Abstract
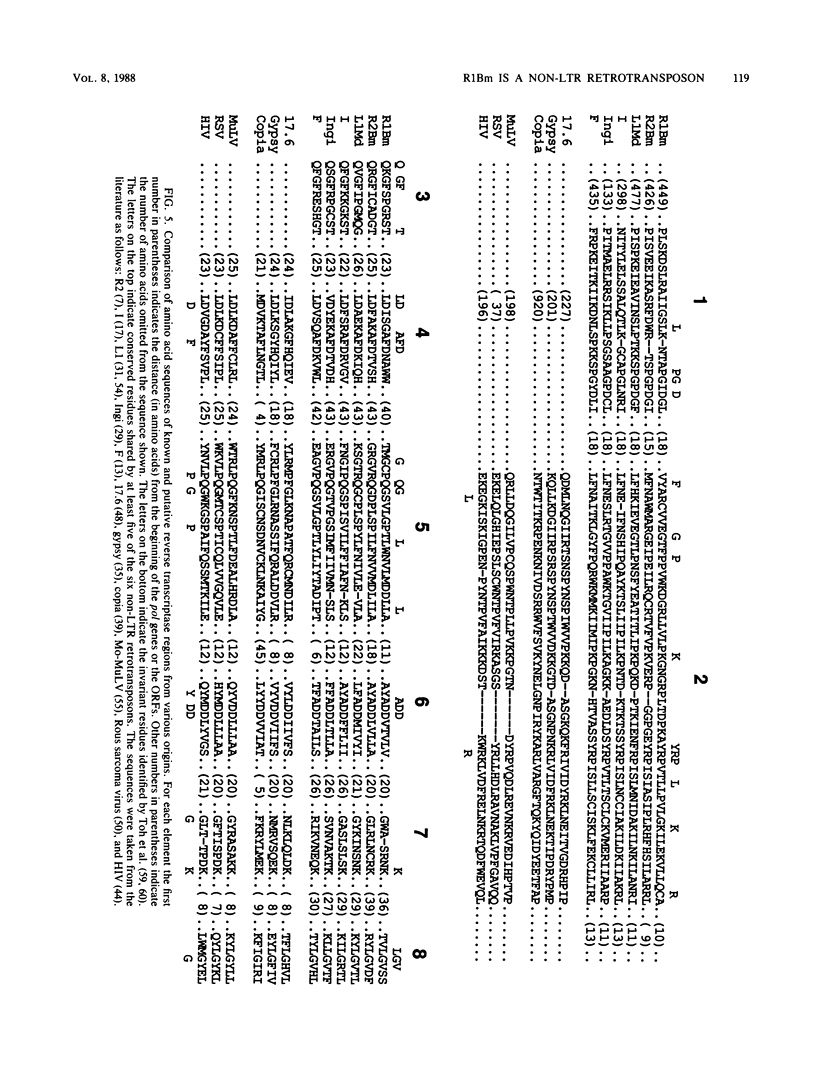
Two types of insertion elements, R1 and R2 (previously called type I and type II), are known to interrupt the 28S ribosomal genes of several insect species. In the silkmoth, Bombyx mori, each element occupies approximately 10% of the estimated 240 ribosomal DNA units, while at most only a few copies are located outside the ribosomal DNA units. We present here the complete nucleotide sequence of an R1 insertion from B. mori (R1Bm). This 5.1-kilobase element contains two overlapping open reading frames (ORFs) which together occupy 88% of its length. ORF1 is 461 amino acids in length and exhibits characteristics of retroviral gag genes. ORF2 is 1,051 amino acids in length and contains homology to reverse transcriptase-like enzymes. The analysis of 3' and 5' ends of independent isolates from the ribosomal locus supports the suggestion that R1 is still functioning as a transposable element. The precise location of the element within the genome implies that its transposition must occur with remarkable insertion sequence specificity. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences from six retrotransposons, R1 and R2 of B. mori, I factor and F element of Drosophila melanogaster, L1 of Mus domesticus, and Ingi of Trypanosoma brucei, reveals a relatively high level of sequence homology in the reverse transcriptase region. Like R1, these elements lack long terminal repeats. We have therefore named this class of related elements the non-long-terminal-repeat (non-LTR) retrotransposons.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. E., Mellor J., Gull K., Sim R. B., Tuite M. F., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. The functions and relationships of Ty-VLP proteins in yeast reflect those of mammalian retroviral proteins. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90761-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back E., Van Meir E., Müller F., Schaller D., Neuhaus H., Aeby P., Tobler H. Intervening sequences in the ribosomal RNA genes of Ascaris lumbricoides: DNA sequences at junctions and genomic organization. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2523–2529. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett T., Rae P. M. A 9.6 kb intervening sequence in D. virilis rDNA, and sequence homology in rDNA interruptions of diverse species of Drosophila and other diptera. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):763–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckingham K., White R. The ribosomal DNA of Calliphora erythrocephala; and analysis of hybrid plasmids containing ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Mar 15;137(4):349–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke W. D., Calalang C. C., Eickbush T. H. The site-specific ribosomal insertion element type II of Bombyx mori (R2Bm) contains the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2221–2230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clare J., Farabaugh P. Nucleotide sequence of a yeast Ty element: evidence for an unusual mechanism of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen E., Strachan T., Dover G. Dynamics of concerted evolution of ribosomal DNA and histone gene families in the melanogaster species subgroup of Drosophila. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 15;158(1):17–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90448-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., d'Auriol L., Betermier M., Cottarel G., Jacquier A., Galibert F., Dujon B. Universal code equivalent of a yeast mitochondrial intron reading frame is expressed into E. coli as a specific double strand endonuclease. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N. Amino acid sequence homology in gag region of reverse transcribing elements and the coat protein gene of cauliflower mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):623–633. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Rebbert M. L. Nucleotide sequences at the boundaries between gene and insertion regions in the rDNA of Drosophilia melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5011–5020. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Casari G. Related polypeptides are encoded by Drosophila F elements, I factors, and mammalian L1 sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5843–5847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G., Coen E. Springcleaning ribosomal DNA: a model for multigene evolution? Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):731–732. doi: 10.1038/290731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H., Kafatos F. C. A walk in the chorion locus of Bombyx mori. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):633–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H., Robins B. Bombyx mori 28S ribosomal genes contain insertion elements similar to the Type I and II elements of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2281–2285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. H., Lister C. K., Kellett E., Finnegan D. J. Transposable elements controlling I-R hybrid dysgenesis in D. melanogaster are similar to mammalian LINEs. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90815-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan D. J. Transposable elements in eukaryotes. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:281–326. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61376-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R., Meselson M. Long terminal repeat nucleotide sequence and specific insertion of the gypsy transposon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4462–4464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara H., Ishikawa H. Molecular mechanism of introduction of the hidden break into the 28S rRNA of insects: implication based on structural studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6393–6401. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara H., Ogura T., Takada N., Miyajima N., Ishikawa H., Maekawa H. Introns and their flanking sequences of Bombyx mori rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6861–6869. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P. Polyploidization of the silk gland of Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 15;86(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(74)80010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaga H., Saigo K. Insertion of a movable genetic element, 297, into the T-A-T-A box for the H3 histone gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4143–4147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Sequence-specific insertion of the Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6. 1984 Jul 26-Aug 1Nature. 310(5975):332–333. doi: 10.1038/310332a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the Rous sarcoma virus pol gene by ribosomal frameshifting. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1237–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.2416054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Dujon B. An intron-encoded protein is active in a gene conversion process that spreads an intron into a mitochondrial gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamrich M., Miller O. L., Jr The rare transcripts of interrupted rRNA genes in Drosophila melanogaster are processed or degraded during synthesis. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1541–1545. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S. J., Glover D. M. Drosophila melanogaster ribosomal DNA containing type II insertions is variably transcribed in different strains and tissues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 5;151(4):645–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90428-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., ole-MoiYoi O. K., Young J. R. Ingi, a 5.2-kb dispersed sequence element from Trypanosoma brucei that carries half of a smaller mobile element at either end and has homology with mammalian LINEs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Blattner F. R. Lambda Charon vectors (Ch32, 33, 34 and 35) adapted for DNA cloning in recombination-deficient hosts. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90187-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Dawid I. B. Expression of ribosomal DNA insertions in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1185–1196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macreadie I. G., Scott R. M., Zinn A. R., Butow R. A. Transposition of an intron in yeast mitochondria requires a protein encoded by that intron. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):395–402. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlor R. L., Parkhurst S. M., Corces V. G. The Drosophila melanogaster gypsy transposable element encodes putative gene products homologous to retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1129–1134. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Fulton S. M., Dobson M. J., Wilson W., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. A retrovirus-like strategy for expression of a fusion protein encoded by yeast transposon Ty1. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):243–246. doi: 10.1038/313243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Lang B. F. Mitochondrial class II introns encode proteins related to the reverse transcriptases of retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):641–643. doi: 10.1038/316641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méric C., Spahr P. F. Rous sarcoma virus nucleic acid-binding protein p12 is necessary for viral 70S RNA dimer formation and packaging. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):450–459. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.450-459.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T. Retroviral DNA integration. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A convenient and adaptable package of DNA sequence analysis programs for microcomputers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):51–59. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C. A convenient and adaptable package of computer programs for DNA and protein sequence management, analysis and homology determination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):643–655. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. M., Kohorn B. D., Wade R. P. The 10 kb Drosophila virilis 28S rDNA intervening sequence is flanked by a direct repeat of 14 base pairs of coding sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3491–3504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roiha H., Miller J. R., Woods L. C., Glover D. M. Arrangements and rearrangements of sequences flanking the two types of rDNA insertion in D. melanogaster. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):749–753. doi: 10.1038/290749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roiha H., Read C. A., Browne M. J., Glover D. M. Widely differing degrees of sequence conservation of the two types of rDNA insertion within the melanogaster species sub-group of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):721–726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Ohishi K., Ogawa Y., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of bovine leukemia virus: its evolutionary relationship to other retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Kugimiya W., Matsuo Y., Inouye S., Yoshioka K., Yuki S. Identification of the coding sequence for a reverse transcriptase-like enzyme in a transposable genetic element in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):659–661. doi: 10.1038/312659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Phosphorylation of murine type C viral p12 proteins regulates their extent of binding to the homologous viral RNA. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Todaro G. J. The genome-associated, specific RNA binding proteins of avian and mammalian type C viruses. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehee W. R., Chao S. F., Loeb D. D., Comer M. B., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Determination of a functional ancestral sequence and definition of the 5' end of A-type mouse L1 elements. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):757–767. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith V. L., Beckingham K. The intron boundaries and flanking rRNA coding sequences of Calliphora erythrocephala rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1707–1724. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Function of the retrovirus long terminal repeat. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90367-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh H., Hayashida H., Miyata T. Sequence homology between retroviral reverse transcriptase and putative polymerases of hepatitis B virus and cauliflower mosaic virus. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):827–829. doi: 10.1038/305827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh H., Kikuno R., Hayashida H., Miyata T., Kugimiya W., Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Close structural resemblance between putative polymerase of a Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6 and pol gene product of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1267–1272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]