Abstract
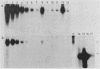
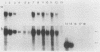
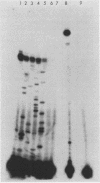
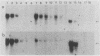
The major urinary proteins of the mouse are encoded by a large multigene family composed of several distinct groups of genes distinguished by differences in sequence and expression characteristics. The genes in the largest group (group 1) show greater than 99% pairwise similarity in their exons. By hybridization between RNA and a specifically designed oligonucleotide, we confirmed that genes of this group are expressed mainly in the liver. By using additional gene-specific oligonucleotide probes, we have been able to distinguish between the species of mRNA corresponding to two of these genes and to measure their abundance in male and female liver. Both mRNAs are present in male liver at high but different levels. Both are also present in female liver, one at a much lower level than in the male and the second at a very low level indeed. Both are present at male levels in the livers of females induced with testosterone. These results show unequivocally that the expression of different group 1 Mup genes is differentially influenced by the hormonal status of the mouse.
Full text
PDF
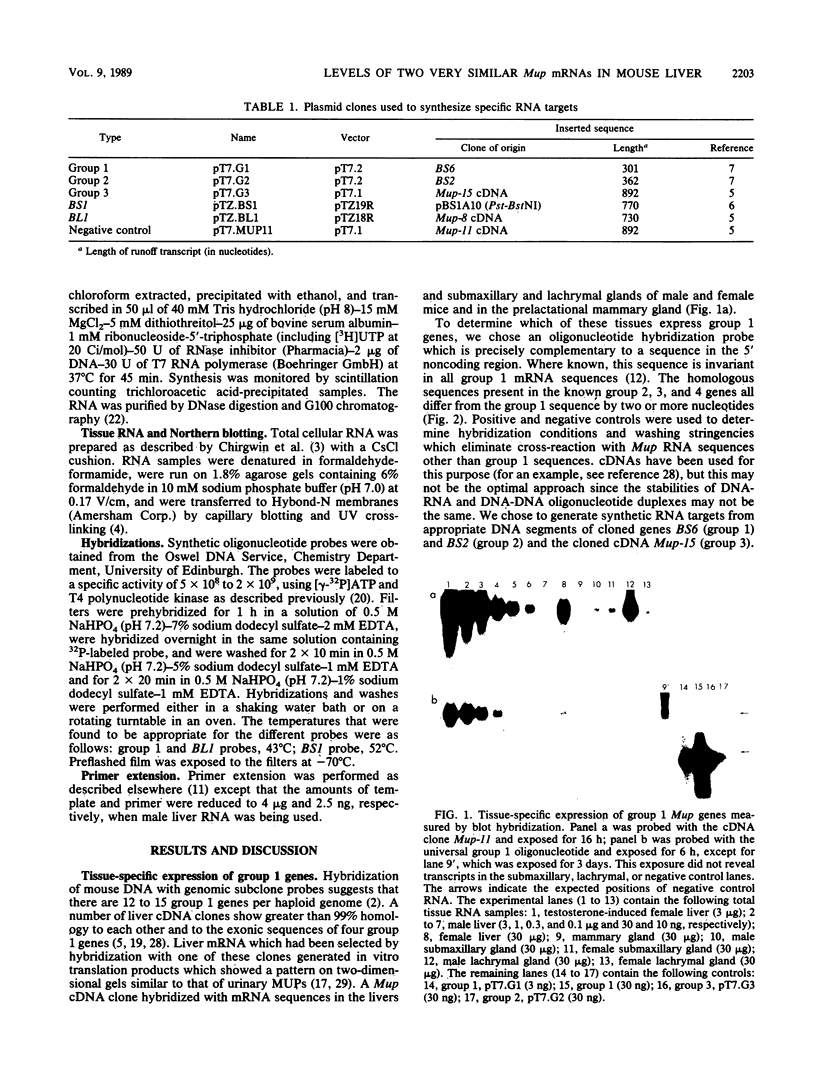




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett K. L., Lalley P. A., Barth R. K., Hastie N. D. Mapping the structural genes coding for the major urinary proteins in the mouse: combined use of recombinant inbred strains and somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1220–1224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Clark A. J., Clissold P. M., Hainey S., Francke U. Two main groups of mouse major urinary protein genes, both largely located on chromosome 4. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):615–620. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Chave-Cox A., Ma X., Bishop J. O. Analysis of mouse major urinary protein genes: variation between the exonic sequences of group 1 genes and a comparison with an active gene out with group 1 both suggest that gene conversion has occurred between MUP genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3167–3171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Clissold P. M., Bishop J. O. Variation between mouse major urinary protein genes isolated from a single inbred line. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Ghazal P., Bingham R. W., Barrett D., Bishop J. O. Sequence structures of a mouse major urinary protein gene and pseudogene compared. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3159–3165. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clissold P. M., Bishop J. O. Variation in mouse major urinary protein (MUP) genes and the MUP gene products within and between inbred lines. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. M., Mahon K. A., Gall J. G. Transcription of a satellite DNA in the newt. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1137–1144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Clark A. J., Bishop J. O. Evolutionary amplification of a pseudogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4182–4185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainey S., Bishop J. O. Allelic variation at several different genetic loci determines the major urinary protein phenotype of inbred mouse strains. Genet Res. 1982 Feb;39(1):31–39. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Bishop J. O. The expression of three abundance classes of messenger RNA in mouse tissues. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):761–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastie N. D., Held W. A., Toole J. J. Multiple genes coding for the androgen-regulated major urinary proteins of the mouse. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Gallagher J. F., Hohman C. M., Kuhn N. J., Sampsell B. M., Hughes R. G., Jr Identification and characterization of functional genes encoding the mouse major urinary proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3705–3712. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf J. L., Gallagher J. F., Held W. A. Differential, multihormonal regulation of the mouse major urinary protein gene family in the liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2232–2240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauter K., Leinwand L., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F., Darnell J. E., Jr Structural genes of the mouse major urinary protein are on chromosome 4. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):414–417. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn N. J., Woodworth-Gutai M., Gross K. W., Held W. A. Subfamilies of the mouse major urinary protein (MUP) multi-gene family: sequence analysis of cDNA clones and differential regulation in the liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6073–6090. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norstedt G., Palmiter R. Secretory rhythm of growth hormone regulates sexual differentiation of mouse liver. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):805–812. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omiecinski C. J., Walz F. G., Jr, Vlasuk G. P. Phenobarbital induction of rat liver cytochromes P-450b and P-450e. Quantitation of specific RNAs by hybridization to synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3247–3250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampsell B. M., Held W. A. Variation in the major urinary protein multigene family in wild-derived mice. Genetics. 1985 Mar;109(3):549–568. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L. Protein structure. One fold among many. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):659–659. doi: 10.1038/327659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahan K., Denaro M., Gilmartin M., Shi Y., Derman E. Expression of six mouse major urinary protein genes in the mammary, parotid, sublingual, submaxillary, and lachrymal glands and in the liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1947–1954. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahan K., Gilmartin M., Derman E. Nucleotide sequences of liver, lachrymal, and submaxillary gland mouse major urinary protein mRNAs: mosaic structure and construction of panels of gene-specific synthetic oligonucleotide probes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1938–1946. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. H., Held W. A., Hastie N. D. The gene family for major urinary proteins: expression in several secretory tissues of the mouse. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):755–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg T., Bishop J. O. Tissue-specific gene expression in mouse hepatocytes cultured in growth-restricting medium. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3338–3344. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]