Abstract
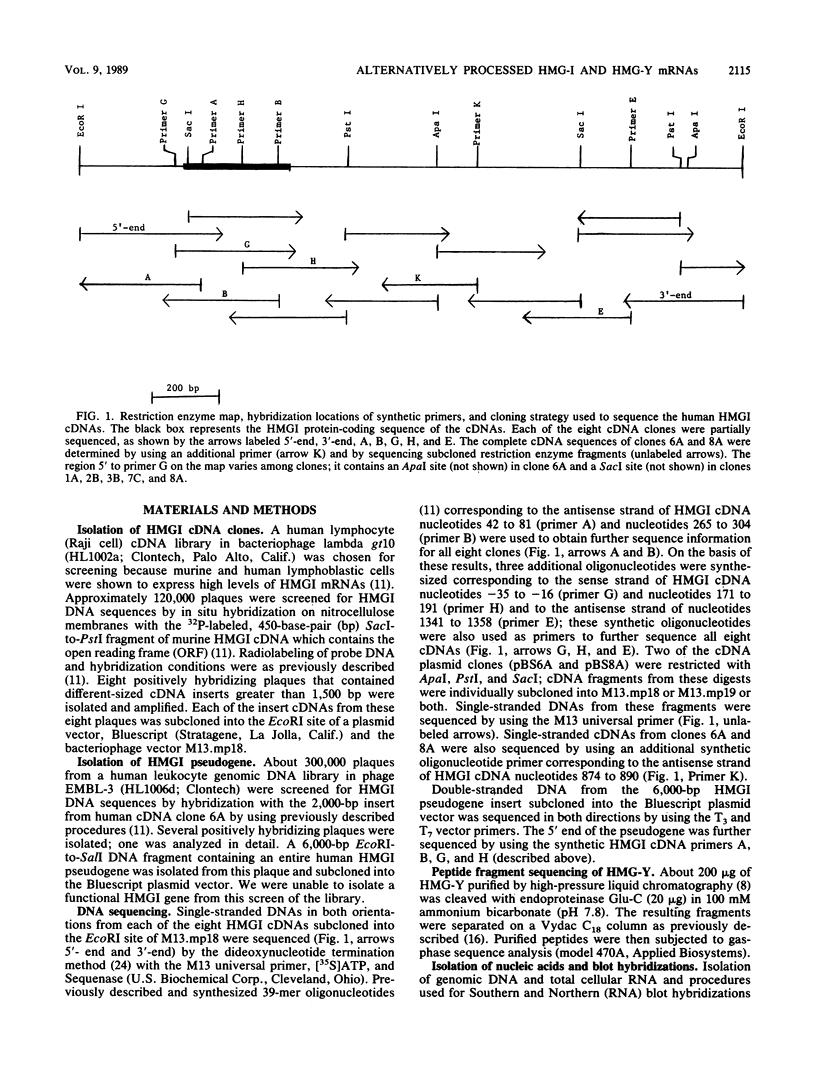
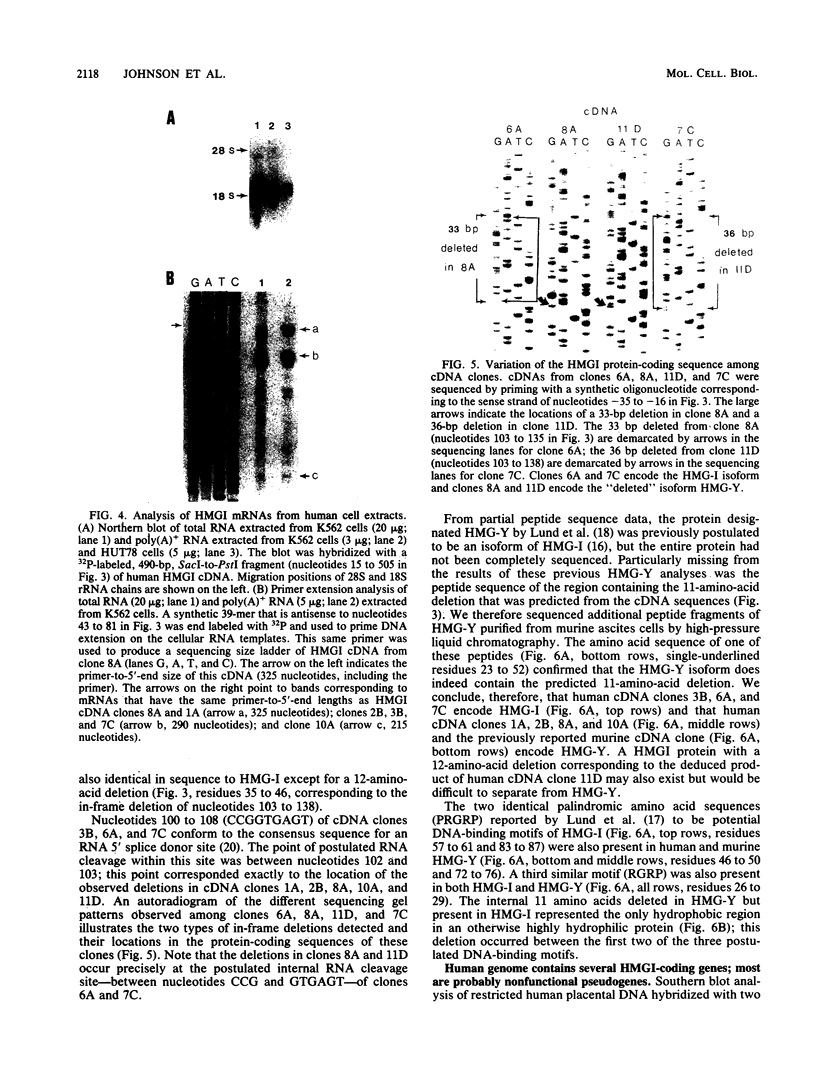
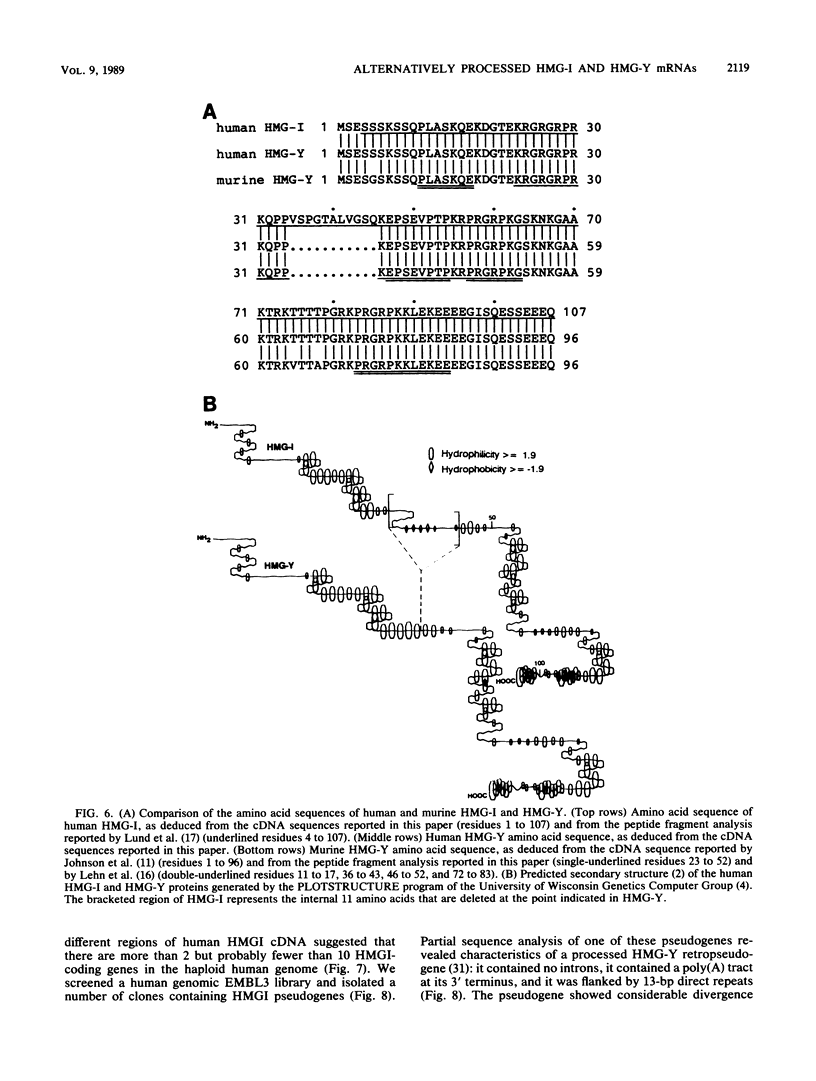
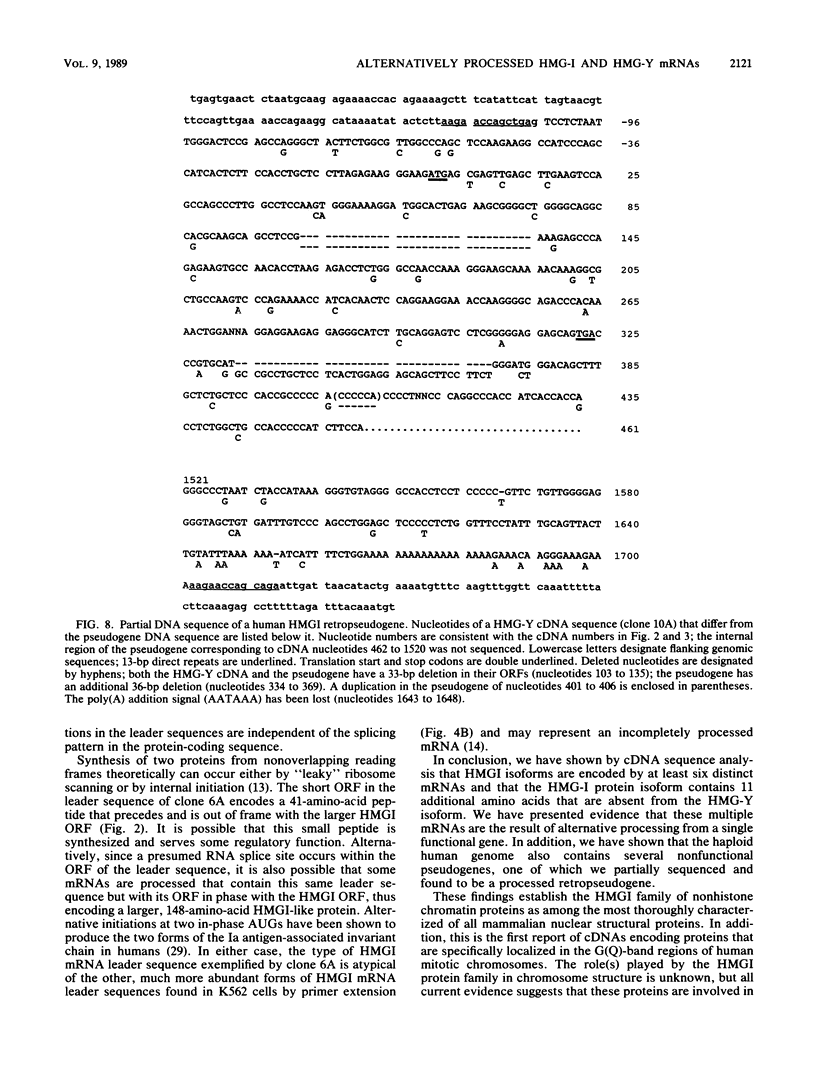
The high-mobility-group protein HMG-I is a well-characterized nonhistone chromosomal protein that is preferentially expressed in rapidly dividing cells, binds to A. T-rich regions of DNA in vitro, and has been localized to particular regions of mammalian metaphase chromosomes. We isolated eight cDNA clones encoding HMG-I and its isoform HMG-Y from a human Raji cell cDNA library and detected blocks of nucleotide sequence rearrangements in the 5'-untranslated regions of these clones. In addition to this leader sequence variation, five of the eight cDNA clones had either a 33- or 36-base-pair in-frame deletion in their open reading frame (ORF); we found that this shortened ORF encodes the HMG-Y protein isoform. We present evidence that the 5'-untranslated-region and ORF heterogeneity of the cDNA clones is the result of alternative processing of RNA transcripts from a single functional gene. Several additional but probably nonfunctional HMG-I or HMG-Y gene copies exist in the human genome; we isolated and partially sequenced one of these pseudogenes and found that it is a processed HMG-Y retropseudogene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elton T. S., Reeves R. Microheterogeneity of the mammalian high mobility group (HMG) proteins 1 and 2 investigated by reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;144(2):403–416. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elton T. S., Reeves R. Microheterogeneity of the mammalian high-mobility group proteins 14 and 17 investigated by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1985 May 1;146(2):448–460. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90568-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elton T. S., Reeves R. Purification and postsynthetic modifications of Friend erythroleukemic cell high mobility group protein HMG-I. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;157(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giancotti V., Pani B., D'Andrea P., Berlingieri M. T., Di Fiore P. P., Fusco A., Vecchio G., Philp R., Crane-Robinson C., Nicolas R. H. Elevated levels of a specific class of nuclear phosphoproteins in cells transformed with v-ras and v-mos oncogenes and by cotransfection with c-myc and polyoma middle T genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1981–1987. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Cockerill P. N., Kellam S., Wright C. A. Fractionation by high-performance liquid chromatography of the low-molecular-mass high-mobility-group (HMG) chromosomal proteins present in proliferating rat cells and an investigation of the HMG proteins present in virus transformed cells. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 15;149(1):47–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Lehn D. A., Elton T. S., Barr P. J., Reeves R. Complete murine cDNA sequence, genomic structure, and tissue expression of the high mobility group protein HMG-I(Y). J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18338–18342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehn D. A., Elton T. S., Johnson K. R., Reeves R. A conformational study of the sequence specific binding of HMG-I (Y) with the bovine interleukin-2 cDNA. Biochem Int. 1988 May;16(5):963–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund T., Dahl K. H., Mørk E., Holtlund J., Laland S. G. The human chromosomal protein HMG I contains two identical palindrome amino acid sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):725–730. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90589-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund T., Holtlund J., Fredriksen M., Laland S. G. On the presence of two new high mobility group-like proteins in HeLa S3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 21;152(2):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen M. S., Friesen P. D. Molecular analysis of the transcriptional regulatory region of an early baculovirus gene. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):493–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.493-503.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Elton T. S., Nissen M. S., Lehn D., Johnson K. R. Posttranscriptional gene regulation and specific binding of the nonhistone protein HMG-I by the 3' untranslated region of bovine interleukin 2 cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6531–6535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renshaw M. W., Capozza M. A., Wang J. Y. Differential expression of type-specific c-abl mRNAs in mouse tissues and cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4547–4551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russnak R. H., Candido E. P., Astell C. R. Interaction of the mouse chromosomal protein HMG-I with the 3' ends of genes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6392–6399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A mammalian high mobility group protein recognizes any stretch of six A.T base pairs in duplex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikantha T., Landsman D., Bustin M. Retropseudogenes for human chromosomal protein HMG-17. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 5;197(3):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90554-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroeher V. L., Gaiser J. C., Garber R. L. Alternative RNA splicing that is spatially regulated: generation of transcripts from the Antennapedia gene of Drosophila melanogaster with different protein-coding regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4143–4154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubin M., Long E. O., Mach B. Two forms of the Ia antigen-associated invariant chain result from alternative initiations at two in-phase AUGs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90626-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartiainen E., Palvimo J., Mahonen A., Linnala-Kankkunen A., Mäenpä P. H. Selective decrease in low-Mr HMG proteins HMG I and HMG Y during differentiation of mouse teratocarcinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80581-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Purification and characterization of a high-mobility-group-like DNA-binding protein that stimulates rRNA synthesis in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3406–3414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]