Abstract
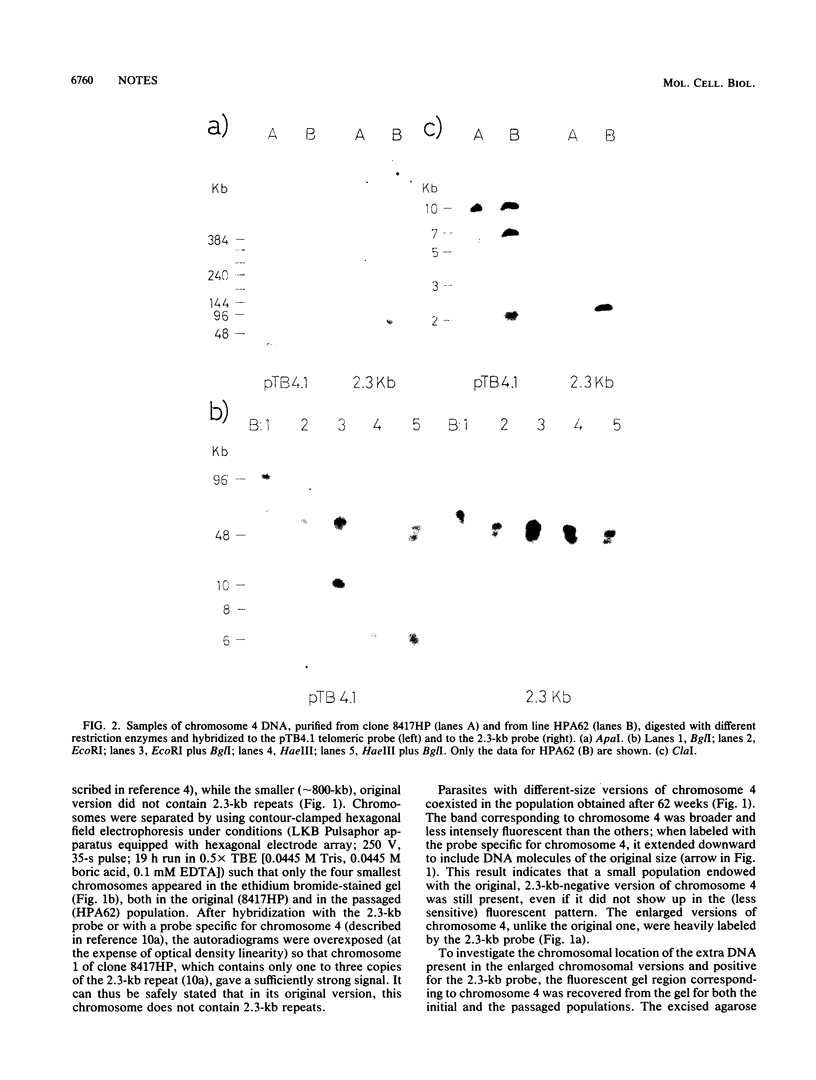
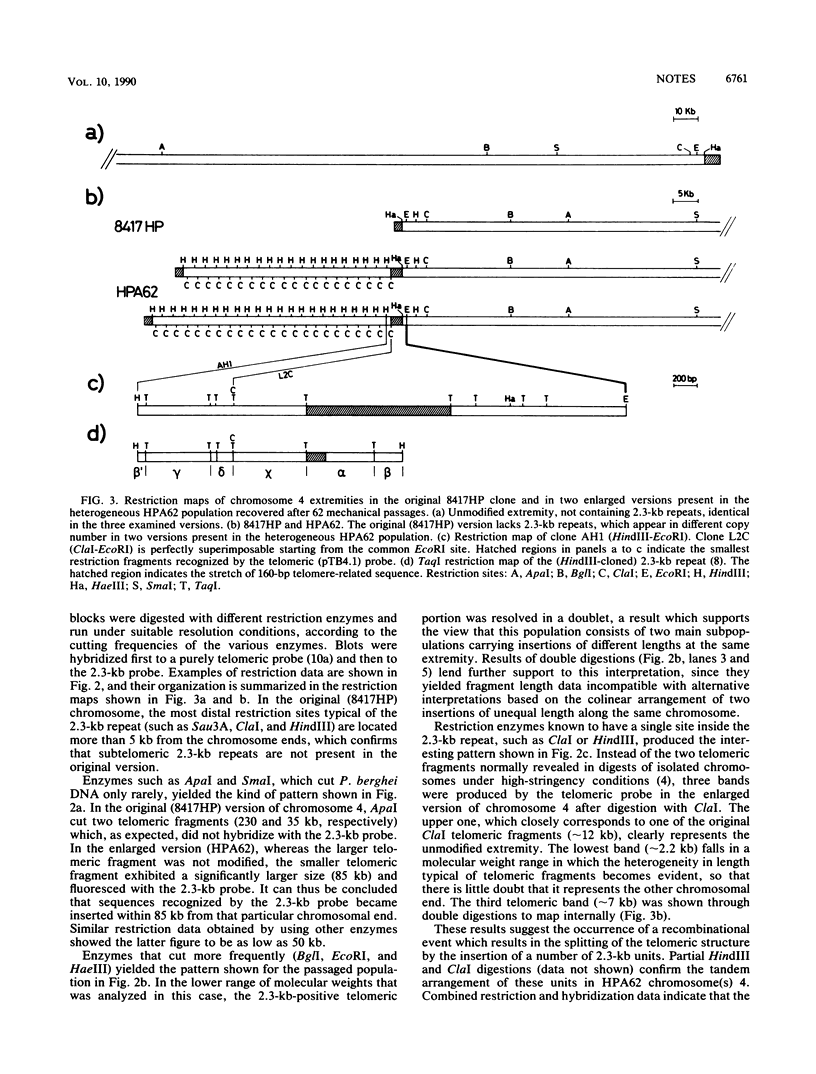
During prolonged in vivo mitotic multiplication of a Plasmodium berghei ANKA clone (8417HP), parasites that contained an enlarged version of chromosome 4 were observed. Restriction mapping and hybridization results demonstrated that the extra DNA present in the enlarged chromosome consists of 2.3-kb tandem repeats, known to be normally located in subtelomeric position at several chromosomal ends but absent in the original chromosome. The inserted 2.3-kb units appeared to interrupt one of the original telomeres and to create an internal (approximately 1-kb-long) telomeric sequence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. Organization of DNA sequences and replication origins at yeast telomeres. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Forsyth K. P., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Kemp D. J. Chromosome size polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum can involve deletions and are frequent in natural parasite populations. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90487-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Thompson J. K., Walliker D., Kemp D. J. Homologous recombination within subtelomeric repeat sequences generates chromosome size polymorphisms in P. falciparum. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dore E., Pace T., Ponzi M., Picci L., Frontali C. Organization of subtelomeric repeats in Plasmodium berghei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2423–2427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B., Szauter P., Pardue M. L., Szostak J. W. Transfer of yeast telomeres to linear plasmids by recombination. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janse C. J., Boorsma E. G., Ramesar J., van Vianen P., van der Meer R., Zenobi P., Casaglia O., Mons B., van der Berg F. M. Plasmodium berghei: gametocyte production, DNA content, and chromosome-size polymorphisms during asexual multiplication in vivo. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Apr;68(3):274–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langsley G., Patarapotikul J., Handunnetti S., Khouri E., Mendis K. N., David P. H. Plasmodium vivax: karyotype polymorphism of field isolates. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Dec;67(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace T., Ponzi M., Dore E., Frontali C. Telomeric motifs are present in a highly repetitive element in the Plasmodium berghei genome. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jun;24(2):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarapotikul J., Langsley G. Chromosome size polymorphism in Plasmodium falciparum can involve deletions of the subtelomeric pPFrep20 sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4331–4340. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pologe L. G., Ravetch J. V. Large deletions result from breakage and healing of P. falciparum chromosomes. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):869–874. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90142-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzi M., Janse C. J., Dore E., Scotti R., Pace T., Reterink T. J., van der Berg F. M., Mons B. Generation of chromosome size polymorphism during in vivo mitotic multiplication of Plasmodium berghei involves both loss and addition of subtelomeric repeat sequences. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Jun;41(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzi M., Pace T., Dore E., Frontali C. Identification of a telomeric DNA sequence in Plasmodium berghei. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2991–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard M., Thompson J. K., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J., Lew A. M. Molecular karyotyping of the rodent malarias Plasmodium chabaudi, Plasmodium berghei and Plasmodium vinckei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Apr;34(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnis P., Wellems T. E. Long-range restriction maps of Plasmodium falciparum chromosomes: crossingover and size variation among geographically distant isolates. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan-Ariya P., Yang Y. F., Kilejian A. Plasmodium falciparum: comparison of the genomic organization of the knob protein gene in knobby and knobless variants. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Dec;67(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Smits M., Ponnudurai T., Vermeulen A., Meuwissen J. H., Langsley G. Chromosome-sized DNA molecules of Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1985 Aug 16;229(4714):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.3895435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernick K. D., McCutchan T. F. Sequence and structure of a Plasmodium falciparum telomere. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Mar;28(2):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walliker D., Quakyi I. A., Wellems T. E., McCutchan T. F., Szarfman A., London W. T., Corcoran L. M., Burkot T. R., Carter R. Genetic analysis of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1661–1666. doi: 10.1126/science.3299700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. W., Chan C. S., Tye B. K., Petes T. D. Unusual DNA sequences associated with the ends of yeast chromosomes. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):157–160. doi: 10.1038/310157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Walliker D., Smith C. L., do Rosario V. E., Maloy W. L., Howard R. J., Carter R., McCutchan T. F. A histidine-rich protein gene marks a linkage group favored strongly in a genetic cross of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):633–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]