Abstract
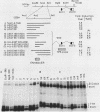
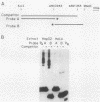
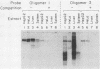
We previously defined two distinct cell-specific DNA elements controlling the transient expression of the transthyretin gene in Hep G2 (human hepatoma) cells: a proximal promoter region (-202 base pairs [bp] to the cap site), and a far-upstream cell-specific enhancer located between 1.6 and 2.15 kilobases (kb) 5' of the cap site (R. H. Costa, E. Lai, and J. E. Darnell, Jr., Mol. Cell. Biol. 6:4697-4708, 1986). In this report, we located the effective transthyretin enhancer element within a 100-bp region between 1.96 and 1.86 kb 5' to the mRNA cap site. In Hep G2 nuclear extracts, three protein-binding sites within this minimal enhancer element were identified by gel mobility and methylation protection experiments. Each binding site was required for full enhancer activity in Hep G2 transient expression assays. Competition experiments in protein-binding assays suggested that two of the three sites were recognized by a similar factor and that the protein interaction with the third site was different. The nuclear protein(s) which bound to the two homologous sites was found mainly or only in cells of hepatic origin, suggesting an involvement of this region in the cell-specific function of this enhancer. The nuclear protein(s) recognizing the third enhancer region was also found in HeLa and spleen cells.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atchison M. L., Perry R. P. The role of the kappa enhancer and its binding factor NF-kappa B in the developmental regulation of kappa gene transcription. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90362-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Friedman J. M., Darnell J. E., Jr Cellular promoters incorporated into the adenovirus genome: effects of viral regulatory elements on transcription rates and cell specificity of albumin and beta-globin promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3798–3806. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Herbst R. S., Bennett A. L., Darnell J. E., Jr Factors that interact with the rat albumin promoter are present both in hepatocytes and other cell types. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):256–267. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Moschonas N., Flavell R. A. Beta + thalassemia: aberrant splicing results from a single point mutation in an intron. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dente L., Cortese R. Cell-specific expression of a transfected human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Pirozzi A., Blance C., Cortese R. Negative control of liver-specific gene expression: cloned human retinol-binding protein gene is repressed in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):631–636. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control of the mouse prealbumin (transthyretin) gene: both promoter sequences and a distinct enhancer are cell specific. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4697–4708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson P. W., Howlett G. J., Schreiber G. Rat transthyretin (prealbumin). Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and gene expression in liver and brain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8214–8219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Babiss L. E., Clayton D. F., Darnell J. E., Jr Cellular promoters incorporated into the adenovirus genome: cell specificity of albumin and immunoglobulin expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3791–3797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Babiss L. E., Weiss M., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatoma variants (C2) are defective for transcriptional and post-transcriptional actions from both endogenous and viral genomes. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1727–1731. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02424.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R., Tilghman S. M. Multiple regulatory elements in the intergenic region between the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):477–487. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O. Enzymic differentiation in mammalian liver injection of fetal rats with hormones causes the premature formation of liver enzymes. Science. 1969 Feb 28;163(3870):891–895. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3870.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O., Federman M., Knox W. E. Cytomorphometry of developing rat liver and its application to enzymic differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Feb;52(2):261–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Krumlauf R., Camper S. A., Brinster R. L., Tilghman S. M. Diversity of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in mice is generated by a combination of separate enhancer elements. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2432657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Nickol J. M., Lieber M. R., Felsenfeld G. Regulated gene expression in transfected primary chicken erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4312–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. Control elements of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre C., Imagawa M., Dana S., Grindlay J., Bodner M., Karin M. Tissue-specific expression of the human growth hormone gene is conferred in part by the binding of a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):971–981. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Palmiter R. D., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Swift G. H., MacDonald R. J. Specific expression of an elastase-human growth hormone fusion gene in pancreatic acinar cells of transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):600–602. doi: 10.1038/313600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Sperling L., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression is conferred by a sequence from the 5' end of the rat albumin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2505–2510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek P. A., Chepelinsky A. B., Khillan J. S., Piatigorsky J., Westphal H. Lens-specific expression and developmental regulation of the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene driven by the murine alpha A-crystallin promoter in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. An albumin enhancer located 10 kb upstream functions along with its promoter to direct efficient, liver-specific expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):268–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soprano D. R., Soprano K. J., Goodman D. S. Retinol-binding protein and transthyretin mRNA levels in visceral yolk sac and liver during fetal development in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7330–7334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Hammer R. E., MacDonald R. J., Brinster R. L. Tissue-specific expression of the rat pancreatic elastase I gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):639–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90258-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theisen M., Stief A., Sippel A. E. The lysozyme enhancer: cell-specific activation of the chicken lysozyme gene by a far-upstream DNA element. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):719–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. C., Morley B. J., Campbell R. D. Cell-specific expression of the human complement protein factor B gene: evidence for the role of two distinct 5'-flanking elements. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]