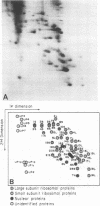
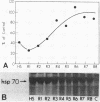
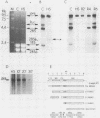
Abstract
In Drosophila tissue culture cells, the synthesis of ribosomal proteins was inhibited by a 1-h 37 degrees C heat shock. Ribosomal protein synthesis was repressed to a greater extent than that of most other proteins synthesized by these cells at 25 degrees C. After a 1-h heat shock, when the cells were returned to 25 degrees C, the ribosomal proteins were much slower than most other 25 degrees C proteins to return to pre-heat shock levels of synthesis. Relative to one another, all the ribosomal proteins were inhibited and later recovered to normal levels of synthesis at the same rate and to the same extent. Unlike the ribosomal proteins, the precursor to the large rRNAs was continually synthesized during heat shock, although at a slightly reduced level, but was not processed. It was rapidly degraded, with a half-life of approximately 16 min. Pre-heat shock levels of synthesis, stability, and correct processing were restored only when ribosomal protein synthesis returned to at least 50% of that seen in non-heat-shocked cells.
Full text
PDF

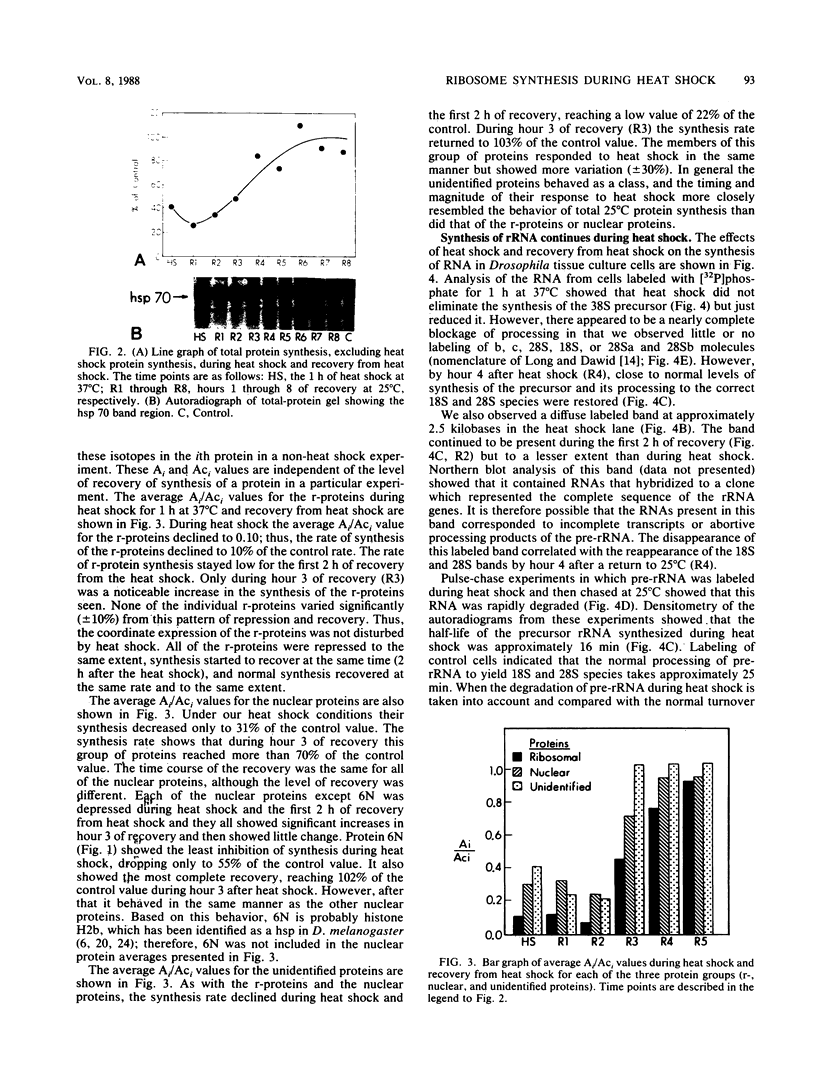


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfageme C. R., Zweidler A., Mahowald A., Cohen L. H. Histones of Drosophila embryos. Electrophoretic isolation and structural studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3729–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger D. G., Pardue M. L. The control of protein synthesis during heat shock in Drosophila cells involves altered polypeptide elongation rates. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. S., Russell D. W., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Cloning and expression of recombinant, functional ricin B chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5640–5644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. Heat shock and recovery are mediated by different translational mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellgaard E. G., Clever U. RNA metabolism during puff induction in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1971;36(1):60–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00326422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell-Towt J., Sanders M. M. Noncoordinate histone synthesis in heat-shocked Drosophila cells is regulated at multiple levels. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2676–2685. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein C., Warner J. R. Coordinate regulation of the synthesis of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1547–1551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel J. A., Ransom L. J., Graham M. L., Pardue M. L. Transcription and metabolism of RNA from the Drosophila melanogaster heat shock puff site 93D. Chromosoma. 1980;80(3):237–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00292683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Penman S. The metabolism of poly (A)+ and poly(A)-hnRNA in cultured Drosophila cells studied with a rapid uridine pulse-chase. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Alternative pathways in the processing of ribosomal RNA precursor in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 25;138(4):873–878. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nover L., Munsche D., Neumann D., Ohme K., Scharf K. D. Control of ribosome biosynthesis in plant cell cultures under heat-shock conditions. Ribosomal RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):297–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Campioni N., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Expression of ribosomal-protein genes in Xenopus laevis development. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Hogness D. S. Effect of heat shock on the synthesis of low molecular weight RNAs in drosophilia: accumulation of a novel form of 5S RNA. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. M. Identification of histone H2b as a heat-shock protein in Drosophila. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):579–583. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santon J. B., Pellegrini M. Expression of ribosomal proteins during Drosophila early development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5649–5653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. W., Warner J. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in a mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective in ribosomal protein synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 May 3;161(2):221–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00274191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanguay R. M., Camato R., Lettre F., Vincent M. Expression of histone genes during heat shock and in arsenite-treated Drosophila Kc cells. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;61(6):414–420. doi: 10.1139/o83-056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaslet C. A., O'Connell P., Izquierdo M., Rosbash M. Isolation and mapping of a cloned ribosomal protein gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):674–676. doi: 10.1038/285674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. In the absence of ribosomal RNA synthesis, the ribosomal proteins of HeLa cells are synthesized normally and degraded rapidly. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):315–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. RNA splicing is interrupted by heat shock and is rescued by heat shock protein synthesis. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]