Abstract
In the title compound, C16H13NO2, the isoxazole ring makes dihedral angles of 17.1 (1)° with the 3-methoxyphenyl ring and 15.2 (1)° with the phenyl group. Centrosymmetric dimers that are realised by pairs of C—H⋯π interactions are observed in the crystal structure.
Related literature
For general background to isoxazole derivaties, see: Sperry & Wright (2005 ▶); Tanaka et al. (2007 ▶). For their biological activity, see: Stevens & Albizati (1984 ▶). For related structures, see: Samshuddin et al. (2011 ▶); Balakrishnan et al. (2011 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H13NO2
M r = 251.27
Orthorhombic,

a = 7.909 (2) Å
b = 27.239 (8) Å
c = 5.9652 (17) Å
V = 1285.1 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.35 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
6838 measured reflections
2898 independent reflections
2256 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.031
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.103
S = 1.03
2898 reflections
174 parameters
2 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97, PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681300740X/zj2101sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681300740X/zj2101Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681300740X/zj2101Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1⋯Cg i | 0.93 | 2.96 | 3.732 (2) | 141 |
| C4—H4⋯Cg ii | 0.93 | 3.06 | 3.768 (3) | 134 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Technology Business Incubator (TBI), CAS in Crystallography, University of Madras, Chennai 600 025, India, for the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Isoxazoles are important class of heteroaromatic molecules which are components in a variety of natural products and medicinally useful compounds (Sperry & Wright, 2005). Isoxazole also finds application in organic synthesis as synthetic intermediates and chiral ligands. The liquid crystalline property of isoxazole derivatives and its potential application in optoelectric devices made them attractive synthetic target (Tanaka et al., 2007)
Isoxazole derivaties bearing different substituents are known to have various biological activities in pharmaceutical and agricultural areas. Isoxazole compounds have been widely studied because they exhibit some fungicidal activity, plant -growth regulating activity and antibacterial activity (Stevens & Albizati, 1984). In the title compound the isoxazole ring makes a dihedral angle of 17.1 (1)° with methoxy phenyl ring C10/C11/C12/C13/C14/C15/O2/C16 and a dihedral angle of 15.2 (1)° with the phenyl ring C1/C2/C3/C4/C5/C6 attached to the planar isoxazole moiety.The geometrical parameters agree well with the reported structure (Samshuddin et al.2011; Balakrishnan et al. 2011). A Centrosymmetric dimers are formed by C—H···π (C1—H1···Cg and C5—H5···Cg) interactions, where Cg is the centroid of the ring C1—C6 (Fig. 2).
Experimental
To solution of 1-phenyl-3-m-tolyl-propynone oxime (251 mg, 1.0 (mmol) in dry dichloromethane (1 ml) was added AuCl3 (3.03 mg, 1 mol%) under N2 atmosphere and stirred for 10 min. After completion of the reaction as indicated by TLC, the reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure and purified by colomn chromatography over silica gel (100–200 mech) using EtOAc/hexane to afford the pure product.
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically and allowed to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H=0.93–0.97 Å and Uiso (H)= 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2 Ueq(C) for other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
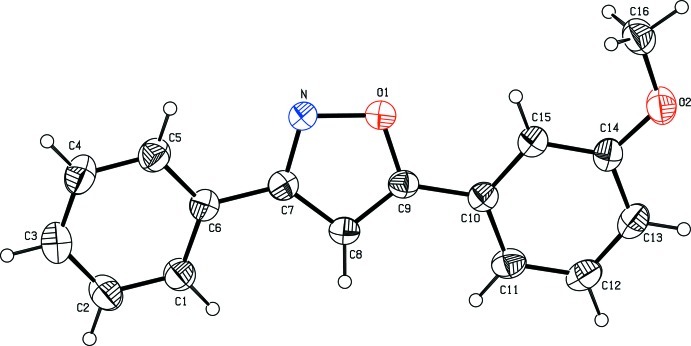
Molecular structure of the title compound, showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.

A view of the C—H···π interactions in the crystal structure of the title compound.
Crystal data
| C16H13NO2 | F(000) = 528 |
| Mr = 251.27 | Dx = 1.299 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pna21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2c -2n | Cell parameters from 2593 reflections |
| a = 7.909 (2) Å | θ = 2.7–28.4° |
| b = 27.239 (8) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 5.9652 (17) Å | T = 295 K |
| V = 1285.1 (6) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.35 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2256 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.031 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 28.4°, θmin = 2.7° |
| ω and φ scan | h = −10→8 |
| 6838 measured reflections | k = −36→32 |
| 2898 independent reflections | l = −7→6 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.103 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.052P)2 + 0.0082P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2898 reflections | Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3 |
| 174 parameters | Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0071 (19) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.6539 (2) | 0.00884 (6) | 0.6796 (4) | 0.0597 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.5895 | 0.0187 | 0.8020 | 0.072* | |
| C2 | 0.7022 (3) | −0.03964 (7) | 0.6594 (4) | 0.0713 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.6680 | −0.0624 | 0.7665 | 0.086* | |
| C3 | 0.8006 (3) | −0.05449 (7) | 0.4817 (4) | 0.0735 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.8334 | −0.0872 | 0.4693 | 0.088* | |
| C4 | 0.8501 (3) | −0.02114 (8) | 0.3231 (5) | 0.0739 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.9178 | −0.0311 | 0.2041 | 0.089* | |
| C5 | 0.7994 (2) | 0.02776 (7) | 0.3393 (4) | 0.0640 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.8317 | 0.0502 | 0.2299 | 0.077* | |
| C6 | 0.70095 (19) | 0.04300 (6) | 0.5184 (3) | 0.0494 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.6472 (2) | 0.09484 (6) | 0.5388 (3) | 0.0485 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.5818 (2) | 0.11998 (6) | 0.7237 (3) | 0.0493 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.5592 | 0.1074 | 0.8655 | 0.059* | |
| C9 | 0.5583 (2) | 0.16697 (6) | 0.6515 (3) | 0.0471 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.49808 (19) | 0.21163 (6) | 0.7641 (3) | 0.0476 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.4136 (2) | 0.20828 (7) | 0.9665 (3) | 0.0584 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.3926 | 0.1777 | 1.0304 | 0.070* | |
| C12 | 0.3606 (2) | 0.25068 (8) | 1.0733 (3) | 0.0637 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.3037 | 0.2485 | 1.2093 | 0.076* | |
| C13 | 0.3916 (2) | 0.29611 (7) | 0.9793 (3) | 0.0619 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.3544 | 0.3244 | 1.0514 | 0.074* | |
| C14 | 0.4776 (2) | 0.29962 (6) | 0.7785 (3) | 0.0520 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.5295 (2) | 0.25759 (6) | 0.6679 (3) | 0.0503 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.5848 | 0.2599 | 0.5307 | 0.060* | |
| C16 | 0.5937 (3) | 0.35244 (7) | 0.4984 (4) | 0.0720 (6) | |
| H16A | 0.5336 | 0.3357 | 0.3813 | 0.108* | |
| H16B | 0.7054 | 0.3390 | 0.5115 | 0.108* | |
| H16C | 0.6011 | 0.3868 | 0.4631 | 0.108* | |
| N | 0.6620 (2) | 0.12403 (5) | 0.3651 (3) | 0.0628 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.60346 (19) | 0.17058 (5) | 0.4372 (2) | 0.0689 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.50660 (17) | 0.34640 (5) | 0.7034 (2) | 0.0704 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0586 (10) | 0.0583 (10) | 0.0624 (12) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0068 (10) | 0.0017 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0738 (12) | 0.0572 (11) | 0.0830 (16) | 0.0021 (9) | 0.0046 (12) | 0.0100 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0691 (12) | 0.0575 (11) | 0.0939 (18) | 0.0050 (9) | −0.0027 (13) | −0.0120 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0713 (12) | 0.0695 (12) | 0.0807 (16) | −0.0010 (10) | 0.0139 (12) | −0.0203 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0665 (11) | 0.0624 (11) | 0.0629 (12) | −0.0055 (9) | 0.0102 (10) | −0.0061 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0423 (8) | 0.0512 (8) | 0.0546 (10) | −0.0051 (7) | −0.0020 (8) | −0.0051 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0439 (8) | 0.0510 (8) | 0.0507 (9) | −0.0073 (7) | 0.0006 (8) | −0.0013 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0507 (8) | 0.0514 (8) | 0.0457 (10) | −0.0020 (7) | 0.0026 (7) | 0.0047 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0464 (8) | 0.0517 (9) | 0.0432 (10) | −0.0046 (7) | −0.0041 (8) | 0.0013 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0423 (8) | 0.0544 (9) | 0.0462 (10) | 0.0012 (7) | −0.0057 (7) | −0.0015 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0543 (10) | 0.0713 (11) | 0.0494 (10) | 0.0017 (8) | −0.0034 (9) | 0.0027 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0578 (11) | 0.0870 (14) | 0.0462 (11) | 0.0111 (9) | 0.0013 (9) | −0.0042 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0558 (10) | 0.0756 (12) | 0.0544 (12) | 0.0154 (8) | −0.0081 (9) | −0.0164 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0462 (9) | 0.0547 (10) | 0.0551 (11) | 0.0043 (7) | −0.0095 (8) | −0.0082 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0448 (9) | 0.0556 (10) | 0.0504 (10) | 0.0016 (7) | −0.0024 (8) | −0.0039 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0820 (14) | 0.0548 (10) | 0.0791 (16) | −0.0039 (9) | −0.0051 (12) | 0.0030 (10) |
| N | 0.0935 (12) | 0.0494 (7) | 0.0455 (9) | 0.0024 (7) | 0.0110 (8) | −0.0002 (6) |
| O1 | 0.1073 (10) | 0.0510 (6) | 0.0485 (8) | 0.0060 (7) | 0.0055 (7) | 0.0026 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0790 (9) | 0.0518 (7) | 0.0805 (10) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0026 (8) | −0.0072 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C2 | 1.380 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.469 (2) |
| C1—C6 | 1.389 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.383 (2) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C10—C15 | 1.400 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.376 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.384 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.369 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.380 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.394 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.381 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.385 (3) | C14—O2 | 1.370 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.384 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.480 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C7—N | 1.311 (2) | C16—O2 | 1.413 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.398 (2) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.363 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C9—O1 | 1.331 (2) | N—O1 | 1.4165 (19) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.42 (19) | C11—C10—C15 | 120.20 (16) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.8 | C11—C10—C9 | 120.10 (15) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.8 | C15—C10—C9 | 119.70 (16) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.3 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.55 (18) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.96 (19) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.50 (19) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.2 (2) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.10 (17) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.08 (19) | O2—C14—C13 | 115.50 (16) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.0 | O2—C14—C15 | 124.32 (17) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.0 | C13—C14—C15 | 120.18 (17) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.94 (16) | C14—C15—C10 | 119.45 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.71 (16) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.3 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.35 (17) | C10—C15—H15 | 120.3 |
| N—C7—C8 | 111.07 (14) | O2—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| N—C7—C6 | 119.20 (16) | O2—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 129.71 (16) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 105.12 (15) | O2—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 127.4 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 127.4 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O1—C9—C8 | 109.67 (16) | C7—N—O1 | 105.89 (14) |
| O1—C9—C10 | 117.72 (15) | C9—O1—N | 108.24 (14) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 132.60 (16) | C14—O2—C16 | 118.23 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.4 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C15 | 162.56 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.4 (3) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | −0.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.8 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 178.65 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.1 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.1 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.7 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.55 (18) | C12—C13—C14—O2 | −177.92 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.1 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 179.22 (17) | O2—C14—C15—C10 | 177.77 (14) |
| C5—C6—C7—N | 14.4 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −1.7 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—N | −165.93 (17) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.9 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −164.38 (18) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | −177.80 (14) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | 15.3 (3) | C8—C7—N—O1 | −0.2 (2) |
| N—C7—C8—C9 | −0.4 (2) | C6—C7—N—O1 | −179.16 (14) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 178.48 (16) | C8—C9—O1—N | −0.93 (19) |
| C7—C8—C9—O1 | 0.81 (18) | C10—C9—O1—N | 178.15 (13) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −178.09 (17) | C7—N—O1—C9 | 0.7 (2) |
| O1—C9—C10—C11 | 165.00 (15) | C13—C14—O2—C16 | −179.83 (16) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −16.2 (3) | C15—C14—O2—C16 | 0.7 (2) |
| O1—C9—C10—C15 | −16.3 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1···Cgi | 0.93 | 2.96 | 3.732 (2) | 141 |
| C4—H4···Cgii | 0.93 | 3.06 | 3.768 (3) | 134 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, z−1/2; (ii) −x, −y+2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZJ2101).
References
- Balakrishnan, B., Praveen, C., Seshadri, P. R. & Perumal, P. T. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2008). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison. Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Samshuddin, S., Butcher, R. J., Akkurt, M., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1975–o1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sperry, J. & Wright, D. (2005). Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 8, 723–740. [PubMed]
- Stevens, R. V. & Albizati, K. F. (1984). Tetrahedron Lett. 25, 4587–4591.
- Tanaka, M., Haino, T., Ideta, K., Kubo, K., Mori, A. & Fukazawa, Y. (2007). Tetrahedron, 63, 652–.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681300740X/zj2101sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681300740X/zj2101Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681300740X/zj2101Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


