Abstract
In the structure of the phenolate salt of the sulfa drug sulfamethazine with 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid, C12H15N4O2S+·C7H3N2O7 −, the dihedral angle between the pyrimidine and benzene rings of the cation is 59.70 (17)°. In the crystal, cation–anion hydrogen-bonding interactions involving pyrimidine–carboxy N+—H⋯O and amine–carboxy N—H⋯O pairs give a cyclic R 2 2(8) motif while secondary N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds between the aniline group and both sulfone and nitro O-atom acceptors give a two-dimensional structure extending in (001).
Related literature
For background to sulfamethazine and its co-crystals, see: O’Neil (2001 ▶); Caira (2007 ▶); Ghosh et al. (2011 ▶). For similar structures, see: Caira (1991 ▶); Lynch et al. (2000 ▶); Smith & Wermuth (2013 ▶). For structures of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid salts, see: Smith et al. (2003 ▶). For graph-set analysis, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).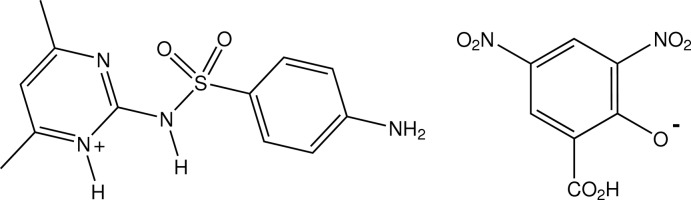
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H15N4O2S+·C7H3N2O7 −
M r = 506.46
Monoclinic,

a = 8.1691 (3) Å
b = 32.0736 (9) Å
c = 8.9869 (3) Å
β = 112.258 (5)°
V = 2179.23 (15) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.22 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.40 × 0.35 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Gemini-S CCD-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.918, T max = 0.980
14977 measured reflections
4264 independent reflections
3645 reflections with I > \2s(I)
R int = 0.039
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.070
wR(F 2) = 0.158
S = 1.10
4264 reflections
318 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.87 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.51 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR92 (Altomare et al., 1993 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶) within WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005631/nk2201sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005631/nk2201Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005631/nk2201Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1A—H1A⋯O11 | 0.88 | 1.75 | 2.617 (4) | 168 |
| N2A—H2A⋯O12 | 0.78 | 1.95 | 2.729 (4) | 170 |
| O12—H12⋯O2 | 0.96 | 1.52 | 2.416 (5) | 154 |
| N41A—H41A⋯O51i | 0.81 | 2.50 | 3.248 (5) | 153 |
| N41A—H42A⋯O12A ii | 0.81 | 2.46 | 3.202 (4) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Australian Reseach Council, the Science and Engineering Faculty and the University Library, Queensland University of Technology.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The drug sulfamethazine (or sulfadimidine) [4-amino-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide] (O'Neil, 2001) has been used as a model for co-crystal formation (Caira, 2007; Ghosh et al., 2011), commonly forming 1:1 adducts with carboxylic acids, predominently the benzoic analogues but including some amides. The structures of a number of these have been reported, e.g. anthranilic acid and 4-aminobenzoic acid (Caira, 1991), 2,4-dinitrobenzoic acid (Lynch et al., 2000), as well as benzamide, 4-hydroxybenzamide and picolinamide (Ghosh et al., 2011). In all of these co-crystals, heterodimers are formed through a cyclic intermolecular hydrogen-bonding motif [graph set R22(8) (Bernstein et al., 1995)], involving amine N—H···Ocarboxyl and carboxylic acid O—H···Npyrimidine pairs.
However, there are no examples of the structures of proton-transfer salts of sulfamethazine with carboxylic acids so we looked at the products from the 1:1 stoichiometric reactions with some strong acids. Crystalline materials were obtained from the 5-nitrosalicylic acid and picric acid reactions, namely the anhydrous (1:1) carboxylate and picrate salts, respectively (Smith & Wermuth, 2013). With 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNSA), the poorly-formed anhydrous 1:1 salt of the title compound, C12H15N4O2S+ C7H3N2O7-, was obtained, and the structure is reported herein. DNSA has been particularly useful in providing crystalline proton-transfer salts with both aliphatic and aromatic amines, the majority of which have been picrates, in which an anti-related acidic proton is retained on the carboxylic acid group rather than on the phenolic group (Smith et al., 2003).
With the title salt, the phenolate anion is found (Fig. 1), providing a variant of the R22(8) cation–anion hydrogen-bonding interaction as found in the non-transfer co-crystal structures, the difference arising from the presence of the transferred acid proton on the pyrimidine nitrogen (N1A). The slight asymmetry in the N1A···O and N2A···O hydrogen bond distances [2.622 (5) and 2.732 (4) Å] (Table 1) is comparable with those in the non-transfer co-crystals. In the DNSA anion, the anti-related acid proton forms the usual intramolecular hydrogen bond with the phenolate O-atom (Smith et al., 2003). Both H-atoms of the aniline group of the cation participate in intermolecular N—H···O hydrogen-bonding interactions with both sulfone and nitro O-atom acceptors, giving extensions along the a and b axes respectively, giving a two-dimensional structure lying along (001) (Fig. 2).
In the sulfamethazine cation, the dihedral angle between the pyrimidinium and phenyl rings is 59.70 (17)°, similar to that found in the picrate salt [58.18 (7)°] (Smith & Wermuth, 2013), but significantly smaller than commonly found with the adduct structures, e.g. 70.3 (4)° in the 2,4-dinitrobenzoic acid co-crystal (Lynch et al., 2000). The two interacting pyrimidine–DNSA moieties are close to coplanar [inter-ring dihedral angle 12.2 (2)°].
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by the reaction of 1 mmol quantities of 4-amino-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonamide (sulfamethazine) with 3,5-dinitrosalicylic in 50 ml of 50% ethanol–water with 10 min refluxing. Partial evaporation of the solvent gave poorly-formed yellow crystal plates (m.p. 457–458 K) from which a specimen was cleaved for the X-ray analysis.
Refinement
Hydrogen atoms potentially involved in hydrogen-bonding interactions were located by difference methods but their positional and isotropic displacement parameters were subsequently allowed to ride in the refinement with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N) or 1.5Ueq(O). Other H atoms were included at calculated positions [C—H (aromatic) = 0.93 Å or C—H (methyl) = 0.96 Å] and also treated as riding, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C)aromatic or 1.5Ueq (C)methyl.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular conformation and atom-numbering scheme for the title compound, with inter-species hydrogen bonds shown as a dashed lines. Non-H atoms are shown as 40% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
The two-dimensional network structure viewed down c, showing hydrogen-bonding associations as dashed lines. Non-associative H atoms are omitted.
Crystal data
| C12H15N4O2S+·C7H3N2O7− | F(000) = 1048 |
| Mr = 506.46 | Dx = 1.544 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point = 457–458 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.1691 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 4751 reflections |
| b = 32.0736 (9) Å | θ = 3.1–28.8° |
| c = 8.9869 (3) Å | µ = 0.22 mm−1 |
| β = 112.258 (5)° | T = 200 K |
| V = 2179.23 (15) Å3 | Plate, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.35 × 0.20 mm |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini-S CCD-detector diffractometer | 4264 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray source | 3645 reflections with I > \2s(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.039 |
| Detector resolution: 16.077 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.1° |
| ω scans | h = −7→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2012) | k = −39→39 |
| Tmin = 0.918, Tmax = 0.980 | l = −11→11 |
| 14977 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.070 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.158 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.10 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0472P)2 + 4.2454P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4264 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.010 |
| 318 parameters | Δρmax = 0.87 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.51 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1A | 0.33370 (9) | 0.09248 (2) | 0.49476 (9) | 0.0225 (2) | |
| O11A | 0.4293 (3) | 0.11377 (7) | 0.6420 (3) | 0.0308 (7) | |
| O12A | 0.1986 (3) | 0.06331 (7) | 0.4858 (3) | 0.0300 (7) | |
| N1A | 0.0333 (4) | 0.16571 (9) | 0.1560 (3) | 0.0347 (9) | |
| N2A | 0.2414 (3) | 0.13221 (8) | 0.3706 (3) | 0.0279 (8) | |
| N3A | 0.0595 (4) | 0.09249 (9) | 0.1533 (3) | 0.0318 (8) | |
| N41A | 0.8562 (4) | 0.00864 (9) | 0.2912 (4) | 0.0352 (9) | |
| C2A | 0.1081 (4) | 0.12918 (10) | 0.2241 (4) | 0.0271 (9) | |
| C4A | −0.0789 (5) | 0.09197 (13) | 0.0121 (4) | 0.0394 (11) | |
| C5A | −0.1668 (5) | 0.12839 (15) | −0.0589 (4) | 0.0487 (13) | |
| C6A | −0.1059 (5) | 0.16547 (14) | 0.0136 (4) | 0.0460 (14) | |
| C11A | 0.4832 (4) | 0.06863 (9) | 0.4269 (4) | 0.0209 (8) | |
| C21A | 0.4332 (4) | 0.03461 (10) | 0.3223 (4) | 0.0281 (9) | |
| C31A | 0.5563 (4) | 0.01481 (10) | 0.2778 (4) | 0.0306 (10) | |
| C41A | 0.7336 (4) | 0.02831 (9) | 0.3364 (4) | 0.0257 (9) | |
| C42A | −0.1332 (6) | 0.05060 (14) | −0.0664 (5) | 0.0582 (16) | |
| C51A | 0.7806 (4) | 0.06280 (10) | 0.4394 (4) | 0.0279 (9) | |
| C61A | 0.6577 (4) | 0.08258 (9) | 0.4841 (4) | 0.0250 (9) | |
| C62A | −0.1833 (7) | 0.20700 (16) | −0.0541 (6) | 0.0709 (17) | |
| O2 | 0.5067 (5) | 0.25084 (9) | 0.7126 (4) | 0.0712 (11) | |
| O11 | 0.1194 (4) | 0.24106 (9) | 0.2706 (4) | 0.0589 (11) | |
| O12 | 0.2967 (4) | 0.21077 (8) | 0.4967 (4) | 0.0606 (10) | |
| O31 | 0.8156 (5) | 0.34132 (12) | 0.8480 (5) | 0.0813 (16) | |
| O32 | 0.6599 (6) | 0.30963 (12) | 0.9593 (4) | 0.0868 (16) | |
| O51 | 0.3439 (7) | 0.42888 (10) | 0.4234 (4) | 0.0993 (19) | |
| O52 | 0.1099 (6) | 0.39640 (11) | 0.2632 (5) | 0.0763 (16) | |
| N3 | 0.6791 (5) | 0.32438 (11) | 0.8427 (5) | 0.0557 (15) | |
| N5 | 0.2539 (7) | 0.39791 (10) | 0.3752 (5) | 0.0568 (16) | |
| C1 | 0.3126 (5) | 0.28407 (11) | 0.4776 (5) | 0.0429 (11) | |
| C2 | 0.4505 (6) | 0.28519 (11) | 0.6290 (5) | 0.0462 (15) | |
| C3 | 0.5295 (6) | 0.32354 (12) | 0.6872 (5) | 0.0456 (14) | |
| C4 | 0.4725 (6) | 0.36005 (11) | 0.6024 (5) | 0.0483 (15) | |
| C5 | 0.3300 (6) | 0.35804 (11) | 0.4587 (5) | 0.0485 (14) | |
| C6 | 0.2494 (6) | 0.32095 (11) | 0.3902 (5) | 0.0464 (15) | |
| C11 | 0.2342 (6) | 0.24260 (11) | 0.4069 (6) | 0.0489 (15) | |
| H1A | 0.07050 | 0.18920 | 0.20720 | 0.0420* | |
| H2A | 0.26120 | 0.15340 | 0.41760 | 0.0330* | |
| H5A | −0.26560 | 0.12730 | −0.15450 | 0.0580* | |
| H21A | 0.31660 | 0.02540 | 0.28290 | 0.0340* | |
| H31A | 0.52240 | −0.00780 | 0.20800 | 0.0370* | |
| H41A | 0.83560 | −0.01550 | 0.26240 | 0.0420* | |
| H42A | 0.95960 | 0.01430 | 0.34240 | 0.0420* | |
| H43A | −0.17740 | 0.03360 | −0.00190 | 0.0870* | |
| H44A | −0.03300 | 0.03720 | −0.07680 | 0.0870* | |
| H45A | −0.22420 | 0.05430 | −0.17100 | 0.0870* | |
| H51A | 0.89660 | 0.07240 | 0.47790 | 0.0330* | |
| H61A | 0.69090 | 0.10540 | 0.55300 | 0.0300* | |
| H63A | −0.15940 | 0.22670 | 0.03180 | 0.1070* | |
| H64A | −0.30880 | 0.20420 | −0.11010 | 0.1070* | |
| H65A | −0.13110 | 0.21660 | −0.12740 | 0.1070* | |
| H4 | 0.52880 | 0.38530 | 0.64130 | 0.0580* | |
| H6 | 0.15680 | 0.32050 | 0.29020 | 0.0560* | |
| H12 | 0.38970 | 0.21900 | 0.59520 | 0.0730* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1A | 0.0178 (4) | 0.0252 (4) | 0.0234 (4) | 0.0015 (3) | 0.0066 (3) | 0.0017 (3) |
| O11A | 0.0251 (11) | 0.0396 (13) | 0.0253 (12) | 0.0024 (10) | 0.0069 (10) | −0.0038 (10) |
| O12A | 0.0210 (11) | 0.0346 (12) | 0.0356 (13) | −0.0023 (9) | 0.0122 (10) | 0.0024 (10) |
| N1A | 0.0303 (15) | 0.0369 (15) | 0.0354 (16) | 0.0092 (13) | 0.0108 (13) | 0.0082 (13) |
| N2A | 0.0235 (13) | 0.0207 (13) | 0.0324 (15) | 0.0026 (10) | 0.0026 (12) | −0.0014 (11) |
| N3A | 0.0270 (14) | 0.0381 (15) | 0.0263 (14) | −0.0019 (12) | 0.0057 (12) | 0.0023 (12) |
| N41A | 0.0307 (15) | 0.0290 (14) | 0.0512 (18) | 0.0007 (12) | 0.0215 (14) | −0.0033 (13) |
| C2A | 0.0186 (15) | 0.0354 (17) | 0.0270 (16) | 0.0058 (13) | 0.0083 (13) | 0.0074 (13) |
| C4A | 0.0289 (18) | 0.061 (2) | 0.0254 (17) | −0.0095 (17) | 0.0071 (14) | 0.0030 (17) |
| C5A | 0.031 (2) | 0.079 (3) | 0.0253 (18) | 0.003 (2) | −0.0016 (16) | 0.0090 (19) |
| C6A | 0.0322 (19) | 0.068 (3) | 0.034 (2) | 0.0196 (19) | 0.0082 (17) | 0.0169 (19) |
| C11A | 0.0166 (14) | 0.0206 (14) | 0.0250 (15) | 0.0019 (11) | 0.0072 (12) | 0.0044 (12) |
| C21A | 0.0212 (15) | 0.0263 (16) | 0.0347 (18) | −0.0045 (13) | 0.0082 (14) | −0.0025 (13) |
| C31A | 0.0294 (17) | 0.0221 (15) | 0.0396 (19) | −0.0044 (13) | 0.0123 (15) | −0.0081 (14) |
| C41A | 0.0272 (16) | 0.0236 (15) | 0.0284 (16) | 0.0042 (13) | 0.0129 (14) | 0.0064 (13) |
| C42A | 0.060 (3) | 0.067 (3) | 0.033 (2) | −0.024 (2) | 0.001 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C51A | 0.0195 (15) | 0.0312 (16) | 0.0329 (17) | −0.0036 (13) | 0.0098 (13) | −0.0001 (14) |
| C61A | 0.0220 (15) | 0.0237 (15) | 0.0271 (16) | −0.0026 (12) | 0.0067 (13) | −0.0022 (12) |
| C62A | 0.065 (3) | 0.076 (3) | 0.059 (3) | 0.040 (3) | 0.009 (2) | 0.028 (3) |
| O2 | 0.074 (2) | 0.0400 (16) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0168 (16) | −0.0036 (18) | 0.0058 (15) |
| O11 | 0.068 (2) | 0.0378 (16) | 0.0570 (19) | 0.0118 (14) | 0.0079 (17) | 0.0055 (14) |
| O12 | 0.076 (2) | 0.0265 (13) | 0.0627 (19) | 0.0072 (14) | 0.0075 (17) | 0.0003 (13) |
| O31 | 0.055 (2) | 0.092 (3) | 0.107 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.042 (2) | −0.017 (2) |
| O32 | 0.116 (3) | 0.083 (3) | 0.055 (2) | −0.032 (2) | 0.025 (2) | −0.0023 (19) |
| O51 | 0.220 (5) | 0.0320 (17) | 0.057 (2) | −0.005 (2) | 0.065 (3) | 0.0031 (15) |
| O52 | 0.096 (3) | 0.067 (2) | 0.085 (3) | 0.039 (2) | 0.056 (2) | 0.041 (2) |
| N3 | 0.065 (3) | 0.0376 (19) | 0.074 (3) | 0.0023 (18) | 0.037 (2) | −0.0111 (18) |
| N5 | 0.116 (4) | 0.0297 (18) | 0.050 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0088 (16) |
| C1 | 0.055 (2) | 0.0275 (18) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0116 (17) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0029 (16) |
| C2 | 0.059 (3) | 0.0238 (17) | 0.065 (3) | 0.0117 (17) | 0.034 (2) | 0.0045 (17) |
| C3 | 0.059 (3) | 0.036 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0036 (18) | 0.030 (2) | −0.0050 (17) |
| C4 | 0.080 (3) | 0.0228 (17) | 0.064 (3) | −0.0029 (18) | 0.052 (3) | −0.0022 (17) |
| C5 | 0.085 (3) | 0.0319 (19) | 0.048 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.0092 (17) |
| C6 | 0.071 (3) | 0.0259 (18) | 0.064 (3) | 0.0116 (18) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0054 (17) |
| C11 | 0.060 (3) | 0.0249 (18) | 0.070 (3) | 0.0087 (18) | 0.034 (2) | 0.0028 (18) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1A—O11A | 1.430 (3) | C6A—C62A | 1.501 (7) |
| S1A—O12A | 1.426 (3) | C11A—C61A | 1.393 (5) |
| S1A—N2A | 1.673 (3) | C11A—C21A | 1.397 (4) |
| S1A—C11A | 1.736 (3) | C21A—C31A | 1.371 (5) |
| O2—C2 | 1.314 (5) | C31A—C41A | 1.409 (5) |
| O11—C11 | 1.230 (6) | C41A—C51A | 1.400 (4) |
| O12—C11 | 1.281 (5) | C51A—C61A | 1.370 (5) |
| O31—N3 | 1.225 (6) | C5A—H5A | 0.9300 |
| O32—N3 | 1.213 (6) | C21A—H21A | 0.9300 |
| O51—N5 | 1.214 (6) | C31A—H31A | 0.9300 |
| O52—N5 | 1.226 (7) | C42A—H45A | 0.9600 |
| O12—H12 | 0.9600 | C42A—H43A | 0.9600 |
| N1A—C6A | 1.352 (5) | C42A—H44A | 0.9600 |
| N1A—C2A | 1.356 (4) | C51A—H51A | 0.9300 |
| N2A—C2A | 1.357 (4) | C61A—H61A | 0.9300 |
| N3A—C4A | 1.342 (5) | C62A—H63A | 0.9600 |
| N3A—C2A | 1.325 (4) | C62A—H64A | 0.9600 |
| N41A—C41A | 1.369 (5) | C62A—H65A | 0.9600 |
| N1A—H1A | 0.8800 | C1—C6 | 1.406 (5) |
| N2A—H2A | 0.7800 | C1—C11 | 1.508 (5) |
| N41A—H42A | 0.8100 | C1—C2 | 1.400 (6) |
| N41A—H41A | 0.8100 | C2—C3 | 1.396 (6) |
| N3—C3 | 1.467 (6) | C3—C4 | 1.378 (5) |
| N5—C5 | 1.494 (5) | C4—C5 | 1.374 (6) |
| C4A—C5A | 1.393 (6) | C5—C6 | 1.386 (5) |
| C4A—C42A | 1.489 (6) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C5A—C6A | 1.357 (6) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| O11A—S1A—O12A | 120.36 (15) | C6A—C5A—H5A | 121.00 |
| O11A—S1A—N2A | 101.75 (13) | C4A—C5A—H5A | 121.00 |
| O11A—S1A—C11A | 108.98 (16) | C11A—C21A—H21A | 120.00 |
| O12A—S1A—N2A | 108.57 (14) | C31A—C21A—H21A | 120.00 |
| O12A—S1A—C11A | 108.88 (15) | C41A—C31A—H31A | 120.00 |
| N2A—S1A—C11A | 107.50 (14) | C21A—C31A—H31A | 120.00 |
| C11—O12—H12 | 110.00 | C4A—C42A—H43A | 109.00 |
| C2A—N1A—C6A | 119.7 (3) | C4A—C42A—H45A | 110.00 |
| S1A—N2A—C2A | 125.8 (2) | C4A—C42A—H44A | 109.00 |
| C2A—N3A—C4A | 117.2 (3) | H44A—C42A—H45A | 109.00 |
| C6A—N1A—H1A | 120.00 | H43A—C42A—H44A | 110.00 |
| C2A—N1A—H1A | 120.00 | H43A—C42A—H45A | 109.00 |
| C2A—N2A—H2A | 121.00 | C61A—C51A—H51A | 120.00 |
| S1A—N2A—H2A | 111.00 | C41A—C51A—H51A | 120.00 |
| H41A—N41A—H42A | 116.00 | C51A—C61A—H61A | 120.00 |
| C41A—N41A—H42A | 117.00 | C11A—C61A—H61A | 120.00 |
| C41A—N41A—H41A | 117.00 | H64A—C62A—H65A | 109.00 |
| O31—N3—C3 | 117.6 (4) | C6A—C62A—H64A | 109.00 |
| O32—N3—C3 | 118.8 (4) | C6A—C62A—H65A | 110.00 |
| O31—N3—O32 | 123.6 (5) | H63A—C62A—H64A | 110.00 |
| O51—N5—C5 | 116.2 (4) | H63A—C62A—H65A | 109.00 |
| O52—N5—C5 | 117.8 (4) | C6A—C62A—H63A | 109.00 |
| O51—N5—O52 | 126.1 (4) | C2—C1—C6 | 120.8 (3) |
| N2A—C2A—N3A | 120.9 (3) | C2—C1—C11 | 119.3 (3) |
| N1A—C2A—N3A | 123.3 (3) | C6—C1—C11 | 120.0 (4) |
| N1A—C2A—N2A | 115.8 (3) | O2—C2—C3 | 120.9 (4) |
| C5A—C4A—C42A | 121.4 (3) | C1—C2—C3 | 118.3 (3) |
| N3A—C4A—C42A | 116.9 (4) | O2—C2—C1 | 120.8 (3) |
| N3A—C4A—C5A | 121.7 (4) | N3—C3—C2 | 118.2 (4) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A | 118.9 (3) | C2—C3—C4 | 122.0 (4) |
| N1A—C6A—C5A | 118.9 (4) | N3—C3—C4 | 119.7 (4) |
| N1A—C6A—C62A | 116.9 (4) | C3—C4—C5 | 117.9 (4) |
| C5A—C6A—C62A | 124.2 (4) | N5—C5—C6 | 118.3 (4) |
| C21A—C11A—C61A | 119.8 (3) | C4—C5—C6 | 123.3 (4) |
| S1A—C11A—C21A | 121.0 (3) | N5—C5—C4 | 118.4 (3) |
| S1A—C11A—C61A | 119.1 (2) | C1—C6—C5 | 117.5 (4) |
| C11A—C21A—C31A | 119.9 (3) | O11—C11—C1 | 119.8 (4) |
| C21A—C31A—C41A | 120.8 (3) | O12—C11—C1 | 115.7 (4) |
| C31A—C41A—C51A | 118.4 (3) | O11—C11—O12 | 124.5 (4) |
| N41A—C41A—C51A | 120.8 (3) | C3—C4—H4 | 121.00 |
| N41A—C41A—C31A | 120.8 (3) | C5—C4—H4 | 121.00 |
| C41A—C51A—C61A | 120.8 (3) | C1—C6—H6 | 121.00 |
| C11A—C61A—C51A | 120.3 (3) | C5—C6—H6 | 121.00 |
| N2A—S1A—C11A—C61A | 89.7 (3) | S1A—C11A—C21A—C31A | −176.2 (3) |
| O11A—S1A—N2A—C2A | −165.7 (3) | C61A—C11A—C21A—C31A | 0.7 (5) |
| O11A—S1A—C11A—C21A | 157.1 (3) | C21A—C11A—C61A—C51A | −0.7 (5) |
| O12A—S1A—C11A—C21A | 24.1 (3) | S1A—C11A—C61A—C51A | 176.4 (3) |
| O12A—S1A—C11A—C61A | −152.9 (3) | C11A—C21A—C31A—C41A | 0.0 (5) |
| O12A—S1A—N2A—C2A | −37.7 (3) | C21A—C31A—C41A—N41A | −179.7 (3) |
| C11A—S1A—N2A—C2A | 79.9 (3) | C21A—C31A—C41A—C51A | −0.9 (5) |
| O11A—S1A—C11A—C61A | −19.9 (3) | C31A—C41A—C51A—C61A | 1.0 (5) |
| N2A—S1A—C11A—C21A | −93.4 (3) | N41A—C41A—C51A—C61A | 179.7 (3) |
| C2A—N1A—C6A—C62A | 179.4 (4) | C41A—C51A—C61A—C11A | −0.2 (5) |
| C6A—N1A—C2A—N3A | 4.6 (6) | C6—C1—C2—O2 | 178.3 (5) |
| C6A—N1A—C2A—N2A | −176.9 (3) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | −3.2 (7) |
| C2A—N1A—C6A—C5A | −0.6 (6) | C11—C1—C2—O2 | −3.0 (7) |
| S1A—N2A—C2A—N1A | 169.1 (2) | C11—C1—C2—C3 | 175.5 (4) |
| S1A—N2A—C2A—N3A | −12.3 (5) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.8 (7) |
| C4A—N3A—C2A—N1A | −4.6 (5) | C11—C1—C6—C5 | −178.0 (4) |
| C2A—N3A—C4A—C42A | −179.8 (4) | C2—C1—C11—O11 | −176.3 (5) |
| C4A—N3A—C2A—N2A | 176.9 (3) | C2—C1—C11—O12 | 3.0 (7) |
| C2A—N3A—C4A—C5A | 0.9 (6) | C6—C1—C11—O11 | 2.5 (7) |
| O32—N3—C3—C4 | 125.6 (5) | C6—C1—C11—O12 | −178.3 (4) |
| O31—N3—C3—C4 | −52.1 (6) | O2—C2—C3—N3 | 1.2 (7) |
| O32—N3—C3—C2 | −55.2 (6) | O2—C2—C3—C4 | −179.6 (5) |
| O31—N3—C3—C2 | 127.1 (5) | C1—C2—C3—N3 | −177.4 (4) |
| O51—N5—C5—C6 | −168.2 (5) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.9 (7) |
| O52—N5—C5—C4 | −167.5 (5) | N3—C3—C4—C5 | −178.9 (4) |
| O52—N5—C5—C6 | 10.2 (7) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.9 (7) |
| O51—N5—C5—C4 | 14.1 (7) | C3—C4—C5—N5 | 173.0 (5) |
| N3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | 2.8 (6) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −4.6 (8) |
| C42A—C4A—C5A—C6A | −176.5 (4) | N5—C5—C6—C1 | −174.3 (4) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A—N1A | −2.9 (6) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 3.3 (8) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A—C62A | 177.1 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1A—H1A···O11 | 0.88 | 1.75 | 2.617 (4) | 168 |
| N2A—H2A···O12 | 0.78 | 1.95 | 2.729 (4) | 170 |
| O12—H12···O2 | 0.96 | 1.52 | 2.416 (5) | 154 |
| N41A—H41A···O51i | 0.81 | 2.50 | 3.248 (5) | 153 |
| N41A—H42A···O12Aii | 0.81 | 2.46 | 3.202 (4) | 152 |
| C5A—H5A···O11Aiii | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.408 (5) | 163 |
| C51A—H51A···O12Aii | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.280 (4) | 147 |
| C61A—H61A···O11A | 0.93 | 2.56 | 2.916 (4) | 103 |
| C62A—H63A···O11 | 0.96 | 2.51 | 3.218 (6) | 131 |
| C62A—H64A···O2iii | 0.96 | 2.29 | 2.960 (7) | 127 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) x−1, y, z−1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NK2201).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Caira, M. R. (1991). J. Crystallogr. Spectrosc. Res. 21, 641–648.
- Caira, M. R. (2007). Mol. Pharm. 4, 310–316. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Ghosh, S., Bag, P. P. & Reddy, C. M. (2011). Cryst. Growth Des. 11, 3489–3503.
- Lynch, D. E., Sandhu, P. & Parsons, S. (2000). Aust. J. Chem. 53, 383–387.
- O’Neil, M. J. (2001). Editor. The Merck Index, 13th ed. p. 1588. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck & Co. Inc.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smith, G. & Wermuth, U. D. (2013). Acta Cryst. C69 Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D., Healy, P. C. & White, J. M. (2003). Aust. J. Chem. 56, 707–713.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005631/nk2201sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005631/nk2201Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005631/nk2201Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




