Abstract
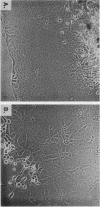
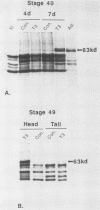
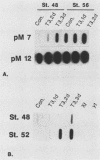
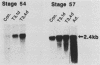
We have used in vitro explant cultures of Xenopus laevis skin to investigate the role that the thyroid hormone triiodothyronine (T3) plays in activating the 63-kilodalton (kDa) keratin genes. The activation of these genes in vivo requires two distinct steps, one independent of T3 and one dependent on T3. In this report we have shown that the same two steps are required to fully activate the 63-kDa keratin genes in skin explant cultures, and we have characterized the T3-mediated step in greater detail. Unlike the induction of transcription by T3 or steroid hormones in adult tissues, there was a long latent period of approximately 2 days between the addition of T3 to skin cultures and an increase in concentration of keratin mRNA. While the T3 induction of 63-kDa keratin gene transcription cannot occur until age 48, a short transient exposure of stage 40 skin cultures to T3 resulted in high-level expression of these genes 5 days later, when normal siblings had reached stage 48. This result indicates that T3 induces a stable change in epidermal cells which can be expressed much later, after extensive cell proliferation has occurred in the absence of T3. Once the 63-kDa keratin genes were induced, they were stably expressed, and by the end of metamorphosis T3 had no further effect on their expression. The results suggest that T3 induces constitutive expression of the 63-kDa keratin genes during metamorphosis.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amasino R. M. Acceleration of nucleic acid hybridization rate by polyethylene glycol. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The role of the kappa enhancer and its binding factor NF-kappa B in the developmental regulation of kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J., Copp R. P., Janocko L., Samuels H. H. 5'-Flanking DNA of the rat growth hormone gene mediates regulated expression by thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11744–11748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattini P. A., Anderson T. R., Baxter J. D., Mellon P., Eberhardt N. L. The human growth hormone gene is negatively regulated by triiodothyronine when transfected into rat pituitary tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13367–13372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFesi C. R., Fels E. C., Surks M. I. L-Triiodothyronine (T3) stimulates growth of cultured GC cells by action early in the G1 period: evidence for mediation by the nuclear T3 receptor. Endocrinology. 1985 May;116(5):2062–2069. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-5-2062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Liegro I., Savettieri G., Cestelli A. Cellular mechanism of action of thyroid hormones. Differentiation. 1987;35(3):165–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierich A., Gaub M. P., LePennec J. P., Astinotti D., Chambon P. Cell-specificity of the chicken ovalbumin and conalbumin promoters. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison T. R., Mathisen P. M., Miller L. Developmental changes in keratin patterns during epidermal maturation. Dev Biol. 1985 Dec;112(2):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90403-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H., Whitear M. Genesis and regression of the figures of Eberth and occurrence of cytokeratin aggregates in the epidermis of anuran larvae. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1986;174(1):73–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00318338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEADY J. E., KOLLROS J. J. HORMONAL MODIFICATION OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF PLICAL SKIN GLANDS. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1964 Apr;4:124–131. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(64)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W., Franz J. K. Amino acid sequence of the carboxy-terminal part of an acidic type I cytokeratin of molecular weight 51 000 from Xenopus laevis epidermis as predicted from the cDNA sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1301–1306. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W., Franz J. K., Franke W. W. Amino acid sequence microheterogeneities of basic (type II) cytokeratins of Xenopus laevis epidermis and evolutionary conservativity of helical and non-helical domains. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Kirschner M. Synergistic induction of mesoderm by FGF and TGF-beta and the identification of an mRNA coding for FGF in the early Xenopus embryo. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Hassell J. R., Star V. L., Cannon F. B., Laurie G. W., Martin G. R. Basement membrane complexes with biological activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):312–318. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Brent G. A., Warne R. L., Larsen P. R., Moore D. D. Thyroid hormone receptor binds to a site in the rat growth hormone promoter required for induction by thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5670–5674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyman D. F., White B. A. Molecular cloning of hepatic mRNAs in Rana catesbeiana responsive to thyroid hormone during induced and spontaneous metamorphosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5233–5237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathisen P. M., Miller L. Thyroid hormone induction of keratin genes: a two-step activation of gene expression during development. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1107–1117. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKearin D. M., Shapiro D. J. Persistent estrogen induction of hepatic Xenopus laevis serum retinol binding protein mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3261–3265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. M., Jr Thyroxine elicits divergent changes in mRNA levels for two urea cycle enzymes and one gluconeogenic enzyme in tadpole liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Nov 15;259(1):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90479-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyborg J. K., Nguyen A. P., Spindler S. R. Relationship between thyroid and glucocorticoid hormone receptor occupancy, growth hormone gene transcription, and mRNA accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12377–12381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney D. F., Pearson-White S. H., Konieczny S. F., Latham K. E., Emerson C. P., Jr Myogenic lineage determination and differentiation: evidence for a regulatory gene pathway. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):781–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves O. R., Laskey R. A. In vitro differentiation of a homogeneous cell population--the epidermis of Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1975 Aug;34(1):75–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. Hormonal regulation of epidermis-specific protein and messenger RNA synthesis in amphibian metamorphosis. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):163–179. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Green H. Enzymatic cross-linking of involucrin and other proteins by keratinocyte particulates in vitro. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Darlington B. G., Heath J. K., Godsave S. F. Mesoderm induction in early Xenopus embryos by heparin-binding growth factors. Nature. 1987 Mar 12;326(6109):197–200. doi: 10.1038/326197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. Early metamorphic competence of Xenopus larvae. Dev Biol. 1968 Nov;18(5):415–440. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. The formation, distribution and function of ribosomes and microsomal membranes during induced amphibian metamorphosis. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):783–801. doi: 10.1042/bj1050783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Melton D. A. A maternal mRNA localized to the vegetal hemisphere in Xenopus eggs codes for a growth factor related to TGF-beta. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):861–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight P. A., Crew M. D., Spindler S. R. Discrete positive and negative thyroid hormone-responsive transcription regulatory elements of the rat growth hormone gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5659–5663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J., Adelstein R. S., Melloul D., Nudel U., Yaffe D., Cedar H. Muscle-specific activation of a methylated chimeric actin gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):409–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90661-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-la-Concha A., Dietrich U., Weigel D., Campos-Ortega J. A. Functional interactions of neurogenic genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):499–508. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]