Abstract
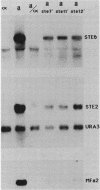
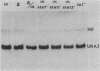
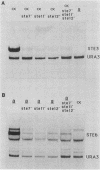
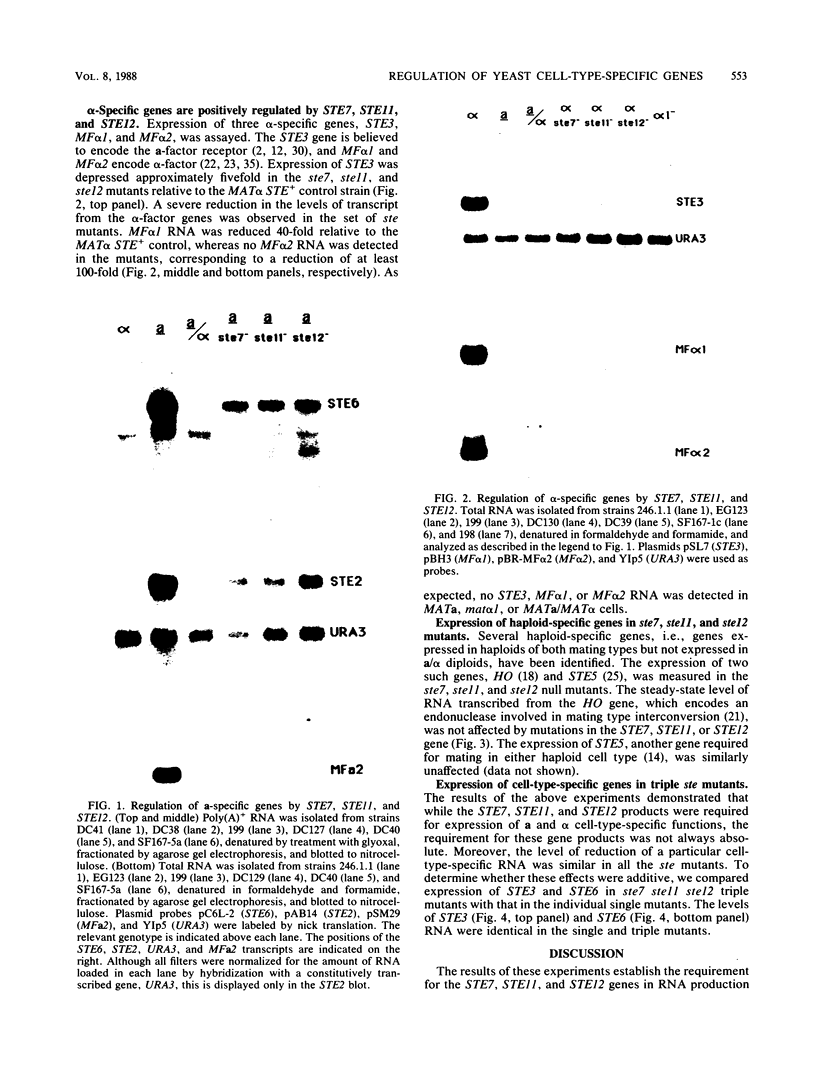
Cell type specialization in yeast haploids involves the mutually exclusive expression of one of two sets of genes, the a-specific and alpha-specific genes. We demonstrated that the products of the STE7, STE11, and STE12 genes were required for the expression of both gene sets. RNA levels transcribed from these gene sets were significantly decreased but not abolished in haploids containing a null mutation in the STE7, STE11, or STE12 gene. Transcript levels from the a- and alpha-specific gene sets were not further reduced in strains harboring mutations in all three STE genes, suggesting that STE7, STE11, and STE12 are required for the same aspect of transcription. We further showed that the requirement for these products was not the same for each member of a particular gene set. However, for any given a- or alpha-specific gene, the effect on RNA levels of any of the three ste mutations was similar.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammerer G., Sprague G. F., Jr, Bender A. Control of yeast alpha-specific genes: evidence for two blocks to expression in MATa/MAT alpha diploids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5855–5859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast peptide pheromones, a-factor and alpha-factor, activate a common response mechanism in their target cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90808-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake A. J., Julius D. J., Thorner J. A functional prepro-alpha-factor gene in Saccharomyces yeasts can contain three, four, or five repeats of the mature pheromone sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1440–1450. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaleff D. T., Tatchell K. Molecular cloning and characterization of the STE7 and STE11 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1878–1886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Melnick L. M., Blair L. C., Thorner J. Extracellular suppression allows mating by pheromone-deficient sterile mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):903–906. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.903-906.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Jacobs E., Jauniaux J. C. Expression of the ROAM mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: involvement of trans-acting regulatory elements and relation with the Ty1 transcription. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1133–1139. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Cardillo T. S., Sherman F., Dubois E., Deschamps J., Wiame J. M. Mating signals control expression of mutations resulting from insertion of a transposable repetitive element adjacent to diverse yeast genes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Herskowitz I. Regulation by the yeast mating-type locus of STE12, a gene required for cell-type-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3818–3821. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Herskowitz I. The yeast STE12 product is required for expression of two sets of cell-type specific genes. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):923–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig A., Holly J., Saari G., MacKay V. L. Multiple regulation of STE2, a mating-type-specific gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2106–2114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae unresponsive to cell division control by polypeptide mating hormone. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. Binding of alpha-factor pheromone to yeast a cells: chemical and genetic evidence for an alpha-factor receptor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90186-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Goldman B. S., Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants unresponsive to alpha-factor pheromone: alpha-factor binding and extragenic suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I. Regulation of yeast mating-type interconversion: feedback control of HO gene expression by the mating-type locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Herskowitz I. A repressor (MAT alpha 2 Product) and its operator control expression of a set of cell type specific genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):237–247. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Strathern J. N., Broach J. R., Hicks J. B. Regulation of transcription in expressed and unexpressed mating type cassettes of yeast. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):239–244. doi: 10.1038/289239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostriken R., Heffron F. The product of the HO gene is a nuclease: purification and characterization of the enzyme. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:89–96. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J. Alpha-factor structural gene mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on alpha-factor production and mating. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):787–796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay V. L. Cloning of yeast STE genes in 2 microns vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:325–343. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay V., Manney T. R. Mutations affecting sexual conjugation and related processes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Isolation and phenotypic characterization of nonmating mutants. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):255–271. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay V., Manney T. R. Mutations affecting sexual conjugation and related processes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Genetic analysis of nonmating mutants. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):273–288. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manney T. R., Woods V. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae resistant to the alpha mating-type factor. Genetics. 1976 Apr;82(4):639–644. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey G., Clay F. J., Kelsay K., Sprague G. F., Jr Identification and regulation of a gene required for cell fusion during mating of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2680–2690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. P., Herskowitz I. Activation of meiosis and sporulation by repression of the RME1 product in yeast. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):738–742. doi: 10.1038/319738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Miyajima A., Arai K. Nucleotide sequences of STE2 and STE3, cell type-specific sterile genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2643–2648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Transcription and regulatory signals at the mating type locus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A., Chen E. Y., Lugovoy J. M., Chang C. N., Hitzeman R. A., Seeburg P. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains two discrete genes coding for the alpha-factor pheromone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4049–4063. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr, Blair L. C., Thorner J. Cell interactions and regulation of cell type in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:623–660. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr, Jensen R., Herskowitz I. Control of yeast cell type by the mating type locus: positive regulation of the alpha-specific STE3 gene by the MAT alpha 1 product. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):409–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J., Hicks J., Herskowitz I. Control of cell type in yeast by the mating type locus. The alpha 1-alpha 2 hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague M. A., Chaleff D. T., Errede B. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast regulatory gene STE7 predicts a protein homologous to protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7371–7375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L., Herskowitz I. Negative regulation of STE6 gene expression by the alpha 2 product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2420–2427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L., Herskowitz I. Sequences upstream of the STE6 gene required for its expression and regulation by the mating type locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2536–2540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]