Abstract
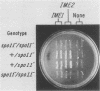
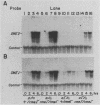
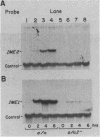
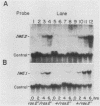
Two signals activate meiosis in yeast: starvation and expression of the a1 and alpha 2 products of the mating-type locus. Prior studies suggest that these signals stimulate expression of an activator of meiosis, the IME1 (inducer of meiosis) product. We have cloned a gene, IME2, with properties similar to those of IME1: both genes are required for meiosis, and both RNAs are induced in meiotic cells. Elevated dosage of IME1 or IME2 stimulates the meiotic recombination pathway without starvation; thus, the IME products may be part of the switch that activates meiosis. IME1 was found to be required for IME2 expression, and a multicopy IME2 plasmid permitted meiosis in an ime1 deletion mutant. Accordingly, we propose that the IME1 product stimulates meiosis mainly through activation of IME2 expression.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breviario D., Hinnebusch A., Cannon J., Tatchell K., Dhar R. Carbon source regulation of RAS1 expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the phenotypes of ras2- cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4152–4156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron S., Levin L., Zoller M., Wigler M. cAMP-independent control of sporulation, glycogen metabolism, and heat shock resistance in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90572-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. F., Gibbs J. B., Tatchell K. Suppressors of the ras2 mutation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1986 Jun;113(2):247–264. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. F., Tatchell K. Characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes encoding subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2653–2663. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy M. J., Buten-Magee B., Straight D. J., Kennedy A. L., Partridge R. M., Magee P. T. Isolation of genes expressed preferentially during sporulation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3000–3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. The yeast SCG1 gene: a G alpha-like protein implicated in the a- and alpha-factor response pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. The major promoter element of rRNA transcription in yeast lies 2 kb upstream. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E. Genes controlling meiosis and spore formation in yeast. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):215–225. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Herskowitz I. Regulation by the yeast mating-type locus of STE12, a gene required for cell-type-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3818–3821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G. On ras gene function in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4740–4744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlin-Ninfa E., Kaback D. B. Isolation and functional analysis of sporulation-induced transcribed sequences from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2185–2197. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutte C., Johnson A. D. a1 protein alters the DNA binding specificity of alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90429-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Hereford L., Herskowitz I. Targeting of E. coli beta-galactosidase to the nucleus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis M. A., Holland M. J., McCabe P. C., Cole G. E., Wittman V. P., Tal R., Watt K. W., Gelfand D. H., Holland J. P., Meade J. H. Expression, Glycosylation, and Secretion of an Aspergillus Glucoamylase by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):21–26. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4695.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I. Regulation of yeast mating-type interconversion: feedback control of HO gene expression by the mating-type locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassir Y., Granot D., Simchen G. IME1, a positive regulator gene of meiosis in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):853–862. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassir Y., Simchen G. Regulation of mating and meiosis in yeast by the mating-type region. Genetics. 1976 Feb;82(2):187–206. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., McGill C., Fasano O., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genetic analysis of yeast RAS1 and RAS2 genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. A new mapping method employing a meiotic rec-mutant of yeast. Genetics. 1982 Mar;100(3):387–412. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Waddell C. S., Esposito R. E. The role of the SPO11 gene in meiotic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 1985 Jun;110(2):187–216. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Strathern J. N., Broach J. R., Hicks J. B. Regulation of transcription in expressed and unexpressed mating type cassettes of yeast. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):239–244. doi: 10.1038/289239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law D. T., Segall J. The SPS100 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is activated late in the sporulation process and contributes to spore wall maturation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):912–922. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay V., Manney T. R. Mutations affecting sexual conjugation and related processes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Genetic analysis of nonmating mutants. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):273–288. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T. Initiation of meiosis in yeast mutants defective in adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90461-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., MacKay V. L., Nasmyth K. A. Identification and comparison of two sequence elements that confer cell-type specific transcription in yeast. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):598–603. doi: 10.1038/314598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. P., Herskowitz I. Activation of meiosis and sporulation by repression of the RME1 product in yeast. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):738–742. doi: 10.1038/319738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. P. Two switches govern entry into meiosis in yeast. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;267:47–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Nakafuku M., Nakayama N., Brenner C., Miyajima A., Kaibuchi K., Arai K., Kaziro Y., Matsumoto K. GPA1, a haploid-specific essential gene, encodes a yeast homolog of mammalian G protein which may be involved in mating factor signal transduction. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Astell C., Smith M. A position effect in the control of transcription at yeast mating type loci. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):244–250. doi: 10.1038/289244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olempska-Beer Z., Freese E. Initiation of meiosis and sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae does not require a decrease in cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2141–2147. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Segall J. Characterization and mutational analysis of a cluster of three genes expressed preferentially during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2443–2451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Segall J. Isolation of DNA sequences preferentially expressed during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):142–150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J., Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I. rme1 Mutation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: map position and bypass of mating type locus control of sporulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;1(10):958–960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.10.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN F., ROMAN H. Evidence for two types of allelic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 1963 Feb;48:255–261. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo V., Simchen G., Shilo B. Initiation of meiosis in cell cycle initiation mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Mar 15;112(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Identification of the DNA sequences controlling the expression of the MAT alpha locus of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2320–2324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Transcription and regulatory signals at the mating type locus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G., Piñon R., Salts Y. Sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: premeiotic DNA synthesis, readiness and commitment. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Nov;75(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr, Blair L. C., Thorner J. Cell interactions and regulation of cell type in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:623–660. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J., Hicks J., Herskowitz I. Control of cell type in yeast by the mating type locus. The alpha 1-alpha 2 hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Chaleff D. T., DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M. Requirement of either of a pair of ras-related genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for spore viability. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):523–527. doi: 10.1038/309523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D., Astell C., Smith M. In vitro mutation analysis of the mating-type locus in yeast. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90357-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K. RAS genes and growth control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):364–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.364-367.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Robinson L. C., Breitenbach M. RAS2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for gluconeogenic growth and proper response to nutrient limitation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3785–3789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Scott J. D., McMullen B., Hurwitz M., Krebs E. G., Wigler M. Cloning and characterization of BCY1, a locus encoding a regulatory subunit of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1371–1377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Cameron S., Sass P., Zoller M., Wigler M. Three different genes in S. cerevisiae encode the catalytic subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90223-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. T., Frackman S., Kowalisyn J., Esposito R. E., Elder R. Developmental regulation of SPO13, a gene required for separation of homologous chromosomes at meiosis I. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1425–1435. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L., Herskowitz I. Negative regulation of STE6 gene expression by the alpha 2 product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2420–2427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]