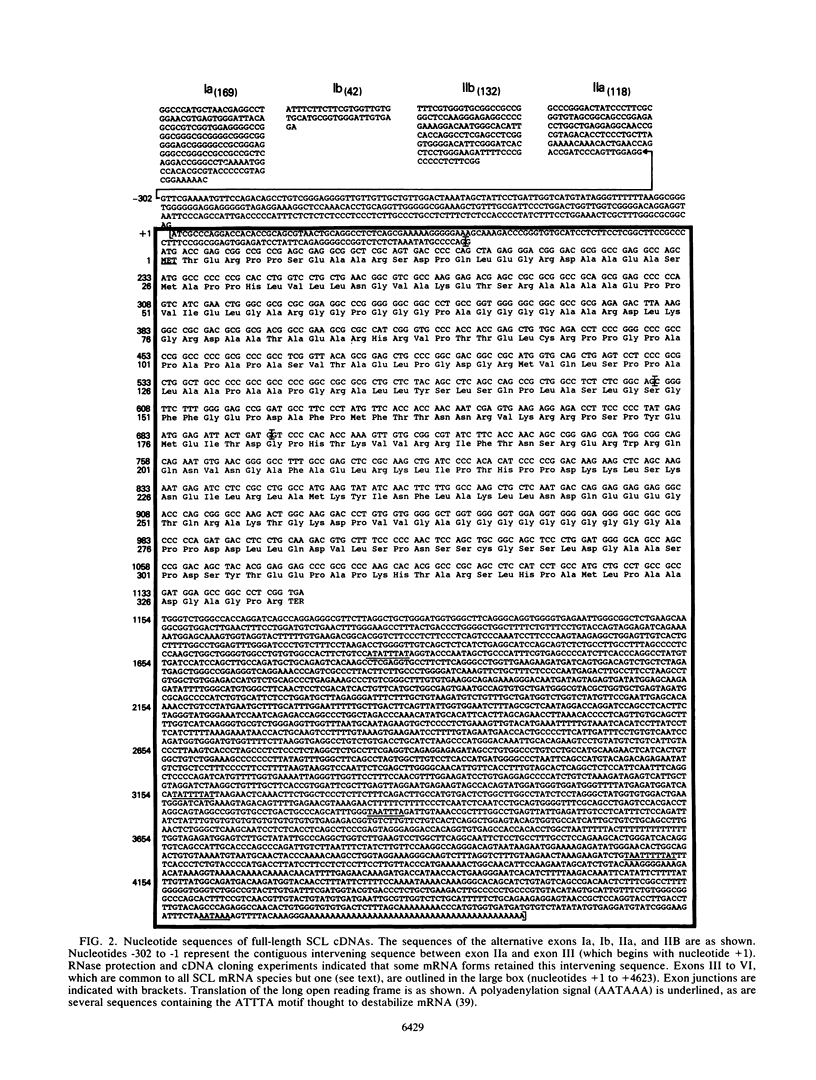
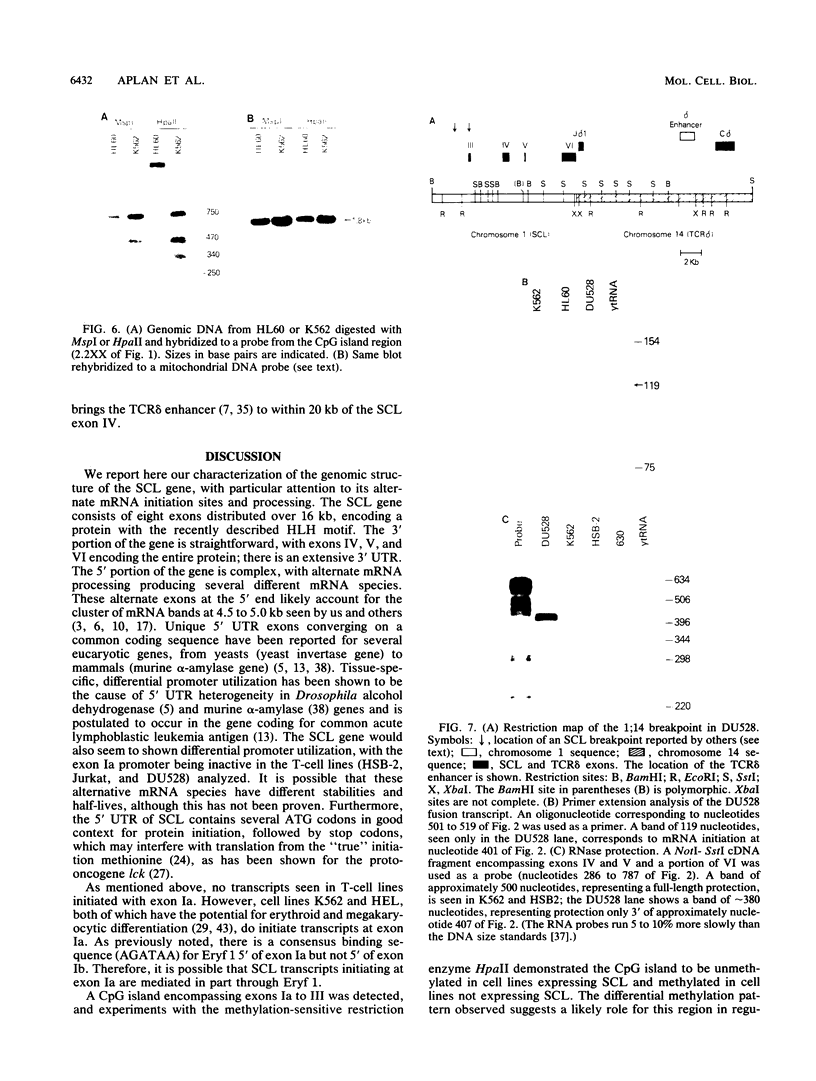
We describe the structural organization of the human SCL gene, a helix-loop-helix family member which we believe plays a fundamental role in hematopoietic differentiation. The SCL locus is composed of eight exons distributed over 16 kb. SCL shows a pattern of expression quite restricted to early hematopoietic tissues, although in malignant states expression of the gene may be somewhat extended into later developmental stages. A detailed analysis of the transcript(s) arising from the SCL locus revealed that (i) the 5' noncoding portion of the SCL transcript, which resides within a CpG island, has a complex pattern of alternative exon utilization as well as two distinct transcription initiation sites; (ii) the 5' portions of the SCL transcript contain features that suggest a possible regulatory role for these segments; (iii) the pattern of utilization of the 5' exons is cell lineage dependent; and (iv) all of the currently studied chromosomal aberrations that affect the SCL locus either structurally or functionally eliminate the normal 5' transcription initiation sites. These data suggest that the SCL gene, and specifically its 5' region, may be a target for regulatory interactions during early hematopoietic development.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. A., Flowers A., Davis B. J. Direct implantation and serial transplantation of human acute lymphoblastic leukemia in hamsters, SB-2. Cancer Res. 1968 Jun;28(6):1121–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begley C. G., Aplan P. D., Davey M. P., Nakahara K., Tchorz K., Kurtzberg J., Hershfield M. S., Haynes B. F., Cohen D. I., Waldmann T. A. Chromosomal translocation in a human leukemic stem-cell line disrupts the T-cell antigen receptor delta-chain diversity region and results in a previously unreported fusion transcript. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begley C. G., Aplan P. D., Denning S. M., Haynes B. F., Waldmann T. A., Kirsch I. R. The gene SCL is expressed during early hematopoiesis and encodes a differentiation-related DNA-binding motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10128–10132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Guglielmi P., Jonveaux P., Cherif D., Gisselbrecht S., Mauchauffe M., Berger R., Larsen C. J., Mathieu-Mahul D. Two distinct mechanisms for the SCL gene activation in the t(1;14) translocation of T-cell leukemias. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1990 Jan;1(3):194–208. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bories J. C., Loiseau P., d'Auriol L., Gontier C., Bensussan A., Degos L., Sigaux F. Regulation of transcription of the human T cell antigen receptor delta chain gene. A T lineage-specific enhancer element is located in the J delta 3-C delta intron. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):75–83. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q., Cheng J. T., Tasi L. H., Schneider N., Buchanan G., Carroll A., Crist W., Ozanne B., Siciliano M. J., Baer R. The tal gene undergoes chromosome translocation in T cell leukemia and potentially encodes a helix-loop-helix protein. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):415–424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Adamio L., Shipp M. A., Masteller E. L., Reinherz E. L. Organization of the gene encoding common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (neutral endopeptidase 24.11): multiple miniexons and separate 5' untranslated regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7103–7107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Greve J., Battey J., Fedorko J., Birrer M., Evan G., Kaye F., Sausville E., Minna J. The human L-myc gene encodes multiple nuclear phosphoproteins from alternatively processed mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4381–4388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger L. R., Kagan J., Christopher G., Kurtzberg J., Hershfield M. S., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Involvement of the TCL5 gene on human chromosome 1 in T-cell leukemia and melanoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5039–5043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Kurtzberg J., Harden E., Moore J. O., Whang-Peng J., Haynes B. F. Conversion of a stem cell leukemia from a T-lymphoid to a myeloid phenotype induced by the adenosine deaminase inhibitor 2'-deoxycoformycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):253–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch I. R., Brown J. A., Lawrence J., Korsmeyer S. J., Morton C. C. Translocations that highlight chromosomal regions of differentiated activity. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1985 Oct;18(2):159–171. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(85)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koning F., Yokoyama W. M., Maloy W. L., Stingl G., McConnell T. J., Cohen D. I., Shevach E. M., Coligan J. E. Expression of C gamma 4 T cell receptors and lack of isotype exclusion by dendritic epidermal T cell lines. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2057–2062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzberg J., Bigner S. H., Hershfield M. S. Establishment of the DU.528 human lymphohemopoietic stem cell line. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1561–1578. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Krystal G., Lebacq-Verheyden A. M., Way J., Sausville E. A., Battey J. Transcriptional activation and DNase I hypersensitive sites are associated with selective expression of the gastrin-releasing peptide gene. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):808–815. doi: 10.1172/JCI113683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Overell R. W., Meier K. E., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Translational activation of the lck proto-oncogene. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):171–173. doi: 10.1038/332171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Zon L. I., Mutter G., Orkin S. H. Expression of an erythroid transcription factor in megakaryocytic and mast cell lineages. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):444–447. doi: 10.1038/344444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Papayannopoulou T. HEL cells: a new human erythroleukemia cell line with spontaneous and induced globin expression. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1233–1235. doi: 10.1126/science.6177045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellentin J. D., Smith S. D., Cleary M. L. lyl-1, a novel gene altered by chromosomal translocation in T cell leukemia, codes for a protein with a helix-loop-helix DNA binding motif. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ntambi J. M., Buhrow S. A., Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., Sibley E., Kelly T. J., Jr, Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Characterization of a differentially expressed gene encoding stearoyl-CoA desaturase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17291–17300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redondo J. M., Hata S., Brocklehurst C., Krangel M. S. A T cell-specific transcriptional enhancer within the human T cell receptor delta locus. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1225–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.2156339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo P. H., Prandini M. H., Joulin V., Mignotte V., Prenant M., Vainchenker W., Marguerie G., Uzan G. Megakaryocytic and erythrocytic lineages share specific transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):447–449. doi: 10.1038/344447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Pittet A. C. Two promoters of different strengths control the transcription of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a in the parotid gland and the liver. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L. Developmental biology of T cell receptors. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):943–950. doi: 10.1126/science.2658058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetteroo P. A., Massaro F., Mulder A., Schreuder-van Gelder R., von dem Borne A. E. Megakaryoblastic differentiation of proerythroblastic K562 cell-line cells. Leuk Res. 1984;8(2):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(84)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]