Abstract
In the title compound, C16H16N2O3·H2O, the dihedral angle between the benzene rings is 30.27 (7)°. In the crystal, the components are linked by N—H⋯O, O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O interactions into a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For the applications and biological activity of Schiff bases, see: Musharraf et al. (2012 ▶); Khan et al. (2012 ▶). For the crystal structures of related compounds, see: Taha et al. (2012 ▶); Baharudin et al. (2012 ▶).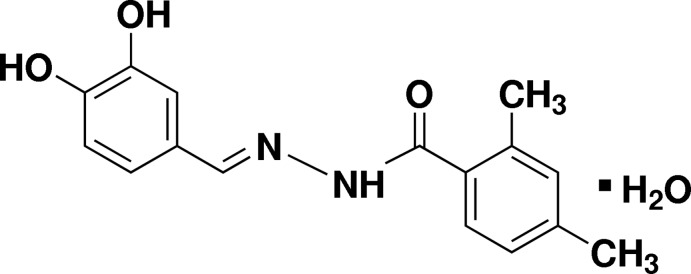
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H16N2O3·H2O
M r = 302.32
Monoclinic,
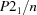
a = 8.1373 (3) Å
b = 13.9025 (5) Å
c = 13.7886 (5) Å
β = 92.913 (1)°
V = 1557.87 (10) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.30 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.973, T max = 0.991
9012 measured reflections
2897 independent reflections
2535 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.016
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.111
S = 1.05
2897 reflections
221 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL, PARST (Nardelli, 1995 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005692/pv2622sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005692/pv2622Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005692/pv2622Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1W—H1W1⋯N2i | 0.87 (2) | 2.20 (2) | 3.059 (2) | 169 (2) |
| O1W—H2W1⋯O1 | 0.94 (2) | 2.01 (2) | 2.935 (2) | 173 (2) |
| N1—H1A⋯O3ii | 0.91 (2) | 2.08 (2) | 2.962 (2) | 163 (2) |
| O2—H2A⋯O1i | 0.88 (2) | 1.94 (2) | 2.791 (2) | 162 (2) |
| O3—H3A⋯O1W iii | 0.85 (2) | 1.79 (2) | 2.629 (2) | 172 (2) |
| C8—H8A⋯O3ii | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.382 (2) | 145 |
| C15—H15B⋯O2i | 0.96 | 2.52 | 3.351 (2) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 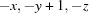 ; (ii)
; (ii) 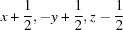 ; (iii)
; (iii) 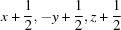 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Research Management Institute of UiTM for financial support under the Dana Kecemerlangan Grant Scheme [grant No. 600-RMI/DANA 5/3 RIF (143/2012)].
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Structurally diverse range of benzohydrazides have been extensively studied in order to explore the structural features that may be responsible for different biological activities (Musharraf et al., 2012; Khan et al., 2012). The title compound is yet another benzohydrazide monohydrate, obtained as a part of our ongoing research that has been studied by X-ray crystallographic method and reported in this article.
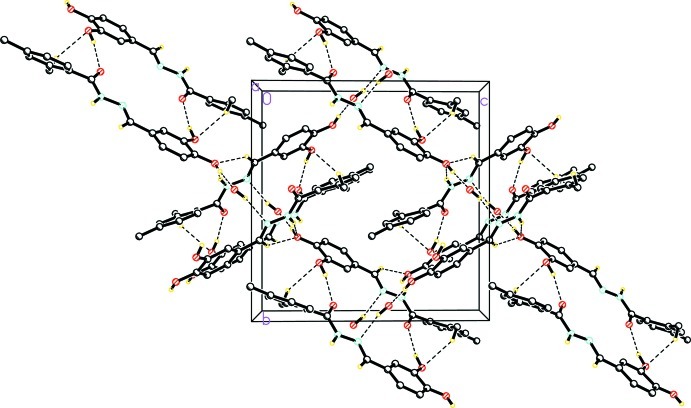
In the title compound (Fig. 1) dimethyl and dihydroxy substituted benzene rings (C1–C6 and C9–C14, respectively) are each planner with a dihedral angle 30.27 (7)° between their mean-planes. The azomethine double bond, N2═C8 (1.2729 (19) Å) adopts an E configuration. The bond lengths and angle are similar to the corresponding bond lengths and angles reported in structurally related benzohydrazide derivatives (Taha et al., 2012; Baharudin et al., 2012). The crystal structure is stabilized by N1—H1A···N2, O2—H2A···O1, C8—H8A···O3 and C15—H15B···O2 intermolecular interactions. The ineteractions further extend the structure to a three dimentional network via O1W—H2W1···O1, O1W—H1A···O3 and O3—H3A···O1W interactions involving the water of hydration (Table 2 and Fig. 2).
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by reacting (0.328 g, 2 mmol) 2,4-dimethylbenzohydrazide and (0.276 g, 2 mmol) 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde as starting meterial under the same conditions and solvents as described previously for the synthesis of benzohydrazides (Taha et al., 2012). The title compound was recrystalized by dissolving in methanol to obtain colorless needles (0.499 g, 88% yield). All chemicals were purchased by Sigma Aldrich Germany.
Refinement
H atoms on methyl and benzene ring were positioned geometrically with C—H = 0.96 and 0.93 Å, respectively and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(benzene) or 1.5Ueq(methyl). The H atoms on oxygen and nitrogen were located in difference Fourier map and refined isotropically. A rotating group model was applied to the methyl groups.
Figures
Fig. 1.
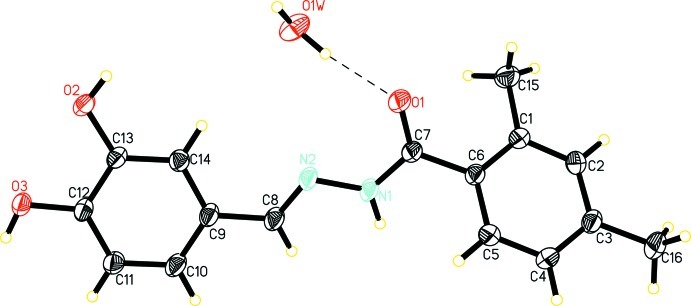
The molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound. Only hydrogen atoms involved in hydrogen bonding are shown.
Crystal data
| C16H16N2O3·H2O | F(000) = 640 |
| Mr = 302.32 | Dx = 1.289 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 4856 reflections |
| a = 8.1373 (3) Å | θ = 2.8–28.2° |
| b = 13.9025 (5) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 13.7886 (5) Å | T = 298 K |
| β = 92.913 (1)° | Block, brown |
| V = 1557.87 (10) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2897 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2535 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.016 |
| ω scan | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.973, Tmax = 0.991 | k = −16→16 |
| 9012 measured reflections | l = −16→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.111 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0596P)2 + 0.3352P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2897 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 221 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.15363 (13) | 0.55077 (8) | −0.16328 (8) | 0.0569 (3) | |
| O1W | −0.12355 (15) | 0.45259 (10) | −0.07769 (9) | 0.0612 (3) | |
| O2 | −0.04800 (12) | 0.26761 (9) | 0.22605 (8) | 0.0505 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.16469 (13) | 0.15980 (8) | 0.32684 (7) | 0.0460 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.34634 (15) | 0.43523 (9) | −0.14057 (9) | 0.0454 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.28104 (14) | 0.40196 (9) | −0.05580 (8) | 0.0435 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.30375 (16) | 0.56844 (10) | −0.36100 (10) | 0.0395 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.40413 (18) | 0.60048 (11) | −0.43273 (10) | 0.0446 (3) | |
| H2C | 0.3561 | 0.6153 | −0.4935 | 0.054* | |
| C3 | 0.57324 (17) | 0.61142 (11) | −0.41767 (10) | 0.0435 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.64410 (17) | 0.58608 (11) | −0.32796 (11) | 0.0455 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.7574 | 0.5911 | −0.3166 | 0.055* | |
| C5 | 0.54846 (16) | 0.55358 (10) | −0.25556 (10) | 0.0423 (3) | |
| H5A | 0.5981 | 0.5371 | −0.1956 | 0.051* | |
| C6 | 0.37828 (16) | 0.54484 (9) | −0.27016 (10) | 0.0366 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.28131 (16) | 0.51150 (10) | −0.18789 (10) | 0.0397 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.35766 (18) | 0.33077 (11) | −0.01702 (11) | 0.0464 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.4495 | 0.3069 | −0.0465 | 0.056* | |
| C9 | 0.30656 (17) | 0.28538 (10) | 0.07190 (10) | 0.0421 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.41516 (19) | 0.22570 (11) | 0.12370 (12) | 0.0514 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.5192 | 0.2145 | 0.1011 | 0.062* | |
| C11 | 0.37047 (19) | 0.18256 (11) | 0.20869 (12) | 0.0499 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.4448 | 0.1431 | 0.2432 | 0.060* | |
| C12 | 0.21552 (16) | 0.19792 (9) | 0.24262 (10) | 0.0390 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.10379 (16) | 0.25680 (10) | 0.18973 (10) | 0.0376 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.14912 (16) | 0.29972 (10) | 0.10553 (10) | 0.0392 (3) | |
| H14A | 0.0745 | 0.3387 | 0.0705 | 0.047* | |
| C15 | 0.12199 (18) | 0.55713 (14) | −0.38483 (12) | 0.0571 (4) | |
| H15A | 0.1029 | 0.5506 | −0.4538 | 0.086* | |
| H15B | 0.0648 | 0.6128 | −0.3628 | 0.086* | |
| H15C | 0.0825 | 0.5008 | −0.3531 | 0.086* | |
| C16 | 0.6765 (2) | 0.65068 (14) | −0.49624 (13) | 0.0615 (5) | |
| H16A | 0.6324 | 0.6293 | −0.5584 | 0.092* | |
| H16B | 0.7875 | 0.6280 | −0.4863 | 0.092* | |
| H16C | 0.6755 | 0.7197 | −0.4941 | 0.092* | |
| H2A | −0.099 (3) | 0.3180 (16) | 0.1996 (15) | 0.077 (6)* | |
| H1A | 0.436 (2) | 0.4053 (13) | −0.1634 (13) | 0.061 (5)* | |
| H1W1 | −0.165 (3) | 0.4883 (17) | −0.0335 (16) | 0.080 (7)* | |
| H3A | 0.239 (2) | 0.1248 (15) | 0.3533 (15) | 0.071 (6)* | |
| H2W1 | −0.029 (3) | 0.4798 (17) | −0.1022 (16) | 0.091 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0495 (6) | 0.0633 (7) | 0.0601 (7) | 0.0209 (5) | 0.0261 (5) | 0.0182 (5) |
| O1W | 0.0486 (6) | 0.0766 (9) | 0.0595 (7) | −0.0124 (6) | 0.0122 (5) | −0.0274 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0399 (5) | 0.0578 (7) | 0.0557 (7) | 0.0085 (5) | 0.0200 (5) | 0.0140 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0453 (6) | 0.0499 (6) | 0.0442 (6) | 0.0056 (5) | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0141 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0462 (6) | 0.0506 (7) | 0.0414 (7) | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0227 (5) | 0.0112 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0453 (6) | 0.0477 (7) | 0.0393 (6) | 0.0066 (5) | 0.0194 (5) | 0.0077 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0360 (7) | 0.0429 (7) | 0.0400 (7) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0051 (6) | 0.0011 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0478 (8) | 0.0505 (8) | 0.0358 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0062 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0437 (7) | 0.0430 (8) | 0.0448 (8) | −0.0010 (6) | 0.0136 (6) | 0.0037 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0335 (7) | 0.0506 (8) | 0.0530 (9) | −0.0033 (6) | 0.0068 (6) | 0.0038 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0383 (7) | 0.0488 (8) | 0.0396 (7) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0048 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0360 (7) | 0.0379 (7) | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0023 (5) | 0.0085 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0378 (7) | 0.0434 (7) | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0050 (6) | 0.0105 (6) | 0.0030 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0484 (8) | 0.0466 (8) | 0.0463 (8) | 0.0108 (7) | 0.0218 (6) | 0.0064 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0468 (8) | 0.0393 (7) | 0.0418 (7) | 0.0055 (6) | 0.0176 (6) | 0.0046 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0468 (8) | 0.0526 (9) | 0.0572 (9) | 0.0149 (7) | 0.0263 (7) | 0.0122 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0469 (8) | 0.0496 (9) | 0.0547 (9) | 0.0156 (7) | 0.0171 (7) | 0.0154 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0441 (7) | 0.0352 (7) | 0.0388 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0145 (6) | 0.0039 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0370 (7) | 0.0365 (7) | 0.0405 (7) | 0.0007 (5) | 0.0128 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0420 (7) | 0.0361 (7) | 0.0401 (7) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0082 (6) | 0.0034 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0401 (8) | 0.0788 (12) | 0.0521 (9) | −0.0036 (7) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0037 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0567 (9) | 0.0699 (11) | 0.0598 (10) | −0.0030 (8) | 0.0225 (8) | 0.0146 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C7 | 1.2364 (16) | C5—C6 | 1.3945 (19) |
| O1W—H1W1 | 0.87 (2) | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| O1W—H2W1 | 0.94 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.4884 (18) |
| O2—C13 | 1.3645 (15) | C8—C9 | 1.4581 (19) |
| O2—H2A | 0.88 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| O3—C12 | 1.3599 (16) | C9—C10 | 1.384 (2) |
| O3—H3A | 0.85 (2) | C9—C14 | 1.3988 (19) |
| N1—C7 | 1.3398 (18) | C10—C11 | 1.382 (2) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3877 (15) | C10—H10A | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1A | 0.913 (19) | C11—C12 | 1.3835 (19) |
| N2—C8 | 1.2729 (19) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.3878 (19) | C12—C13 | 1.4004 (19) |
| C1—C6 | 1.4026 (19) | C13—C14 | 1.3725 (19) |
| C1—C15 | 1.5069 (19) | C14—H14A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.390 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2C | 0.9300 | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.384 (2) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C3—C16 | 1.507 (2) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.373 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| H1W1—O1W—H2W1 | 112 (2) | C10—C9—C14 | 119.07 (13) |
| C13—O2—H2A | 110.5 (13) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.44 (12) |
| C12—O3—H3A | 110.4 (13) | C14—C9—C8 | 121.48 (13) |
| C7—N1—N2 | 121.02 (11) | C11—C10—C9 | 120.62 (13) |
| C7—N1—H1A | 119.8 (11) | C11—C10—H10A | 119.7 |
| N2—N1—H1A | 119.2 (11) | C9—C10—H10A | 119.7 |
| C8—N2—N1 | 114.37 (11) | C10—C11—C12 | 120.24 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.91 (12) | C10—C11—H11A | 119.9 |
| C2—C1—C15 | 119.00 (13) | C12—C11—H11A | 119.9 |
| C6—C1—C15 | 123.05 (12) | O3—C12—C11 | 123.41 (13) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.88 (13) | O3—C12—C13 | 117.06 (11) |
| C1—C2—H2C | 118.6 | C11—C12—C13 | 119.52 (12) |
| C3—C2—H2C | 118.6 | O2—C13—C14 | 123.35 (12) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.05 (13) | O2—C13—C12 | 116.69 (12) |
| C4—C3—C16 | 120.85 (13) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.96 (12) |
| C2—C3—C16 | 121.10 (13) | C13—C14—C9 | 120.57 (13) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.53 (13) | C13—C14—H14A | 119.7 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.7 | C9—C14—H14A | 119.7 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.7 | C1—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.27 (13) | C1—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.4 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.4 | C1—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.32 (12) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.57 (12) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 122.11 (12) | C3—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 122.17 (12) | C3—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—C6 | 123.86 (12) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 113.96 (11) | C3—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—C9 | 122.36 (12) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| N2—C8—H8A | 118.8 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 118.8 | ||
| C7—N1—N2—C8 | −178.10 (14) | C5—C6—C7—N1 | −45.73 (18) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.1 (2) | C1—C6—C7—N1 | 134.90 (14) |
| C15—C1—C2—C3 | −178.87 (15) | N1—N2—C8—C9 | −179.45 (13) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 2.2 (2) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | −163.72 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—C16 | −177.21 (15) | N2—C8—C9—C14 | 17.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.7 (2) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | −1.5 (2) |
| C16—C3—C4—C5 | 177.66 (15) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 179.34 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.2 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.9 (2) | C10—C11—C12—O3 | −178.29 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.49 (13) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.5 (2) | O3—C12—C13—O2 | −2.27 (19) |
| C15—C1—C6—C5 | 177.23 (14) | C11—C12—C13—O2 | 178.79 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 178.88 (13) | O3—C12—C13—C14 | 178.14 (12) |
| C15—C1—C6—C7 | −3.4 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.8 (2) |
| N2—N1—C7—O1 | −5.9 (2) | O2—C13—C14—C9 | −179.69 (13) |
| N2—N1—C7—C6 | 172.84 (12) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −0.1 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | 133.03 (16) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 1.3 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | −46.3 (2) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | −179.59 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1W—H1W1···N2i | 0.87 (2) | 2.20 (2) | 3.059 (2) | 169 (2) |
| N1—H1A···O3ii | 0.91 (2) | 2.08 (2) | 2.962 (2) | 163 (2) |
| O1W—H2W1···O1 | 0.94 (2) | 2.01 (2) | 2.935 (2) | 173 (2) |
| O2—H2A···O1i | 0.88 (2) | 1.94 (2) | 2.791 (2) | 162 (2) |
| O3—H3A···O1Wiii | 0.85 (2) | 1.79 (2) | 2.629 (2) | 172 (2) |
| C8—H8A···O3ii | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.382 (2) | 145 |
| C15—H15B···O2i | 0.96 | 2.52 | 3.351 (2) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z; (ii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PV2622).
References
- Baharudin, M. S., Taha, M., Ismail, N. H., Shah, S. A. A. & Yousuf, S. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o3255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2000). SADABS, SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Khan, K. M., Taha, M., Naz, F., Siddiqui, S., Rahim, F., Perveen, S. & Choudhary, M. I. (2012). Med. Chem. 8, 705–710. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Musharraf, S. G., Bibi, A., Shahid, N., Najam-ul-Haq, M., Khan, M., Taha, M., Mughal, U. R. & Khan, K. M. (2012). Am. J. Anal. Chem. 3, 779-789.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Taha, M., Naz, H., Rahman, A. A., Ismail, N. H. & Sammer, Y. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005692/pv2622sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005692/pv2622Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813005692/pv2622Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report