Abstract
The exact etiology of the coronary slow flow phenomenon (CSFP) is not certain. CSFP is not a normal variant as it is an absolutely pathological entity. Furthermore, CSFP not only leads to myocardial ischemia but it can also cause classical acute ST elevation myocardial infarction, which necessitates coronary angiography for a definite diagnosis.
Keywords: Slow-flow phenomenon, Acute anterior wall myocardial infarction
Introduction
Coronary slow flow phenomenon (CSFP) is defined as the delayed distal contrast opacification of normal or near normal coronary arteries. Here, we report a patient who has coronary slow flow presented with acute myocardial infarction.
Case
Recently, a 39 year-old female patient was admitted to our emergency room with new onset chest pain. The chest pain was described as a pressure-like sensation in the center of her chest, 8/10 in severity, and radiated down her left arm. She had no previous medical history. Also, she had no inherent risk factors except for smoking. Her electrocardiography revealed an ST elevation of approximately 3 mm in the anterior precordial leads (Fig. 1). This patient was immediately taken into the catheter laboratory with a diagnosis of hyperacute anterior myocardial infarction. Coronary angiography showed slow dye flow and delayed distal vessel clearance in the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) (Fig. 2). Coronary arteries were normal except for some plague in the left and right coronary artery (RCA). Her corrected Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) frame count (CTFC) for the LAD was 34.1 (normal range 21±3). The TIMI frame count for the RCA was 15 and the circumflex artery was 20 (Fig. 3). Following the angiography, her chest pain stopped. The ST elevation came to the isolelectric line. T waves were negative in V 3-6 leads (Fig. 4). The troponin T level elevated mildly to 0.28 ng/mL (>0.1 ng/mL positive) but the creatine kinase-MB level was normal. Her laboratory findings were completely normal. Her body mass index was 26. Transthoracic echocardiography revealed normal left ventricular function, and mild mitral regurgitation without no segmentary wall motion disturbance. During hospitalization, the patient was stable and chest pain did not recur. The patient was discharged with 100 mg acetylsalicylic acid and 5 mg nebivolol treatment after 3 days of hospitalization.
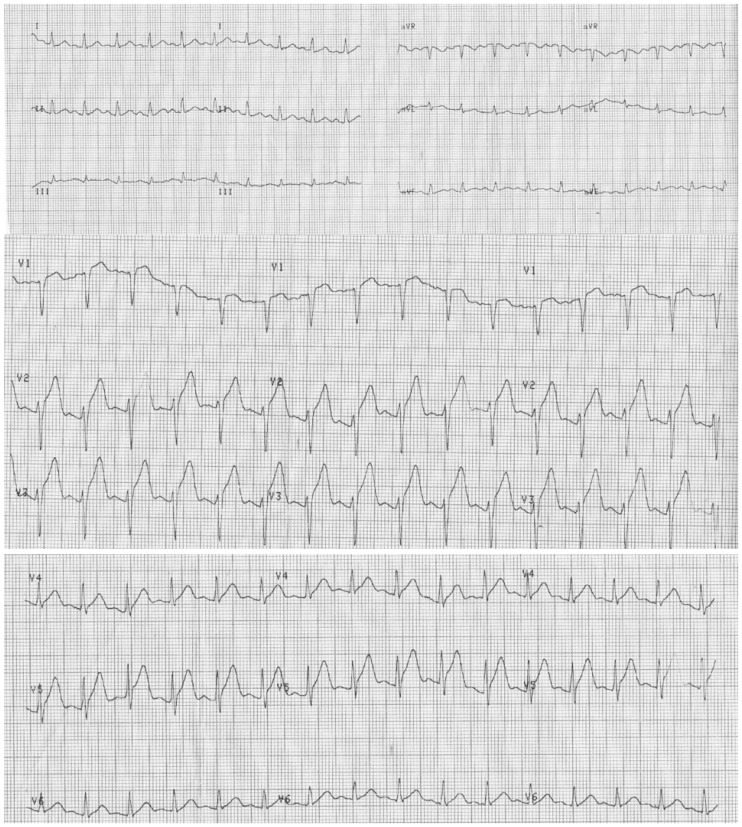
Fig. 1.
The ECG shows marked ST elevation in the anterior precordial leads. This ECG leads to a diagnosis of hyperacute anterior myocardial infarction. ECG: electrocardiography.
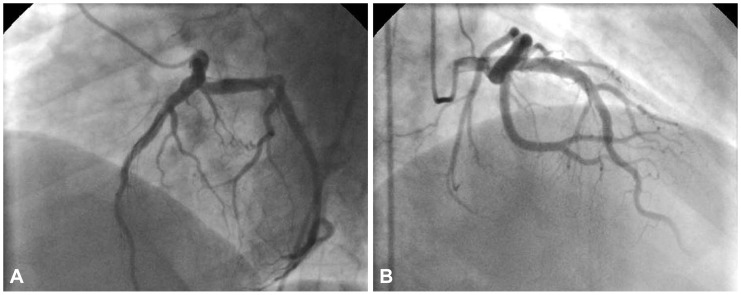
Fig. 2.
This angiographical image (A: left anterior oblique cranial view, B: right anterior oblique view) reveals left sided normal coronary arteries except slow coronary flow in the left anterior descending artery.
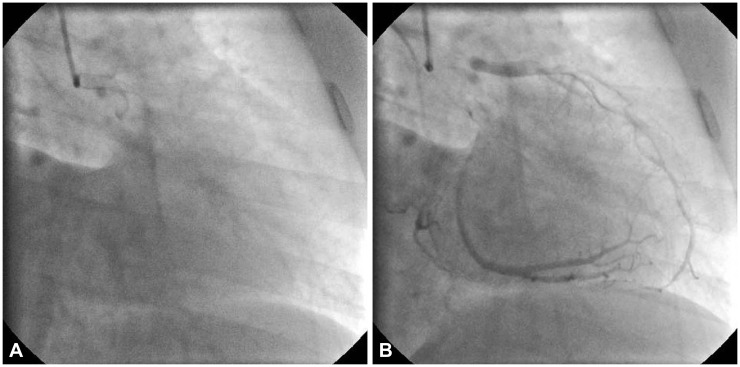
Fig. 3.
The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) frame count for the left anterior descending coronary artery (A and B) was 67-9=58. The corrected TIMI frame count was calculated as 58/1.7=34.1 (normal range 21±3).
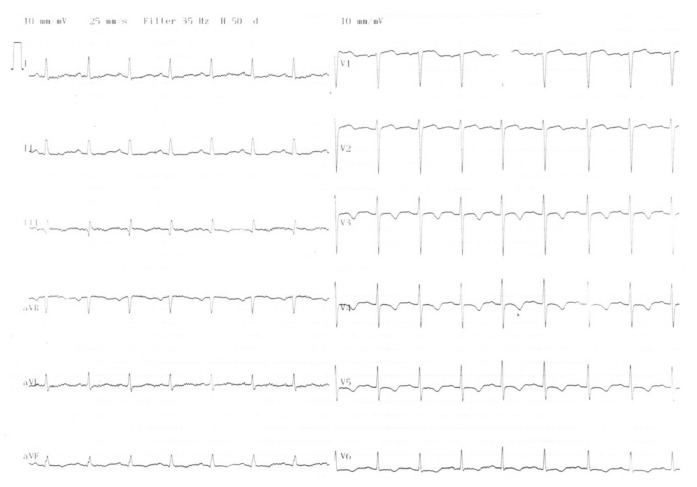
Fig. 4.
After the chest pain ceased, the electrocardiography showed the resolution ST elevation and negative T waves between V 3-6 leads.
Discussion
The exact pathophysiological mechanism of CSFP is not clear. Some underlying etiologies such as abnormally high microvascular resistance and widespread atherosclerosis of coronary arteries have been proposed.1),2) Most (80%) patients experience debilitating recurrent chest pain, commonly resulting in hospital readmission. The overall incidence of CSFP was 1% among patients undergoing coronary angiography.3) TIMI flow method is used to evaluate coronary blood flow. CSFP is defined as CTFC greater than 2 standard deviations from the normal range (21±3).4) Myocardial perfusion scintigraphy shows reversible perfusion abnormalities in 28-75% of patients with CSFP.5) Occasionally, patients may present with acute myocardial infarction.6) Tatli et al.7) demonstrated that the CSFP was not purely an incidental angiographic finding; on the contrary, it may lead to angina pectoris and true myocardial ischemia in their published studies.
In conclusion, although the exact etiology of CSFP is not certain, it is known to not be a normal variant, as it is an absolutely pathological entity. CSFP not only leads to myocardial ischemia as Tatli et al.7) mentioned, but it can also cause classical acute ST elevation myocardial infarction, which necessitates coronary angiography for a definite diagnosis.
Footnotes
The author has no financial conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Mangieri E, Macchiarelli G, Ciavolella M, et al. Slow coronary flow: clinical and histopathological features in patients with otherwise normal epicardial coronary arteries. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1996;37:375–381. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0304(199604)37:4<375::AID-CCD7>3.0.CO;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mosseri M, Yarom R, Gotsman MS, Hasin Y. Histologic evidence for small-vessel coronary artery disease in patients with angina pectoris and patent large coronary arteries. Circulation. 1986;74:964–972. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.74.5.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Singh S, Kothari SS, Bahl VK. Coronary slow flow phenomenon: an angiographic curiosity. Indian Heart J. 2004;56:613–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gibson CM, Cannon CP, Daley WL, et al. TIMI frame count: a quantitative method of assessing coronary artery flow. Circulation. 1996;93:879–888. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.93.5.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Demirkol MO, Yaymaci B, Mutlu B. Dipyridamole myocardial perfusion single photon emission computed tomography in patients with slow coronary flow. Coron Artery Dis. 2002;13:223–229. doi: 10.1097/00019501-200206000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kapoor A, Goel PK, Gupta S. Slow coronary flow--a cause for angina with ST segment elevation and normal coronary arteries. A case report. Int J Cardiol. 1998;67:257–261. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5273(98)00324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tatli E, Yildirim T, Aktoz M. Does coronary slow flow phenomenon lead to myocardial ischemia? Int J Cardiol. 2009;131:e101–e102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.07.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]