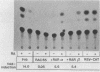
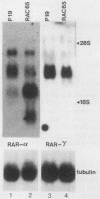
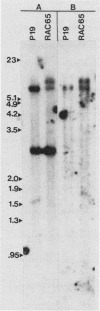
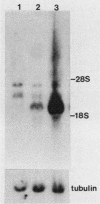
Abstract
Pluripotential embryonal carcinoma cells such as those of the P19 line differentiate when exposed to retinoic acid (RA). The RAC65 cell line is a mutant clone of P19 cells selected to be RA nonresponsive. RAC65 cells carry a rearrangement affecting one of the genes encoding a nuclear retinoic acid receptor (RAR alpha). The mutant gene encodes a protein, RAR alpha', that has lost its 70 C-terminal amino acids, thus truncating the RA-binding domain. The RAR alpha' was found to be a dominant repressor of transcription from an RA-responsive target gene; however, expression of RAR alpha' was insufficient to confer RA nonresponsiveness, suggesting that RAC65 cells carry an additional mutation(s) affecting RA-induced genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adra C. N., Boer P. H., McBurney M. W. Cloning and expression of the mouse pgk-1 gene and the nucleotide sequence of its promoter. Gene. 1987;60(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D., Lernhardt E., Pfahl M. A new retinoic acid receptor identified from a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):669–672. doi: 10.1038/333669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett K. L., Hill R. E., Pietras D. F., Woodworth-Gutai M., Kane-Haas C., Houston J. M., Heath J. K., Hastie N. D. Most highly repeated dispersed DNA families in the mouse genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1561–1571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. W., McBurney M. W. Cell density and cell cycle effects on retinoic acid-induced embryonal carcinoma cell differentiation. Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;138(1):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90182-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladon T. S., Frégeau C. J., McBurney M. W. Synthesis and processing of small B2 transcripts in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4058–4067. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer P. H., Potten H., Adra C. N., Jardine K., Mullhofer G., McBurney M. W. Polymorphisms in the coding and noncoding regions of murine Pgk-1 alleles. Biochem Genet. 1990 Jun;28(5-6):299–308. doi: 10.1007/BF02401419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P. Retinoids, homeobox genes, and limb morphogenesis. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1285–1294. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J. The HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line: proliferation, differentiation, and cellular oncogene expression. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1233–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Ruberte E., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Stoner C. M., Gudas L. J., Chambon P. Differential expression of genes encoding alpha, beta and gamma retinoic acid receptors and CRABP in the developing limbs of the mouse. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):702–705. doi: 10.1038/342702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durston A. J., Timmermans J. P., Hage W. J., Hendriks H. F., de Vries N. J., Heideveld M., Nieuwkoop P. D. Retinoic acid causes an anteroposterior transformation in the developing central nervous system. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):140–144. doi: 10.1038/340140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichele G. Retinoic acid induces a pattern of digits in anterior half wing buds that lack the zone of polarizing activity. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):863–867. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espeseth A. S., Murphy S. P., Linney E. Retinoic acid receptor expression vector inhibits differentiation of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1647–1656. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt S. J., Krumlauf R., Duboule D. Mouse homeo-genes within a subfamily, Hox-1.4, -2.6 and -5.1, display similar anteroposterior domains of expression in the embryo, but show stage- and tissue-dependent differences in their regulation. Development. 1989 Sep;107(1):131–141. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giampaolo A., Acampora D., Zappavigna V., Pannese M., D'Esposito M., Carè A., Faiella A., Stornaiuolo A., Russo G., Simeone A. Differential expression of human HOX-2 genes along the anterior-posterior axis in embryonic central nervous system. Differentiation. 1989 Jun;40(3):191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Ong E. S., Evans R. M., Tabin C. J. Spatial and temporal expression of the retinoic acid receptor in the regenerating amphibian limb. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):566–569. doi: 10.1038/337566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C. K., Lipkin S. M., Devary O. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Positive and negative regulation of gene transcription by a retinoic acid-thyroid hormone receptor heterodimer. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):697–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graupner G., Wills K. N., Tzukerman M., Zhang X. K., Pfahl M. Dual regulatory role for thyroid-hormone receptors allows control of retinoic-acid receptor activity. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):653–656. doi: 10.1038/340653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler M. L., Sherman M. I. Metabolism of retinoids by embryonal carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9552–9558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Labeit S., Poustka A., King T. R., Lehrach H. Cloning of the T gene required in mesoderm formation in the mouse. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):617–622. doi: 10.1038/343617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornbruch A., Wolpert L. Positional signalling by Hensen's node when grafted to the chick limb bud. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1986 Jun;94:257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L., Gudas L. J. Cyclic AMP analogs and retinoic acid influence the expression of retinoic acid receptor alpha, beta, and gamma mRNAs in F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):391–396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Mahdavi V. Thyroid hormone receptor alpha isoforms generated by alternative splicing differentially activate myosin HC gene transcription. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):539–542. doi: 10.1038/334539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., McBurney M. W., Rogers K. A., Kalnins V. I. Retinoic acid induces embryonal carcinoma cells to differentiate into neurons and glial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):253–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., Rudnicki M. A., Harris J. F., McBurney M. W. Retinoic acid-induced neural differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2271–2279. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Brent G. A., Larsen P. R., Chin W. W., Moore D. D. Inhibition of thyroid hormone action by a non-hormone binding c-erbA protein generated by alternative mRNA splicing. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):659–661. doi: 10.1038/337659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruys V. I., Wathelet M. G., Huez G. A. Identification of a translation inhibitory element (TIE) in the 3' untranslated region of the human interferon-beta mRNA. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruys V., Wathelet M., Poupart P., Contreras R., Fiers W., Content J., Huez G. The 3' untranslated region of the human interferon-beta mRNA has an inhibitory effect on translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6030–6034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. Early retinoic acid-induced F9 teratocarcinoma stem cell gene ERA-1: alternate splicing creates transcripts for a homeobox-containing protein and one lacking the homeobox. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3906–3917. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langille R. M., Paulsen D. F., Solursh M. Differential effects of physiological concentrations of retinoic acid in vitro on chondrogenesis and myogenesis in chick craniofacial mesenchyme. Differentiation. 1989 May;40(2):84–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemischka I. R., Farmer S., Racaniello V. R., Sharp P. A. Nucleotide sequence and evolution of a mammalian alpha-tubulin messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):101–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90223-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Effects of vitamin A and its analogs (retinoids) on normal and neoplastic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 12;605(1):33–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M. Vitamin A and pattern formation in the regenerating limb. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):672–675. doi: 10.1038/295672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Simeone A., Boncinelli E., Andrews P. W. Activation of four homeobox gene clusters in human embryonal carcinoma cells induced to differentiate by retinoic acid. Differentiation. 1988;37(1):73–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Reuhl K. R., Ally A. I., Nasipuri S., Bell J. C., Craig J. Differentiation and maturation of embryonal carcinoma-derived neurons in cell culture. J Neurosci. 1988 Mar;8(3):1063–1073. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-03-01063.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Rogers B. J. Isolation of male embryonal carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto K., Okazawa H., Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M., Hamada H. A novel octamer binding transcription factor is differentially expressed in mouse embryonic cells. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90597-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posch K. C., Enright W. J., Napoli J. L. Retinoic acid synthesis by cytosol from the alcohol dehydrogenase negative deermouse. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Oct;274(1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicki M. A., Sawtell N. M., Reuhl K. R., Berg R., Craig J. C., Jardine K., Lessard J. L., McBurney M. W. Smooth muscle actin expression during P19 embryonal carcinoma differentiation in cell culture. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jan;142(1):89–98. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. Repression of transcription mediated at a thyroid hormone response element by the v-erb-A oncogene product. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):242–244. doi: 10.1038/340242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler J., Matthaei K. I., Sherman M. I. Isolation and characterization of mouse mutant embryonal carcinoma cells which fail to differentiate in response to retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1077–1080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shell B., Szurek P., Dunnick W. Interruption of two immunoglobulin heavy-chain switch regions in murine plasmacytoma P3.26Bu4 by insertion of retroviruslike element ETn. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1364–1370. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M. Embryology: we have a morphogen! Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):553–554. doi: 10.1038/327553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Wain-Hobson S., Bougueleret L., Tiollais P., Jacob F., Brûlet P. Nucleotide sequence and evolution of ETn elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3768–3771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaller C., Eichele G. Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):625–628. doi: 10.1038/327625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Cook M., Boncinelli E., Krumlauf R. Segmental expression of Hox-2 homoeobox-containing genes in the developing mouse hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):405–409. doi: 10.1038/341405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. B., Napoli J. L. Metabolism of retinoic acid and retinol during differentiation of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4658–4662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen A., Reece S. L., Albright K. L. Membrane origin for a signal eliciting a program of cell differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jun;152(2):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90651-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Kahn P., Disela C., Vennström B., Leutz A., Keegan K., Hayman M. J., Choi H. R., Yew N., Engel J. D. v-erbA specifically suppresses transcription of the avian erythrocyte anion transporter (band 3) gene. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):107–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90535-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de The H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Differential expression and ligand regulation of the retinoic acid receptor alpha and beta genes. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):429–433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]