Abstract
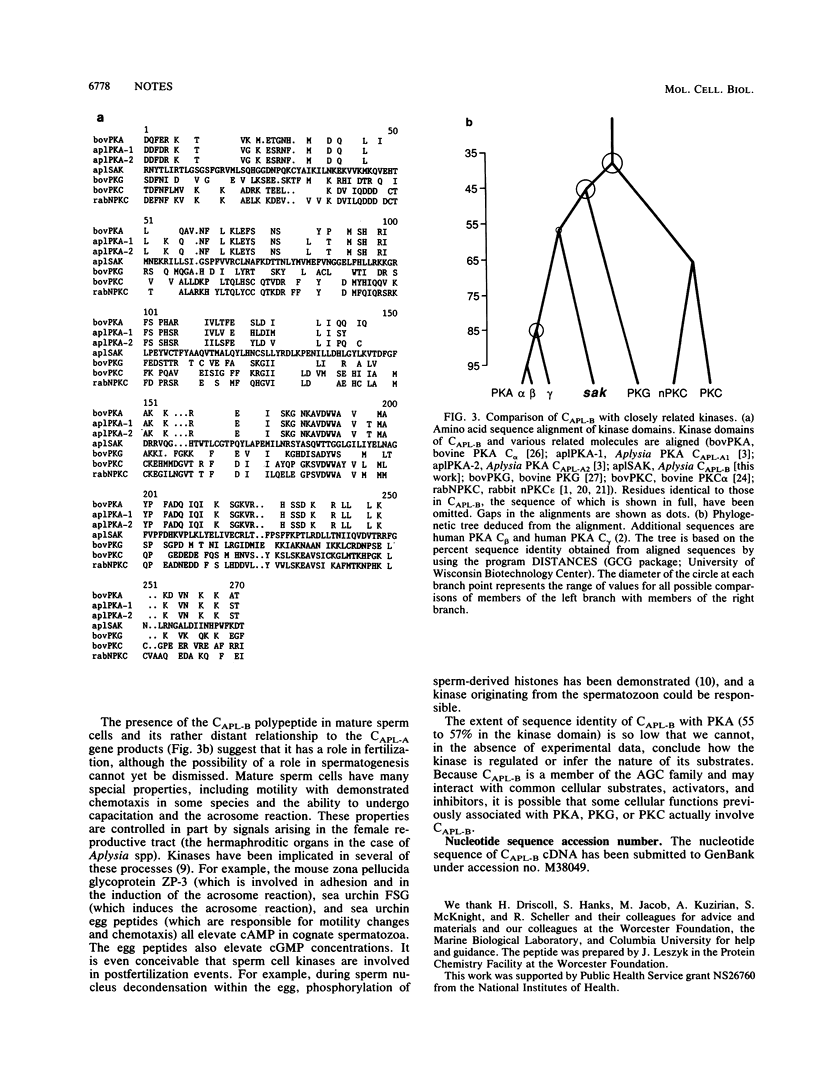
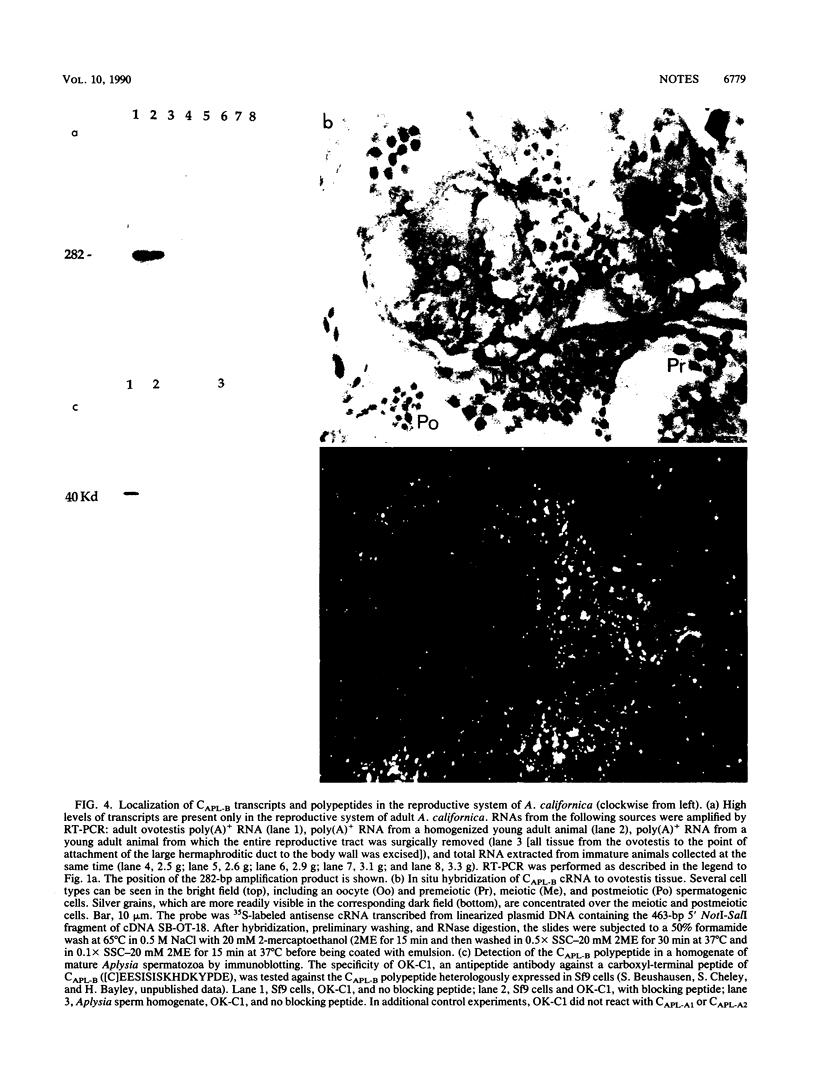
Transcripts encoding CAPL-B, an apparent member of the cyclic-nucleotide-regulated kinase subfamily in Aplysia californica, are found exclusively in the ovotestis and are concentrated in meiotic and postmeiotic spermatogenic cells. The CAPL-B polypeptide is present in mature spermatozoa, suggesting that the kinase plays a part in regulating events associated with fertilization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akita Y., Ohno S., Konno Y., Yano A., Suzuki K. Expression and properties of two distinct classes of the phorbol ester receptor family, four conventional protein kinase C types, and a novel protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):354–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebe S. J., Oyen O., Sandberg M., Frøysa A., Hansson V., Jahnsen T. Molecular cloning of a tissue-specific protein kinase (C gamma) from human testis--representing a third isoform for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):465–475. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beushausen S., Bergold P., Sturner S., Elste A., Roytenberg V., Schwartz J. H., Bayley H. Two catalytic subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase generated by alternative RNA splicing are expressed in Aplysia neurons. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):853–864. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carew T. J. Development assembly of learning in Aplysia. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Oct;12(10):389–394. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrivia J. C., Uhler M. D., McKnight G. S. Characterization of genomic clones coding for the C alpha and C beta subunits of mouse cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5739–5744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Kleene K. C., Hecht N. B. Haploid expression of a mouse testis alpha-tubulin gene. Science. 1984 Apr 6;224(4644):68–70. doi: 10.1126/science.6701535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbers D. L. Molecular basis of fertilization. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:719–742. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. R., Poccia D. L. Phosphorylation of sea urchin sperm H1 and H2B histones precedes chromatin decondensation and H1 exchange during pronuclear formation. Dev Biol. 1985 Mar;108(1):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K. Messenger ribonucleic acid encoding an apparent isoform of phosphorylase kinase catalytic subunit is abundant in the adult testis. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;3(1):110–116. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-1-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Spira A. W., Dixon G. H. Protamine messenger RNA: evidence for early synthesis and accumulation during spermatogenesis in rainbow trout. Dev Biol. 1978 May;64(1):82–98. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Rubin G. M. Isolation and characterization of Drosophila cAMP-dependent protein kinase genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1539–1556. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegstein A. R. Stages in the post-hatching development of Aplysia californica. J Exp Zool. 1977 Feb;199(2):275–288. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401990212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Jinno A., Takagi N., Shibuya M. A novel mammalian protein kinase gene (mak) is highly expressed in testicular germ cells at and after meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2261–2268. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):193–202. doi: 10.1126/science.2937147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Akita Y., Konno Y., Imajoh S., Suzuki K. A novel phorbol ester receptor/protein kinase, nPKC, distantly related to the protein kinase C family. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):731–741. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. The structure, expression, and properties of additional members of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6927–6932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyen O., Myklebust F., Scott J. D., Hansson V., Jahnsen T. Human testis cDNA for the regulatory subunit RII alpha of cAMP-dependent protein kinase encodes an alternate amino-terminal region. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 27;246(1-2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Rosenberg M. P., Vande Woude G. F. Proto-oncogene expression in germ cell development. Trends Genet. 1988 Jul;4(7):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of bovine type II adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3702–3709. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Wade R. D., Smith S. B., Krebs E. G., Walsh K. A., Titani K. Guanosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase, a chimeric protein homologous with two separate protein families. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4207–4218. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., Carmichael D. F., Lee D. C., Chrivia J. C., Krebs E. G., McKnight G. S. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the catalytic subunit of mouse cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1300–1304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]