Abstract
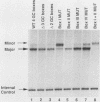
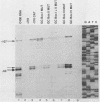
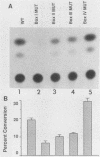
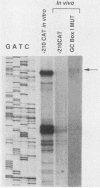
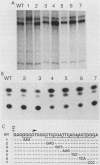
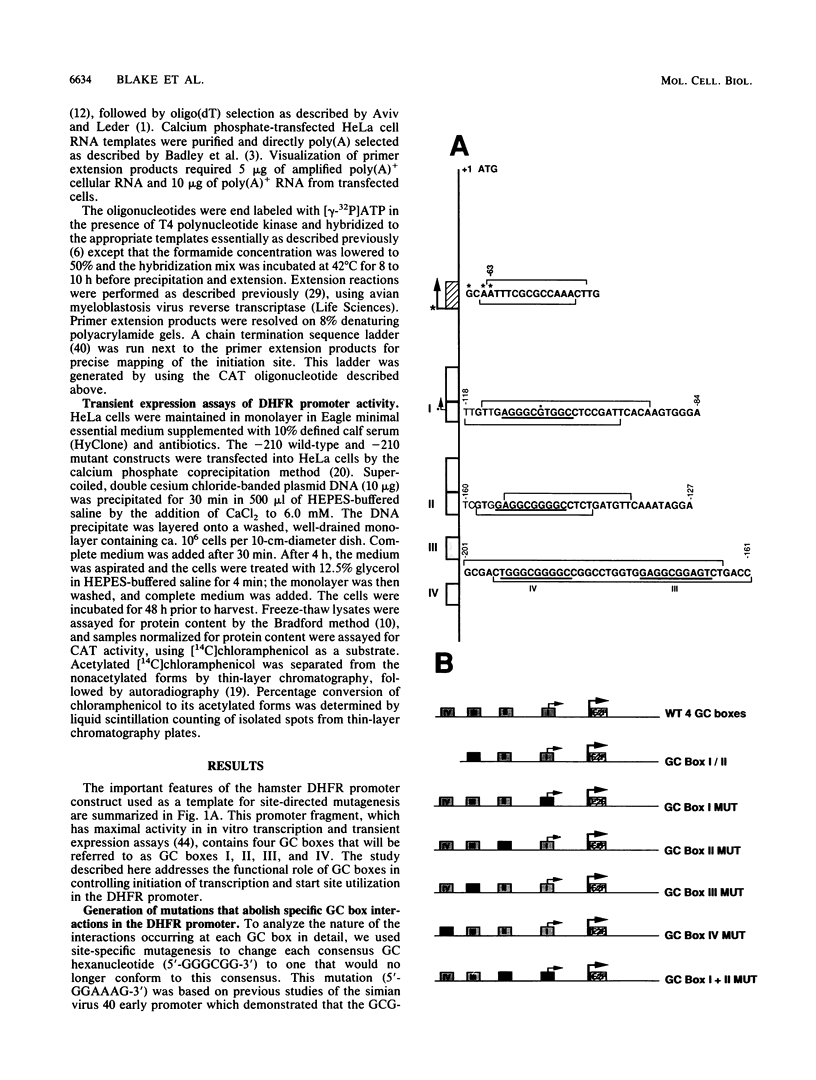
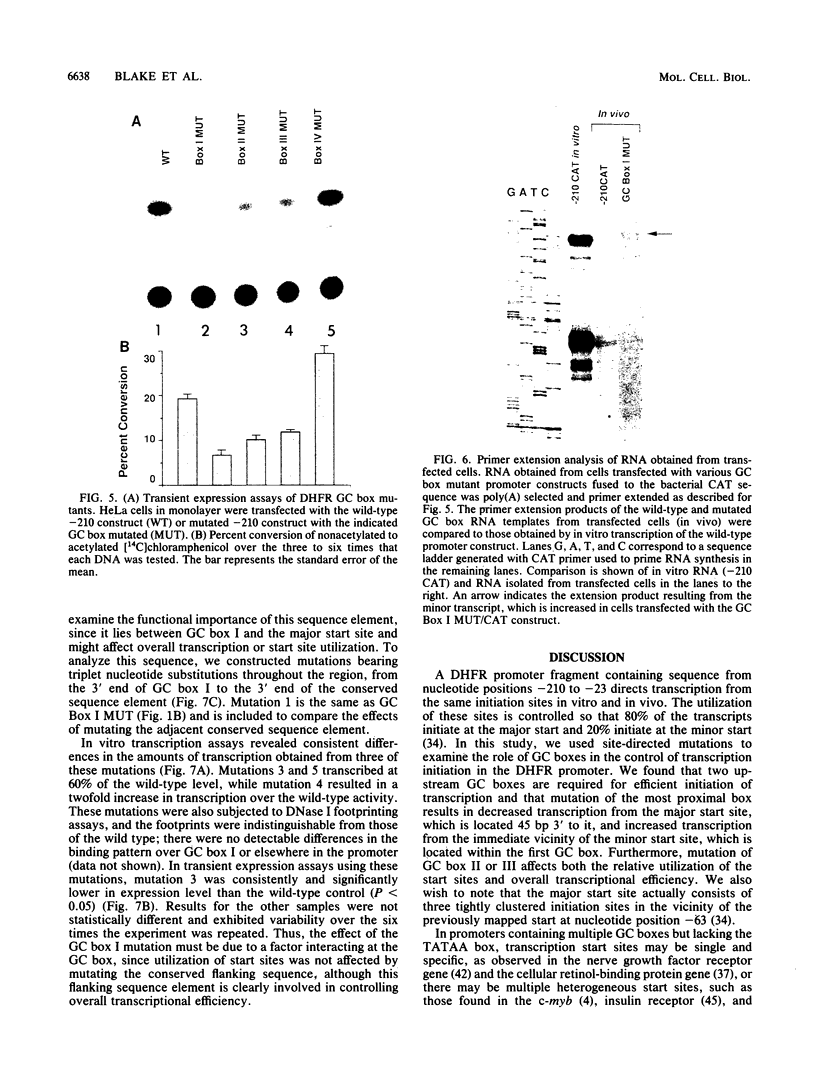
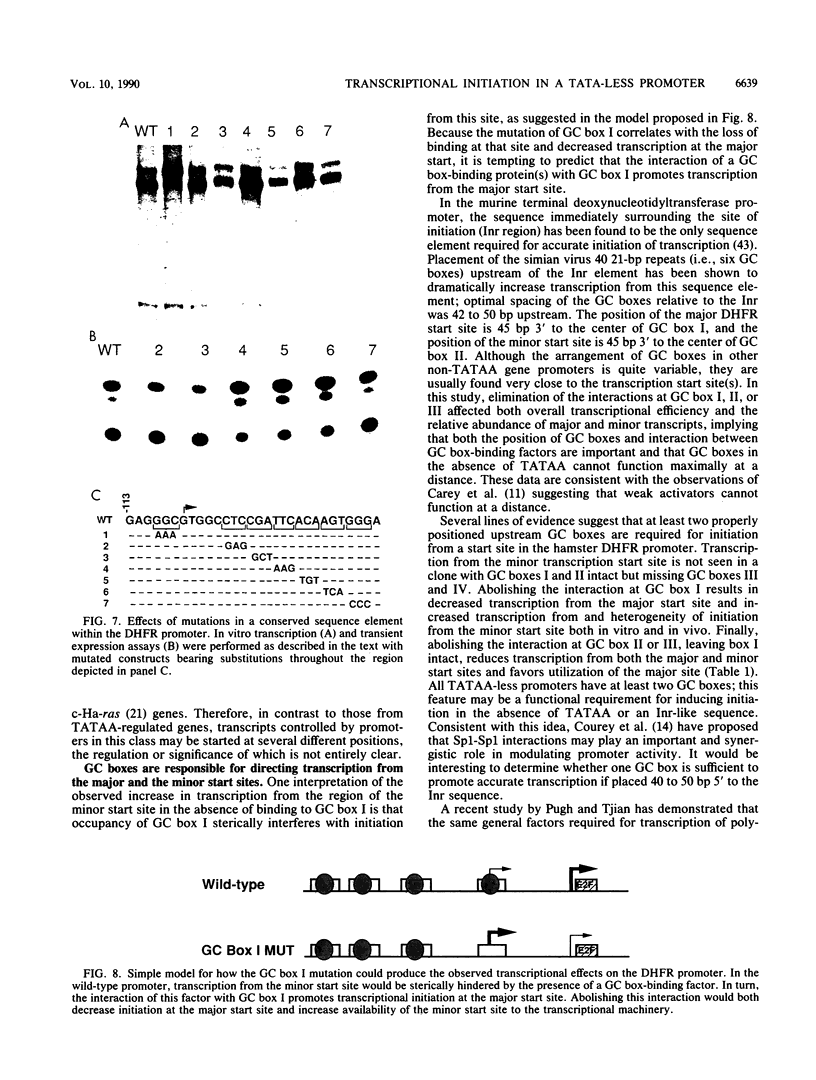
Numerous genes contain TATAA-less promoters, and the control of transcriptional initiation in this important promoter class is not understood. We have determined that protein-DNA interactions at three of the four proximal GC box sequence elements in one such promoter, that of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene, control initiation and relative use of the major and minor start sites. Our results indicate that although the GC boxes are apparently equivalent with respect to factor binding, they are not equivalent with respect to function. At least two properly positioned GC boxes were required for initiation of transcription. Abolishment of DNA-protein interaction by site-specific mutation of the most proximal GC box (box I) resulted in a fivefold decrease in transcription from the major initiation site and a threefold increase in heterogeneous transcripts initiating from the vicinity of the minor start site in vitro and in vivo. Mutations that separately abolished interactions at GC boxes II and III while leaving GC box I intact affected the relative utilization of both the major and minor initiation sites as well as transcriptional efficiency of the promoter template in in vitro transcription and transient expression assays. Interaction at GC box IV when the three proximal boxes were in a wild-type configuration had no effect on transcription of the dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Thus, GC box interactions not only are required for efficient transcription but also regulate start site utilization in this TATAA-less promoter.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azizkhan J. C., Vaughn J. P., Christy R. J., Hamlin J. L. Nucleotide sequence and nuclease hypersensitivity of the Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter region. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6228–6236. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley J. E., Bishop G. A., St John T., Frelinger J. A. A simple, rapid method for the purification of poly A+ RNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):114–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender T. P., Kuehl W. M. Murine myb protooncogene mRNA: cDNA sequence and evidence for 5' heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3204–3208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielinska A., Krasnow S., Nabel G. J. NF-kappa B-mediated activation of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer: site of transcriptional initiation is independent of the TATA box. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4097–4100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4097-4100.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Azizkhan J. C. Transcription factor E2F is required for efficient expression of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4994–5002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasband A. J., Rogers K. T., Chen X. R., Azizkhan J. C., Lee D. C. Characterization of the rat transforming growth factor alpha gene and identification of promoter sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2111–2121. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Leatherwood J., Ptashne M. A potent GAL4 derivative activates transcription at a distance in vitro. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):710–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2405489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Holtzman D. A., Jackson S. P., Tjian R. Synergistic activation by the glutamine-rich domains of human transcription factor Sp1. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90606-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Frisque R. J., Gluzman Y. Identification of a promoter component involved in positioning the 5' termini of simian virus 40 early mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Promoter region of the human Harvey ras proto-oncogene: similarity to the EGF receptor proto-oncogene promoter. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1378–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.2999983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Xu Y. H., Stratton R. H., Roe B. A., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Characterization and sequence of the promoter region of the human epidermal growth factor receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4920–4924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Schlokat U., Vannice J. L., Derynck R., Levinson A. D. The human transforming growth factor alpha promoter directs transcription initiation from a single site in the absence of a TATA sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5549–5554. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Nuclear factor ETF specifically stimulates transcription from promoters without a TATA box. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15508–15514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Heath C., Bertuch A., Hansen U. Specific stimulation of simian virus 40 late transcription in vitro by a cellular factor binding the simian virus 40 21-base-pair repeat promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6025–6029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug M. S., Berger S. L. First-strand cDNA synthesis primed with oligo(dT). Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:316–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Carothers A. M., Han J. H., Harding J. D., Kas E., Venolia L., Chasin L. A. Multiple transcription start sites, DNase I-hypersensitive sites, and an opposite-strand exon in the 5' region of the CHO dhfr gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):425–440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka H., Tennyson G. E., Nikodem V. M. Structural and functional analysis of the rat malic enzyme gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3542–3545. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson M. H., Spurr N. K., Lundvall J., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Human cellular retinol-binding protein gene organization and chromosomal location. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Kao C. C., Pei R., Berk A. J. Yeast TATA-box transcription factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7785–7789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal A., Patil N., Chao M. A constitutive promoter directs expression of the nerve growth factor receptor gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3160–3167. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swick A. G., Blake M. C., Kahn J. W., Azizkhan J. C. Functional analysis of GC element binding and transcription in the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9291–9304. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari D. S., Cook D. M., Taub R. Characterization of the promoter region and 3' end of the human insulin receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16238–16245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerio D., Duyvesteyn M. G., Dekker B. M., Weeda G., Berkvens T. M., van der Voorn L., van Ormondt H., van der Eb A. J. Adenosine deaminase: characterization and expression of a gene with a remarkable promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):437–443. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Rosser D. S., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. A TATA box implicated in E1A transcriptional activation of a simple adenovirus 2 promoter. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):512–515. doi: 10.1038/326512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]